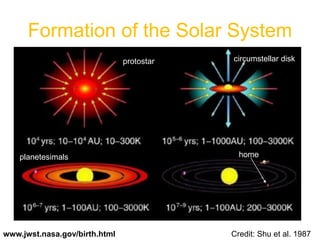
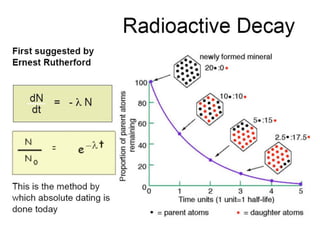
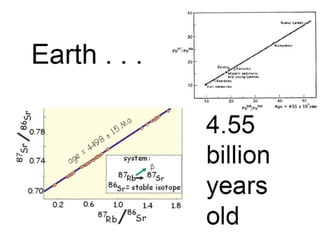
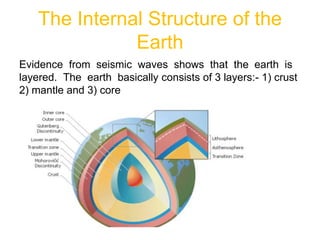
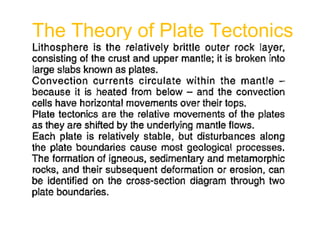
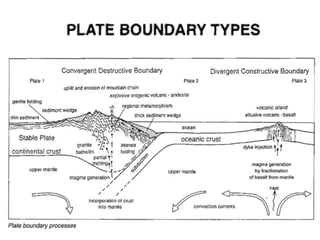
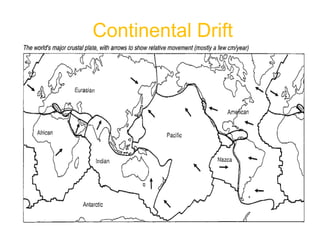
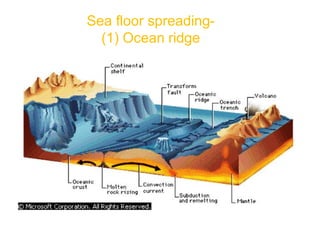
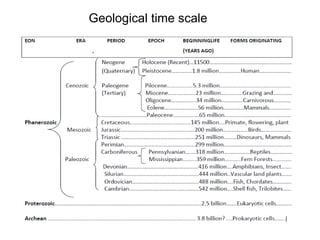
The document provides an overview of the formation and composition of the solar system, detailing the characteristics of the inner terrestrial planets and outer jovian planets. It highlights Earth's unique attributes, including its status as the only known planet to support life, and discusses the internal structure of Earth along with evidence supporting the theory of plate tectonics and continental drift. The document also touches upon methods used by geochronologists to date the Earth and the geological time scale.