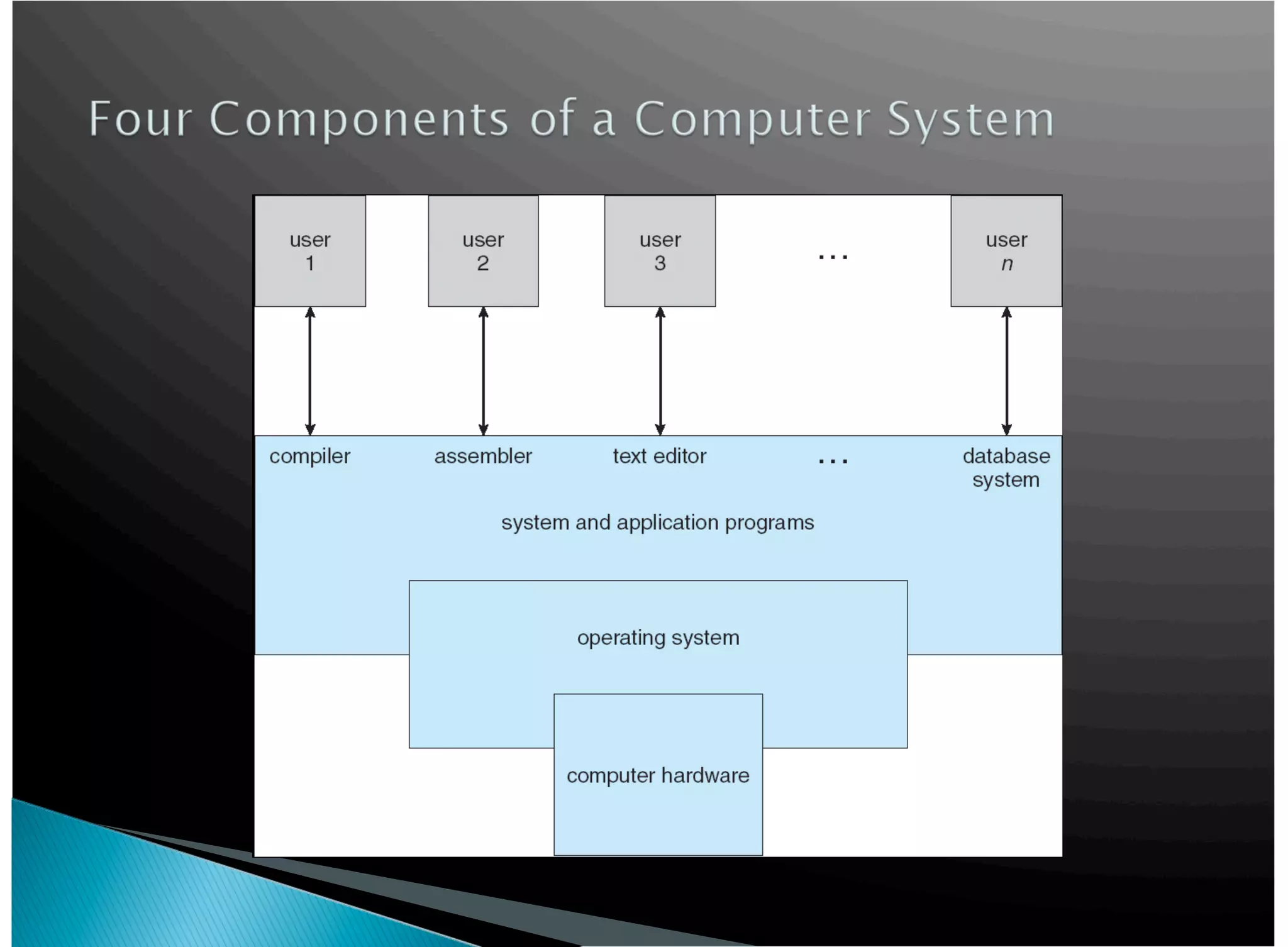
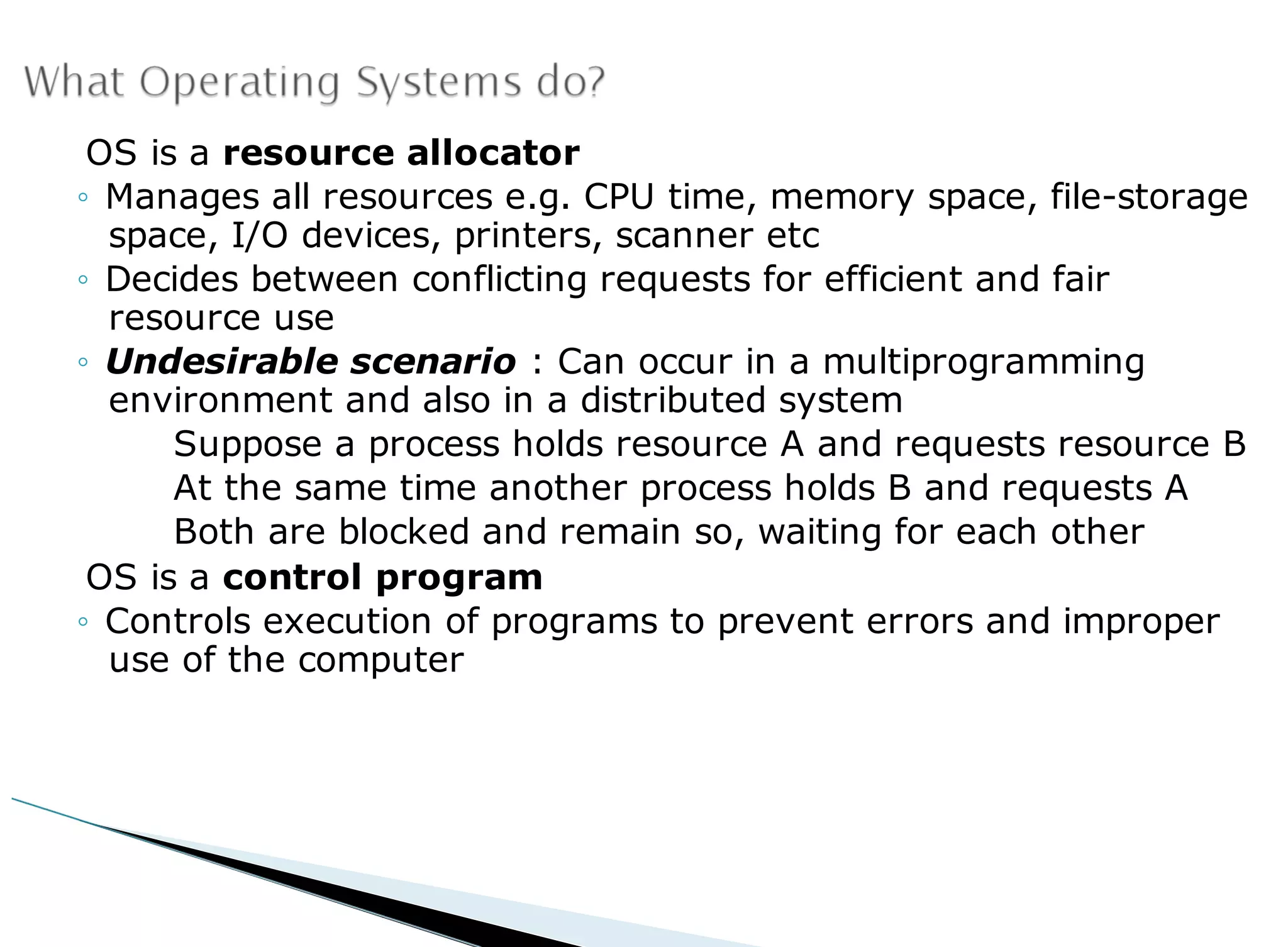
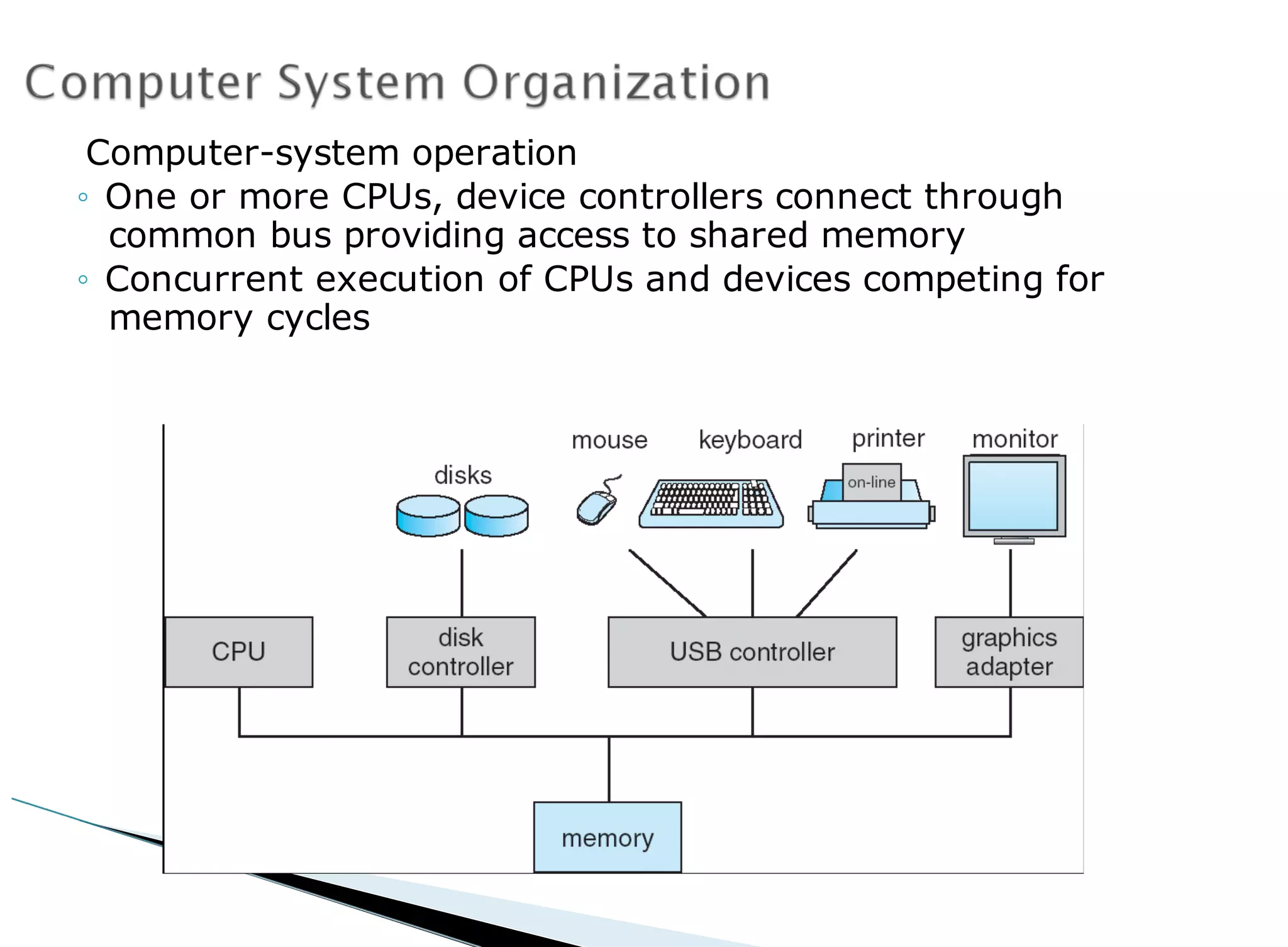
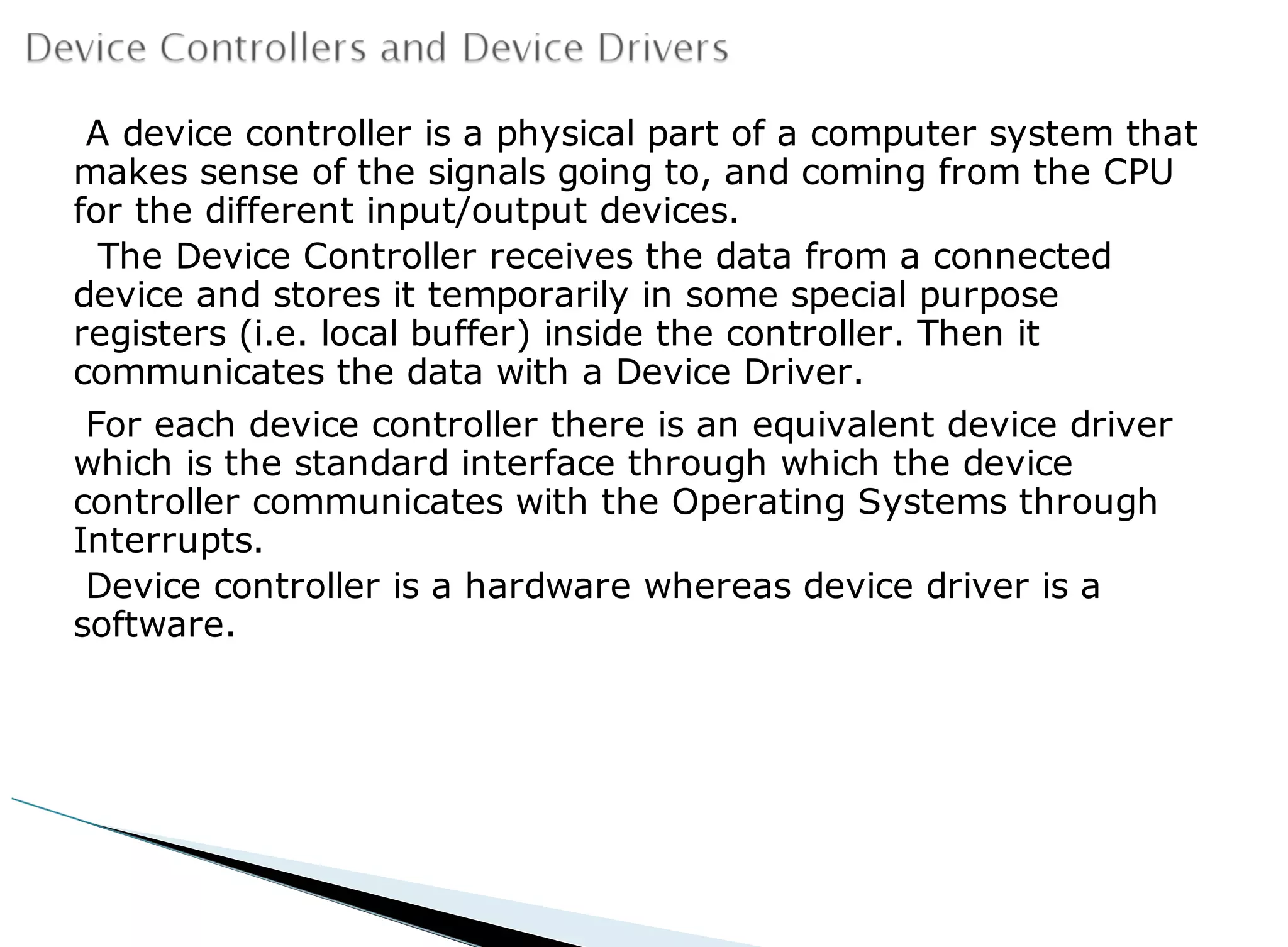
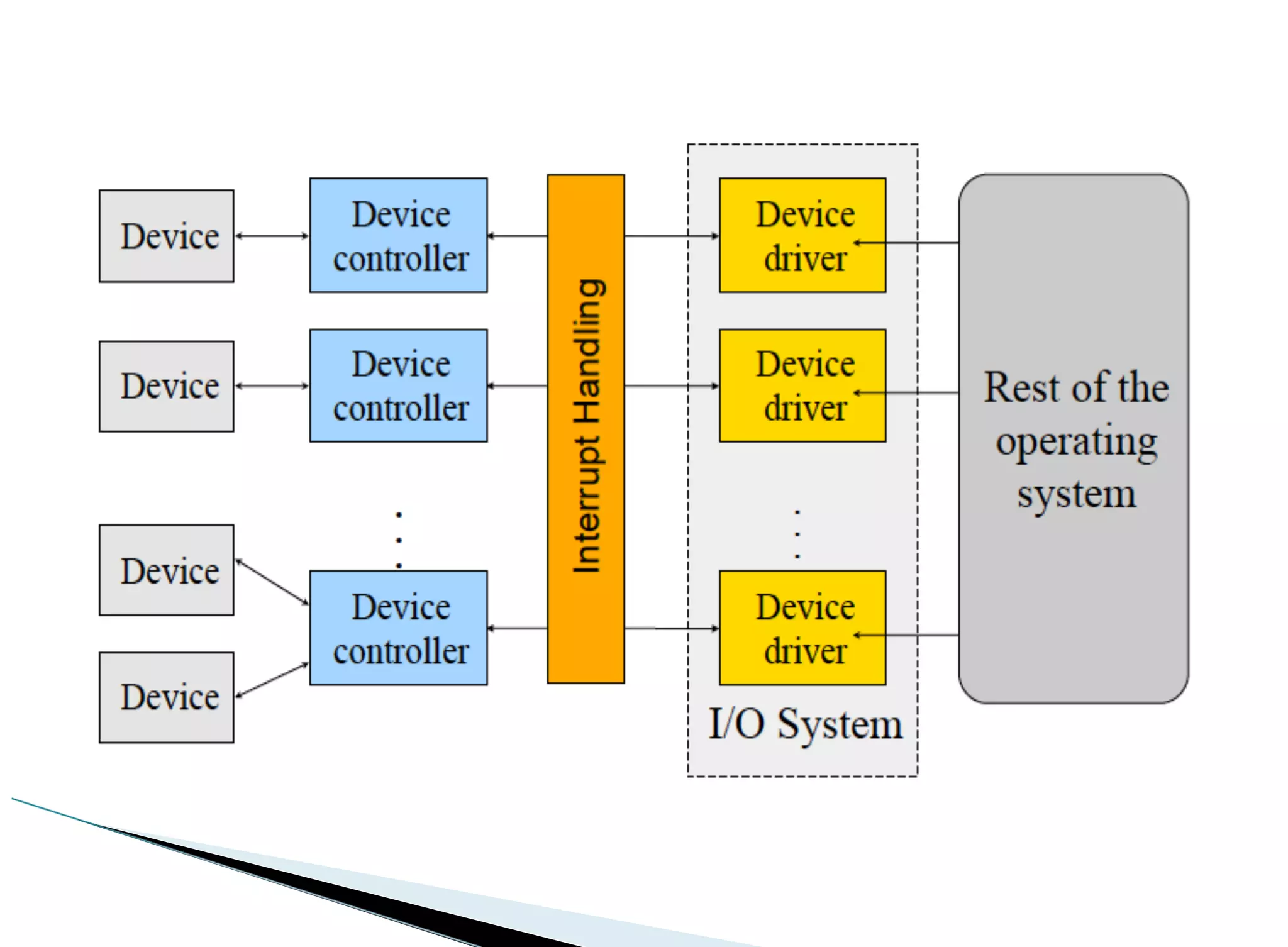
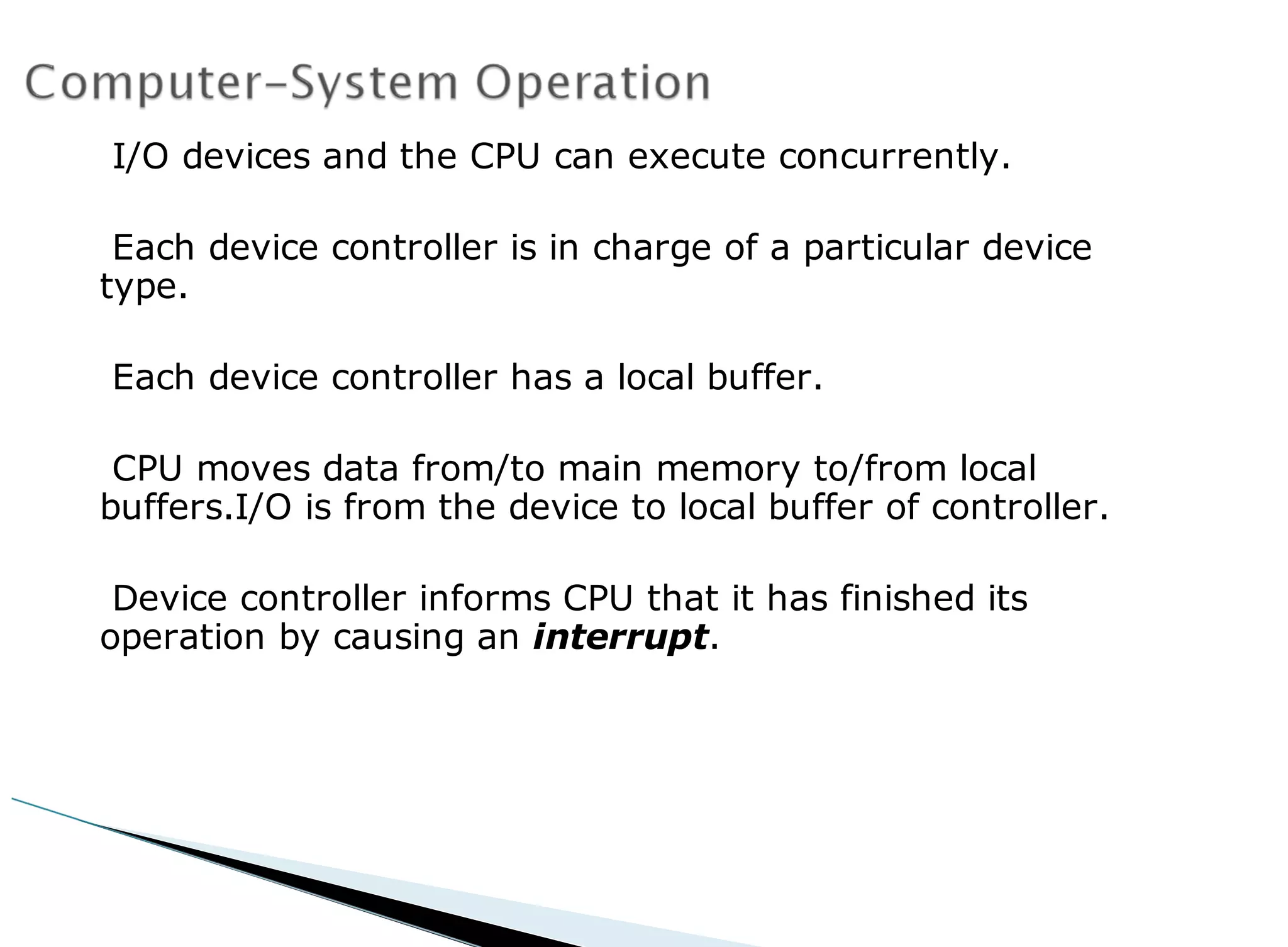
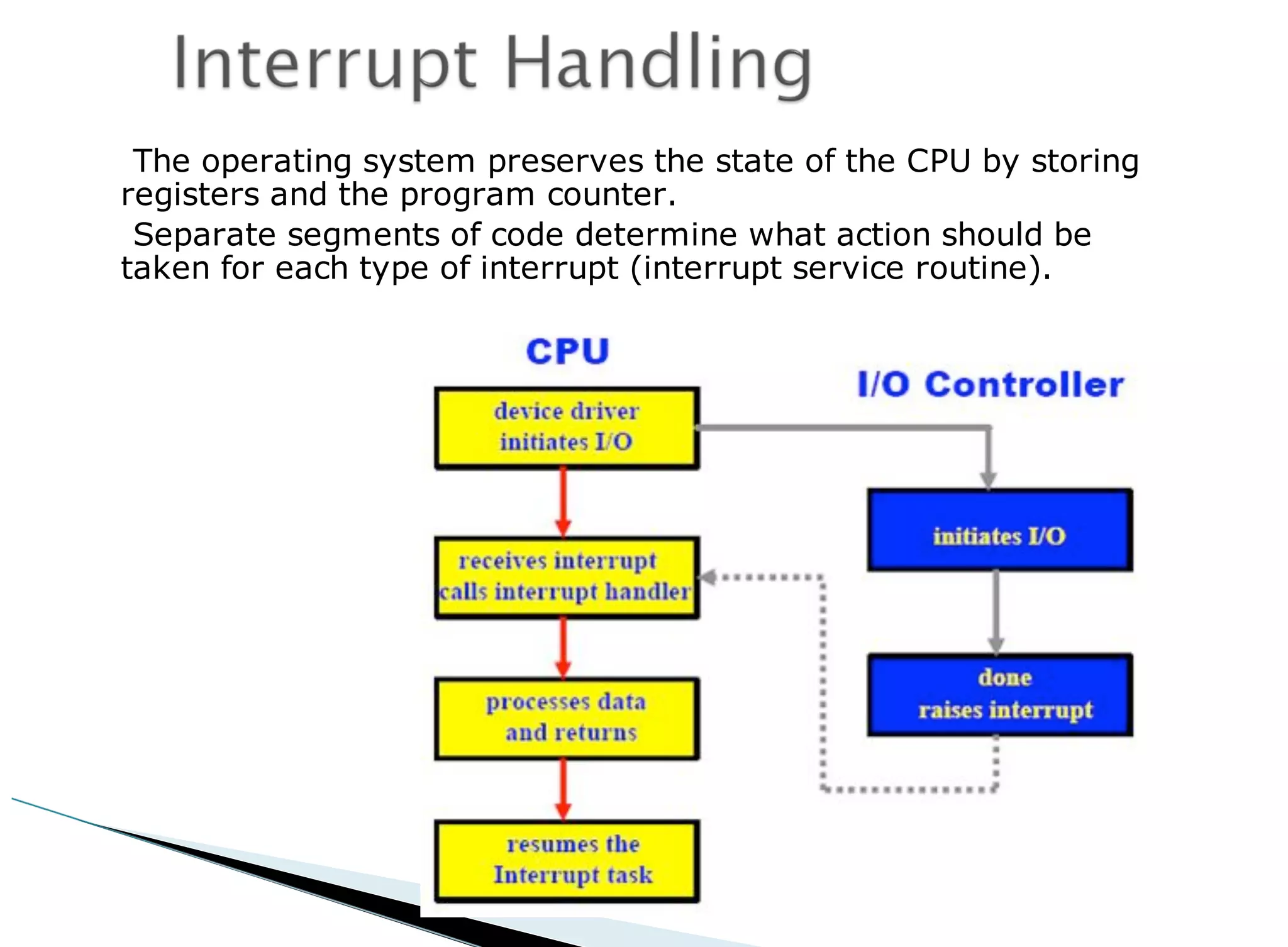
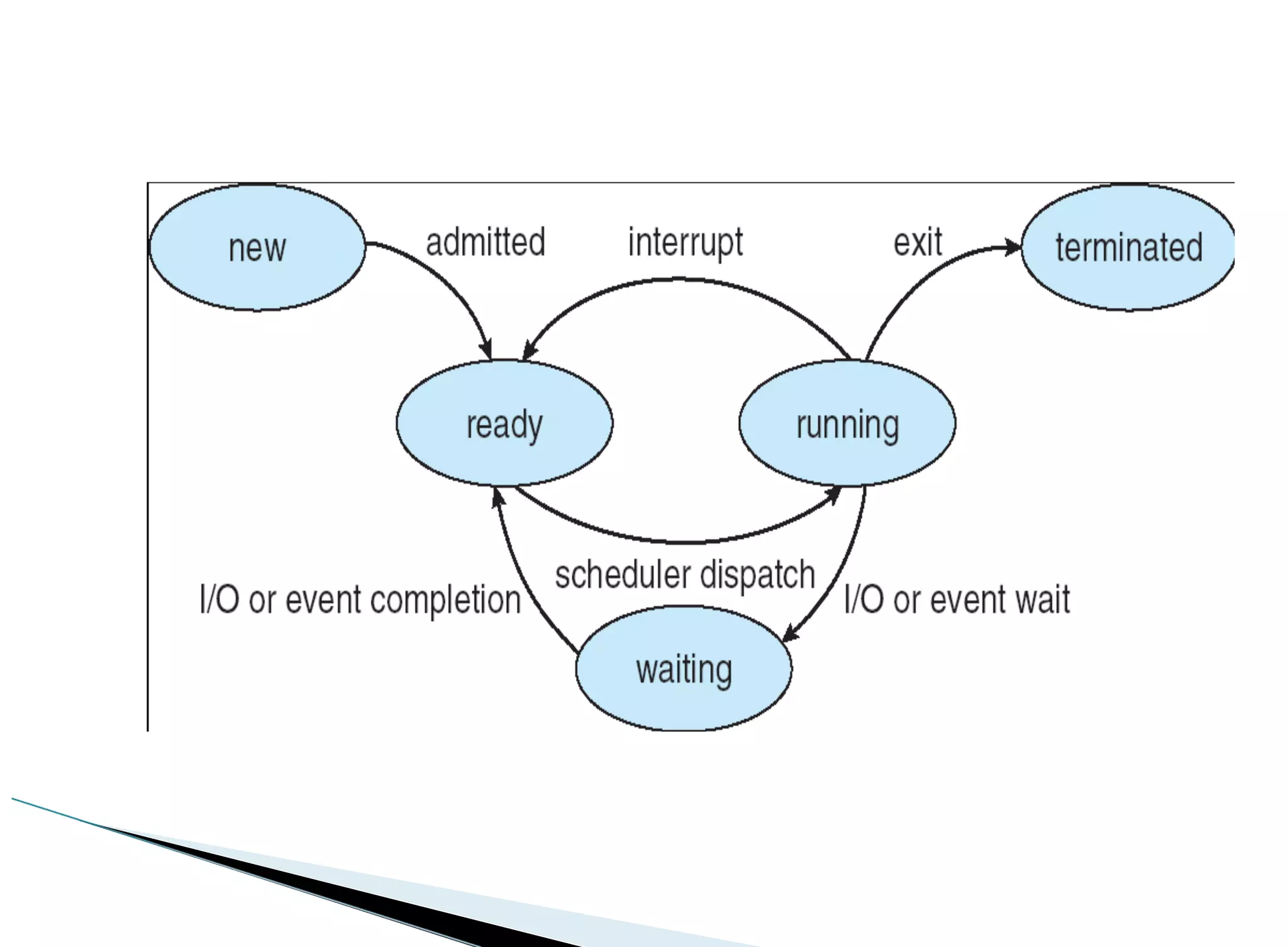
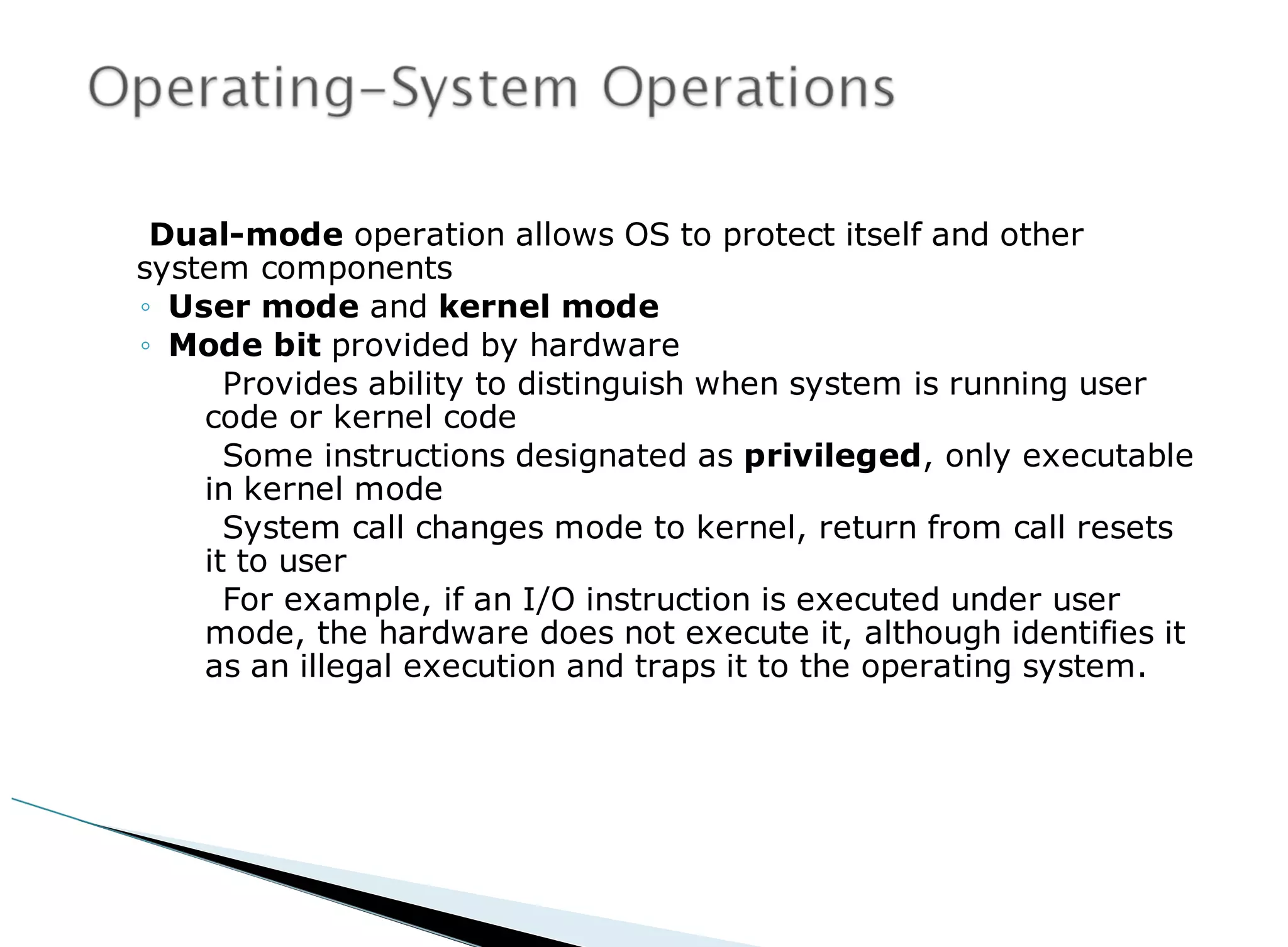
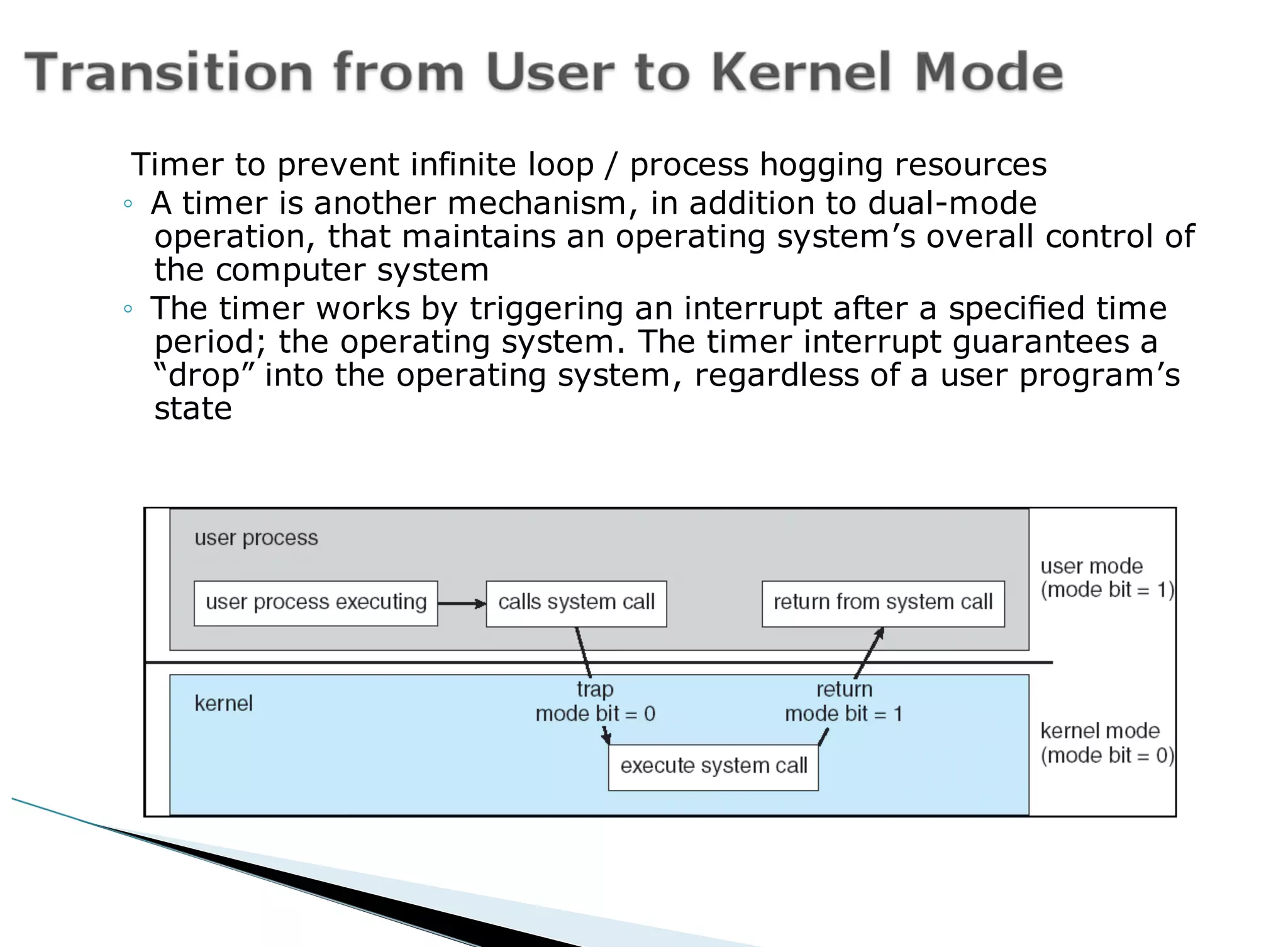
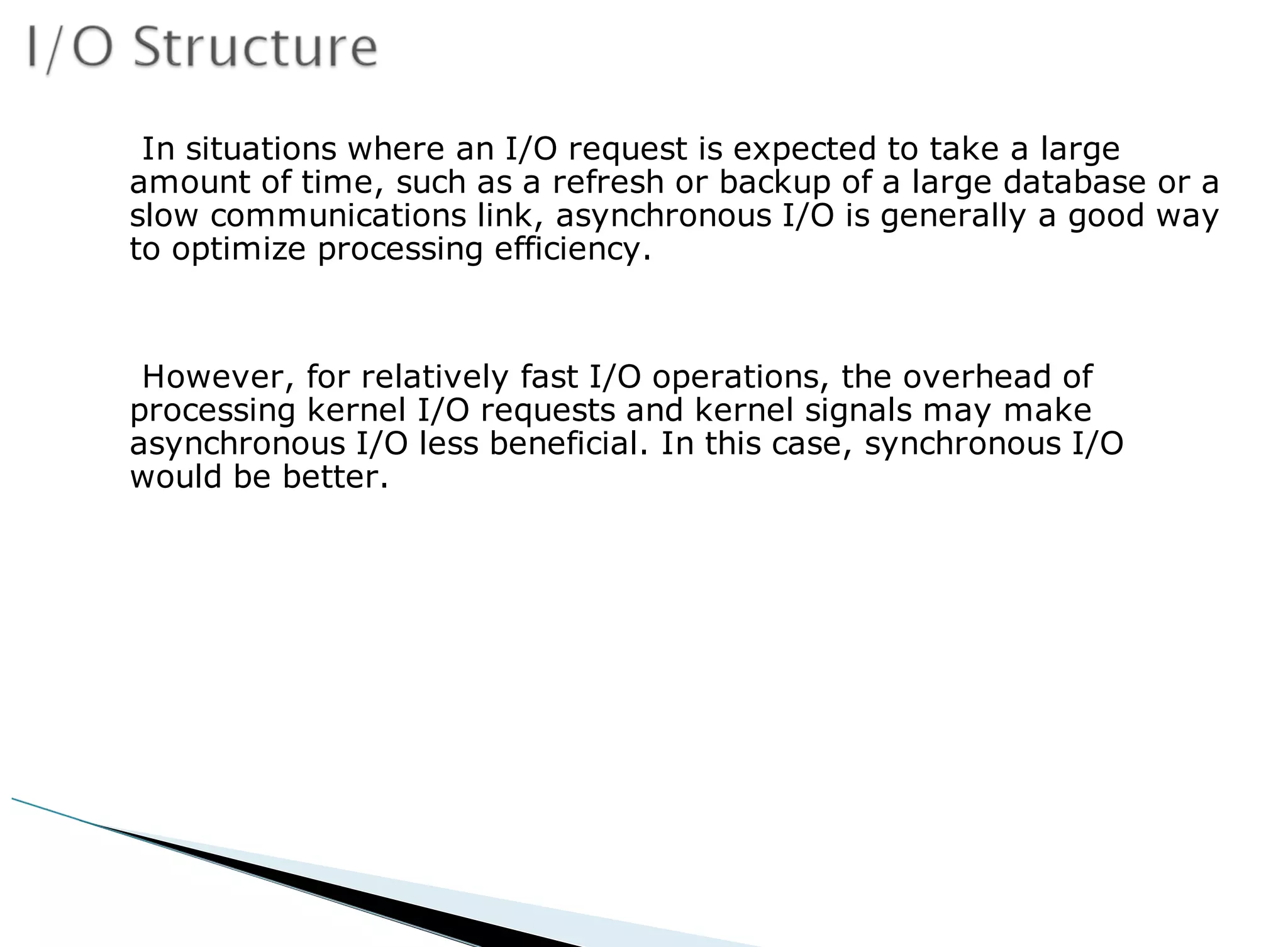
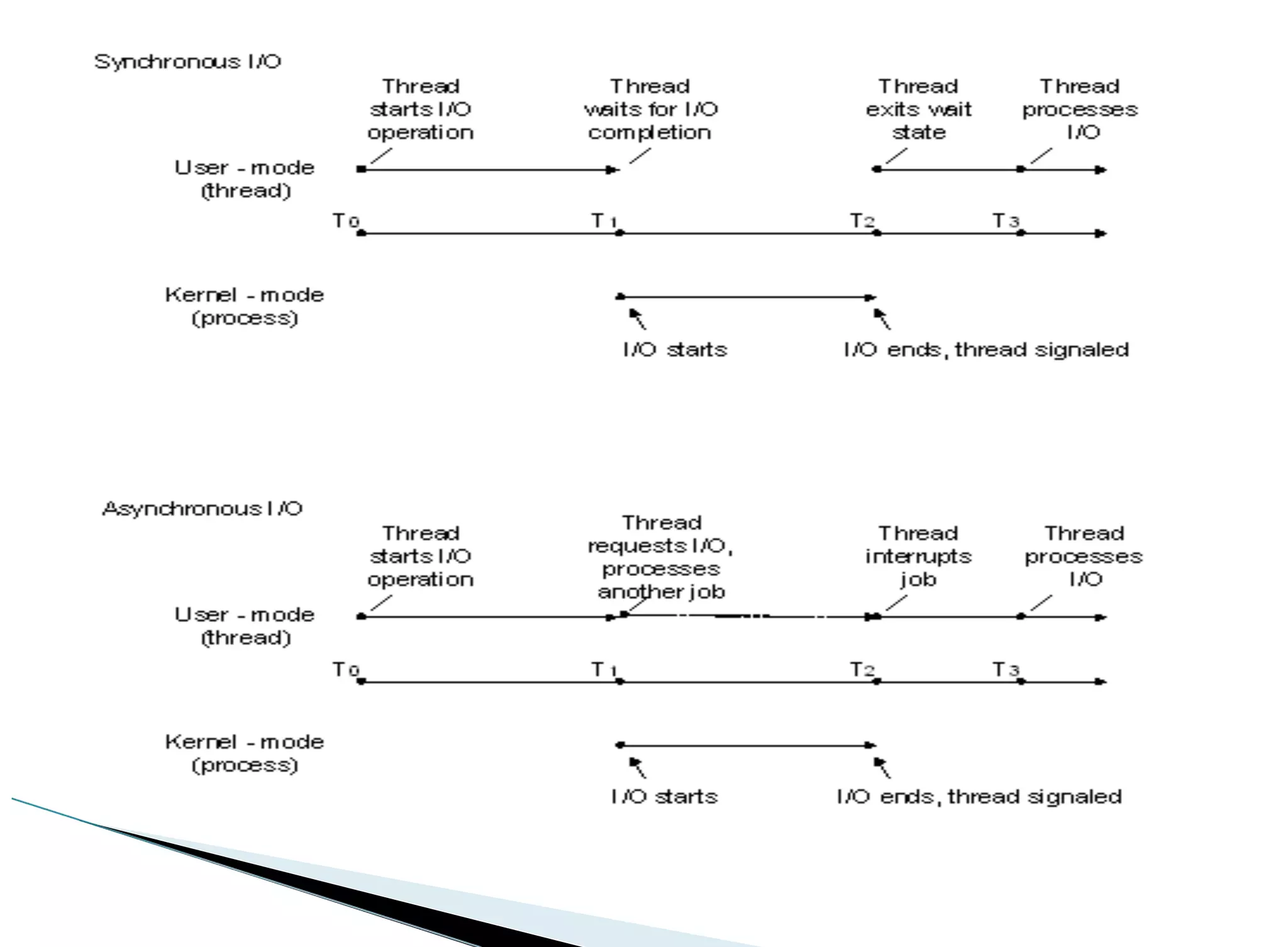
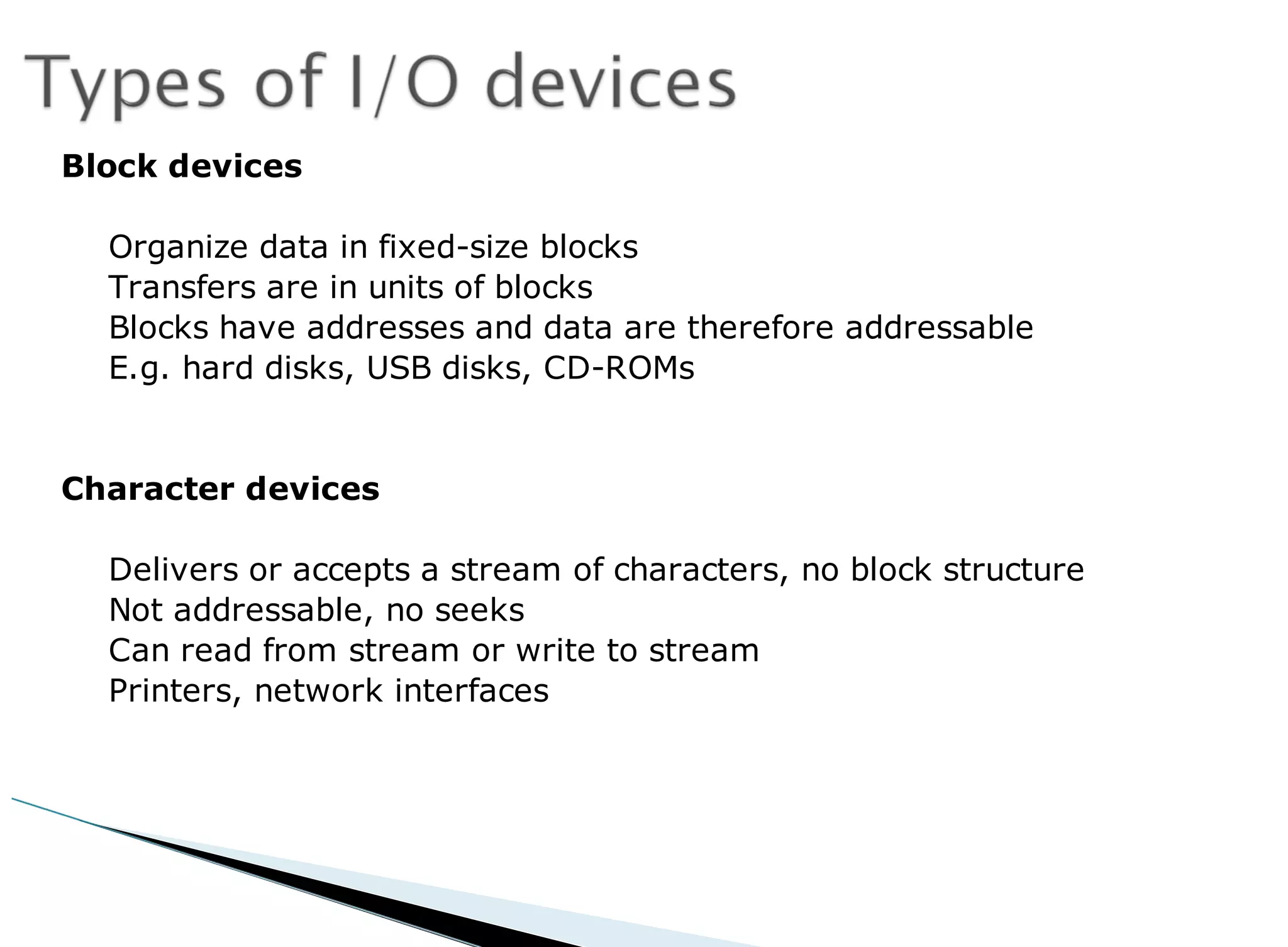
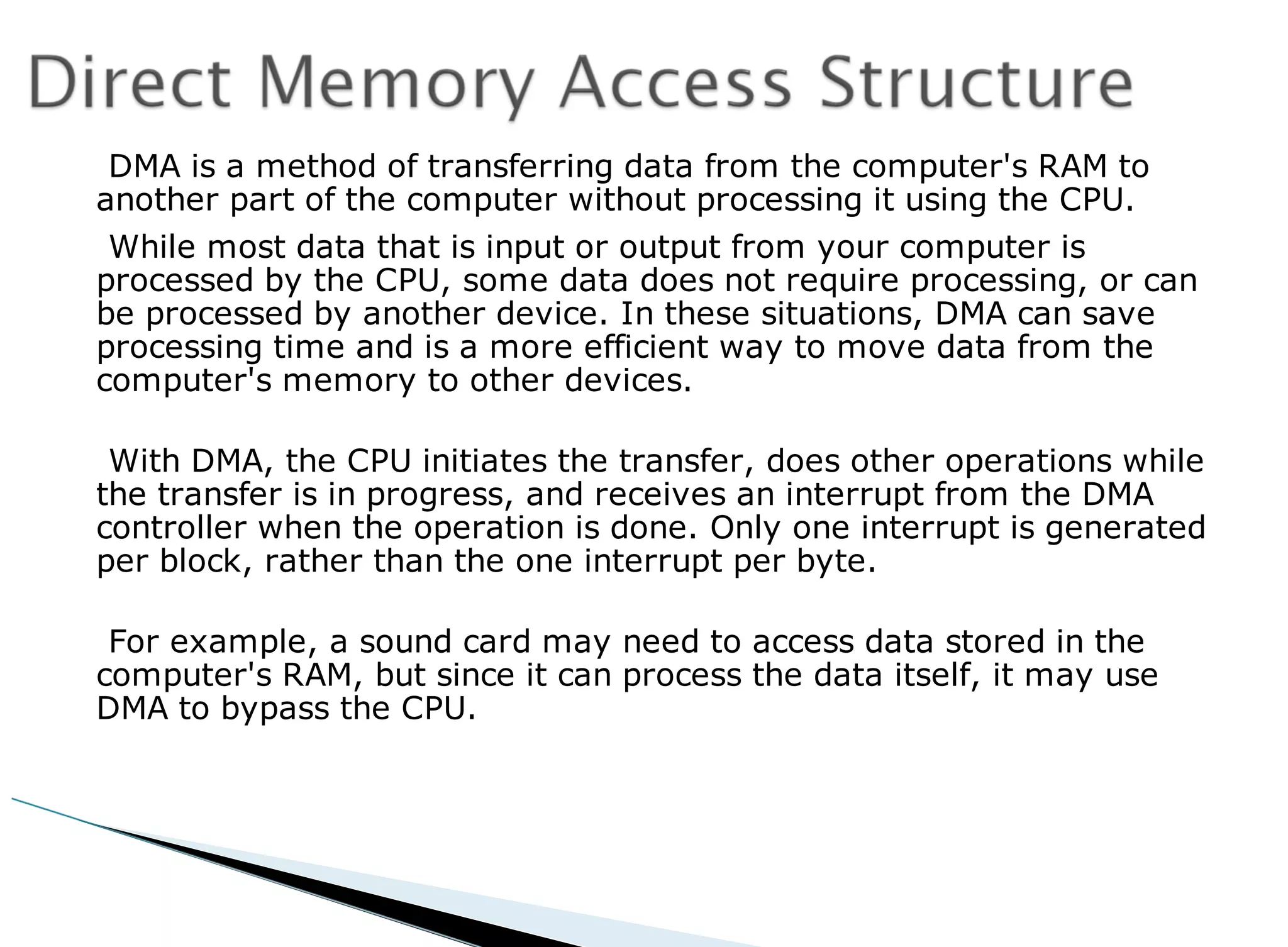
The operating system acts as an intermediary between the user and computer hardware. Its primary goals are to execute user programs, coordinate access to physical resources like the CPU and memory, and make the computer system convenient to use. The operating system controls and coordinates hardware use among applications and users. It manages resources like CPU time and memory allocation to ensure efficient and fair use between processes. The operating system also protects the system through dual-mode operation separating user programs from kernel programs.