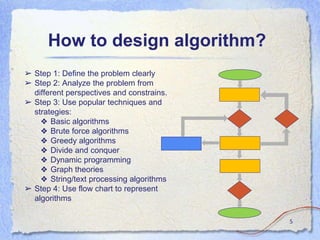
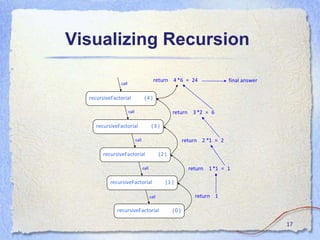
This document introduces algorithms and some common algorithmic techniques. It begins by defining an algorithm as a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem. It then discusses what makes a good algorithm and provides examples of common algorithm design strategies like brute force, greedy, divide-and-conquer, and dynamic programming. The document proceeds to provide examples of algorithms for searching, sorting, finding largest values in matrices, and calculating powers and factorials recursively. It aims to explain fundamental algorithmic concepts and techniques.







![Selection sort
Algorithm selection_sort (A, n):
for iter from 0 to n - 2 do
min_idx = iter;
for idx from (iter + 1) to n - 1 do
if A[idx] < A[min_idx] then
min_idx = idx;
swap (a[iter], a[min_idx]);
Complexity:
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7introductionalgorithms-230403091200-198dbcc1/85/Lecture-7_introduction_algorithms-pptx-9-320.jpg)










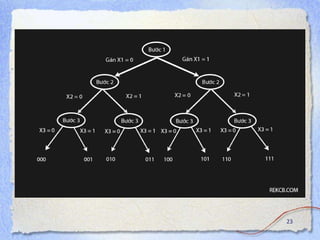
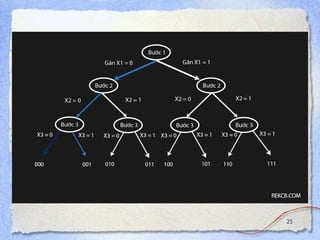
![Find all binary numbers
Problem: Find all binary numbers of length n.
Example: n = 3
000,001,010,011,100,101,110,111
Algorithm binary_number(b, k, n):
for v for 0 to 1 do
b[k] = v;
if (k==n) then
print b;
else
binary number (b, k + 1, n);
Complexity: 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7introductionalgorithms-230403091200-198dbcc1/85/Lecture-7_introduction_algorithms-pptx-22-320.jpg)