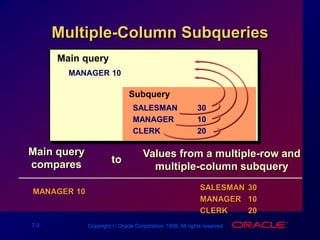
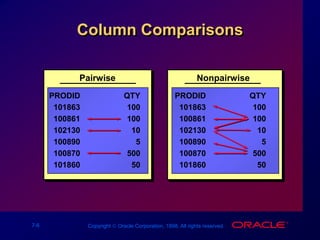
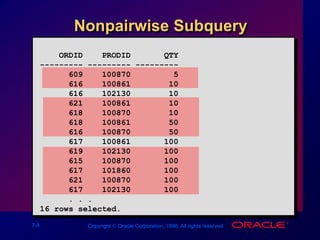
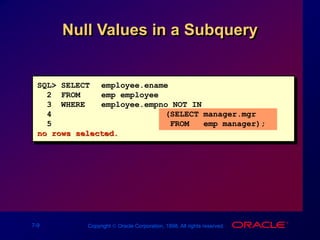
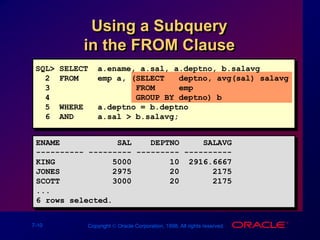
This document discusses multiple-column subqueries in Oracle SQL. It describes how multiple-column subqueries can return multiple columns to compare values pair-wise or non-pair-wise. It also explains how to use a subquery in the FROM clause to join tables and compare columns between the main and subquery results.