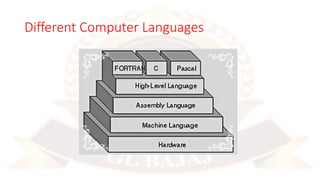
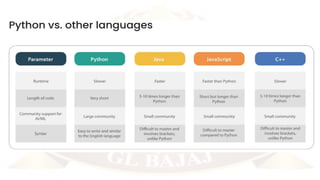
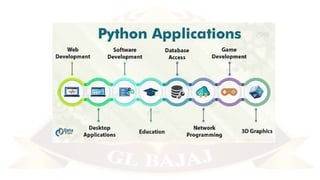
The document outlines a Python Programming course (BCC 402) offered by the Department of Computer Science & Engineering, taught by Dr. Pawan Kumar Mall. It includes course objectives, a detailed syllabus covering Python basics, control flow, complex data types, file operations, and packages, along with a marks breakup for evaluations. Additionally, it highlights various popular Python libraries and development environments.