This document introduces several new features of Symfony2 including the Dependency Injection Container, form framework, and Doctrine2 integration. It discusses how the Dependency Injection Container can be used to define and load services, provides an example of creating a Twitter service, and explains how to enable extensions. It also briefly outlines using the form framework and integrating Doctrine2's DBAL, ORM, and command lines.


![Dependency Injection Container
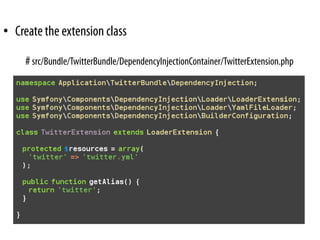
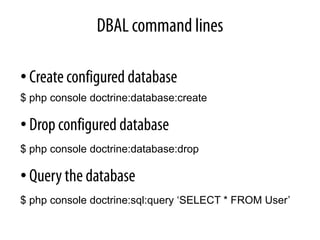
• Dependency Injection Container
–a way to organize dependencies
–Define services
services:
zend.translator:
class: User
arguments: [@user.storage]
user.storage:
class: SessionStorage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/letsplaywithsf2-100709014049-phpapp02/85/Lets-play-with-Symfony2-3-320.jpg)


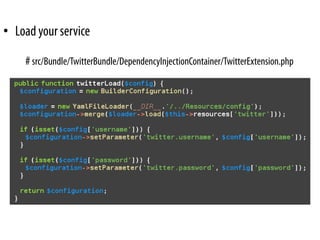
![• Create your own service
–Define your services:
# src/Bundle/TwitterBundle/Resources/config/user.yml
parameters:
twitter.username: ~
twitter.password: ~
services:
twitter:
class: Twitter
arguments: [%twitter.username%, %twitter.password%]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/letsplaywithsf2-100709014049-phpapp02/85/Lets-play-with-Symfony2-6-320.jpg)