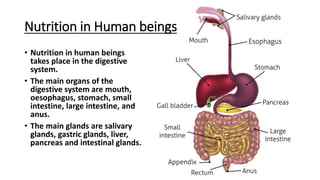
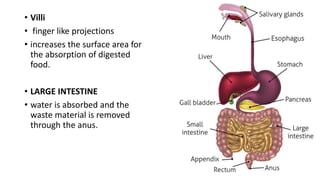
The document discusses several key life processes including nutrition, respiration, and excretion. It describes nutrition as the process of taking in food and utilizing it to build the body, grow, repair damage, and provide energy. Respiration is defined as the process by which food is burned with oxygen to release energy, which is stored in ATP molecules and used by cells. The main organs involved in respiration include the nostrils, trachea, bronchi, lungs and diaphragm. Excretion is the removal of waste from organisms. The document provides details on the human digestive and respiratory systems.