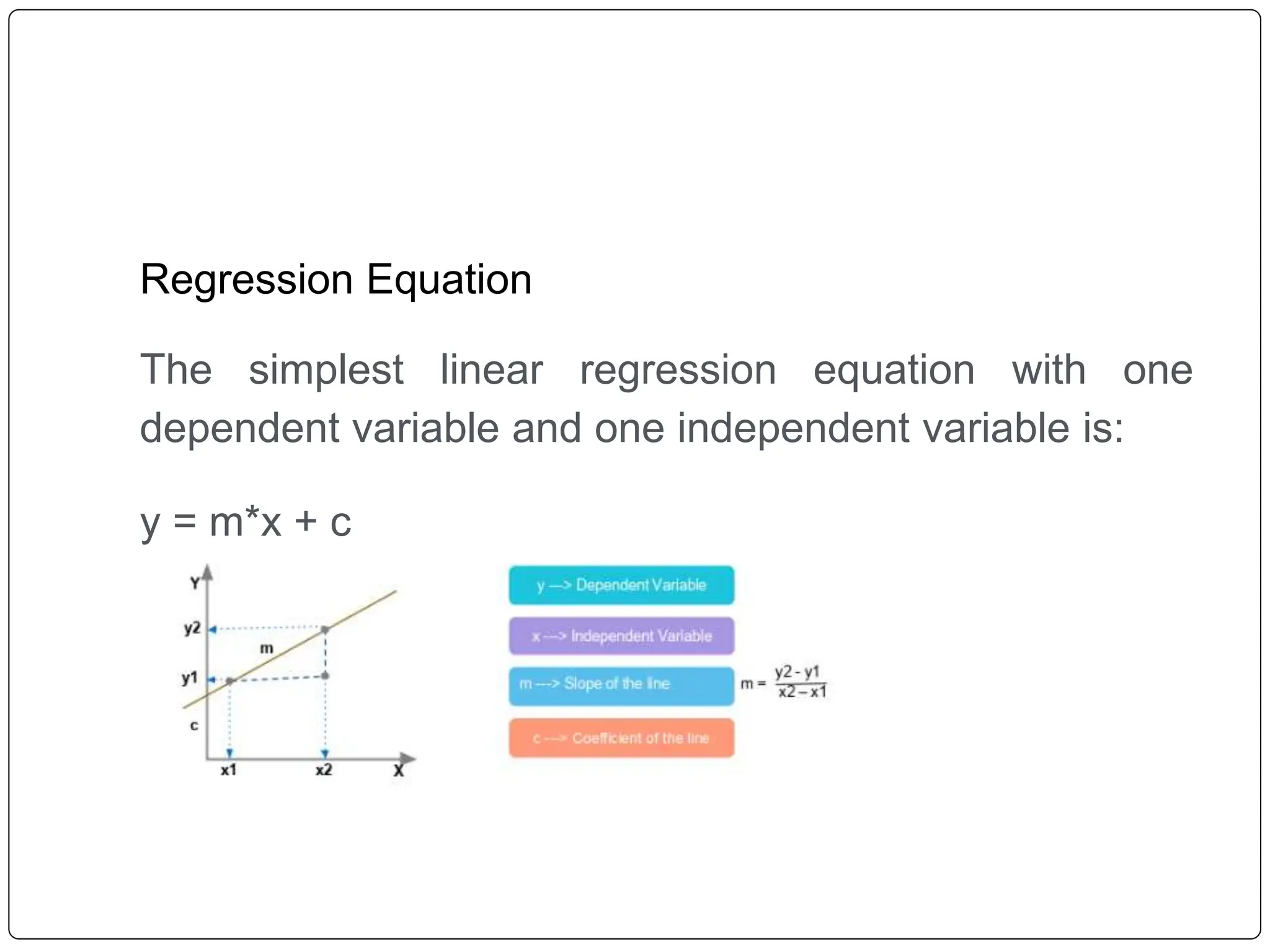
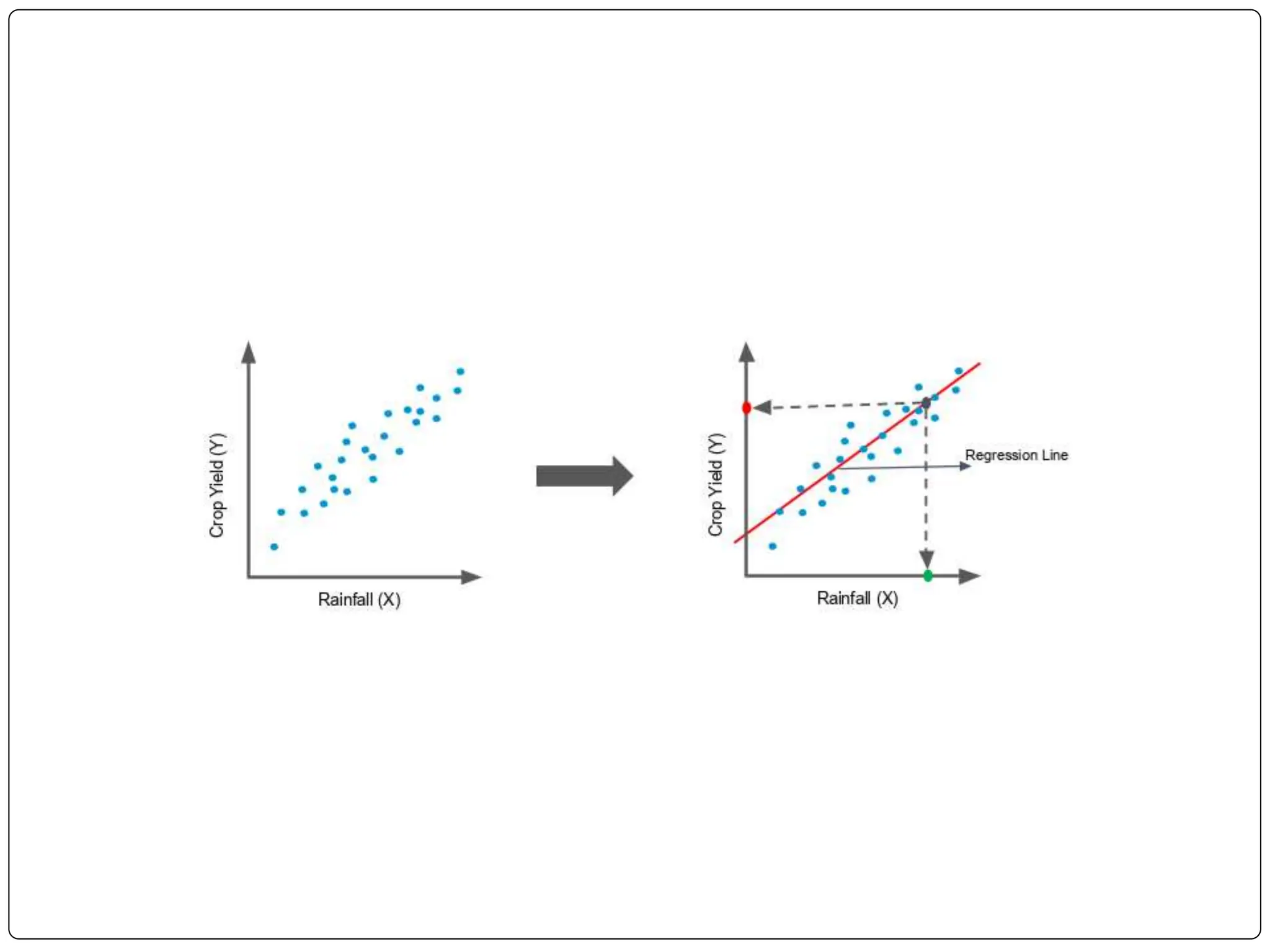
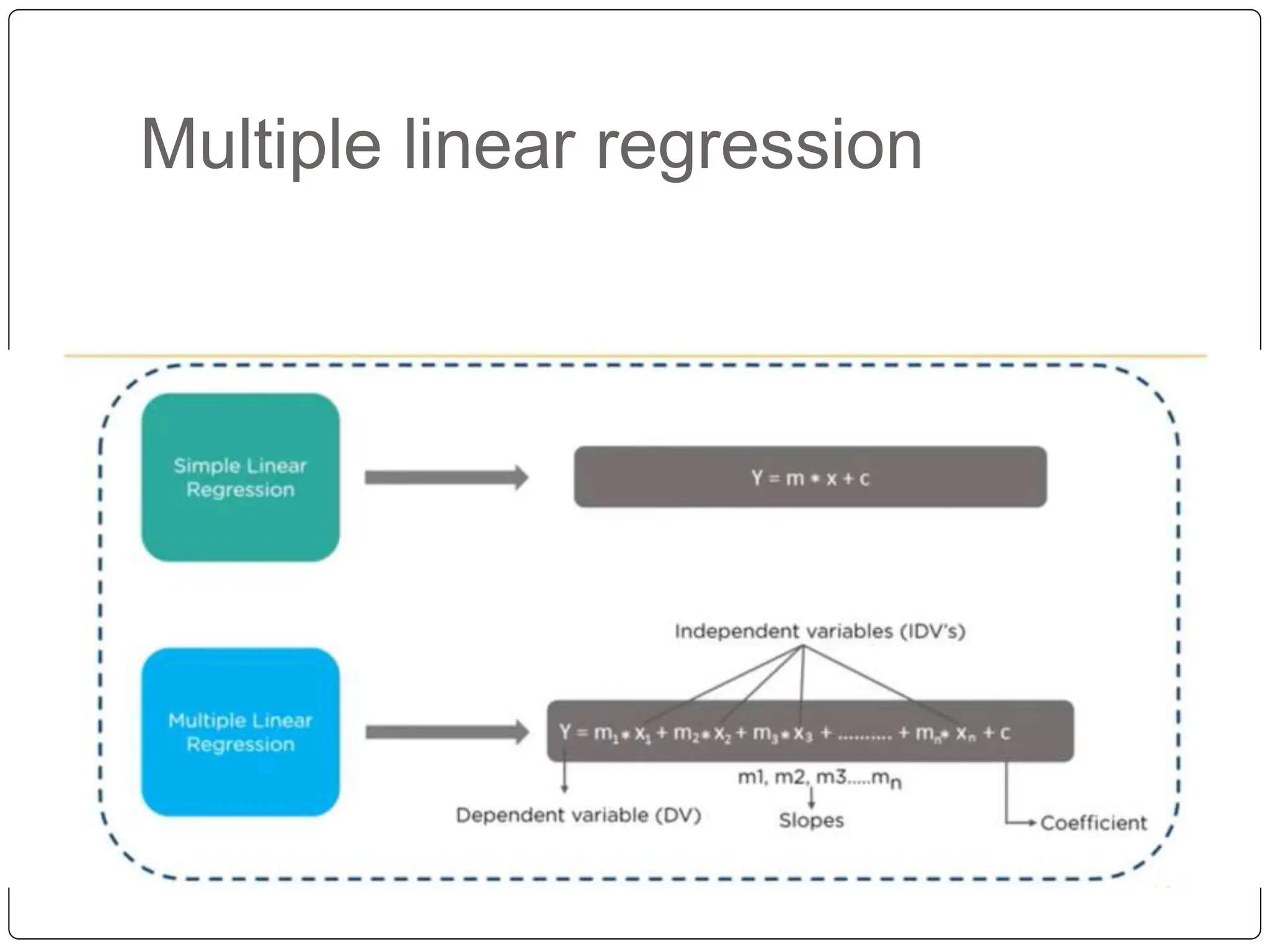
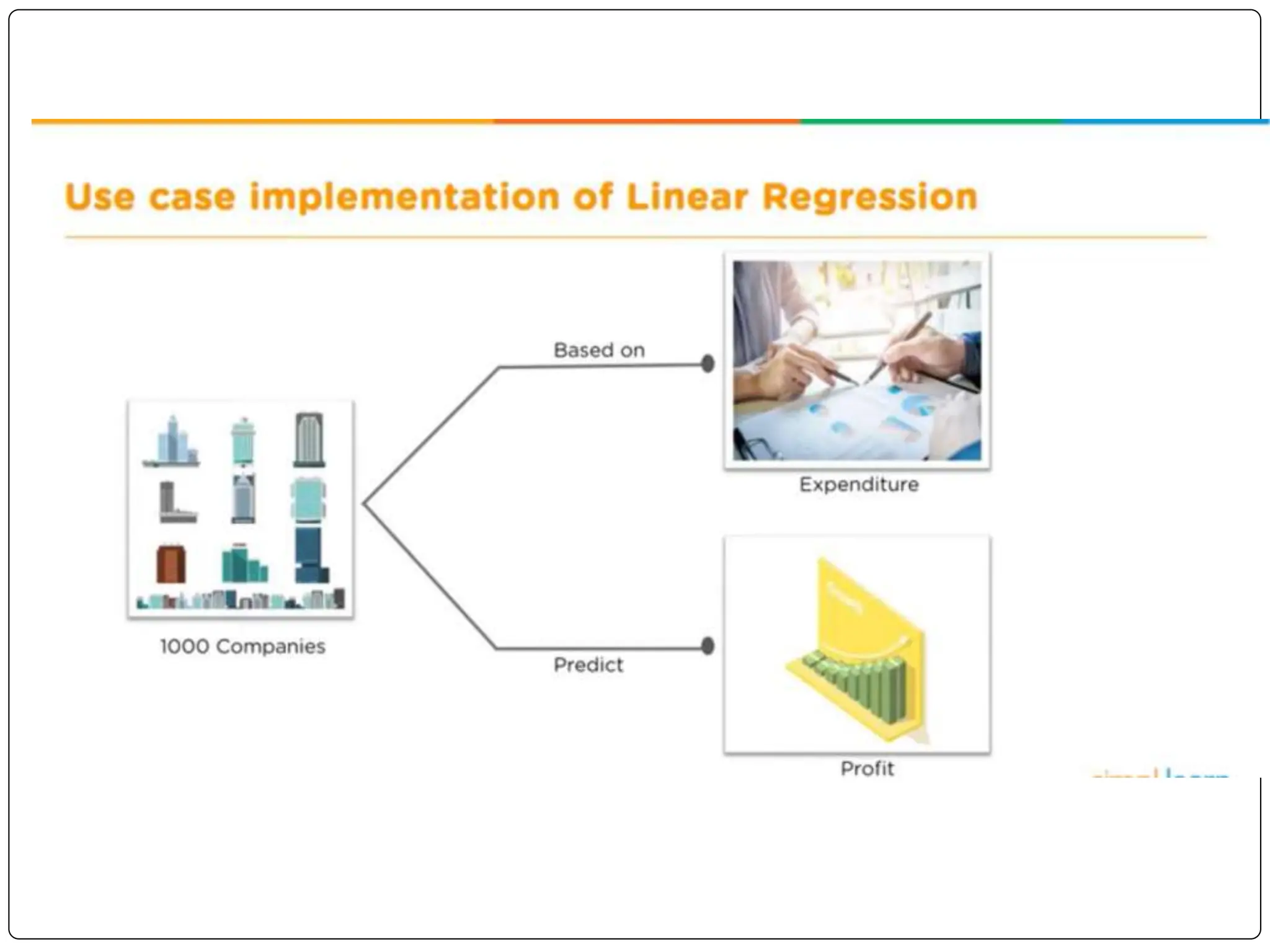
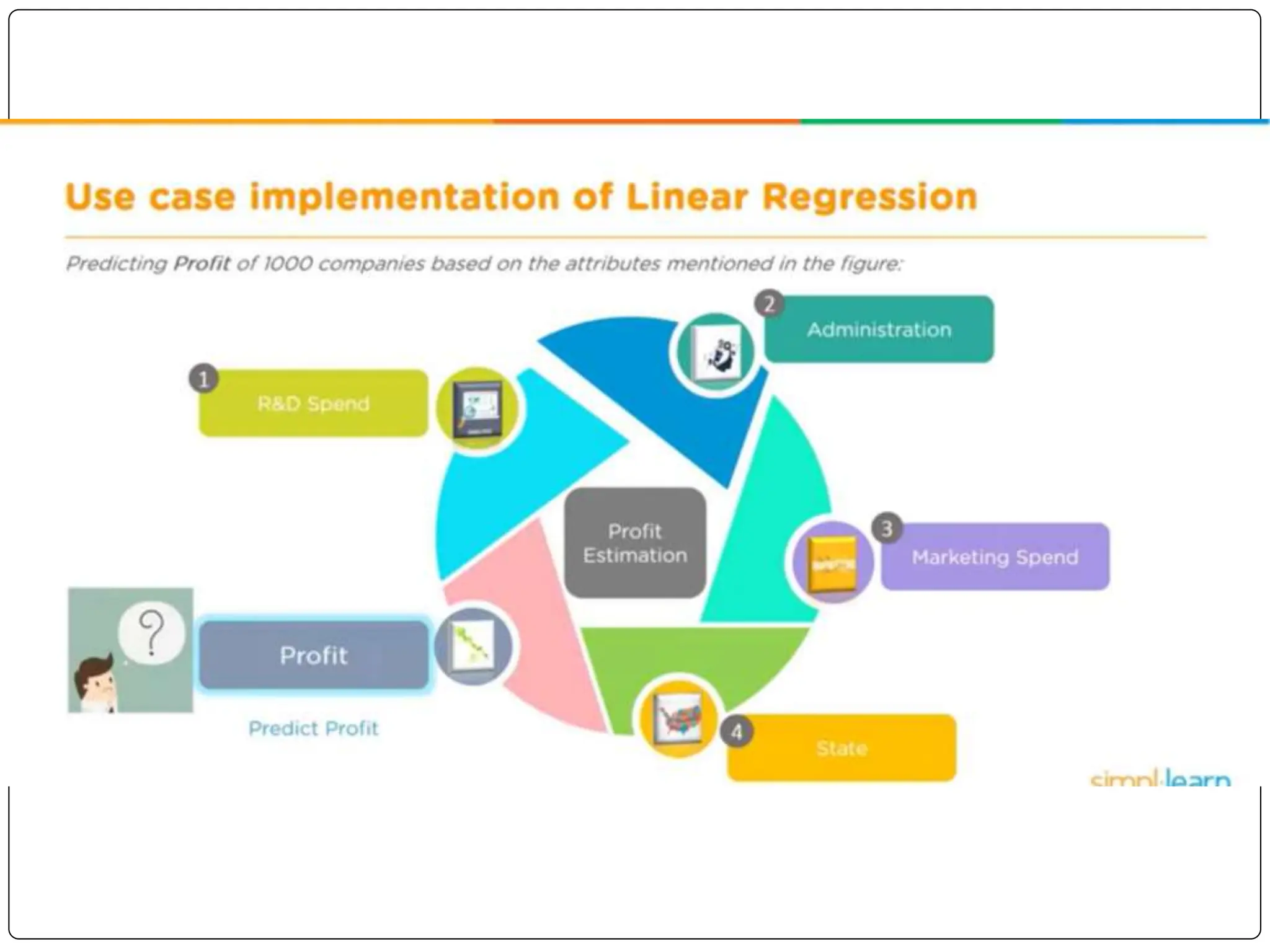
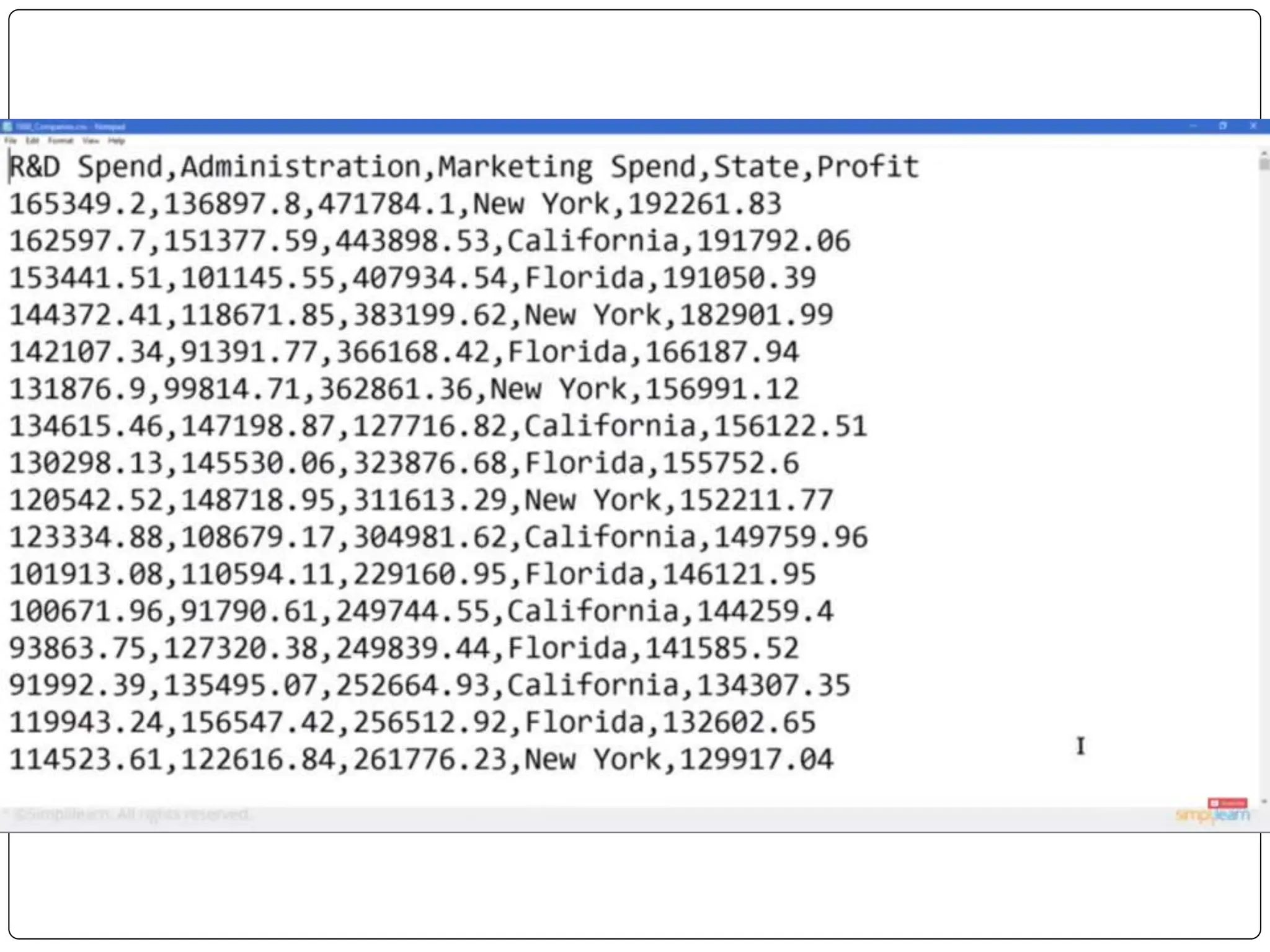
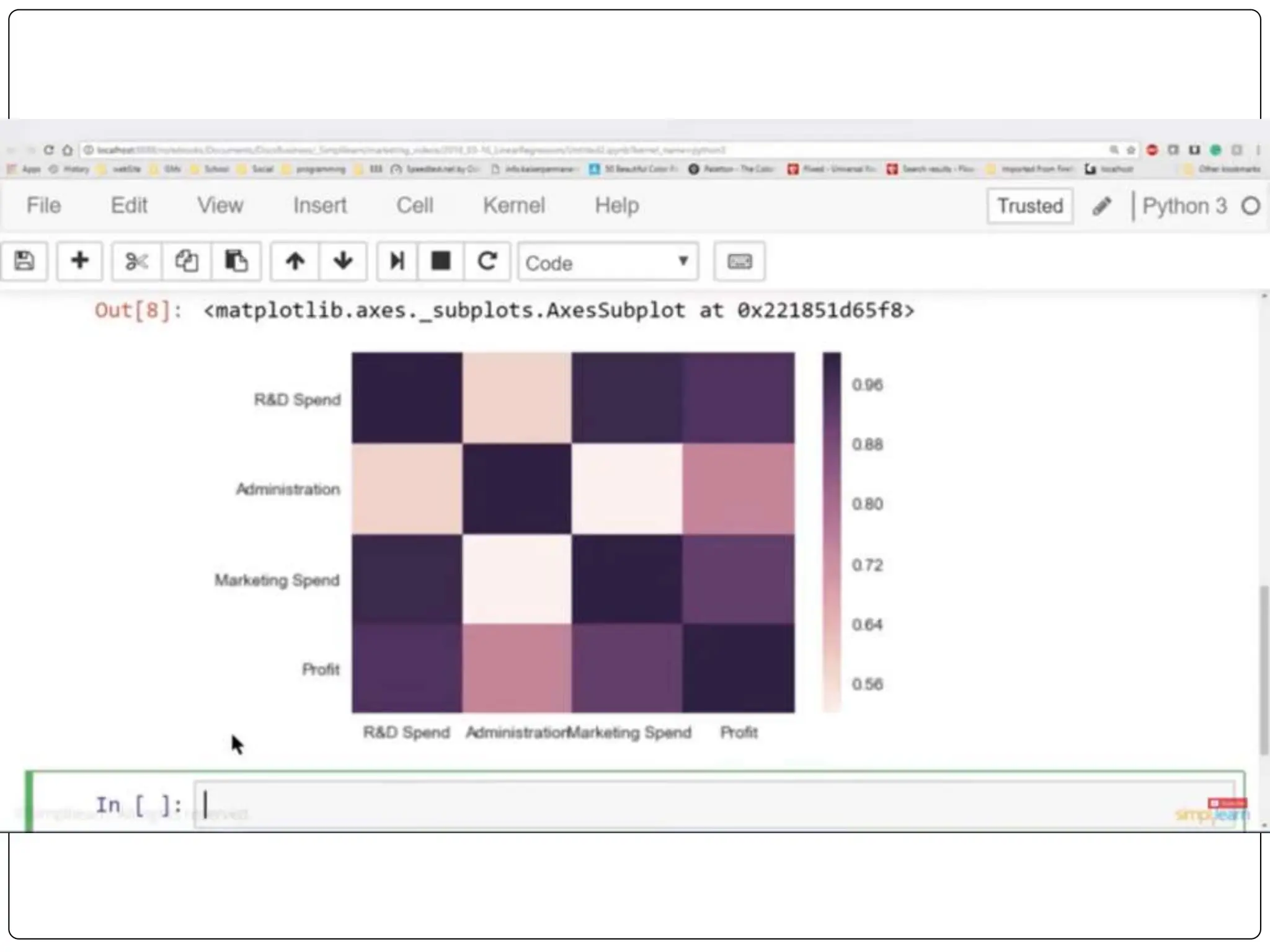
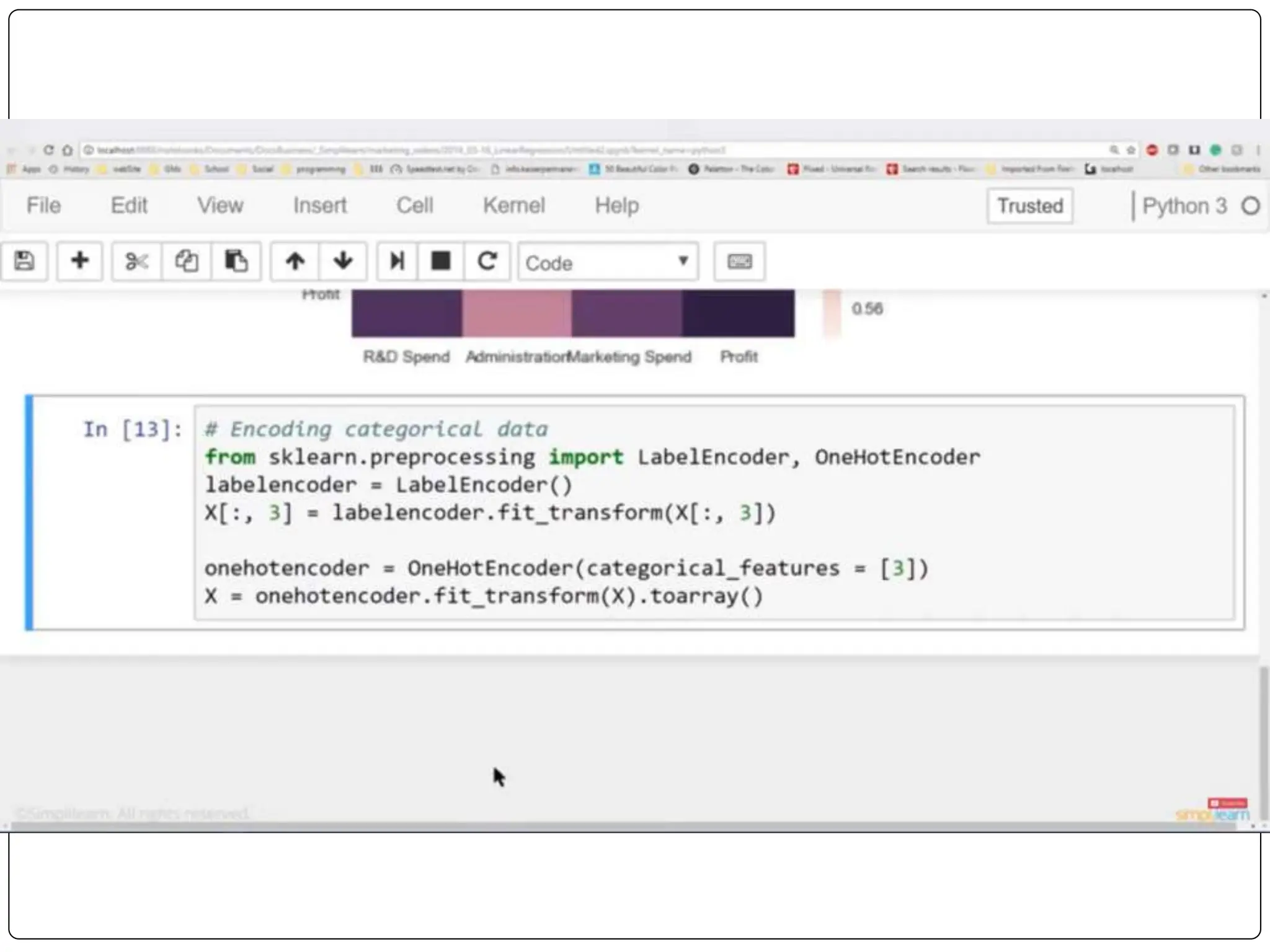
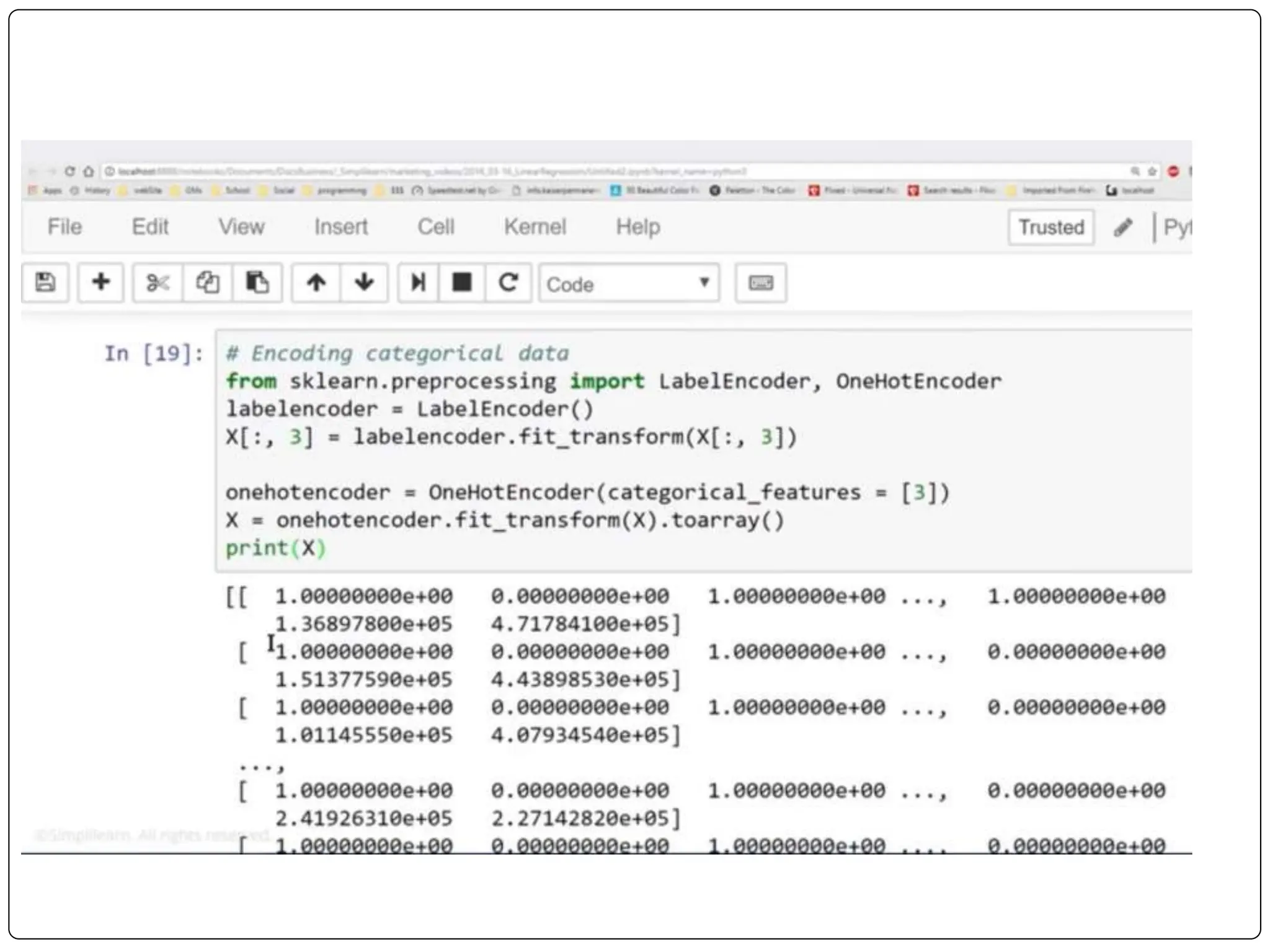
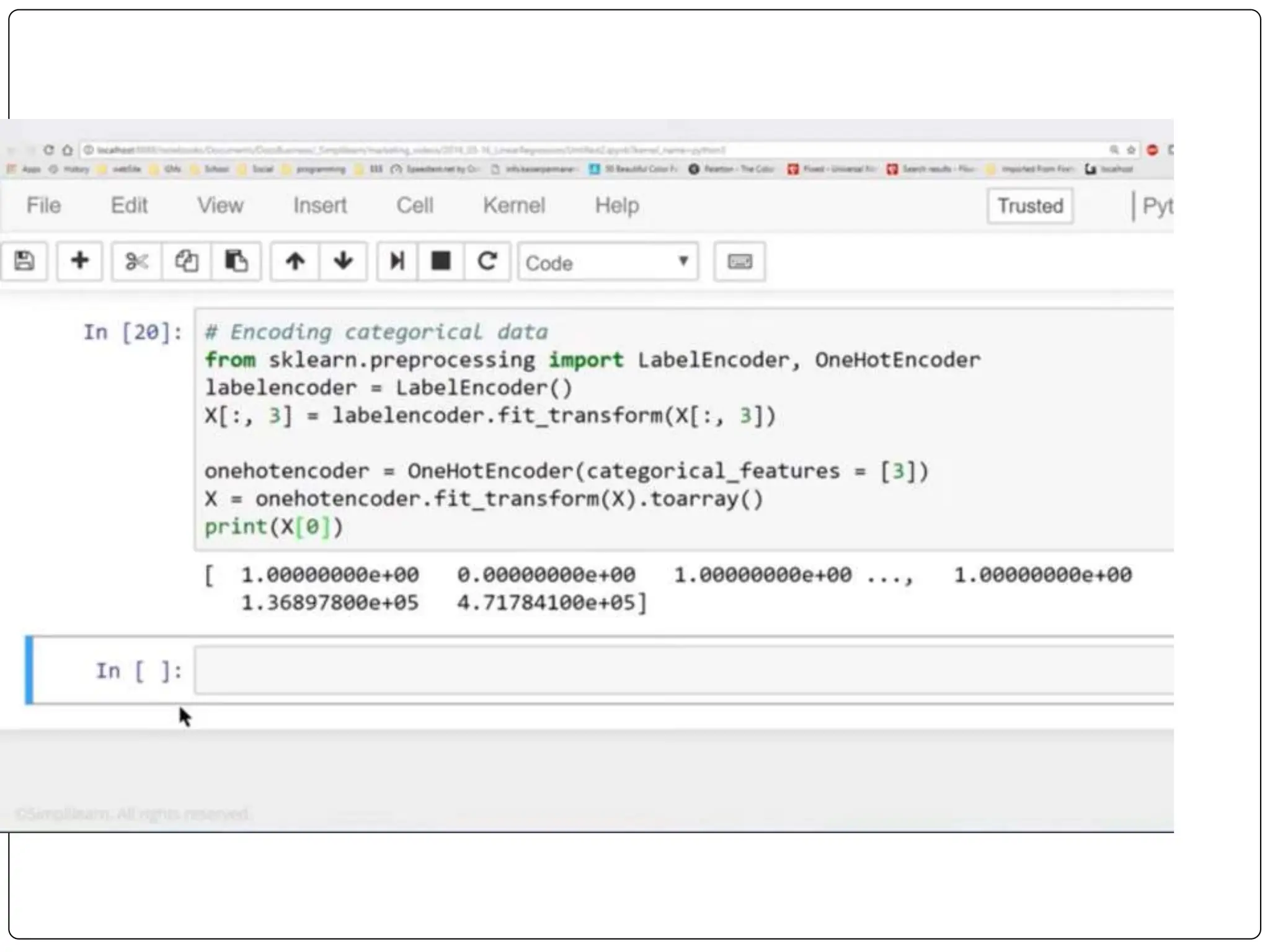
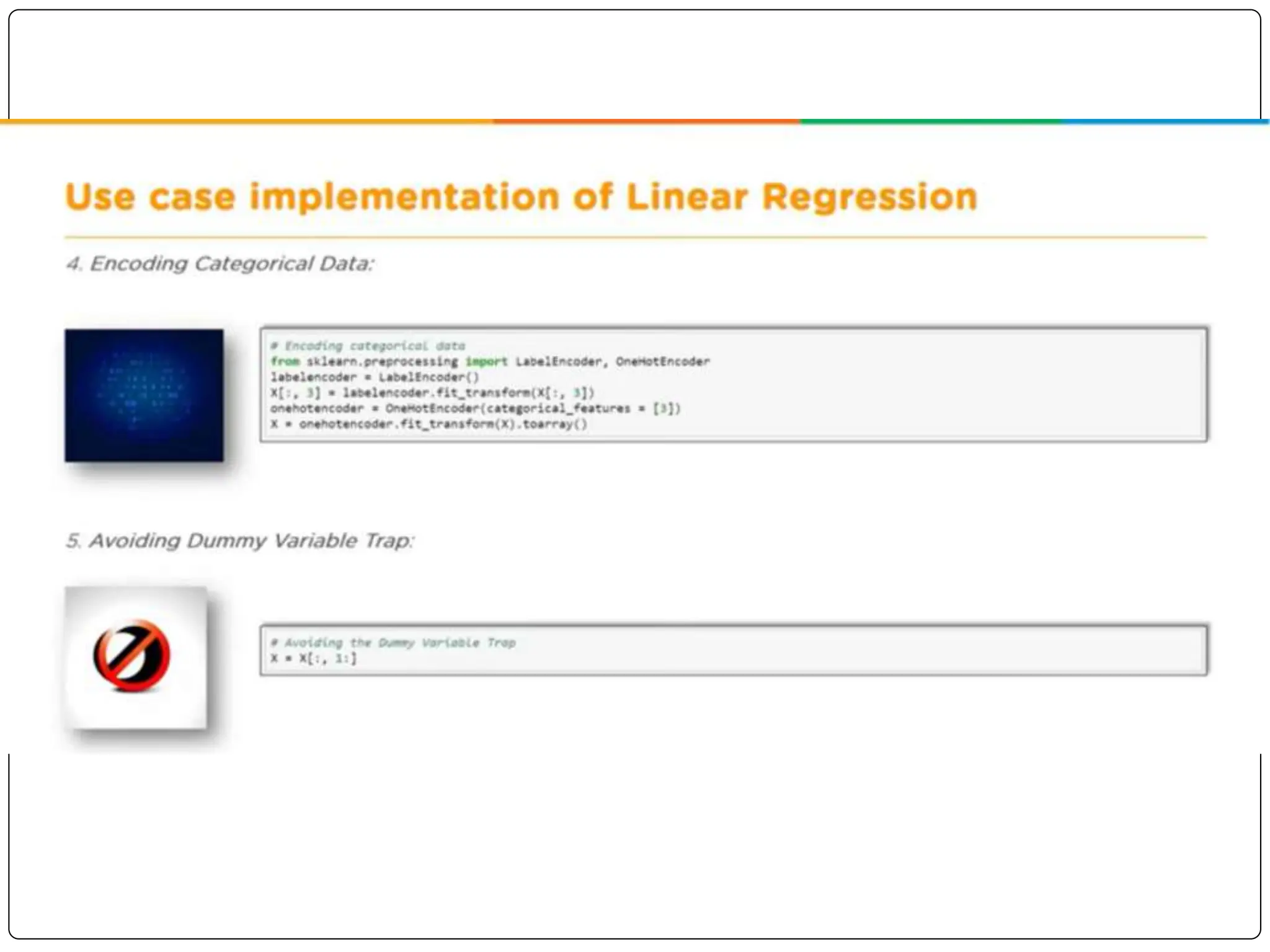
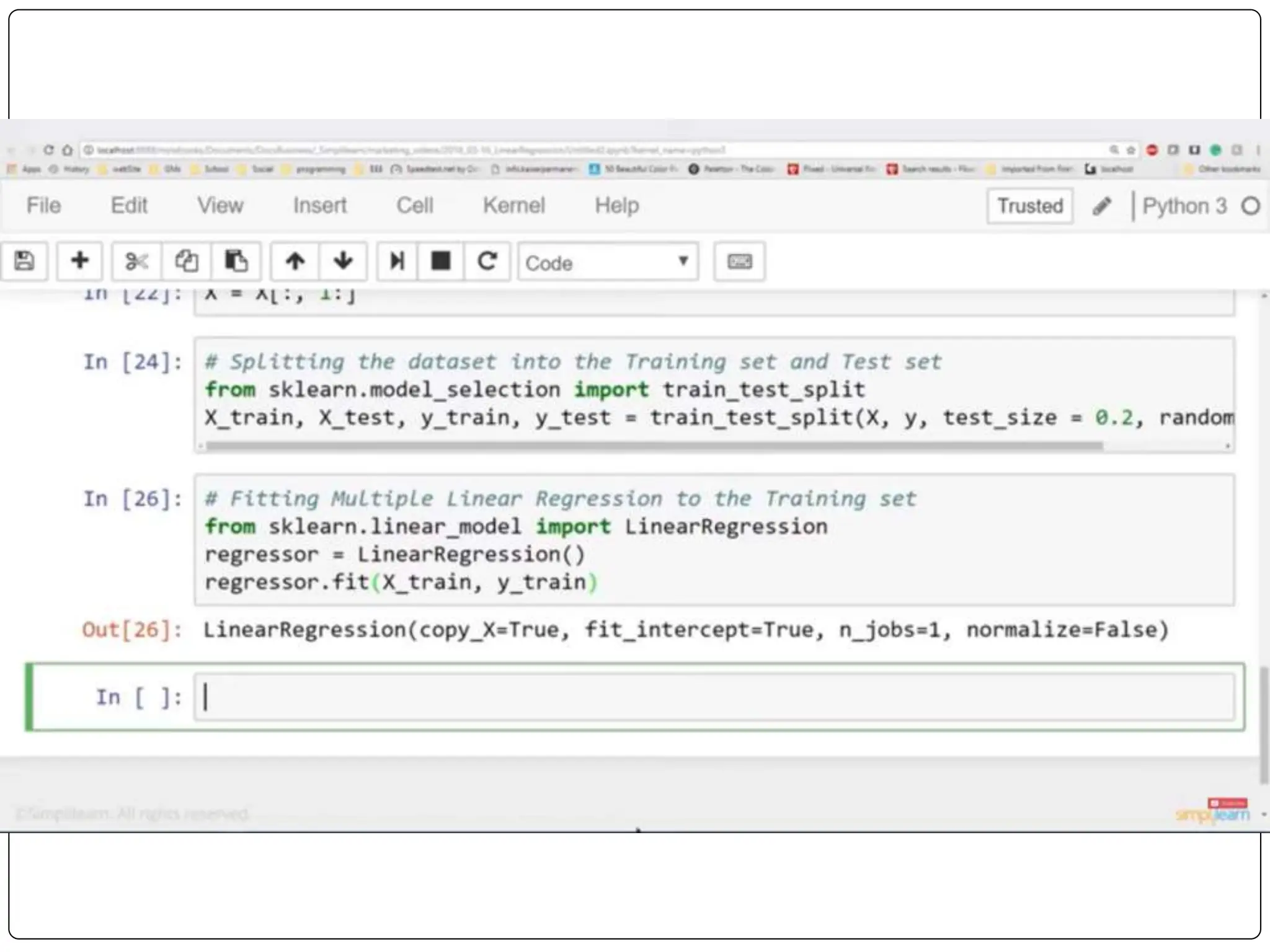
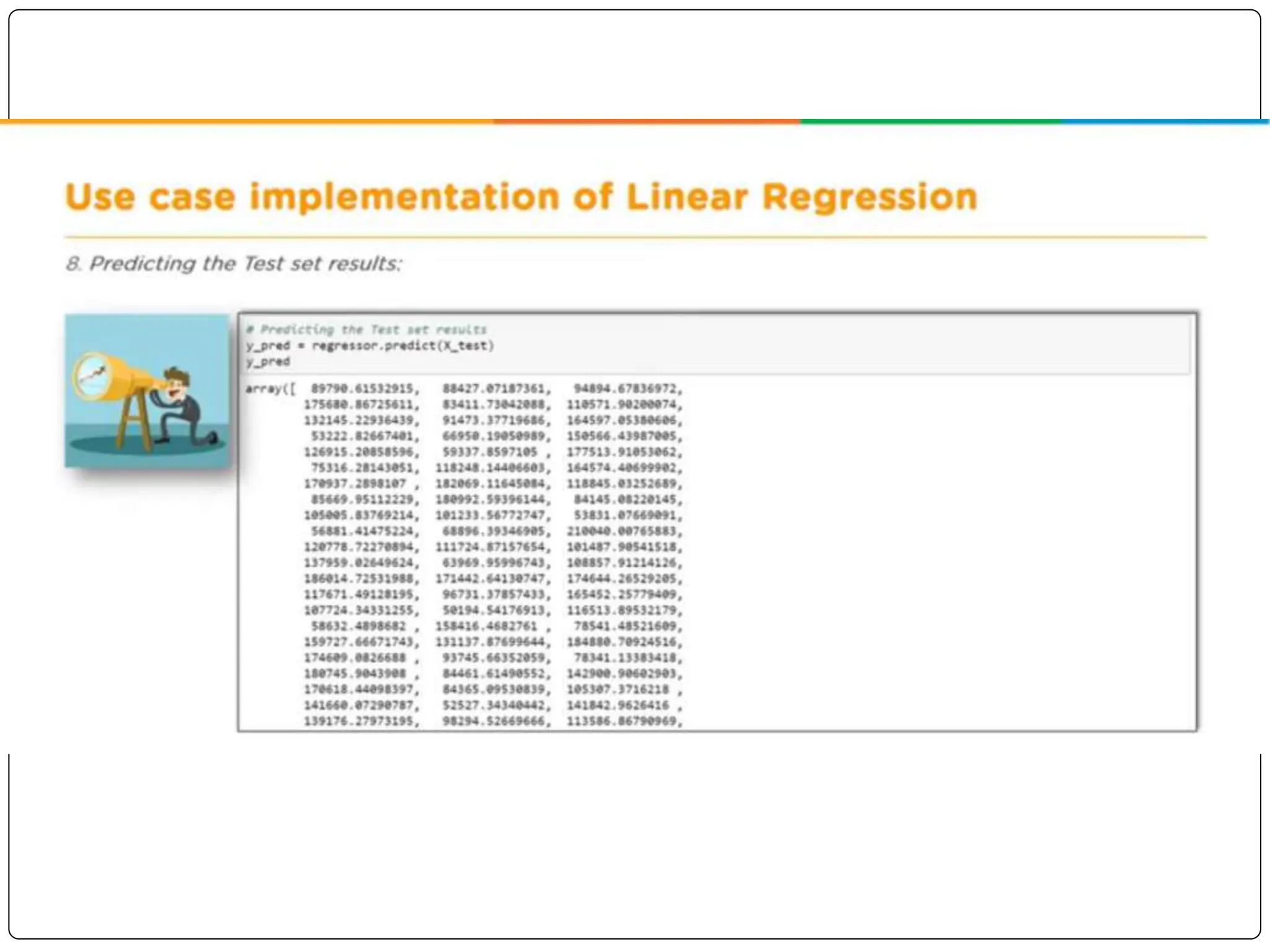
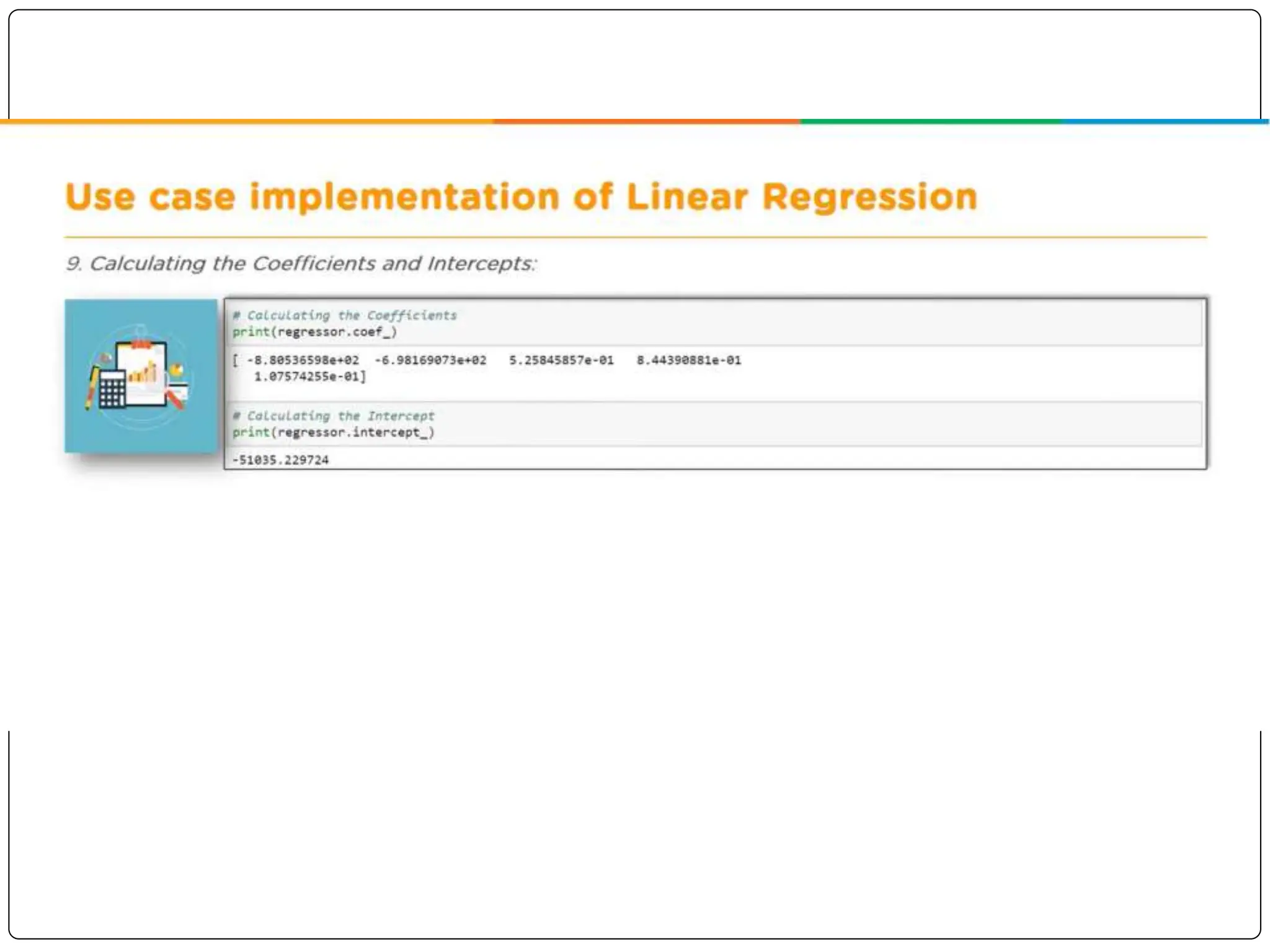
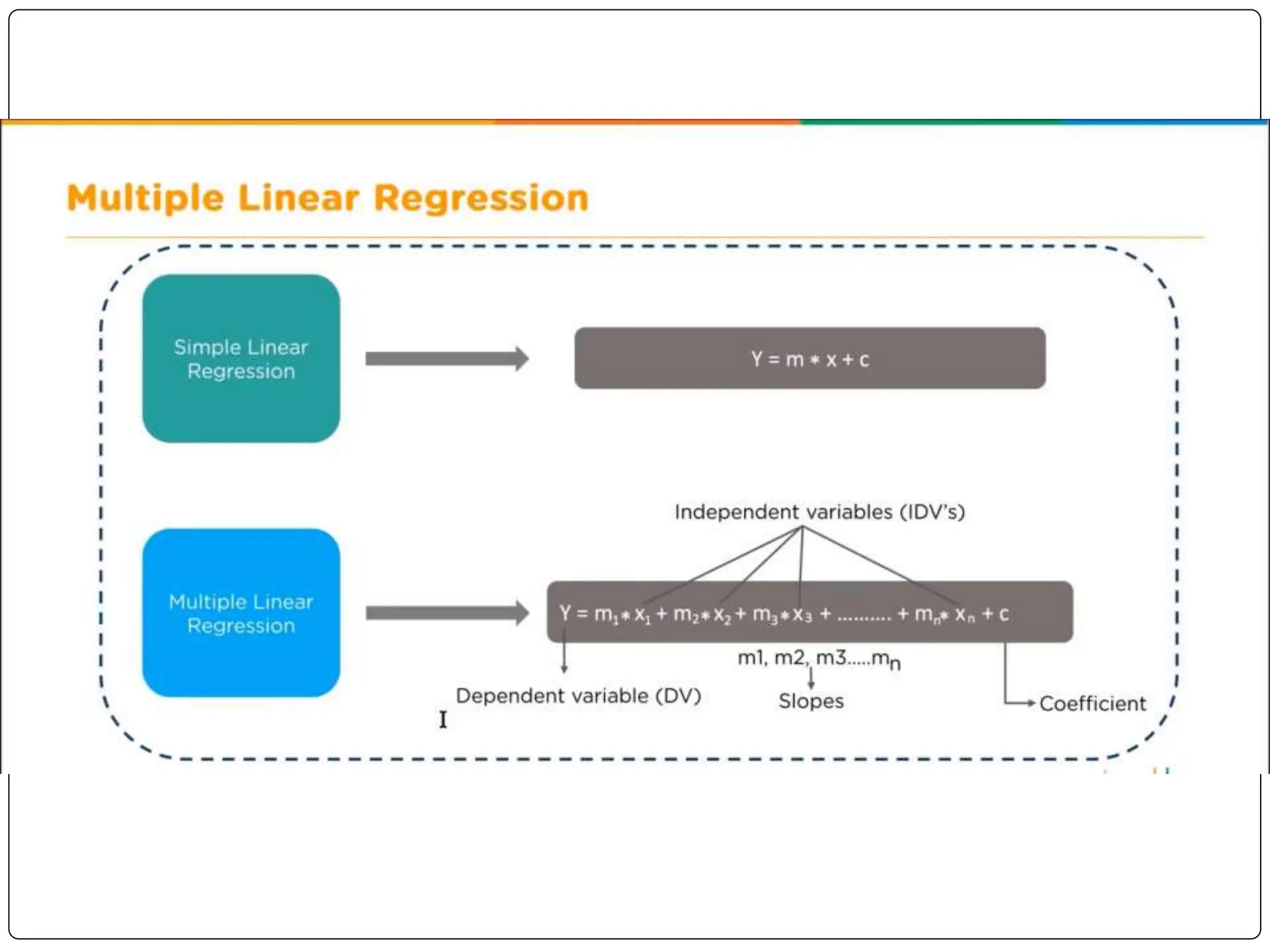
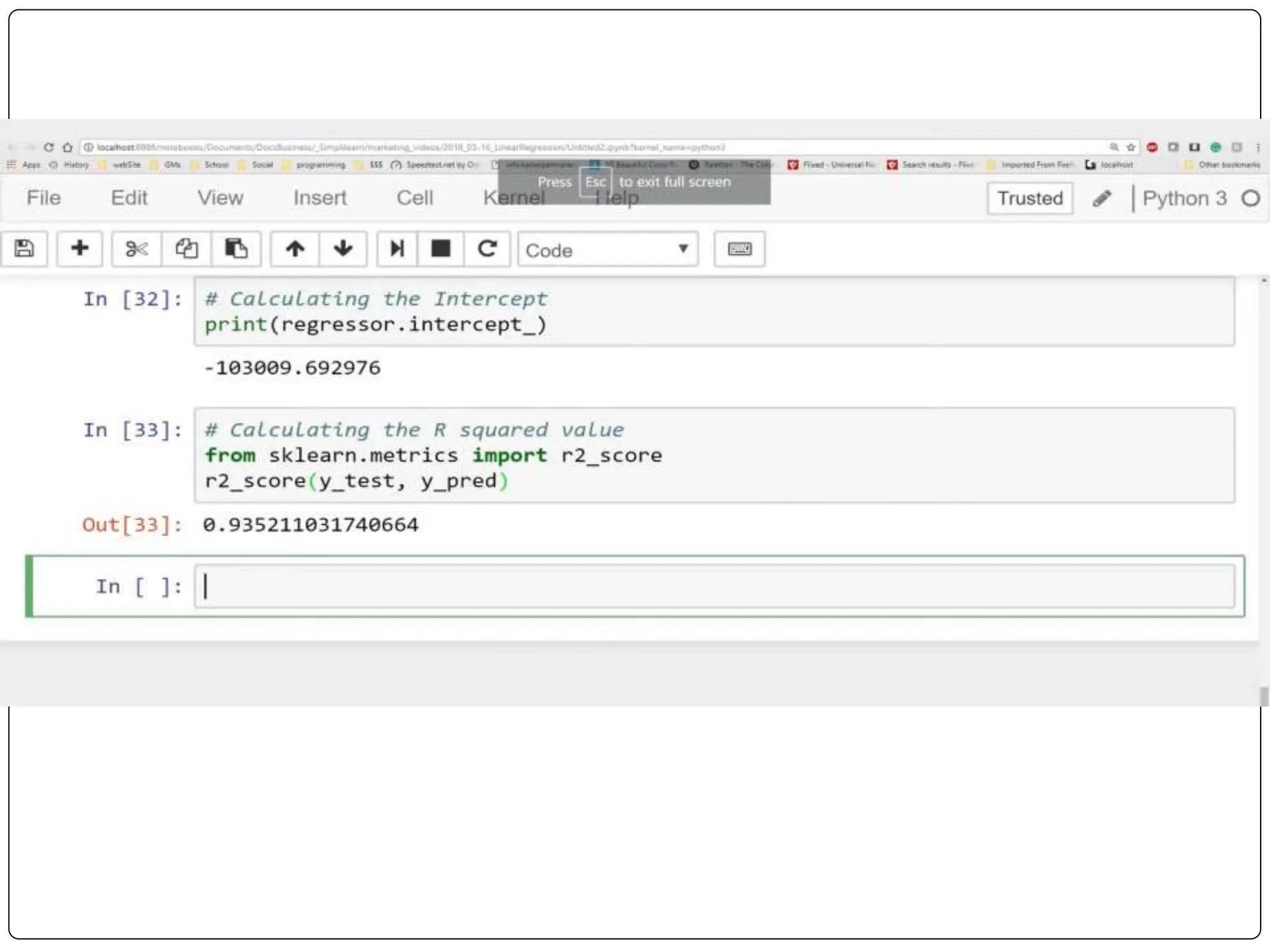
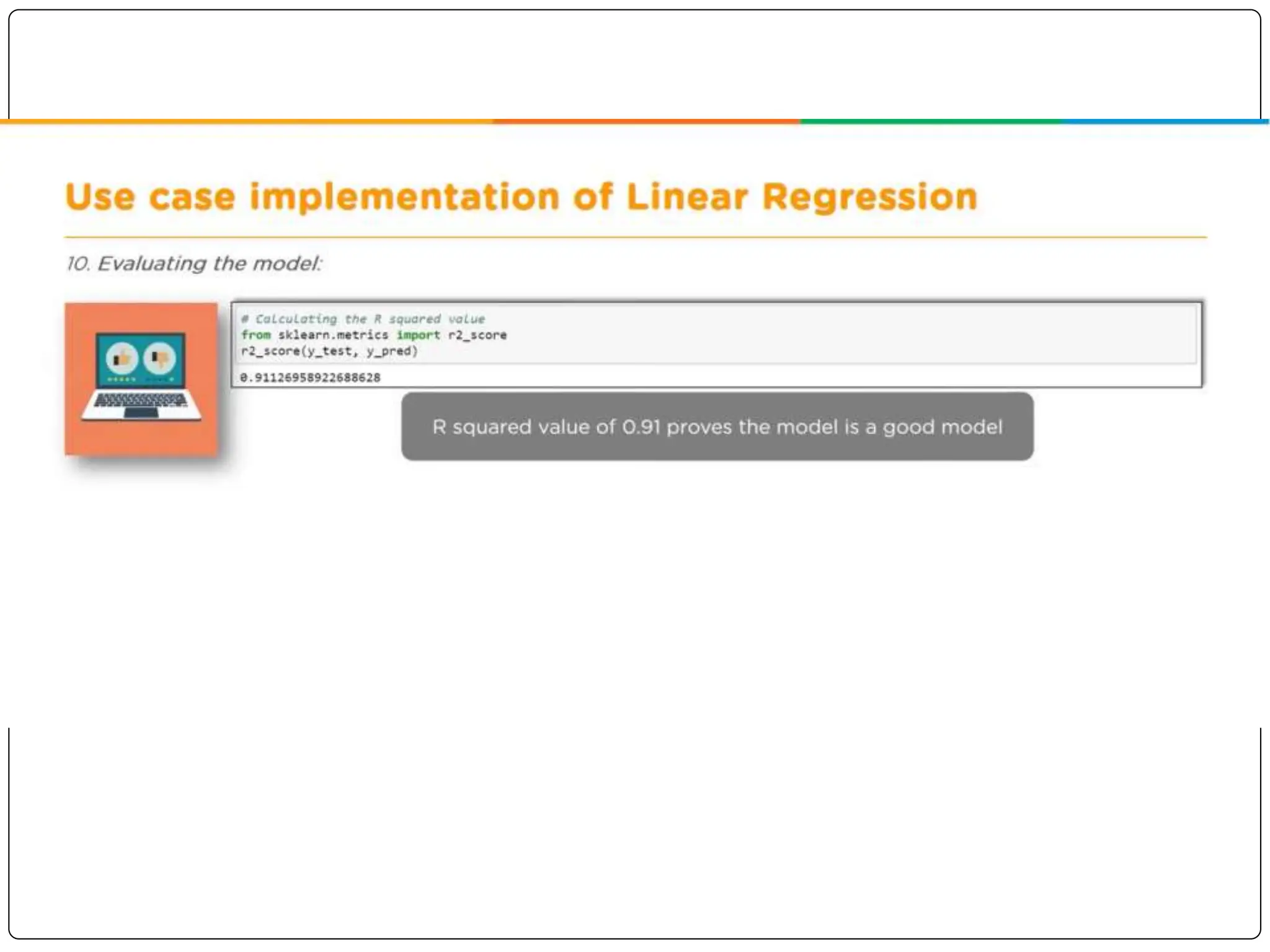
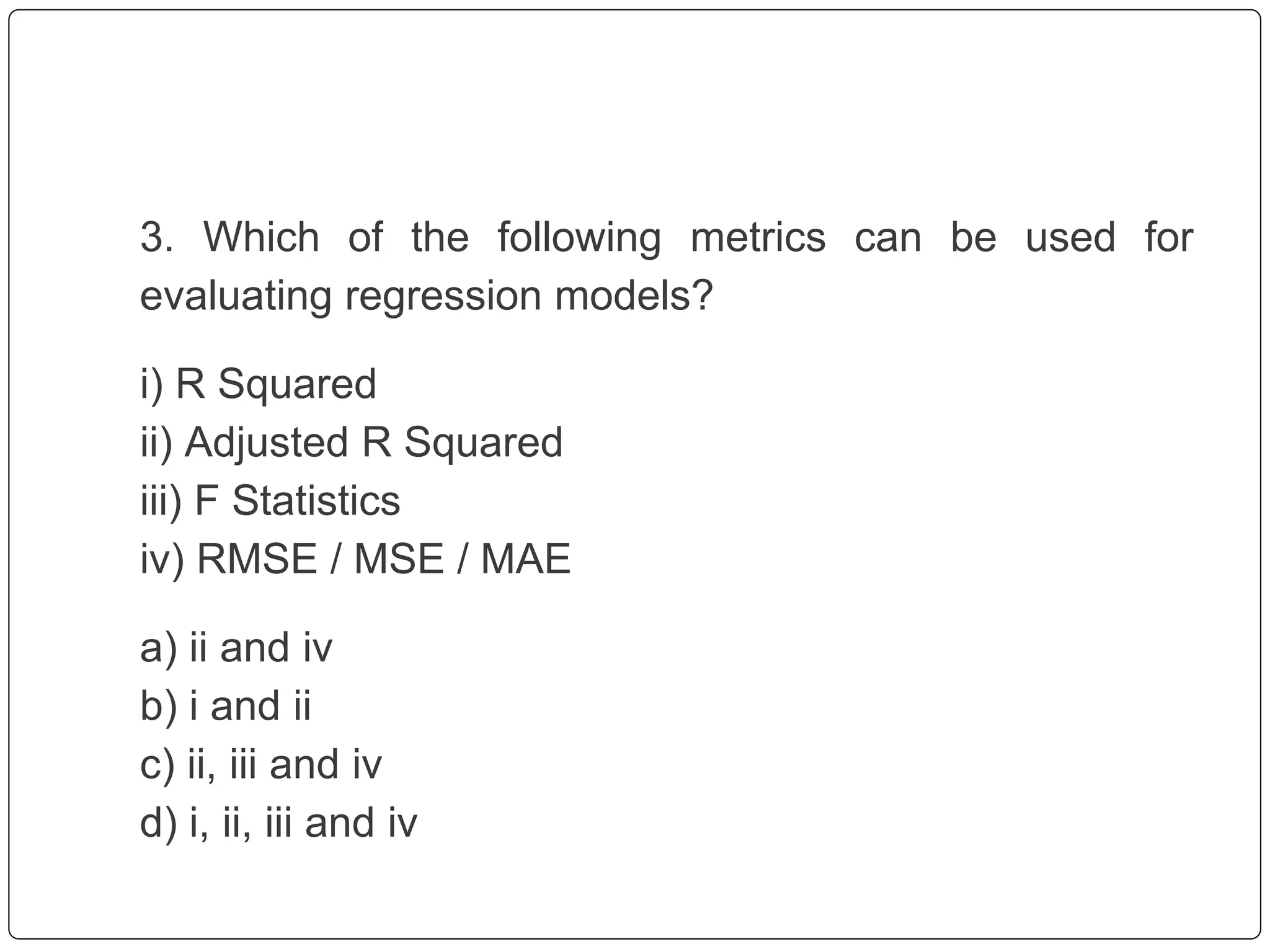
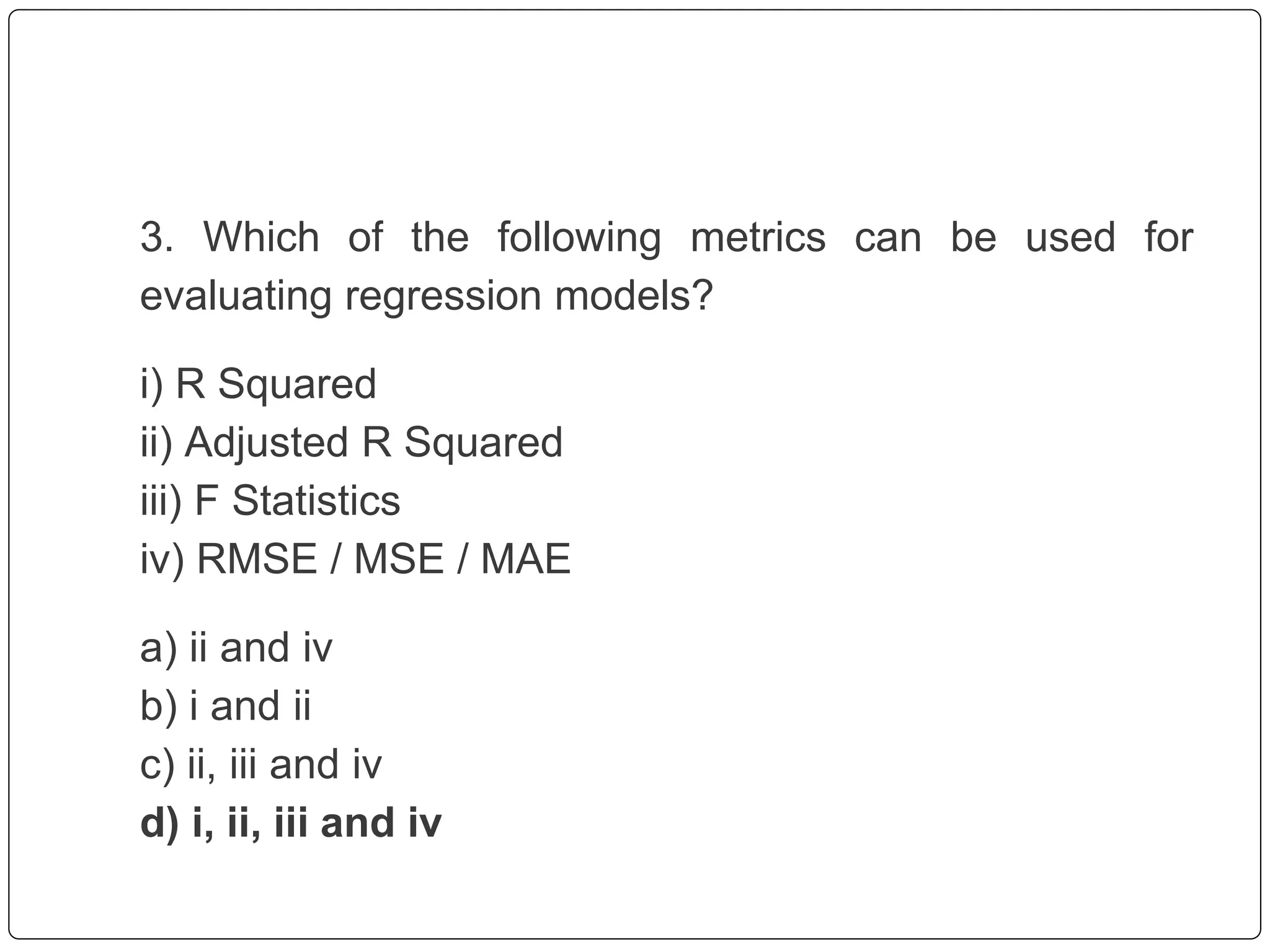
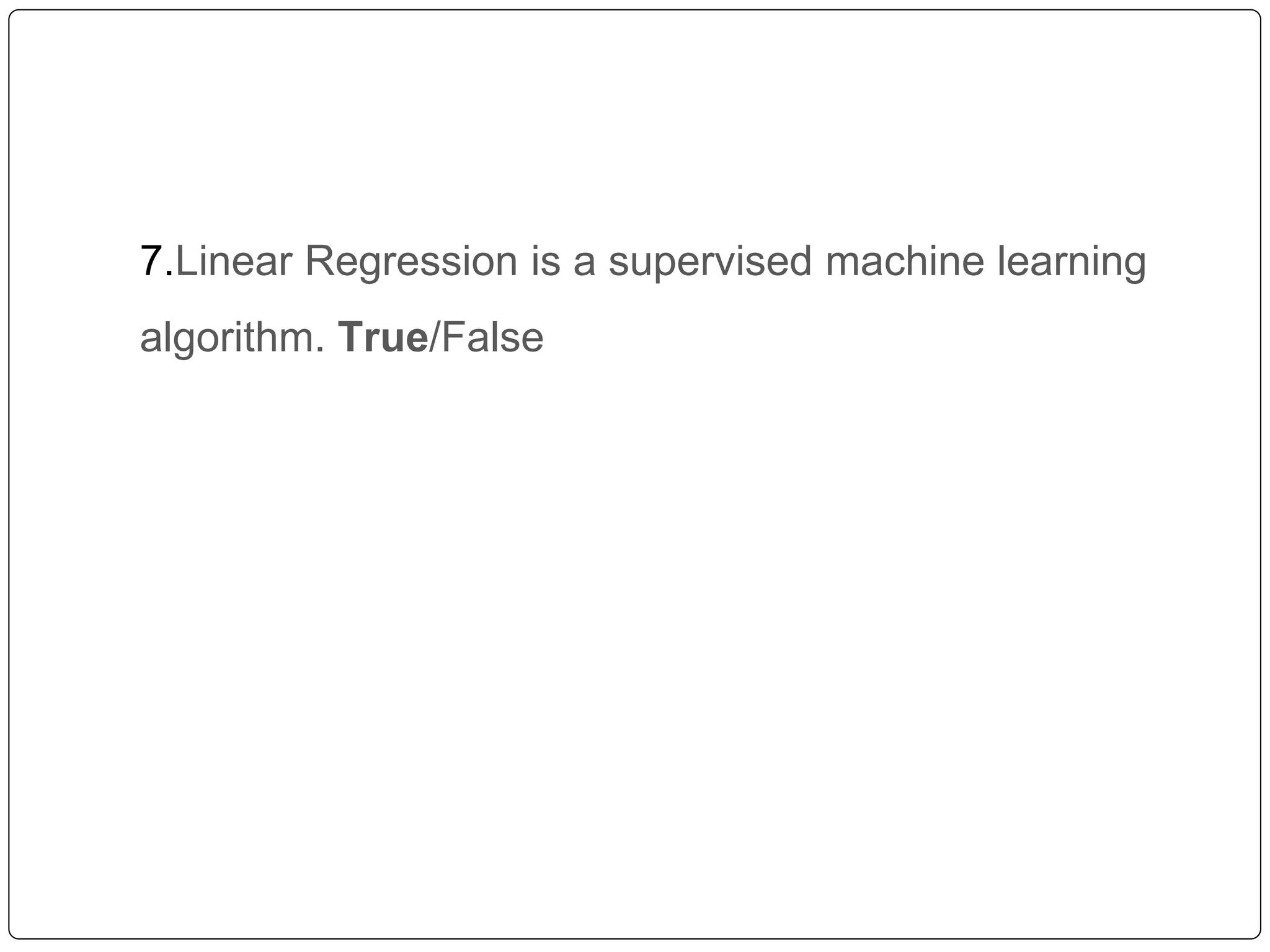
This document discusses multiple linear regression. It begins by explaining linear regression and its applications. It then discusses multiple linear regression, where there is more than one independent variable. As an example, it describes using multiple linear regression to estimate company profits based on various independent variables. The document provides resources for learning more about linear regression in Python.