Here are the key points about how evaluation cost scales with input size:
- For many algorithms, if the input size increases by a factor of k, the running time increases by a factor of k or faster. This is called polynomial time.
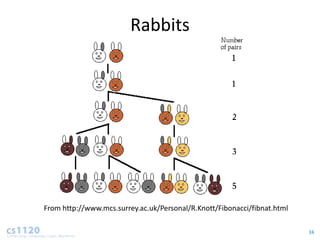
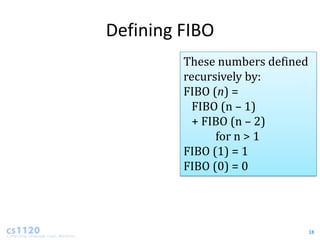
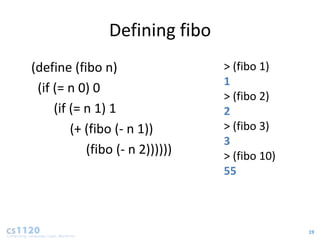
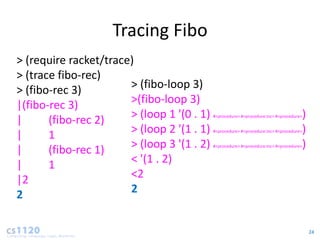
- For recursive algorithms like fibonacci, the running time increases exponentially with input size. Each additional input doubles the number of recursive calls.
- Space usage also often scales with input size. Recursive algorithms use additional stack space proportional to recursion depth, which grows with input.
- Caching/memoization can improve scaling by reusing results of subproblems. But it increases space usage.
- Data structure choice matters - hash tables allow O(1) access vs