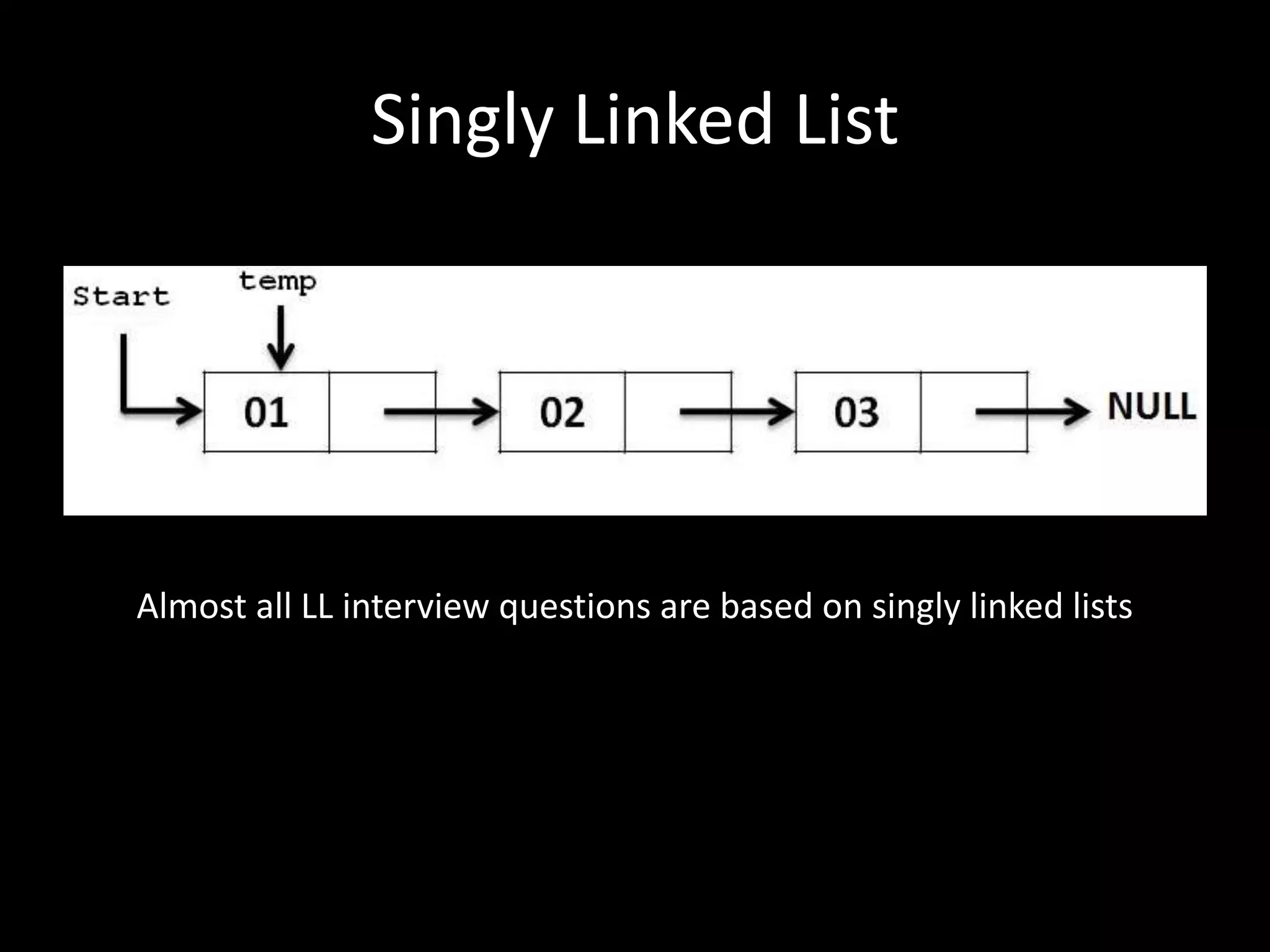
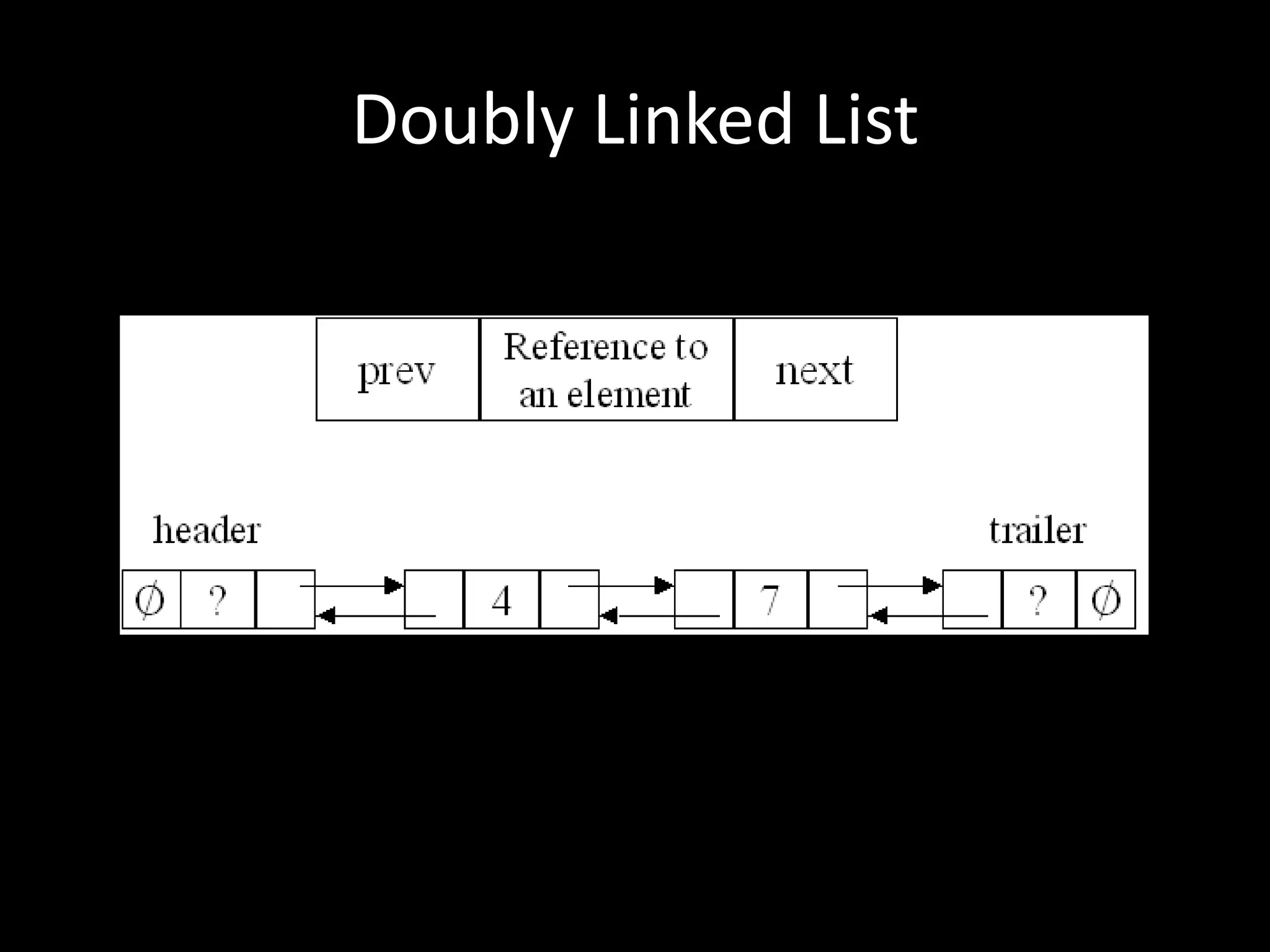
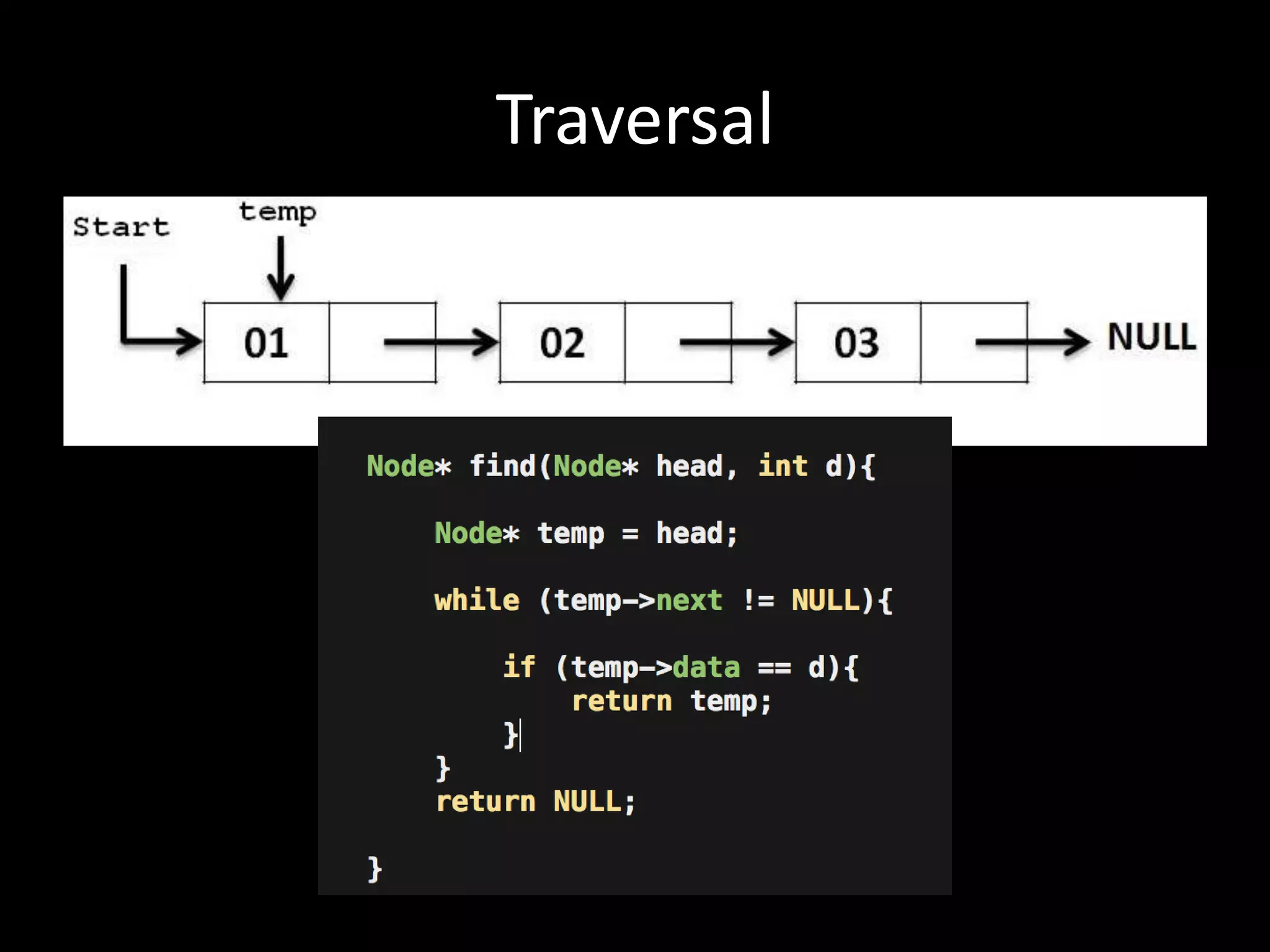
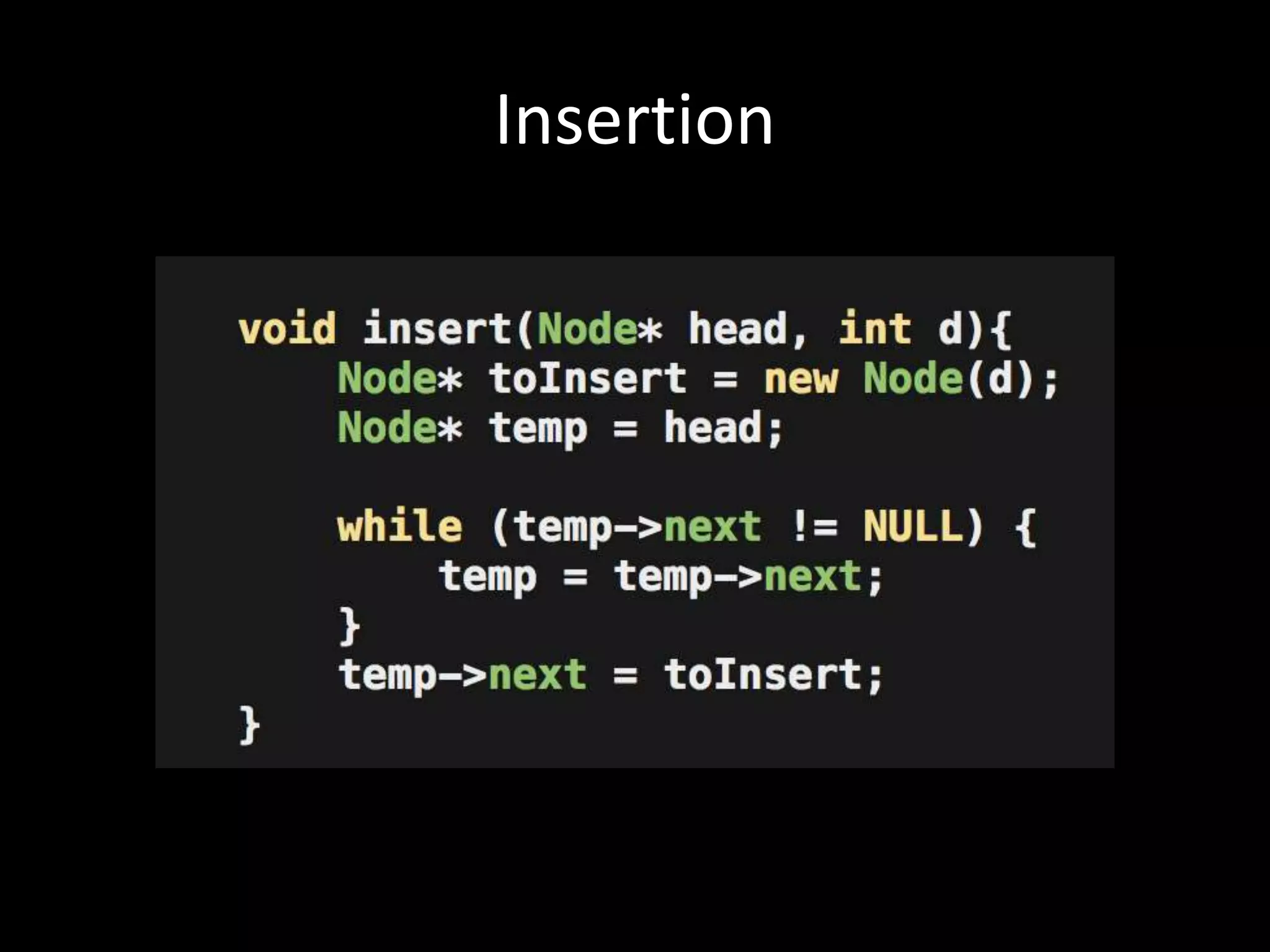
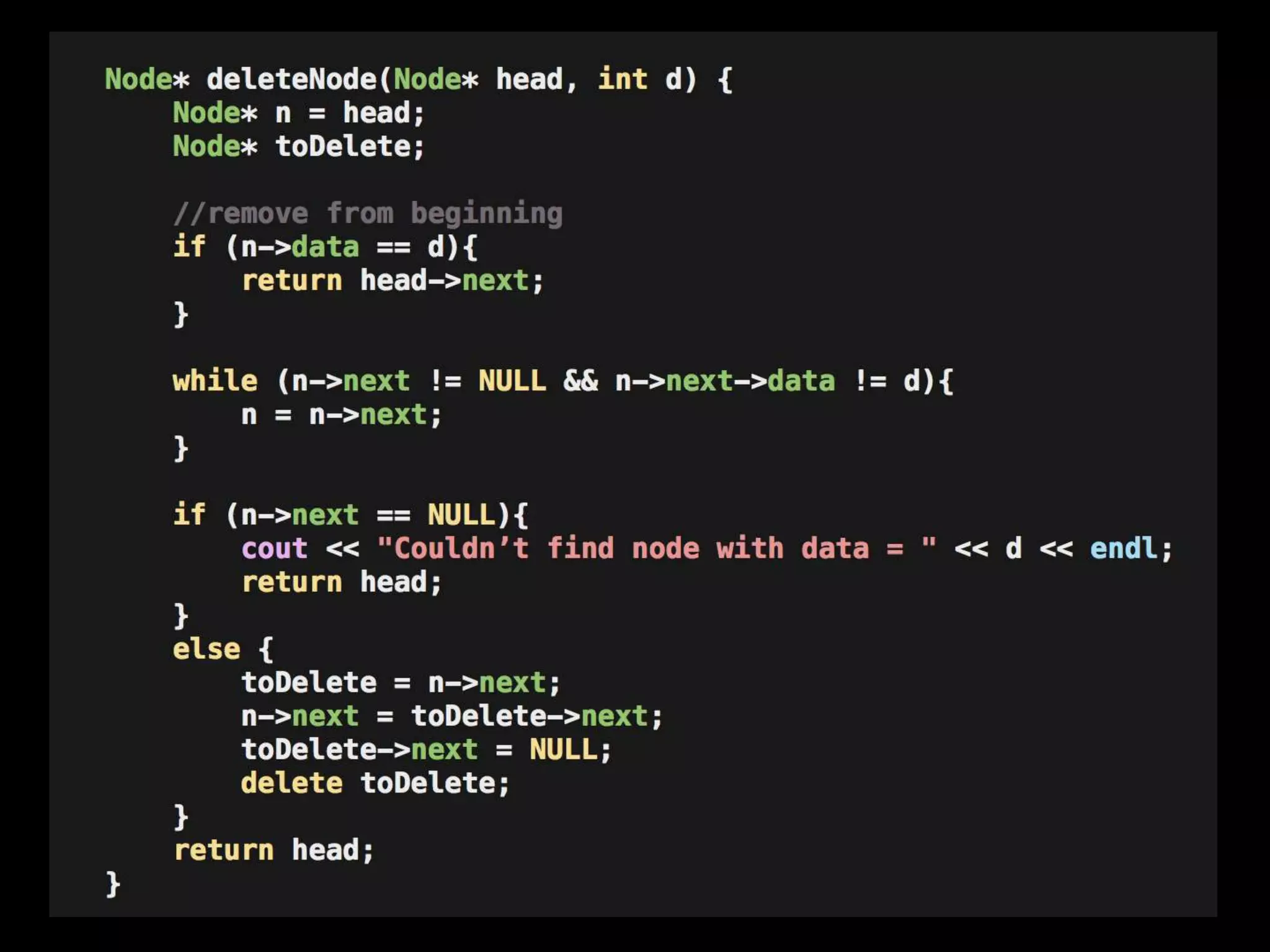
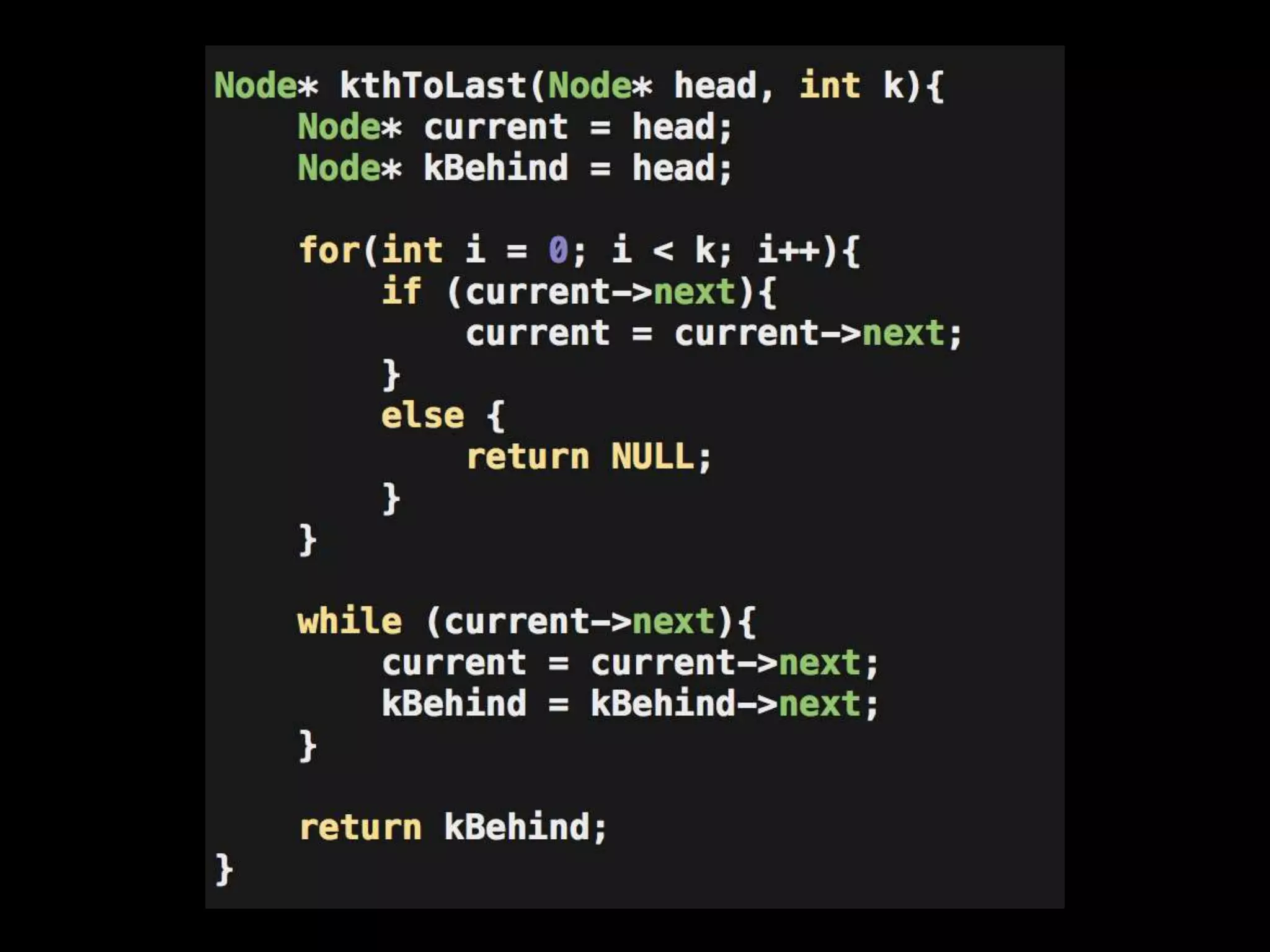
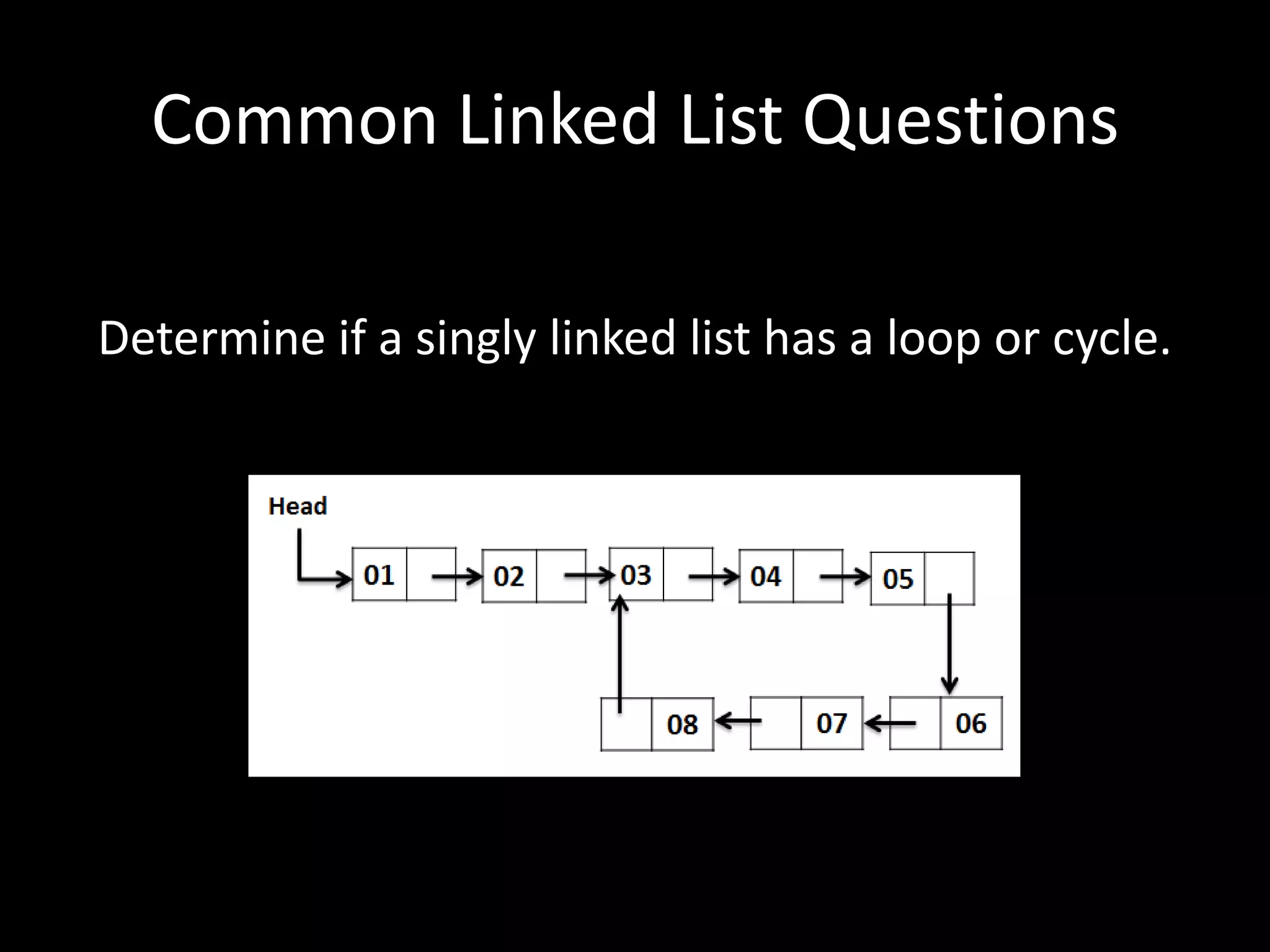
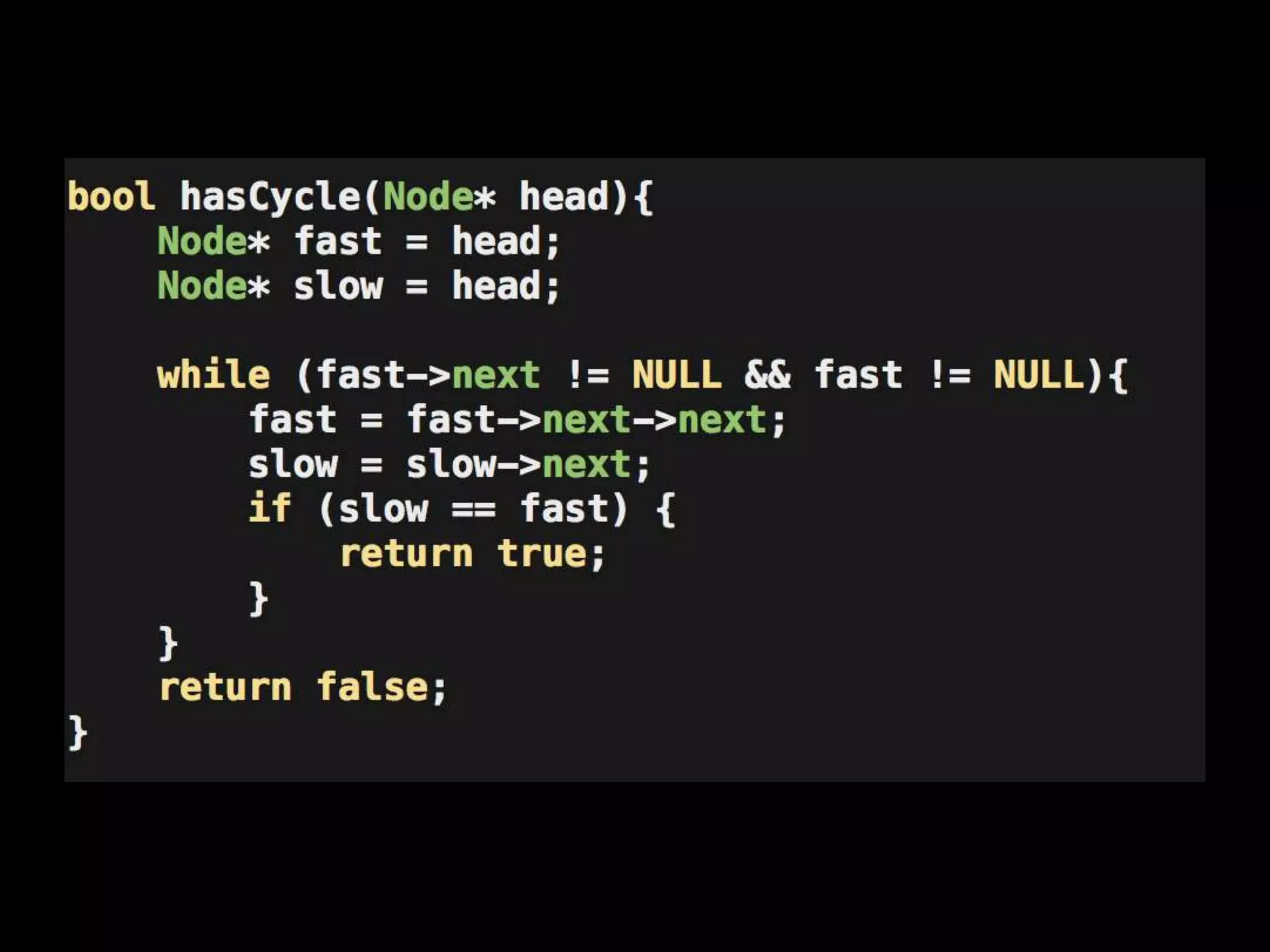
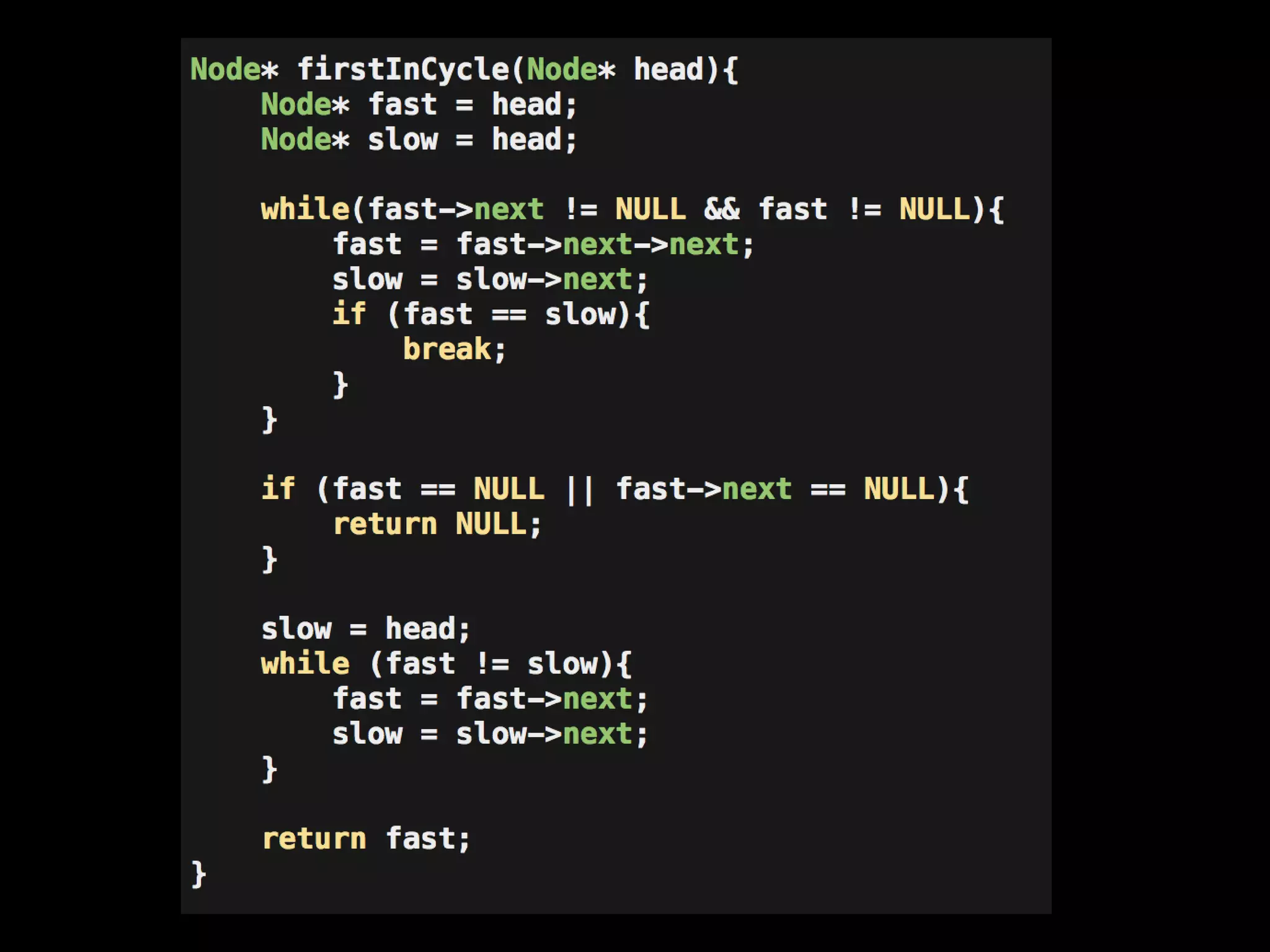
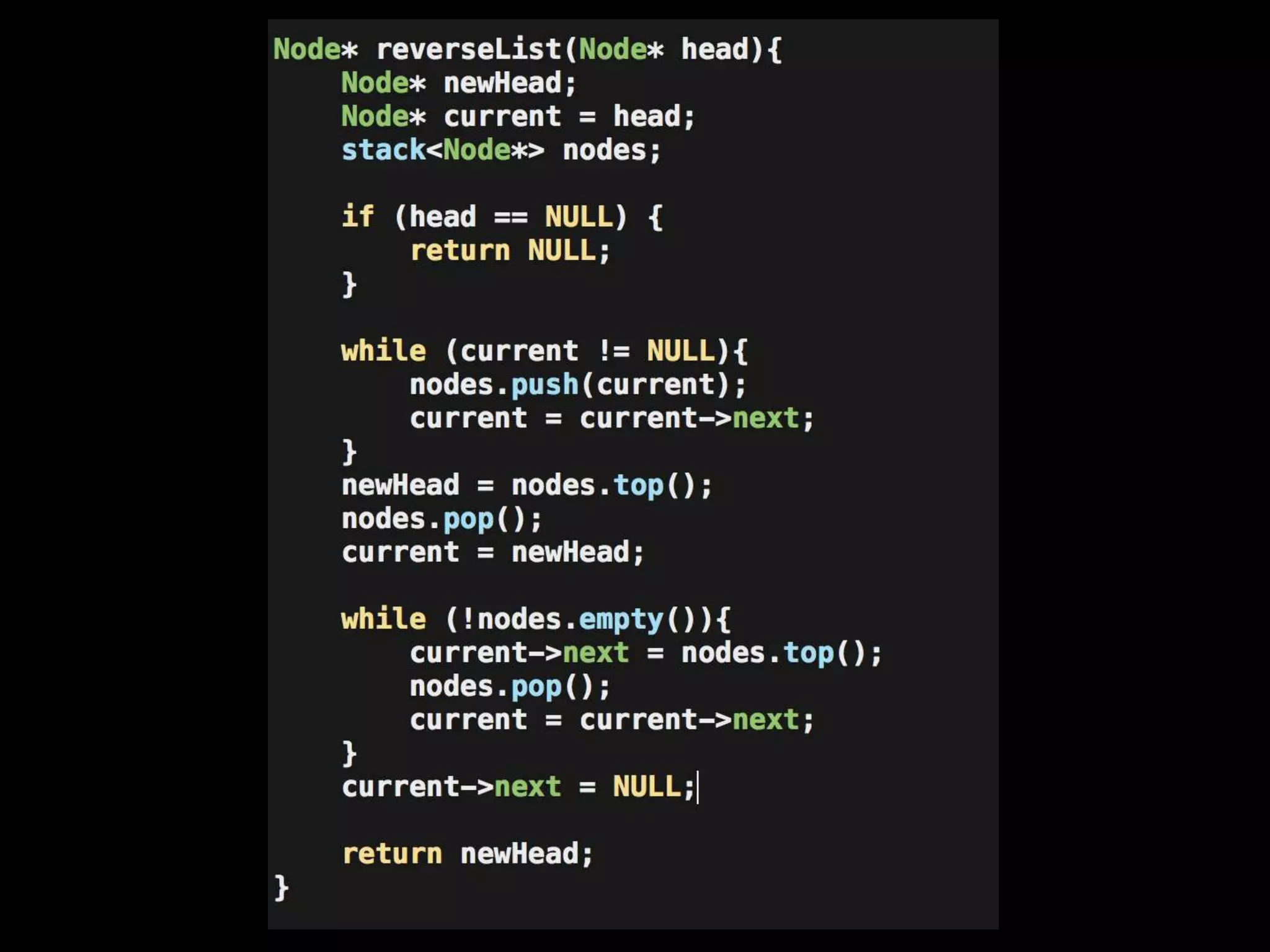
This document provides an overview of linked lists and common interview questions about them. It discusses the basics of singly and doubly linked lists as well as implementation details. Common linked list operations like traversal, insertion, and deletion are covered. Strategies for solving common linked list problems using pointers and additional data structures are presented. Examples of problems discussed include finding the kth to last element, detecting cycles, reversing a list, and removing duplicates. The document concludes with a meeting summary and plans to cover trees and graphs next.