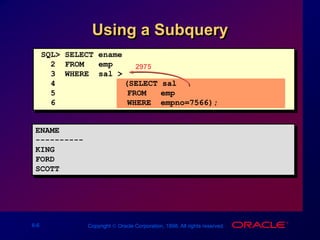
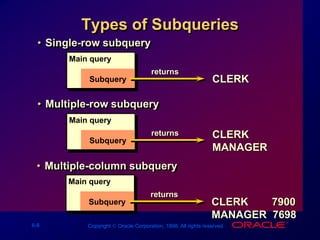
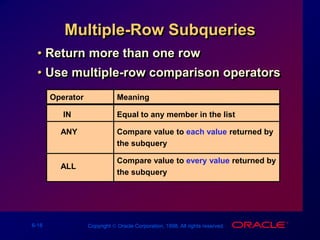
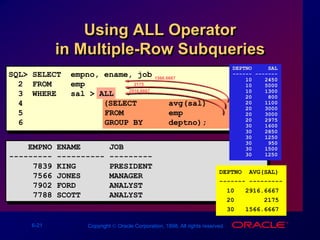
The document discusses subqueries in SQL, including:
- Types of subqueries like single-row and multiple-row subqueries
- Operators used with different subquery types like =, >, IN, ANY, ALL
- Examples of subqueries used to return rows that meet conditions compared to results of inner queries