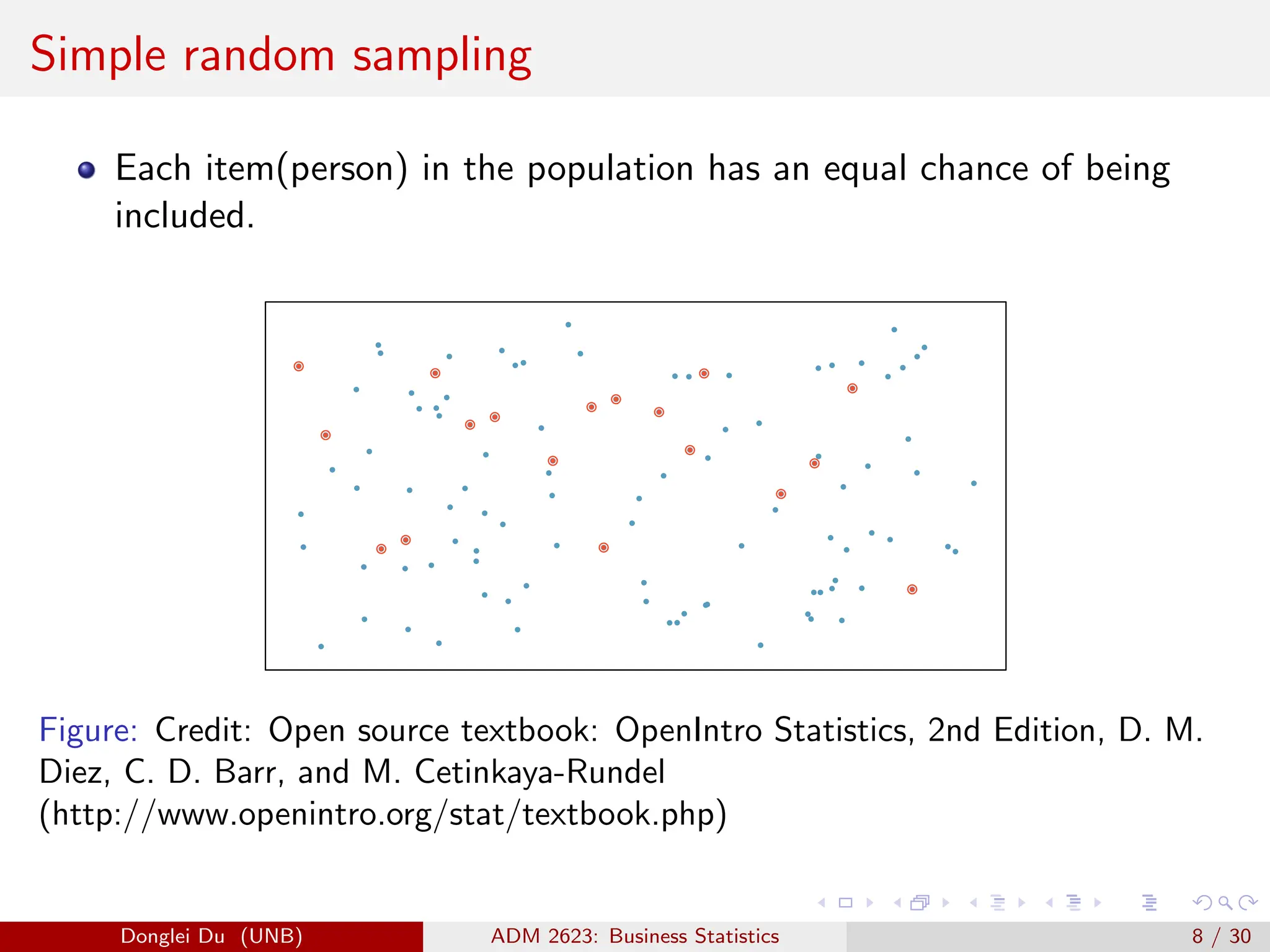
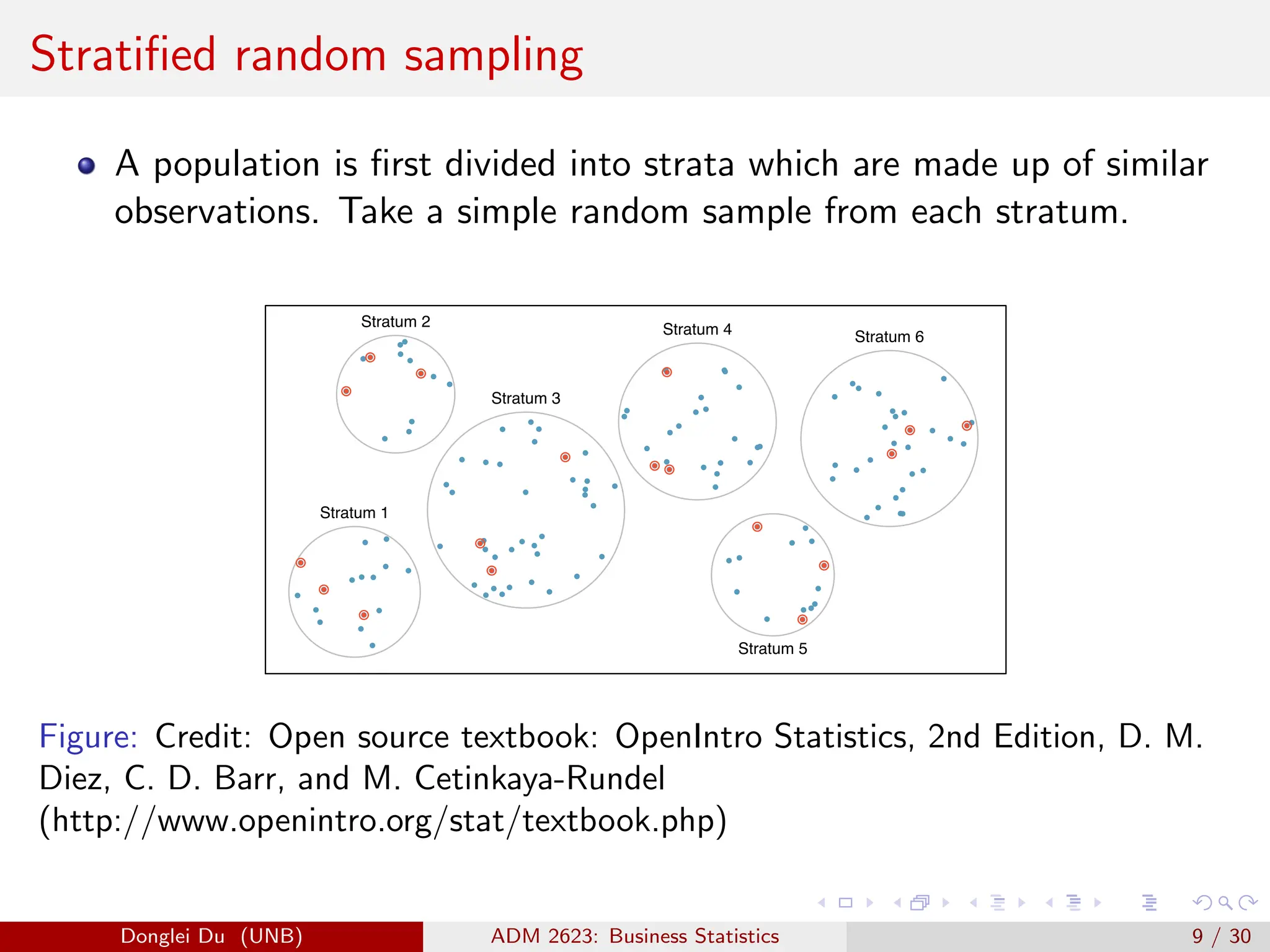
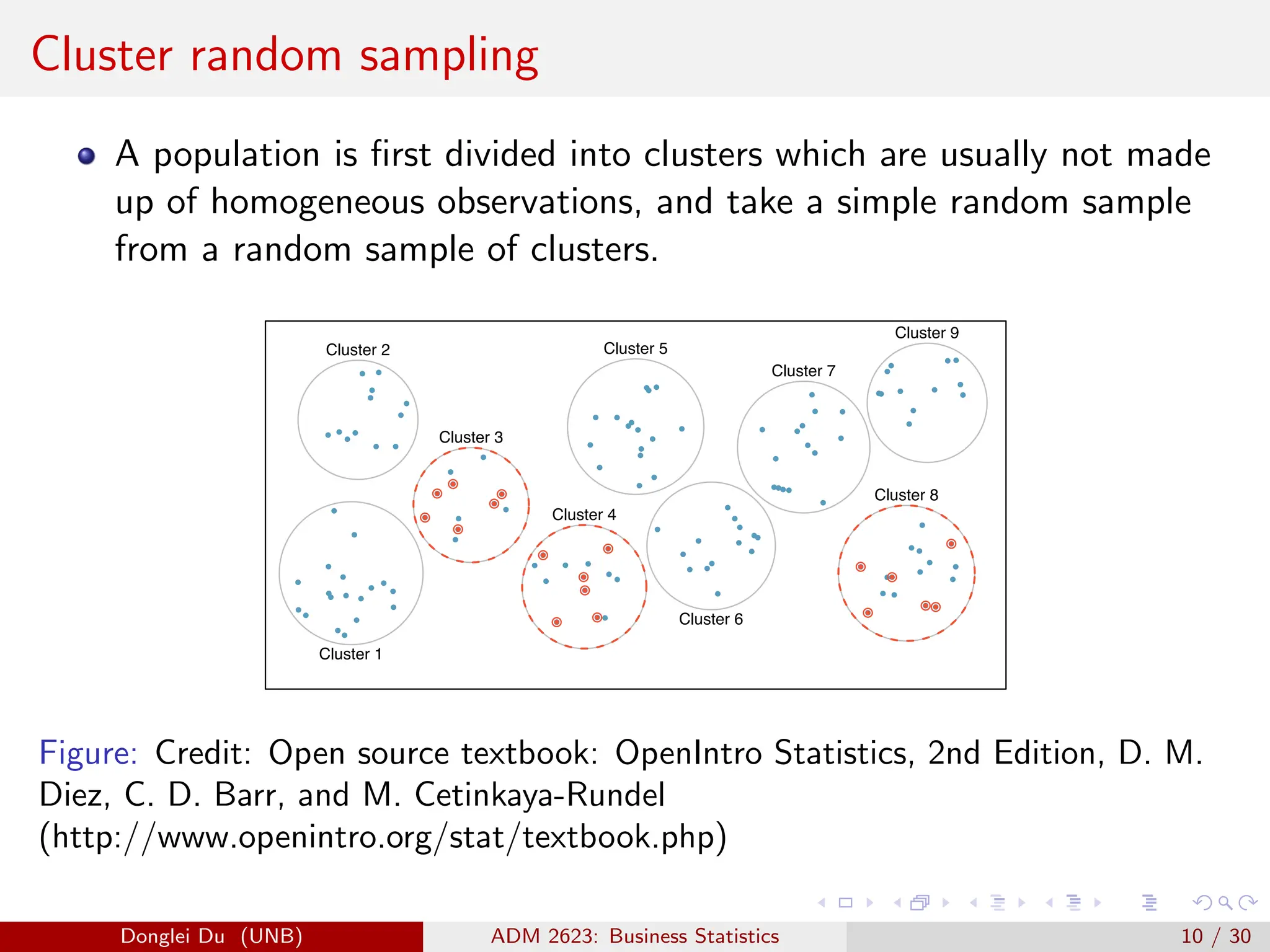
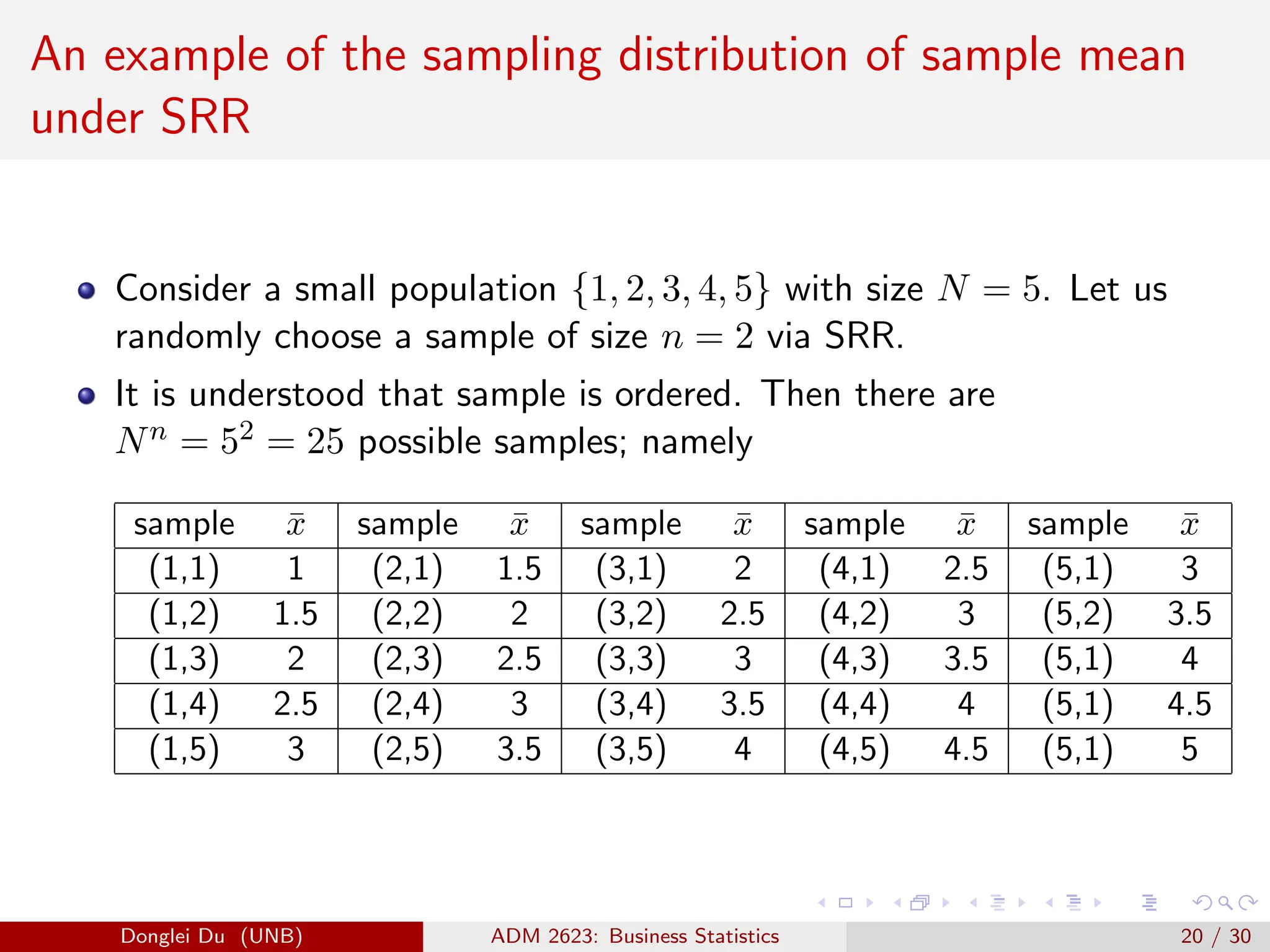
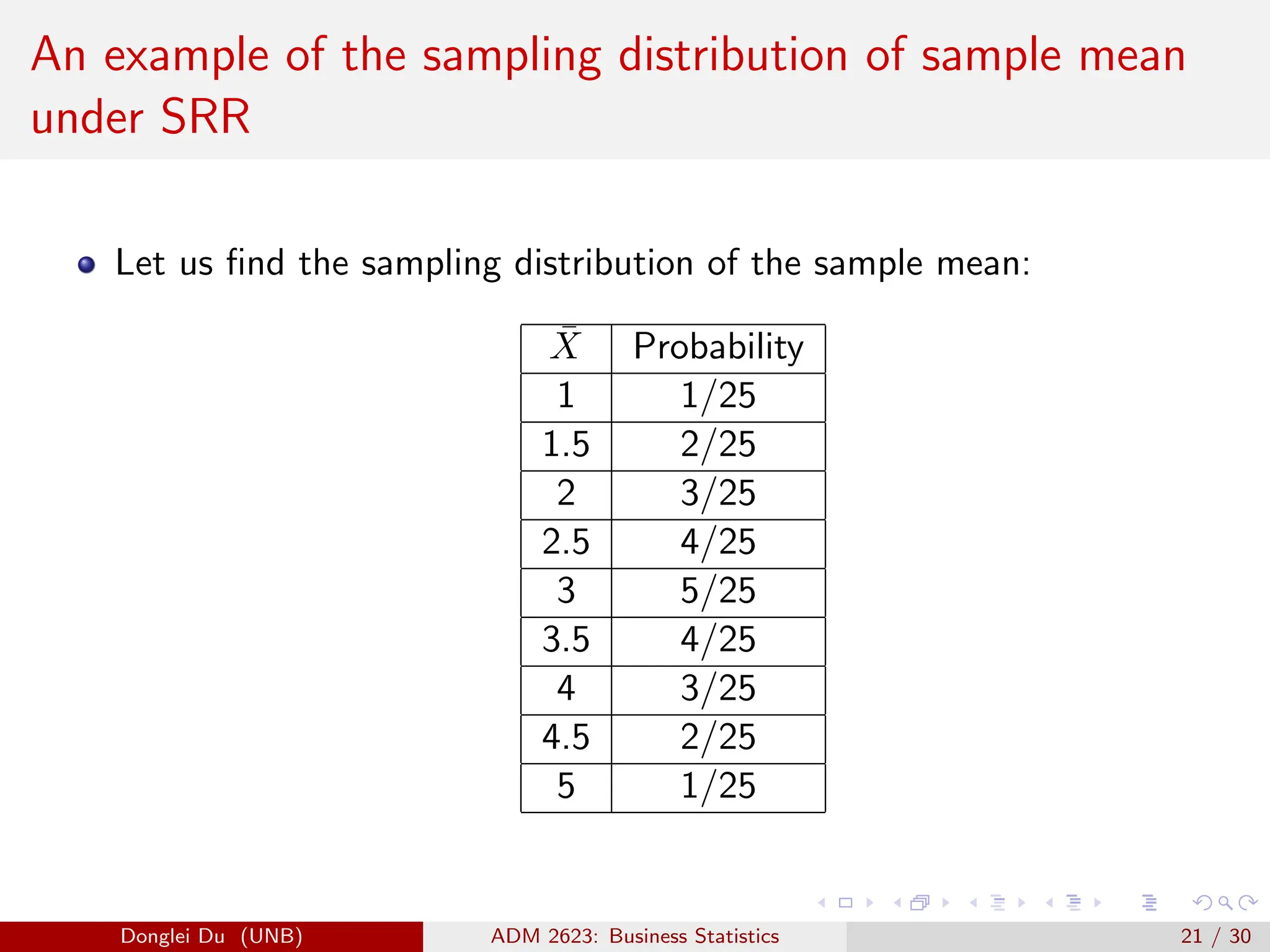
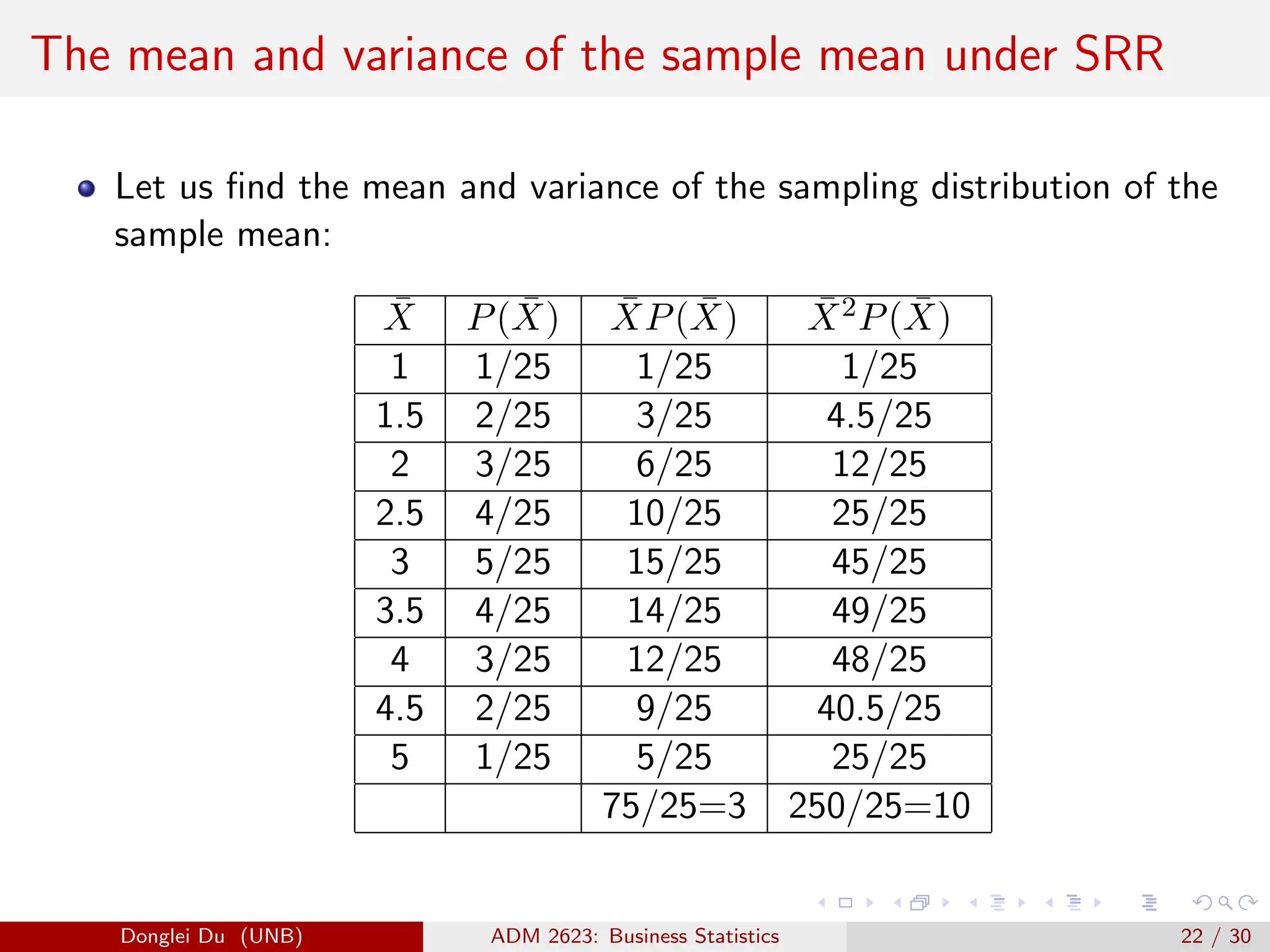
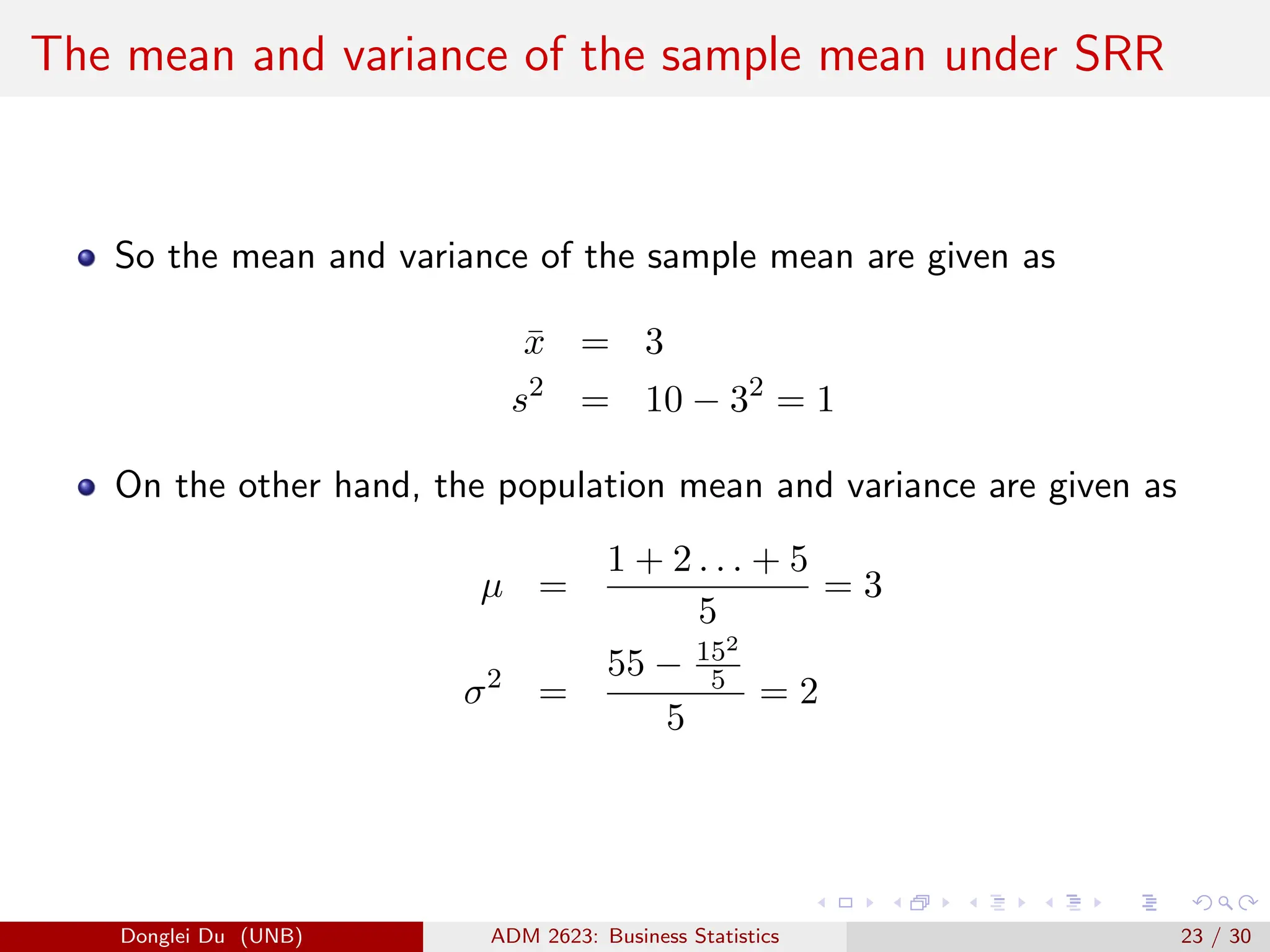
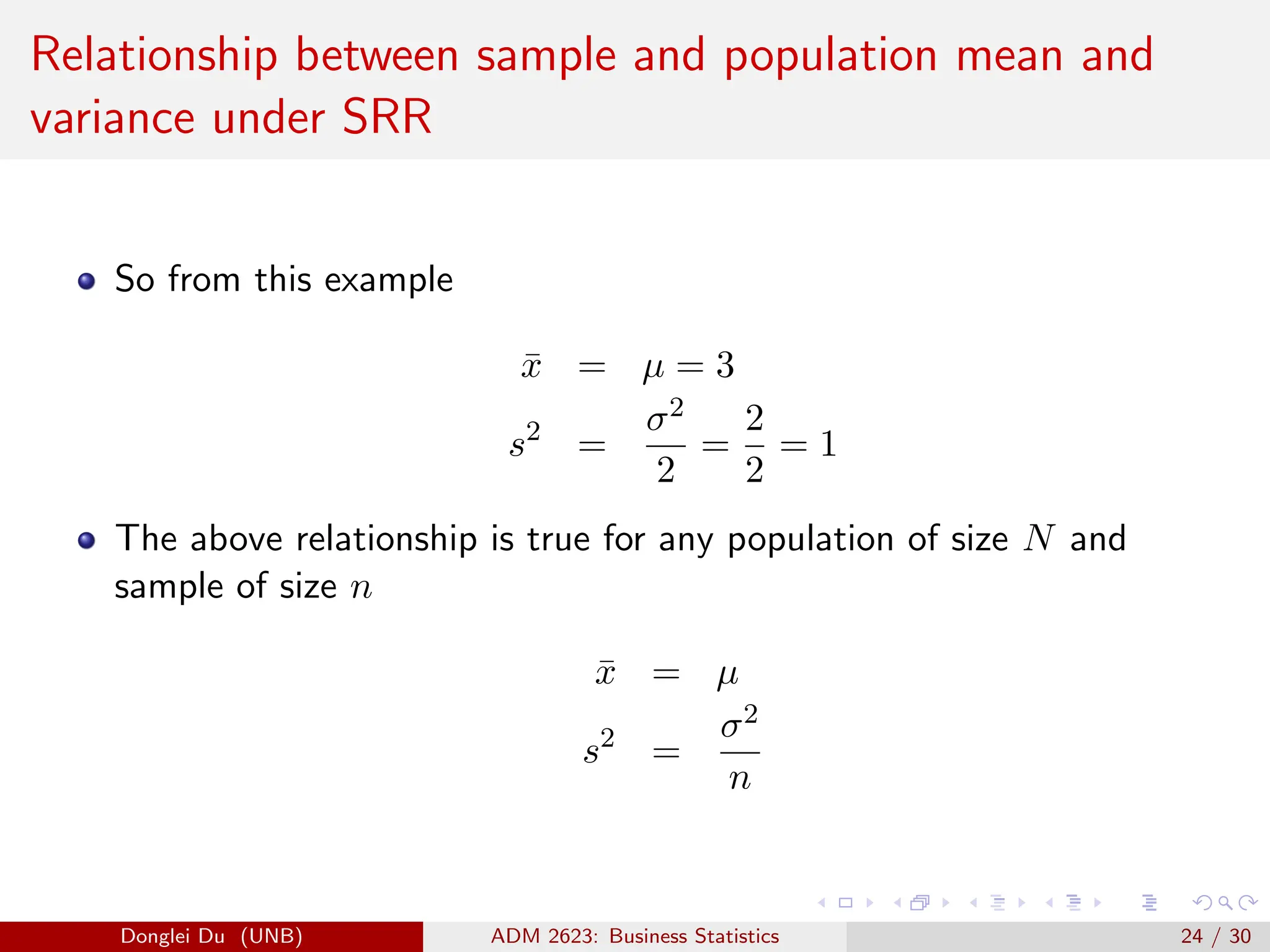
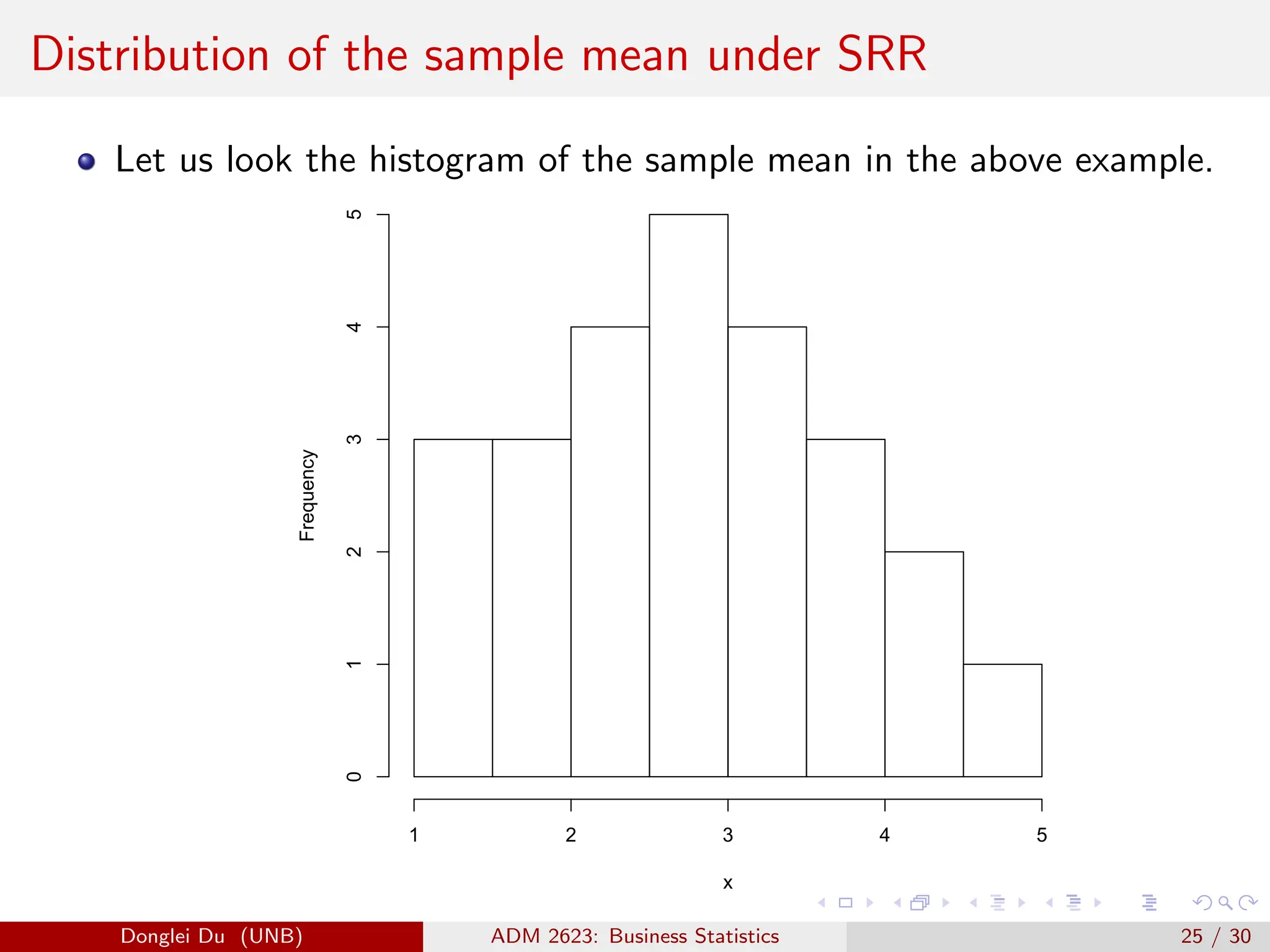
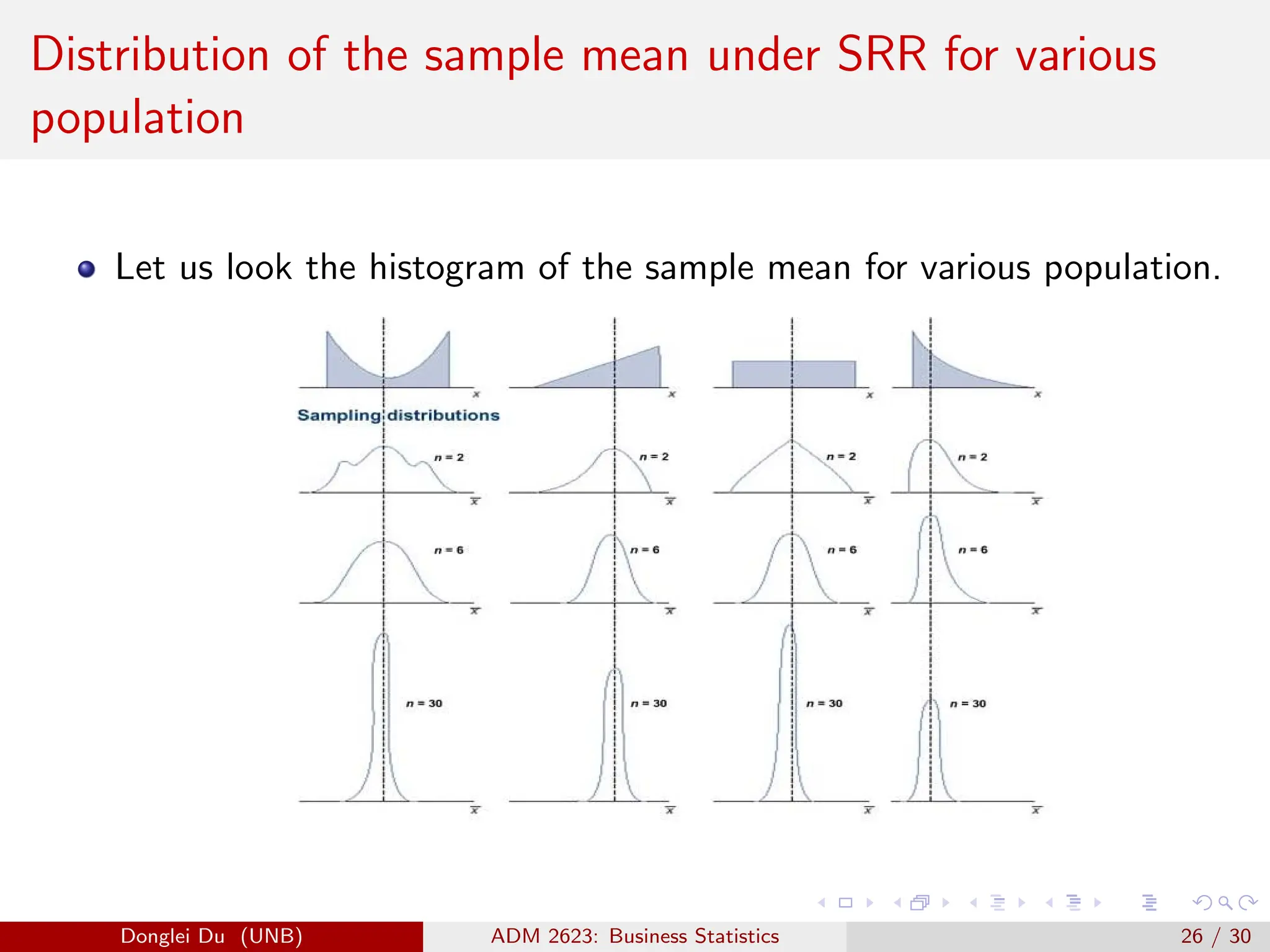
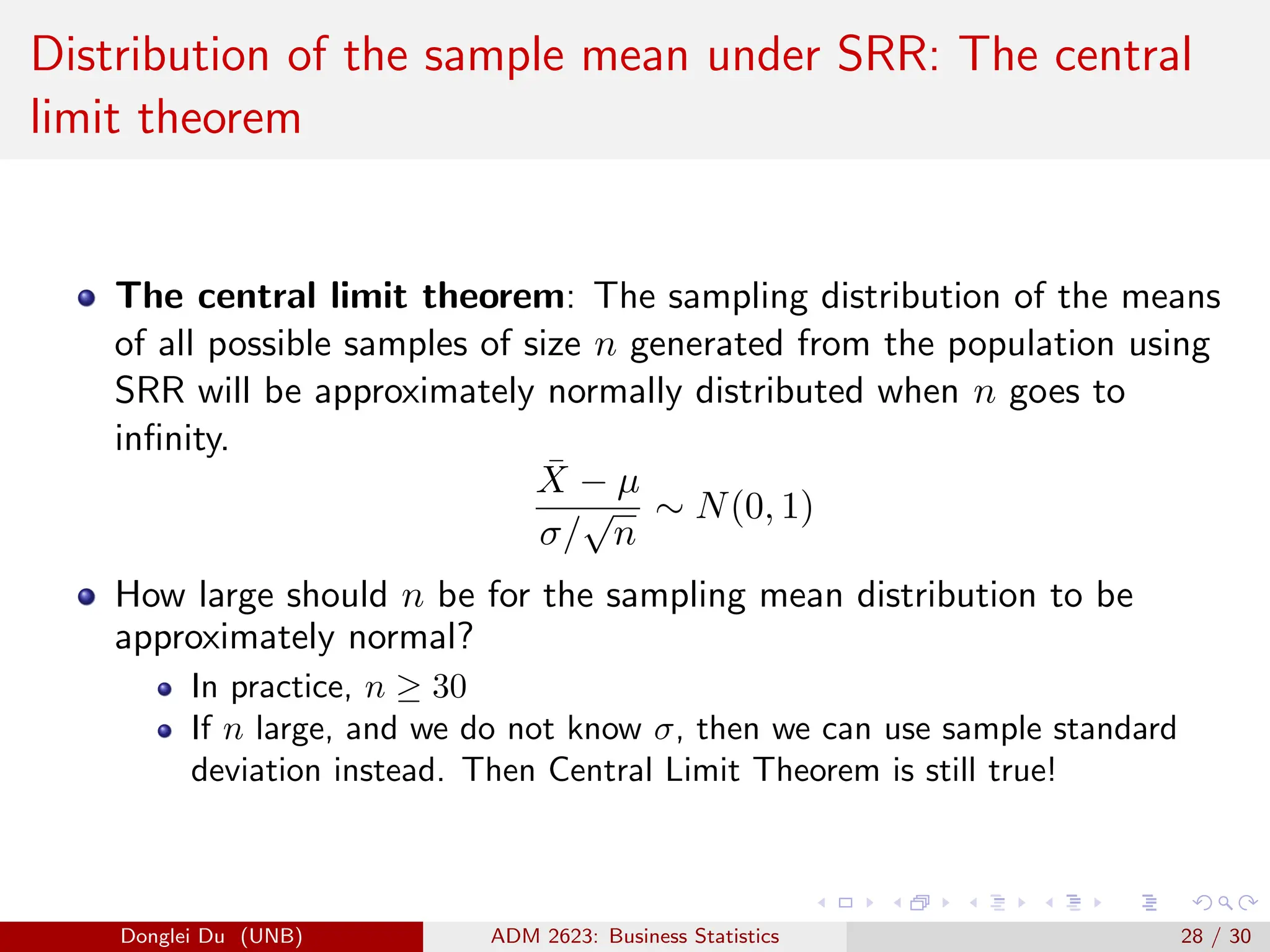
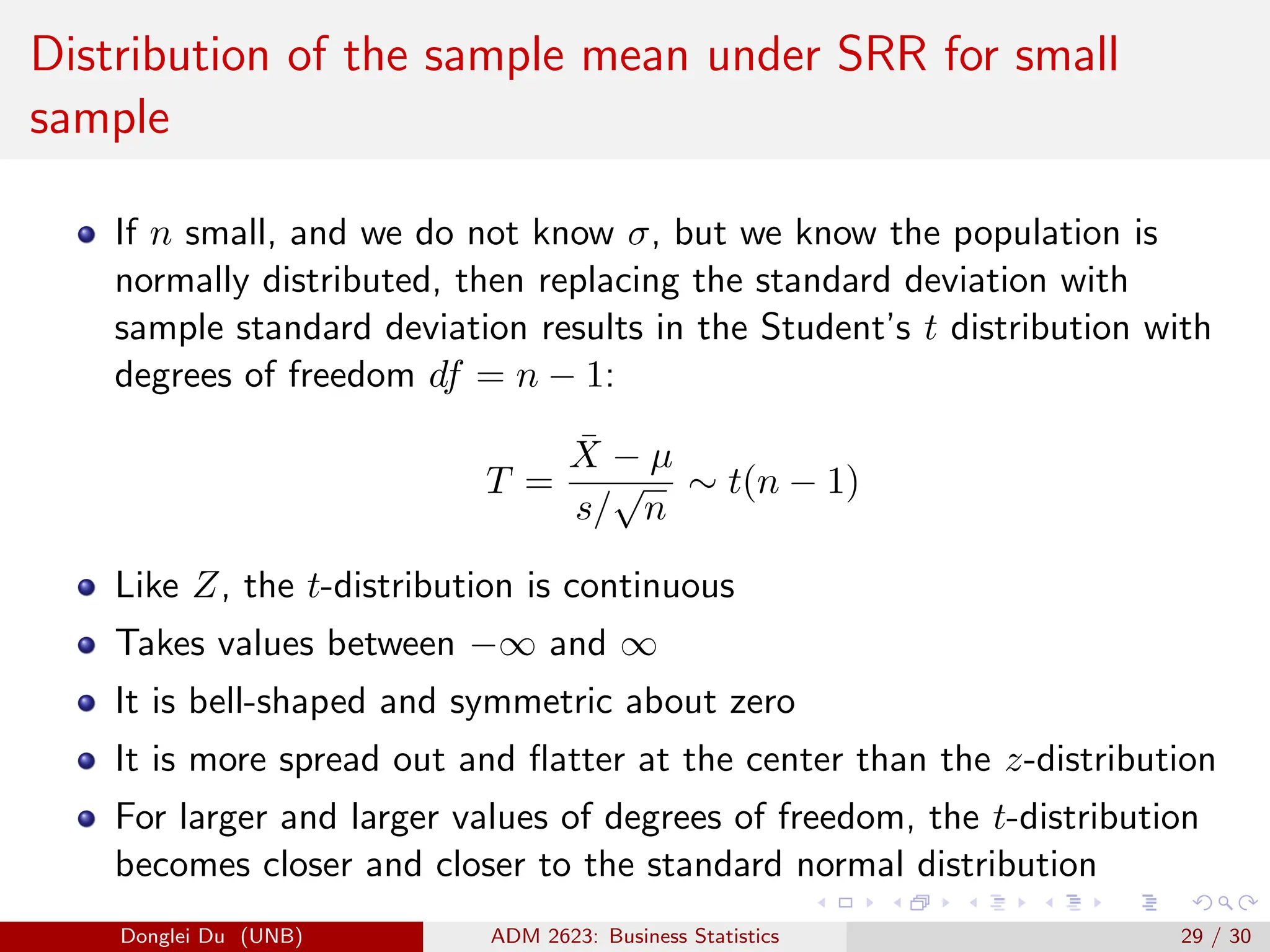
The document discusses various sampling methods used in statistics including probability and non-probability sampling, sampling with and without replacement, simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster random sampling. It provides examples of how to implement simple random sampling with and without replacement in R code. Key concepts covered include sampling error versus non-sampling error and the sampling distribution and central limit theorem as they apply to the sample mean under simple random sampling with replacement.