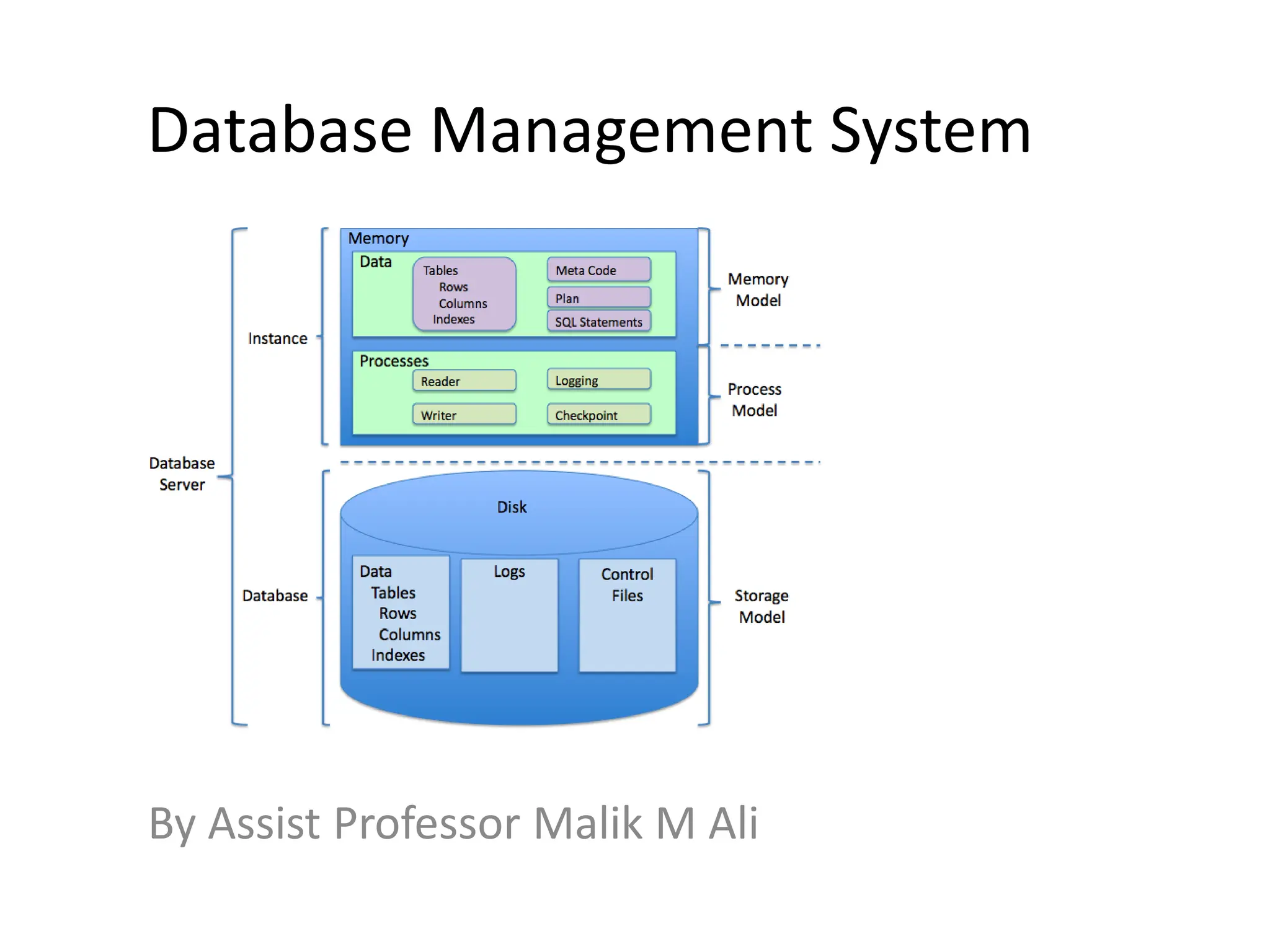
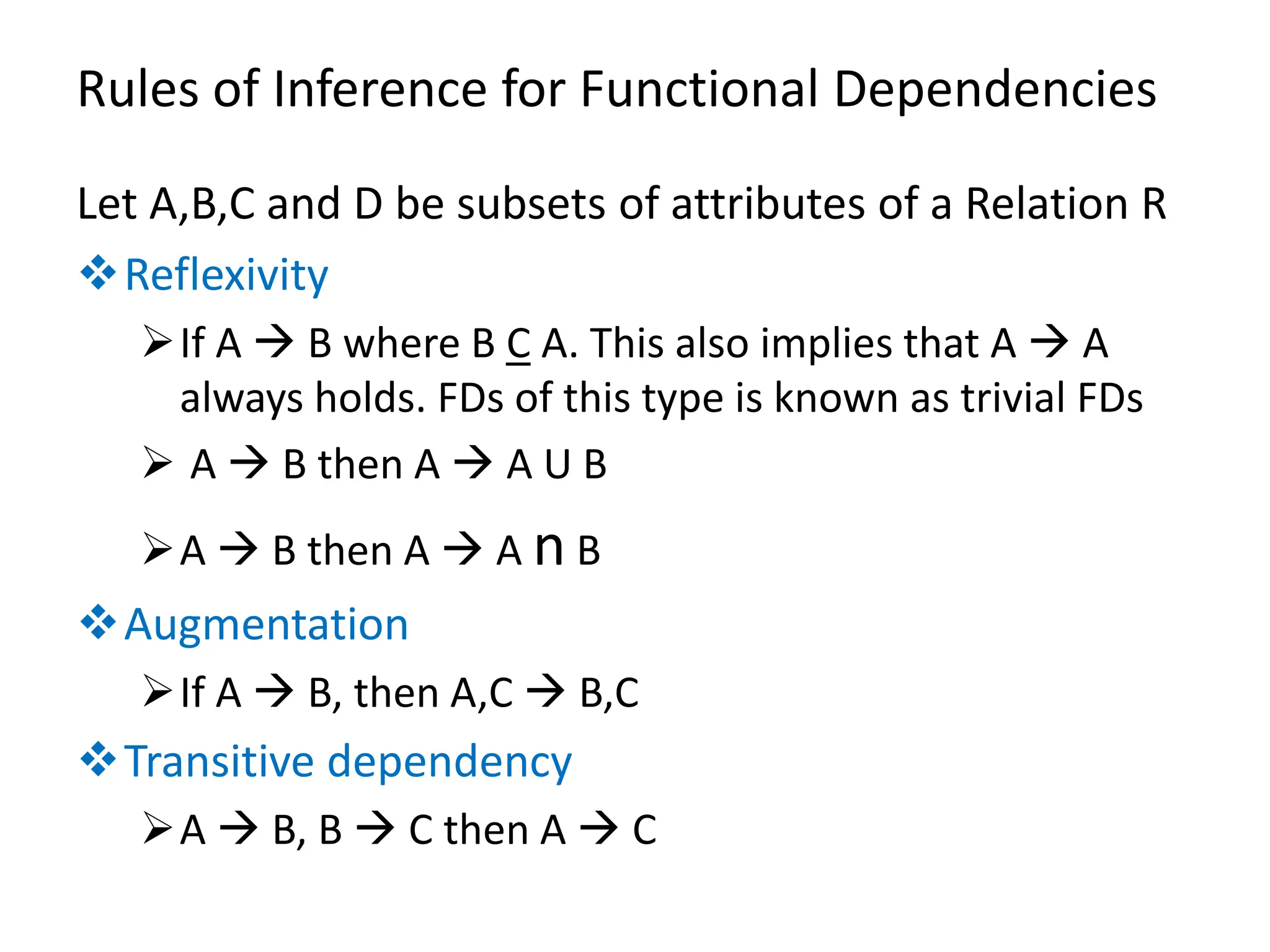
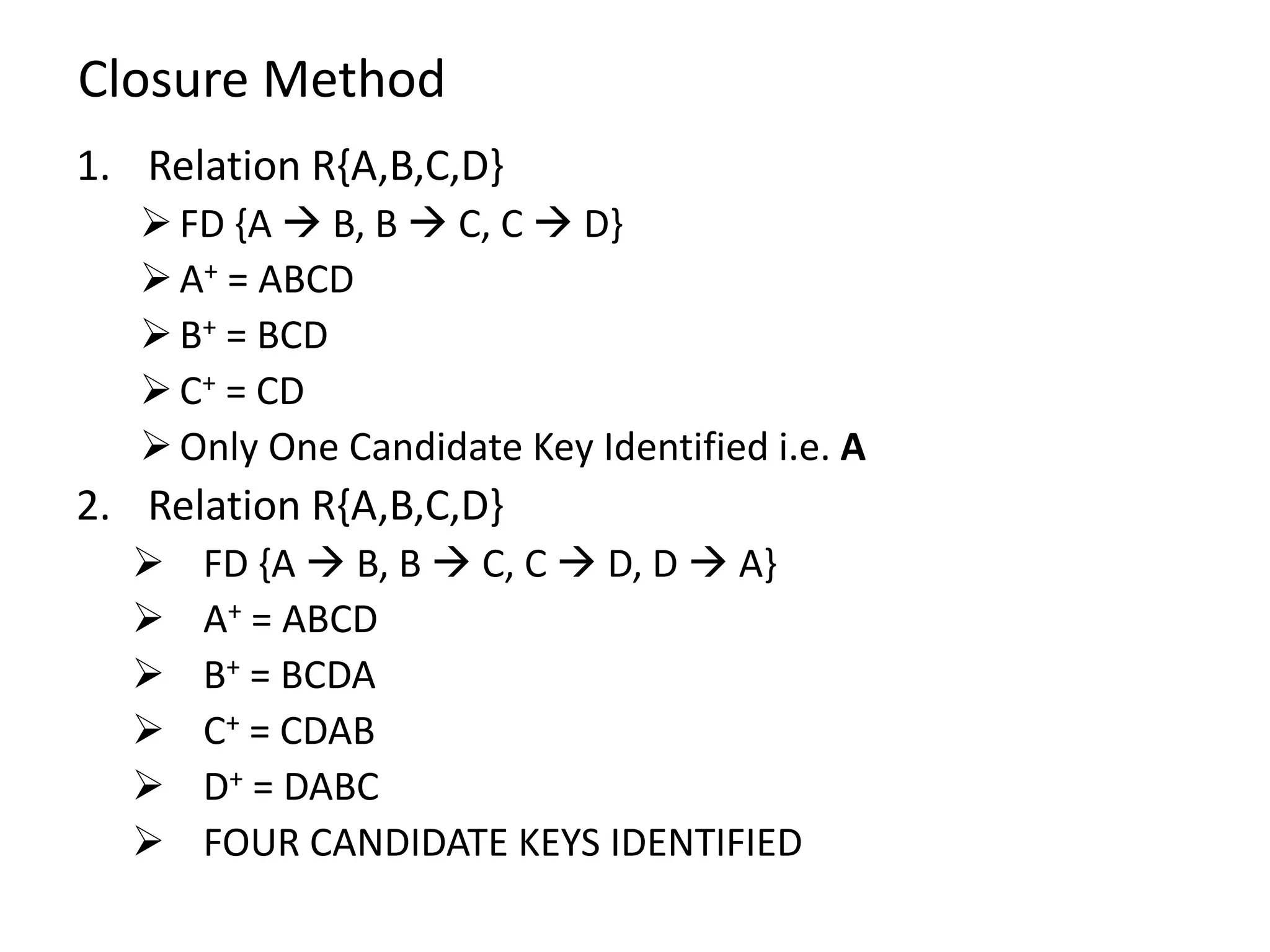
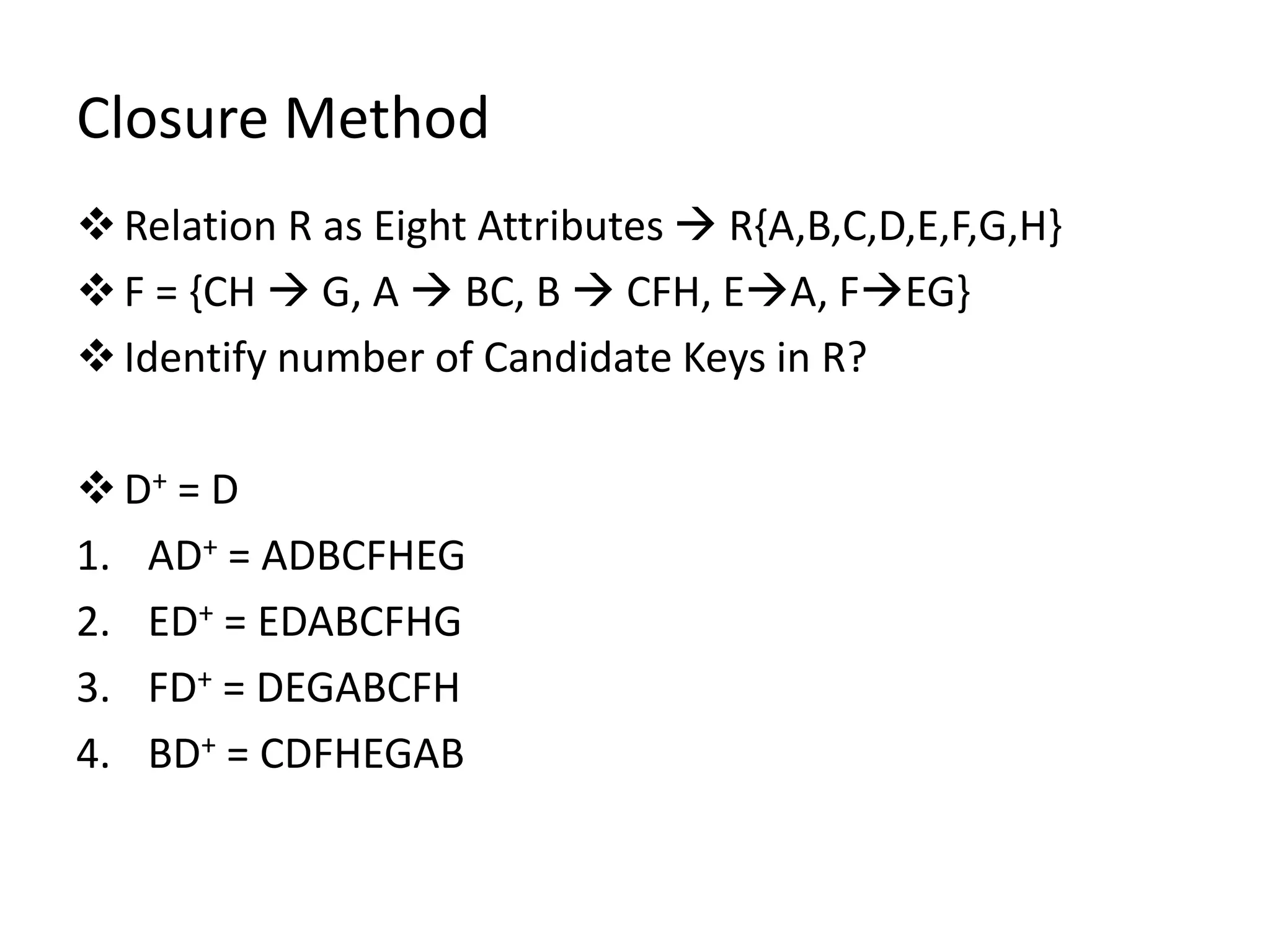
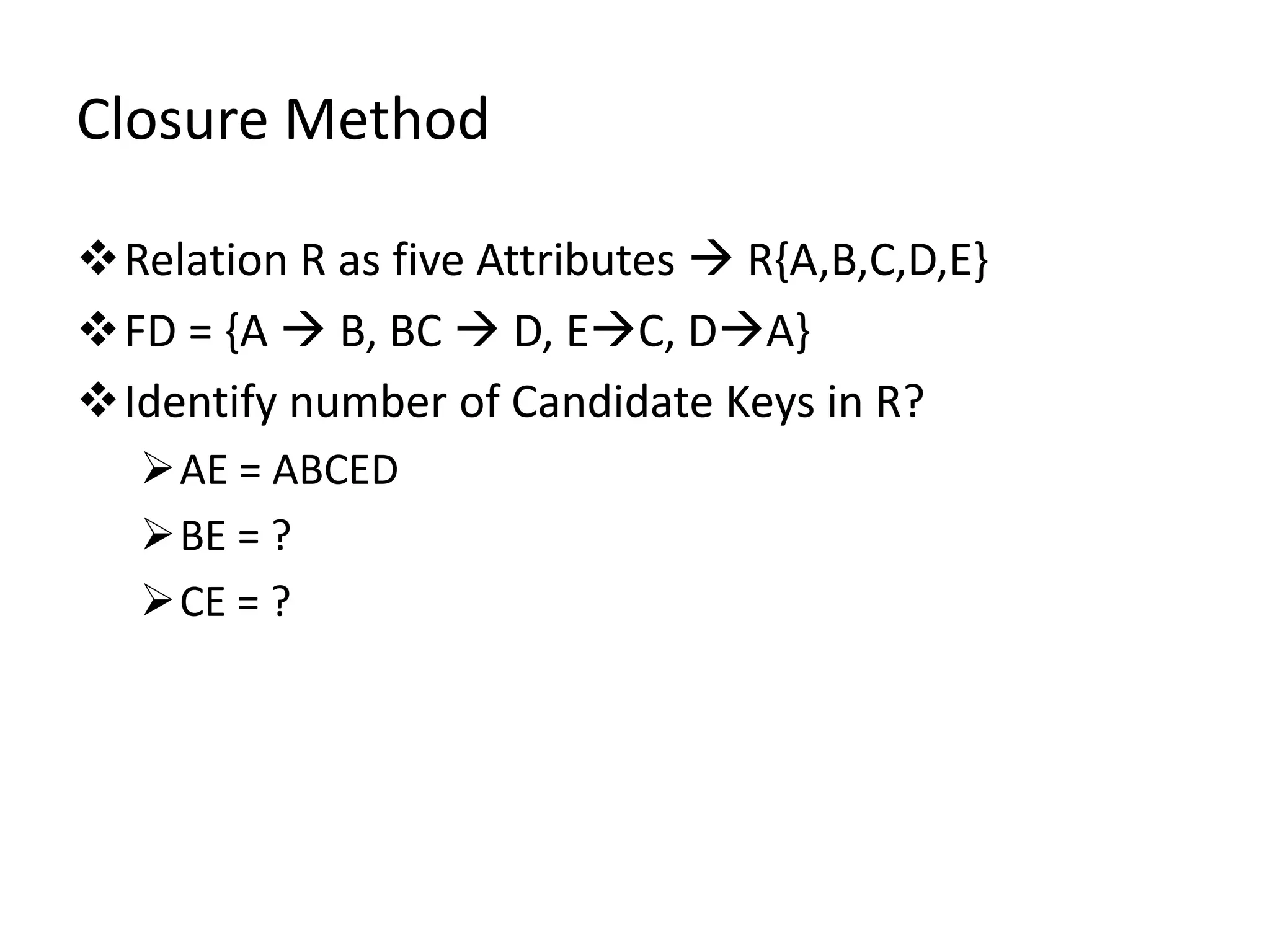
The document outlines rules of inference for functional dependencies in a database management system, including reflexivity, augmentation, transitive dependency, and others. It discusses the identification of candidate keys using the closure method through various examples and attribute sets. The document also addresses the mapping from conceptual schema to logical schema.