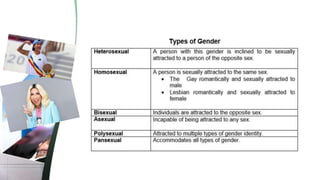
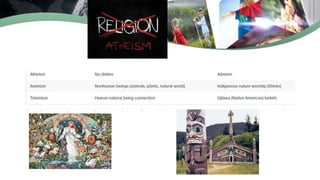
The document explores concepts of nationality and ethnicity, emphasizing the identity tied to nations and the various ethnic groups within them. It discusses social differences, including gender, race, and age, along with socioeconomic class and political identity. Moreover, it introduces cultural variation, ethnocentrism, and cultural relativism, encouraging an understanding of cultures in their own contexts.