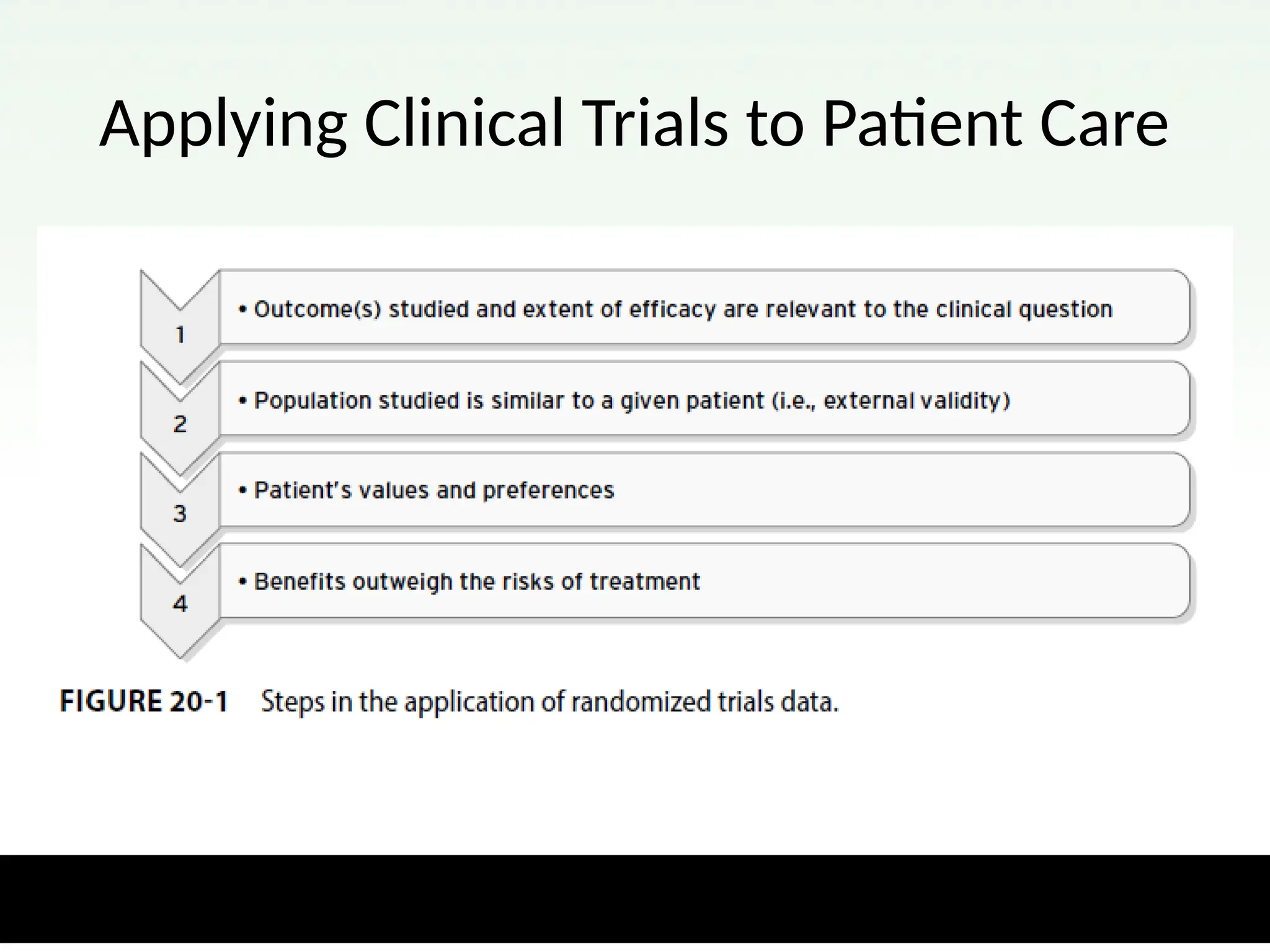
The document discusses the application of evidence-based medicine (EBM) in patient care, emphasizing patient-centered approaches and high-quality evidence for clinical decisions. It outlines considerations for making treatment decisions, including assessing evidence, collaborating with patients, and staying updated with drug information and clinical guidelines. The importance of evaluating interventions that matter to patients and utilizing various methods for keeping informed is also highlighted.