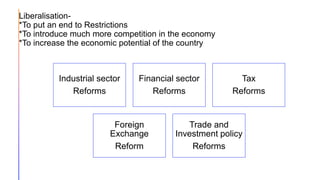
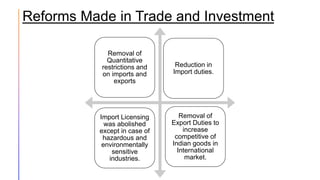
Liberalization in India involved wide-ranging reforms across multiple sectors including industrial, financial, tax, foreign exchange, and trade/investment policies. Key reforms included abolishing licensing for most industries except sensitive sectors like defense; allowing private sector participation in all industries except rail, atomic energy and defense; deregulating prices and distribution in many industries; establishing private banks and increasing foreign investment limits in the financial sector; reducing income and simplifying indirect taxes; allowing market determination of exchange rates; removing restrictions on imports/exports and quantitative limits; and reducing import duties to promote competitiveness. The goal was to reduce the government's role in the economy and introduce greater competition to increase growth.