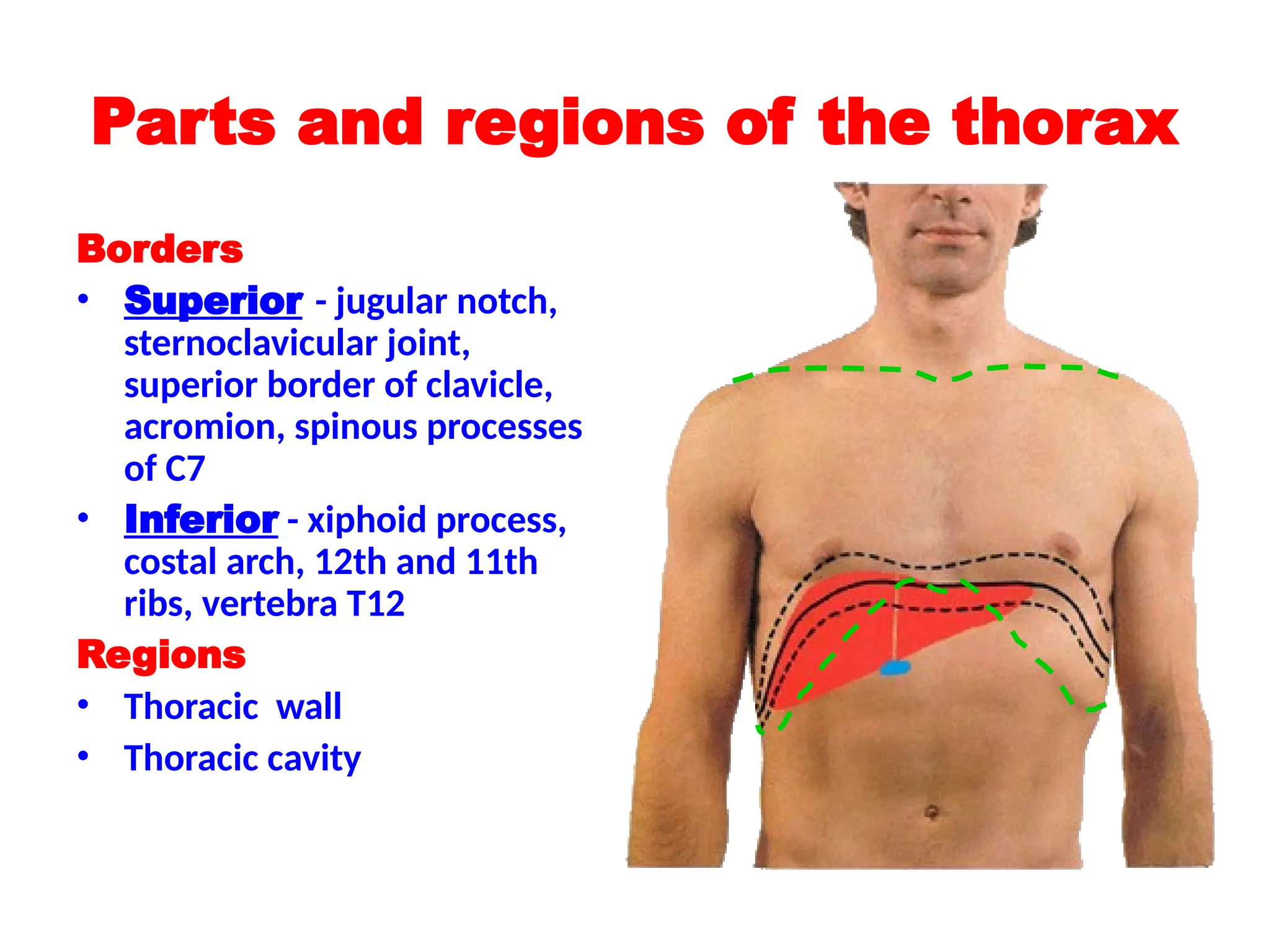
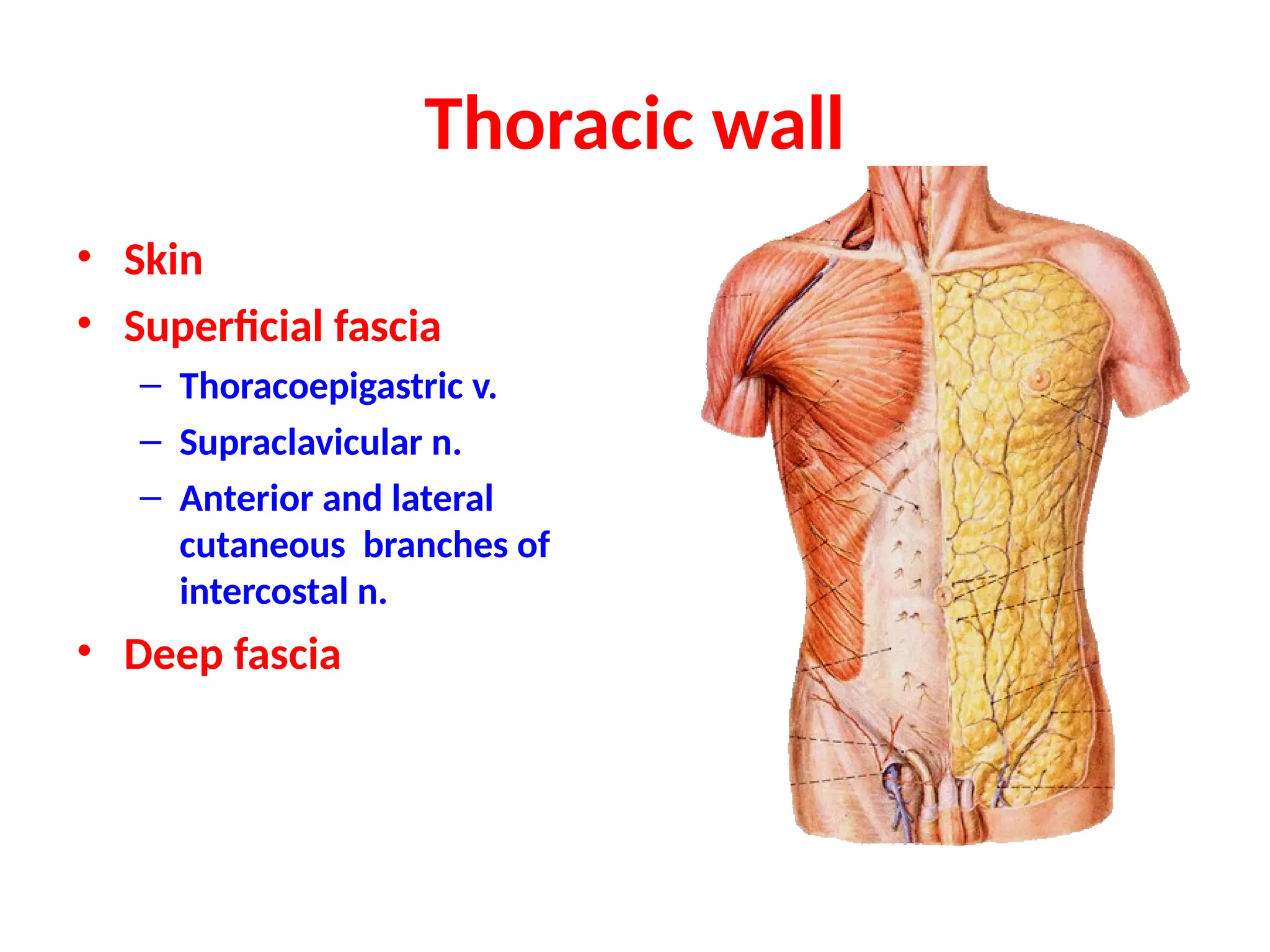
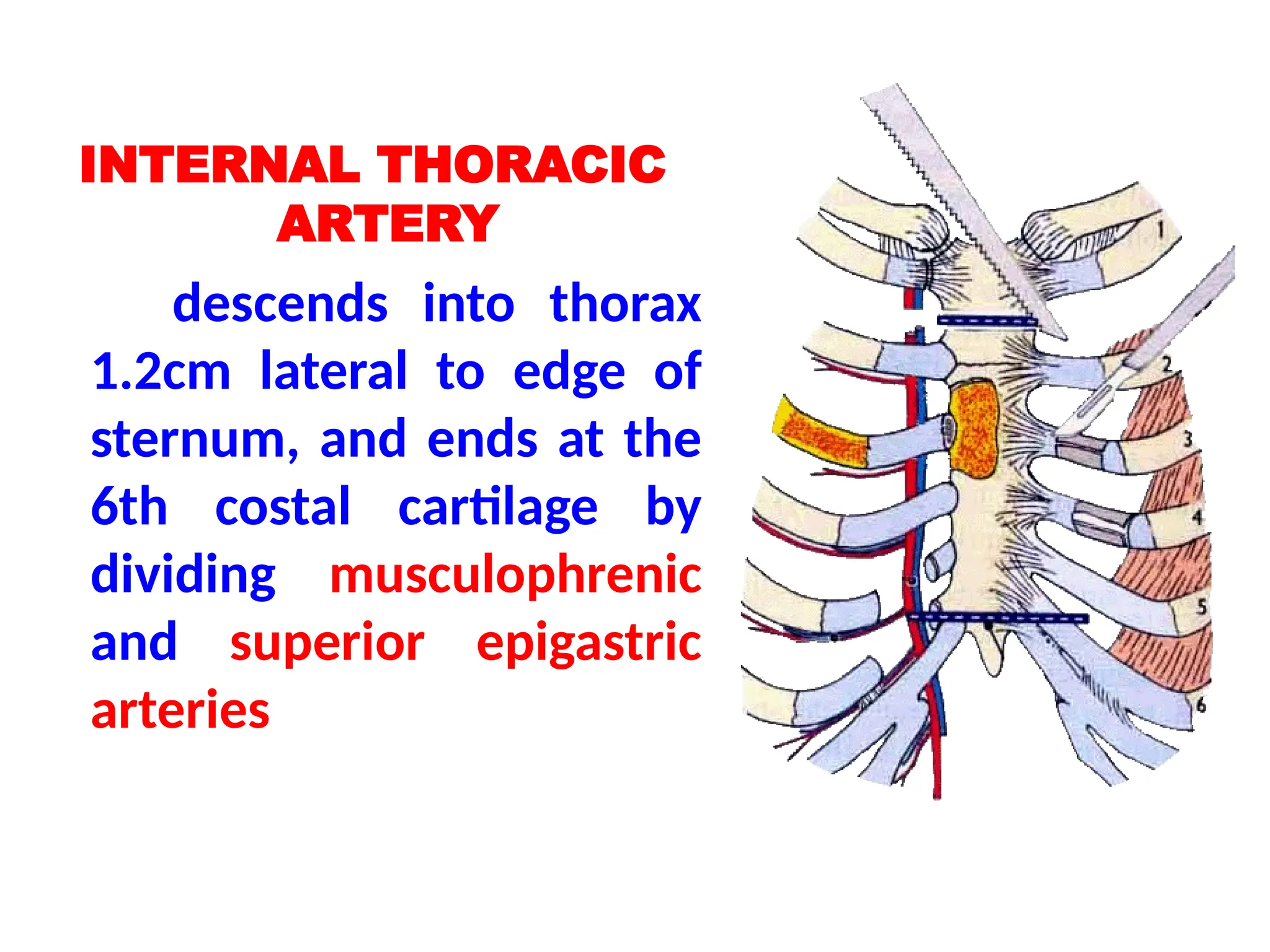
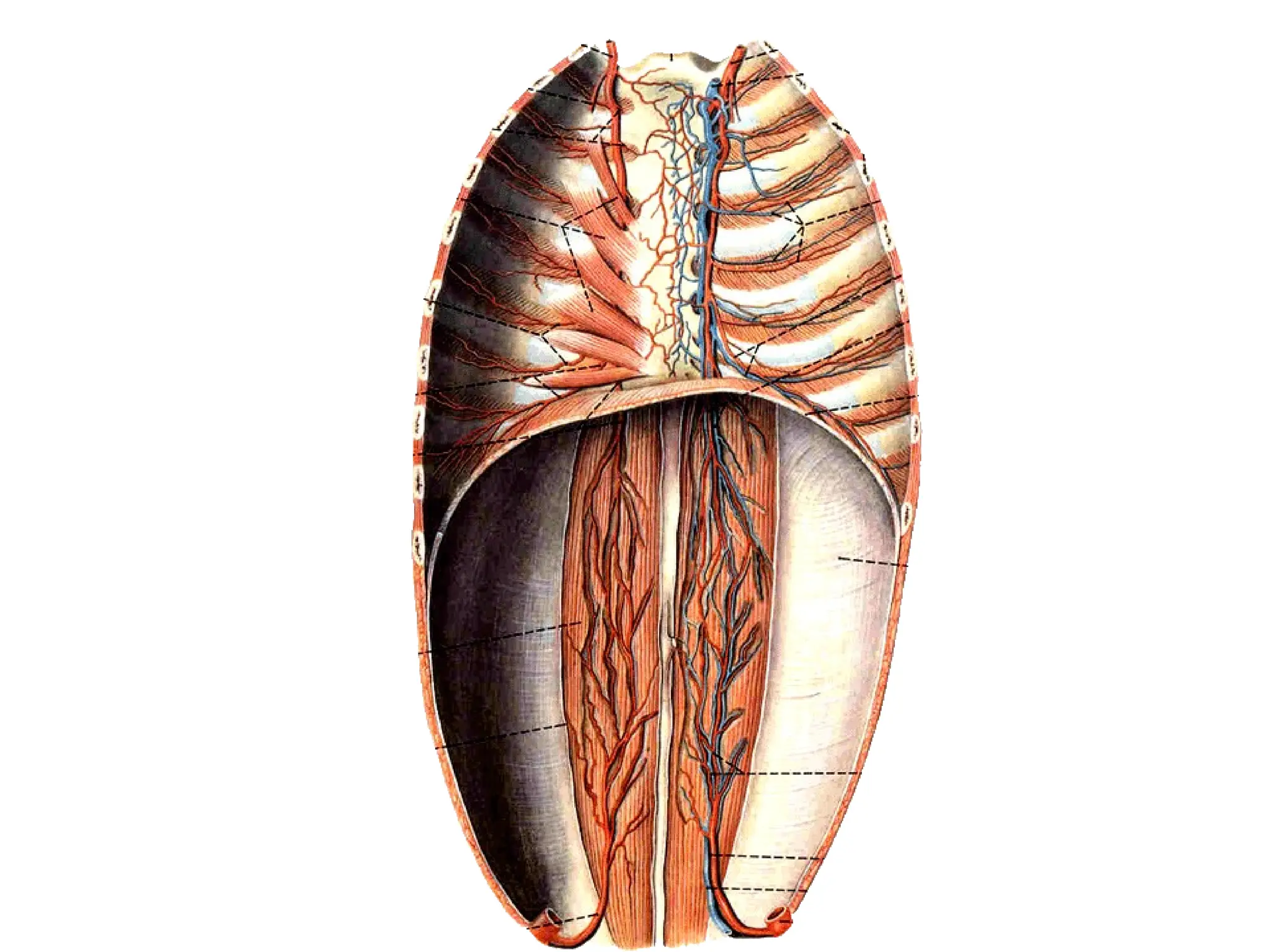
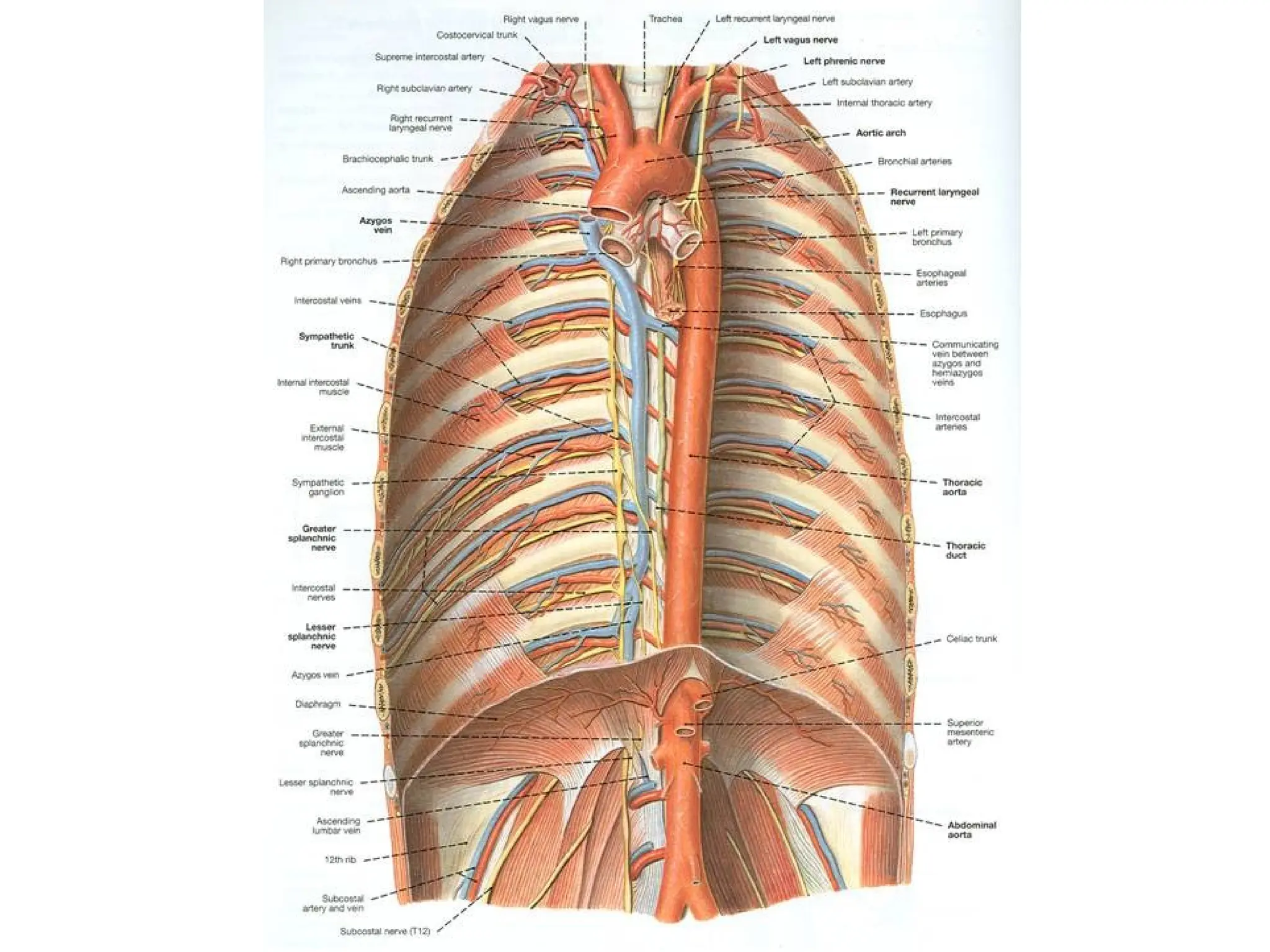
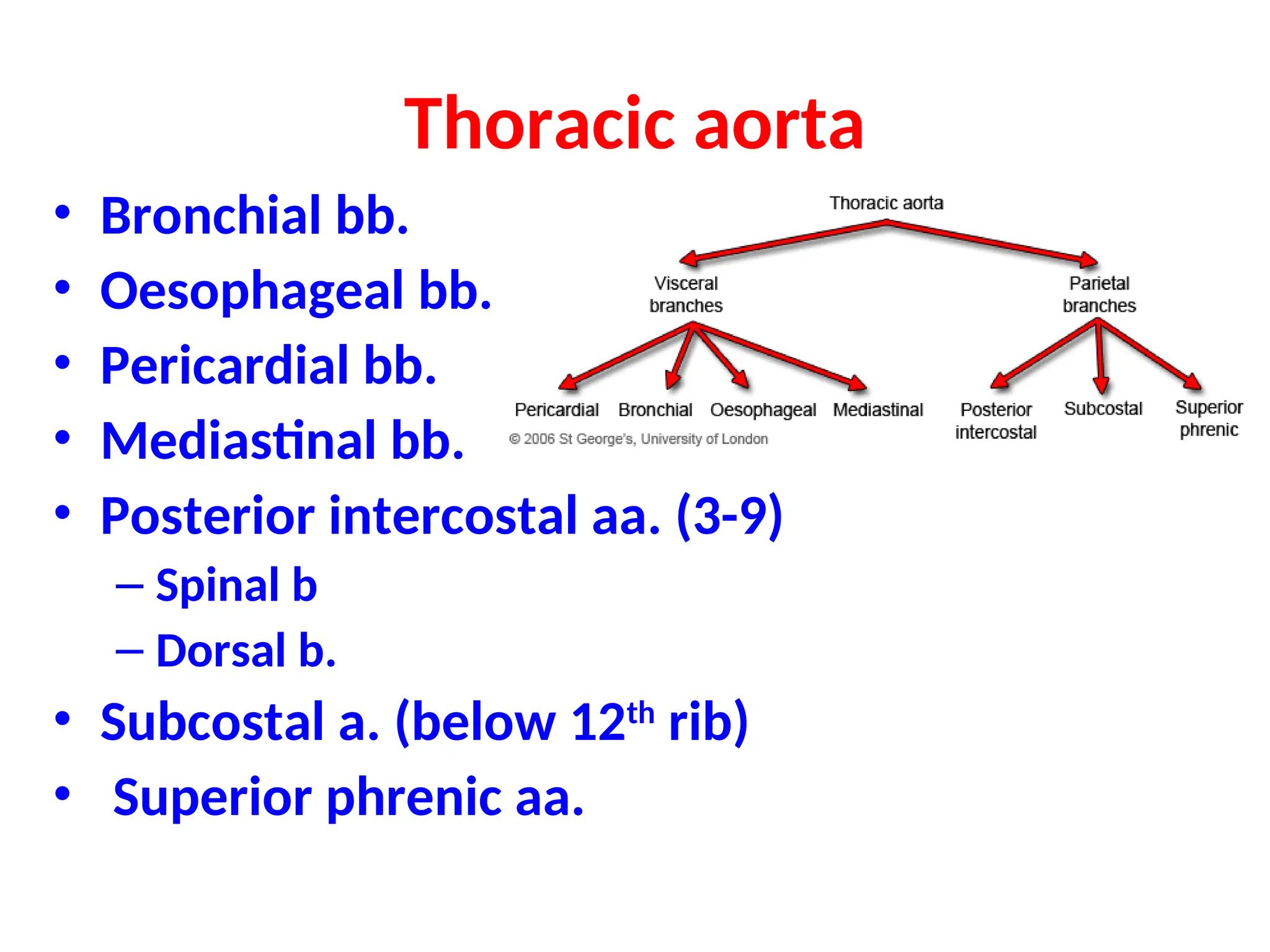
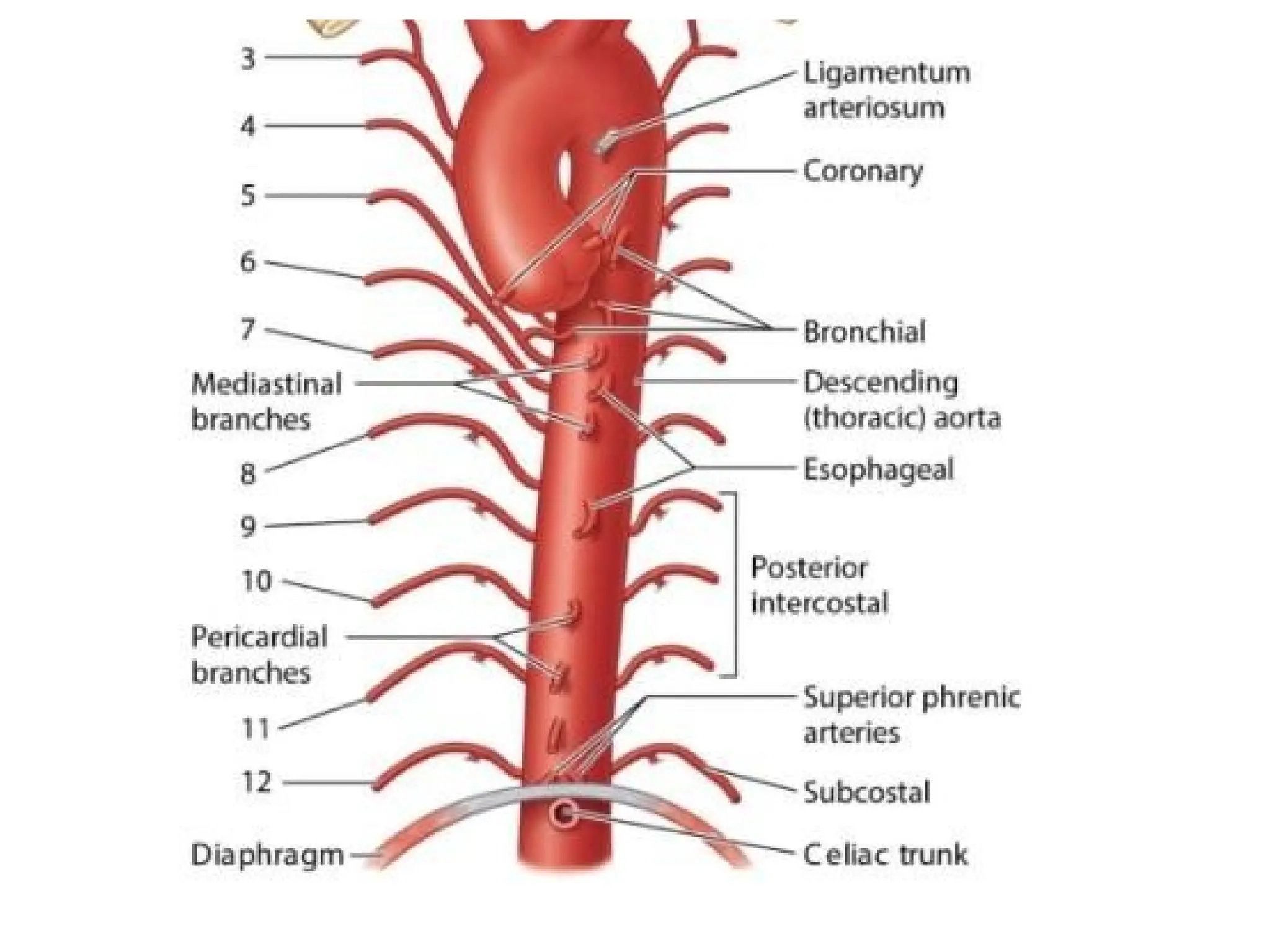
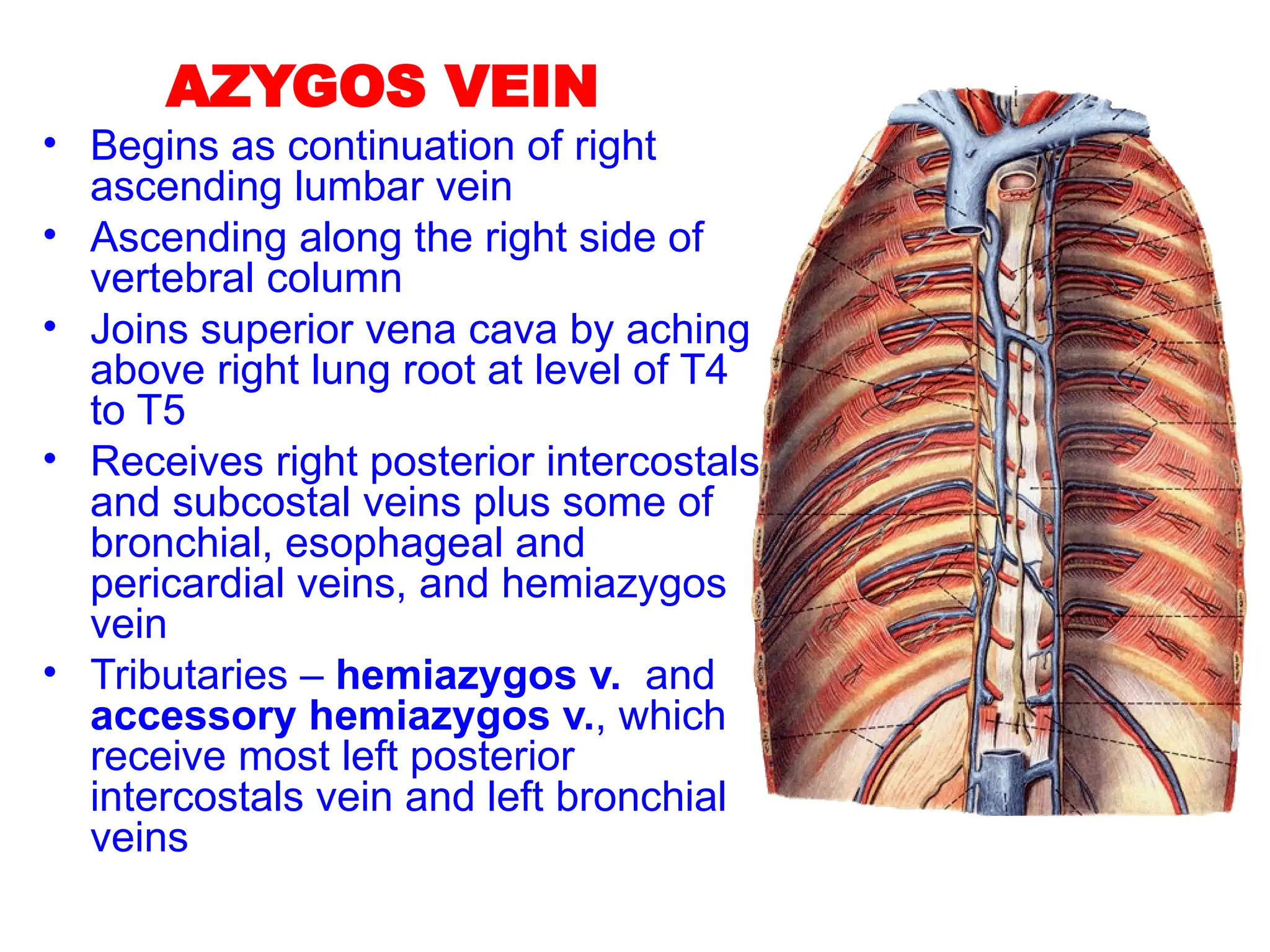
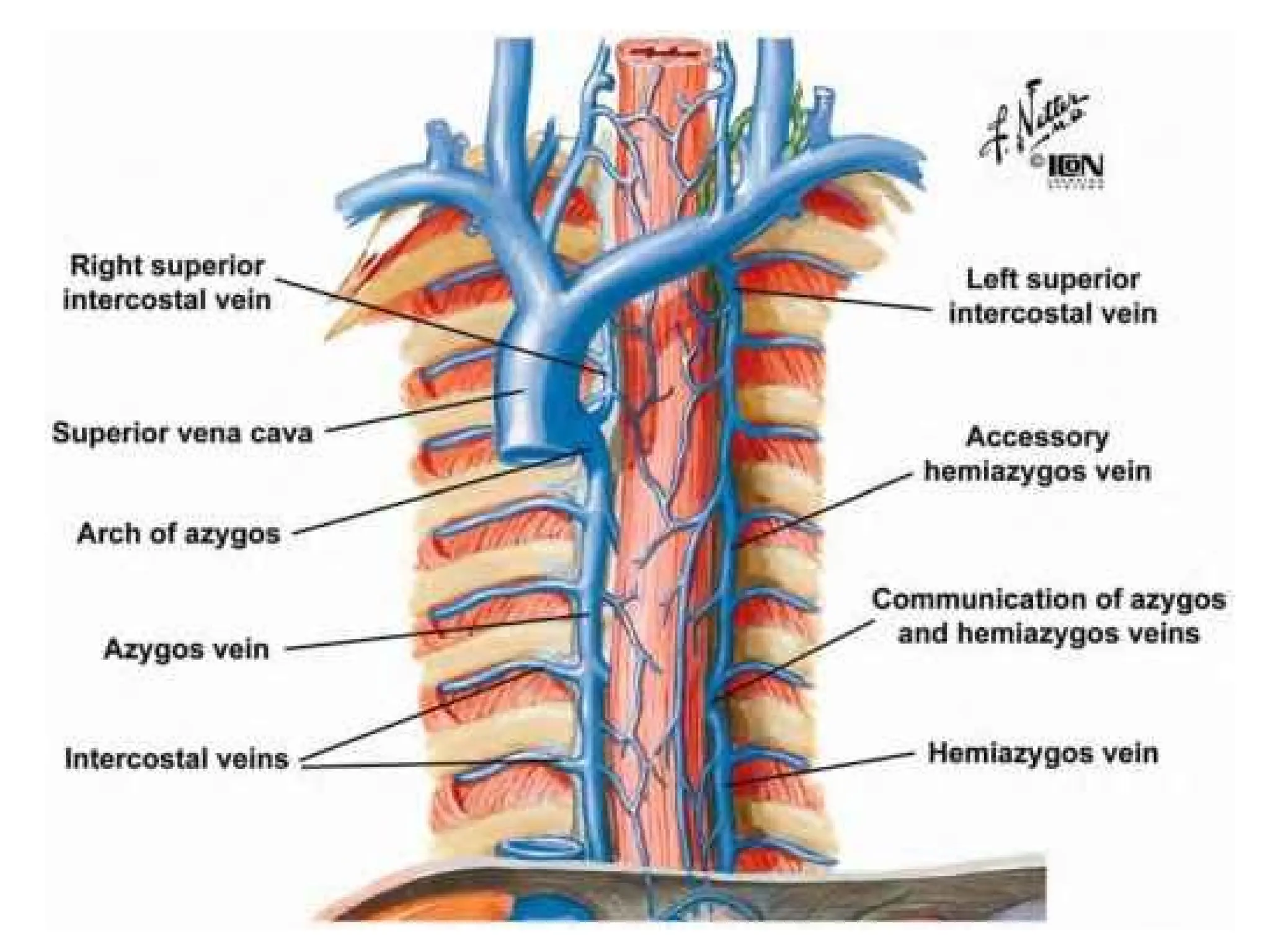
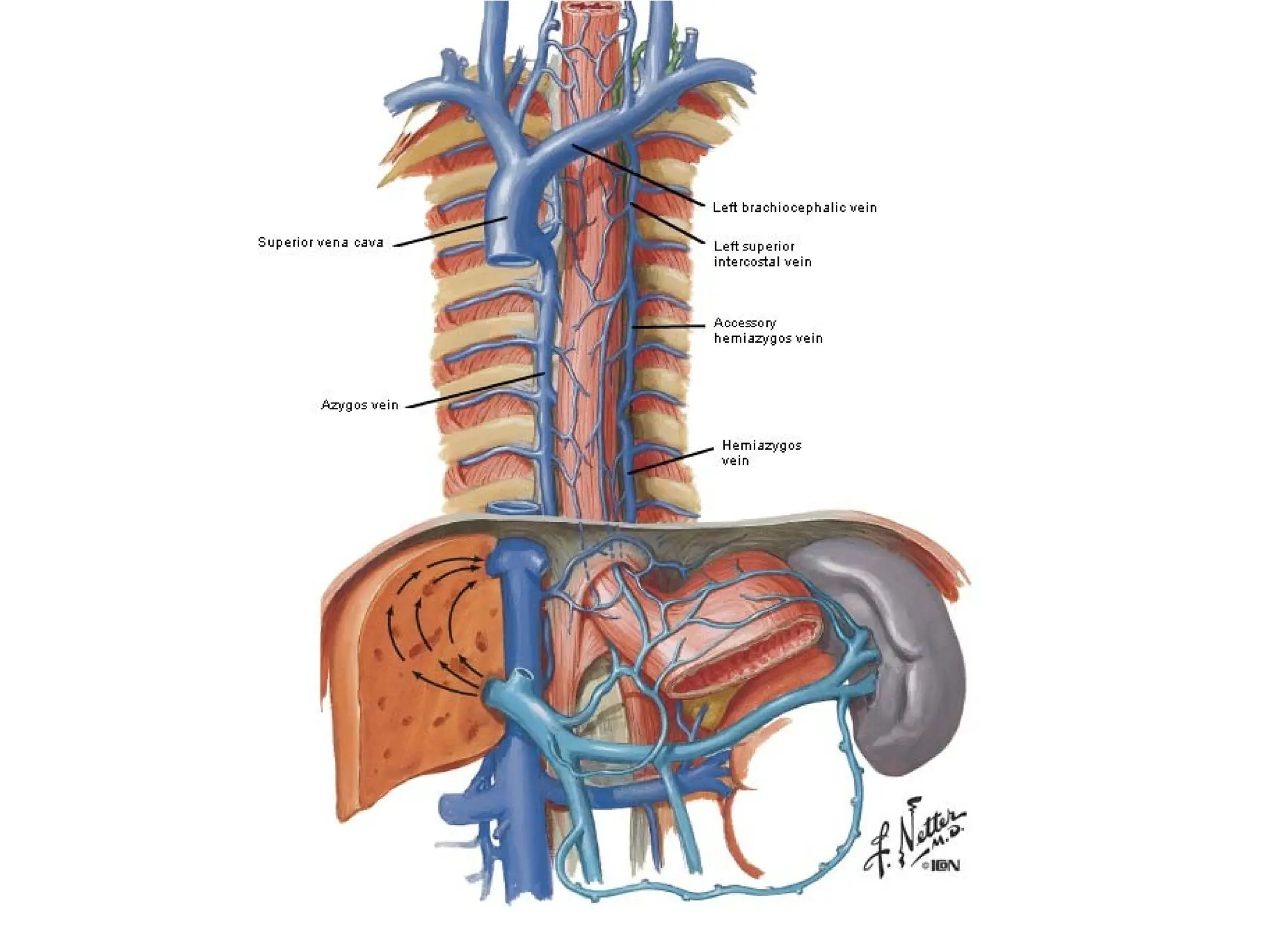
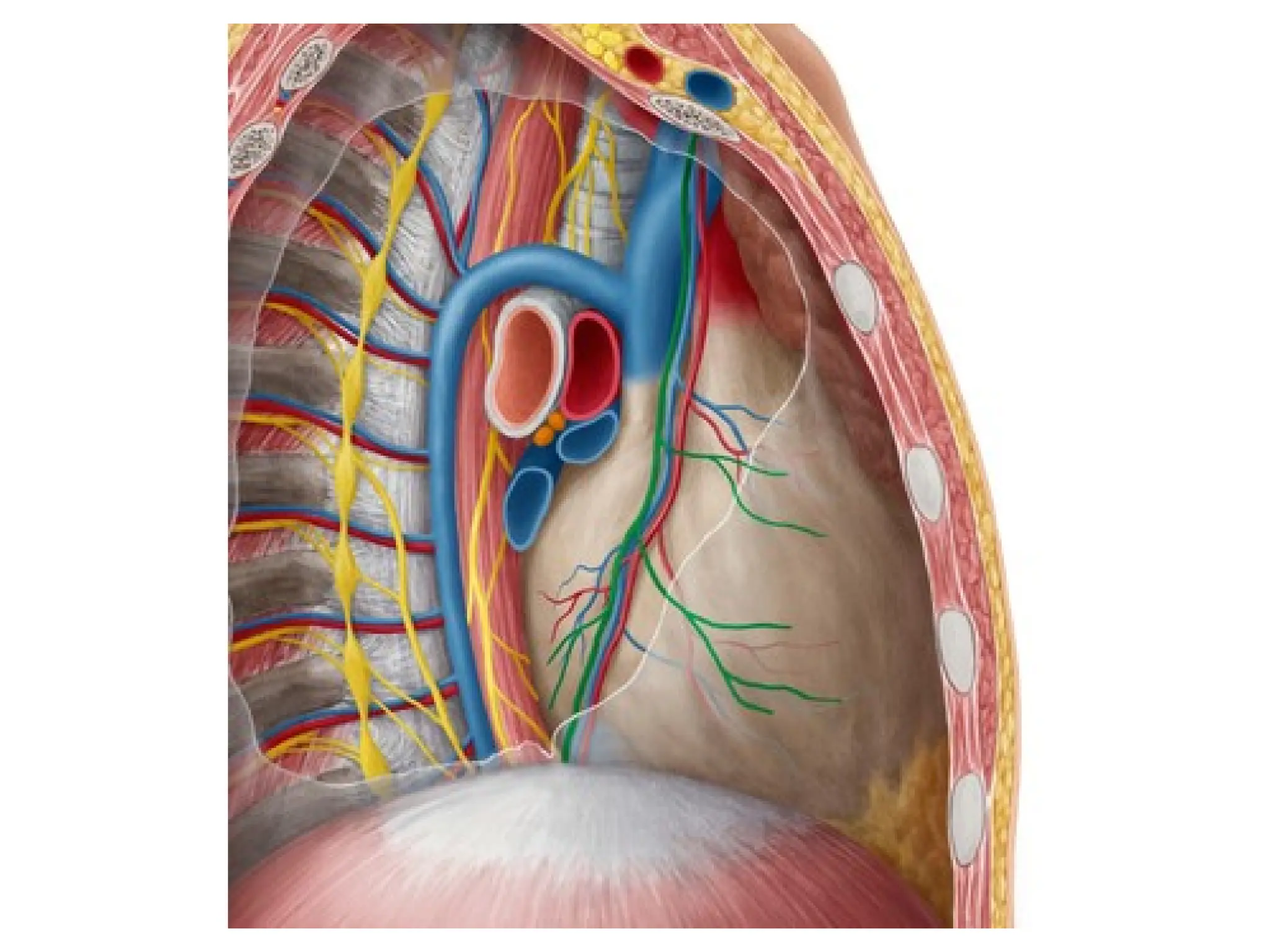
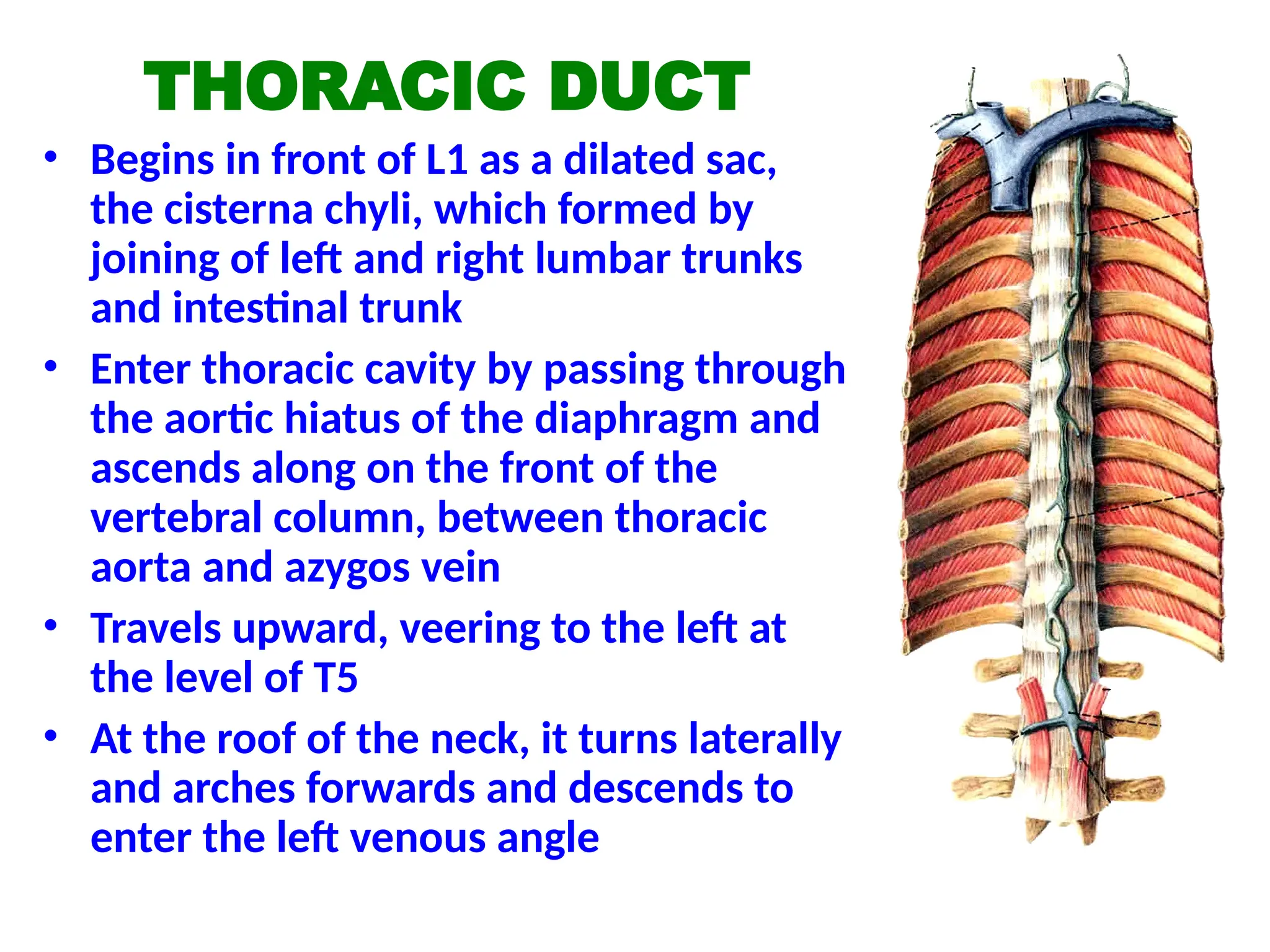
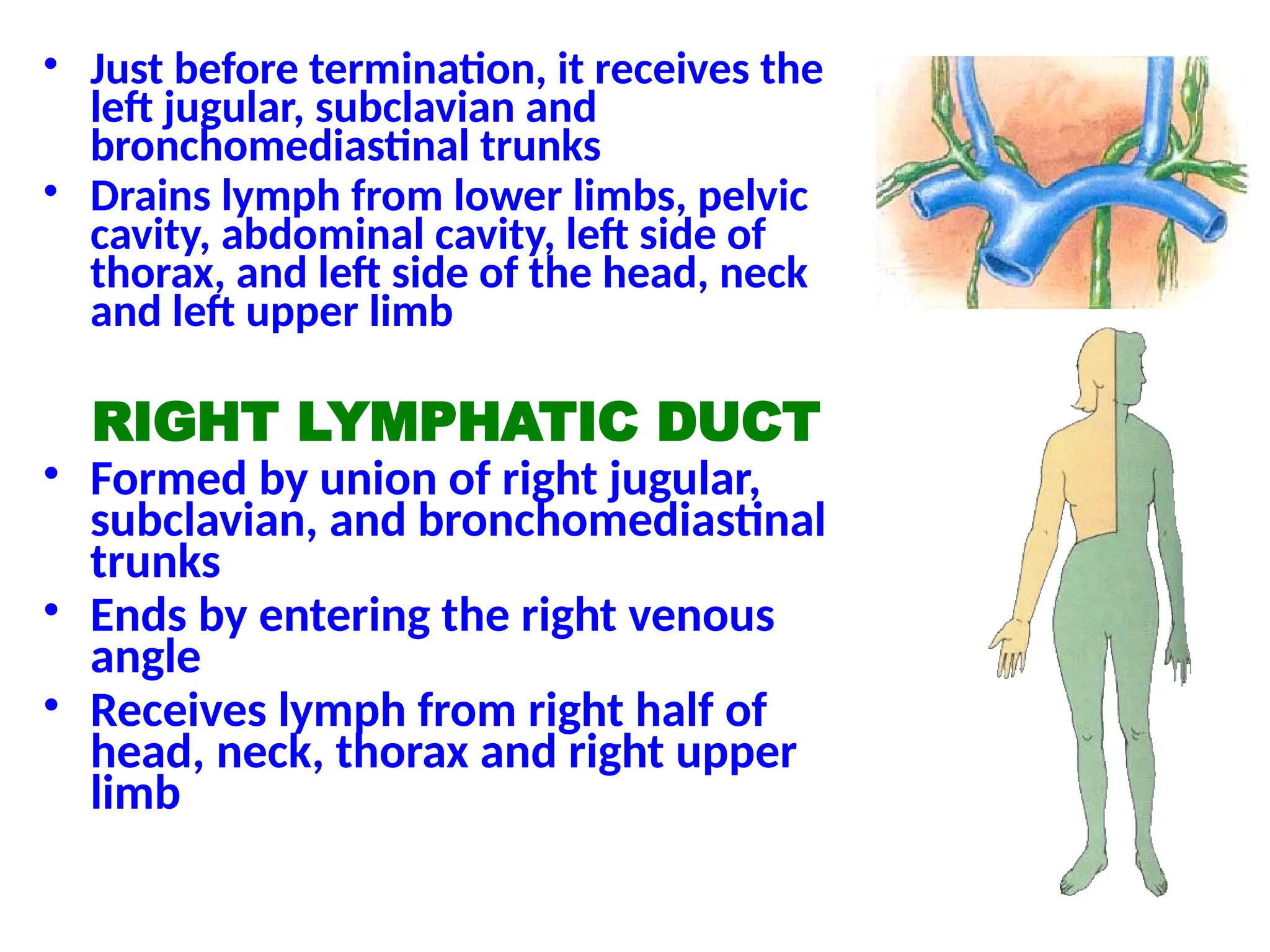
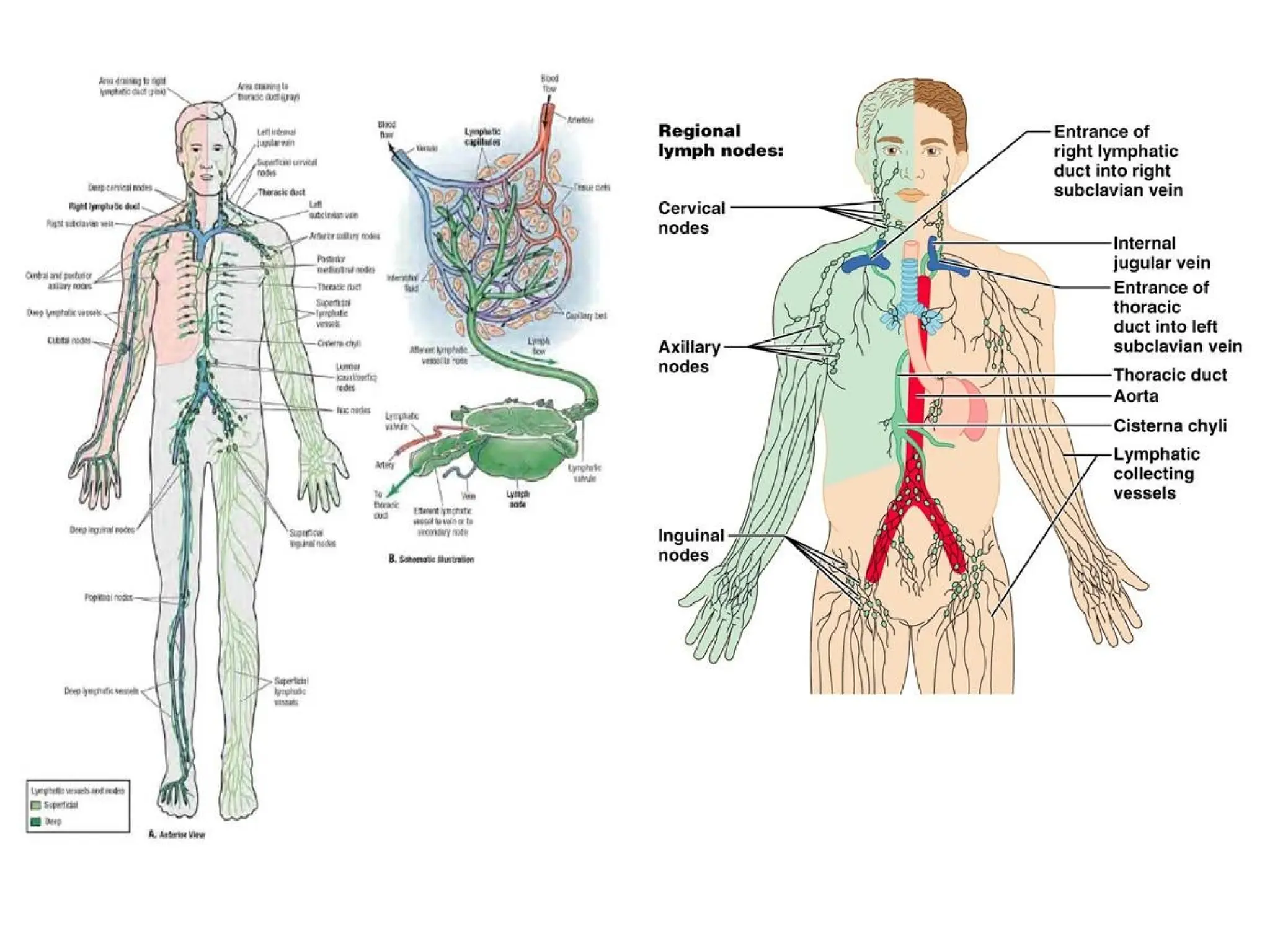
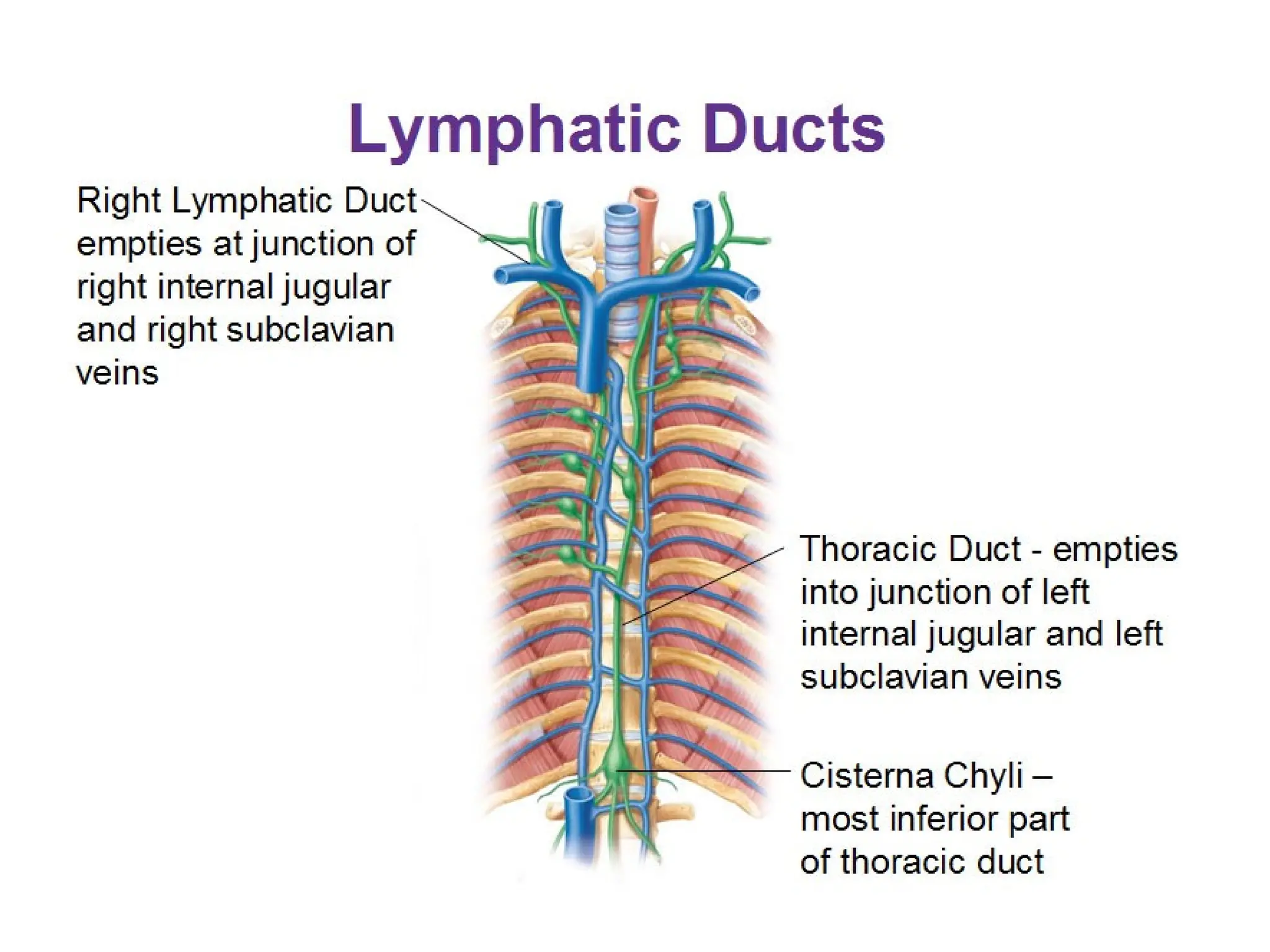
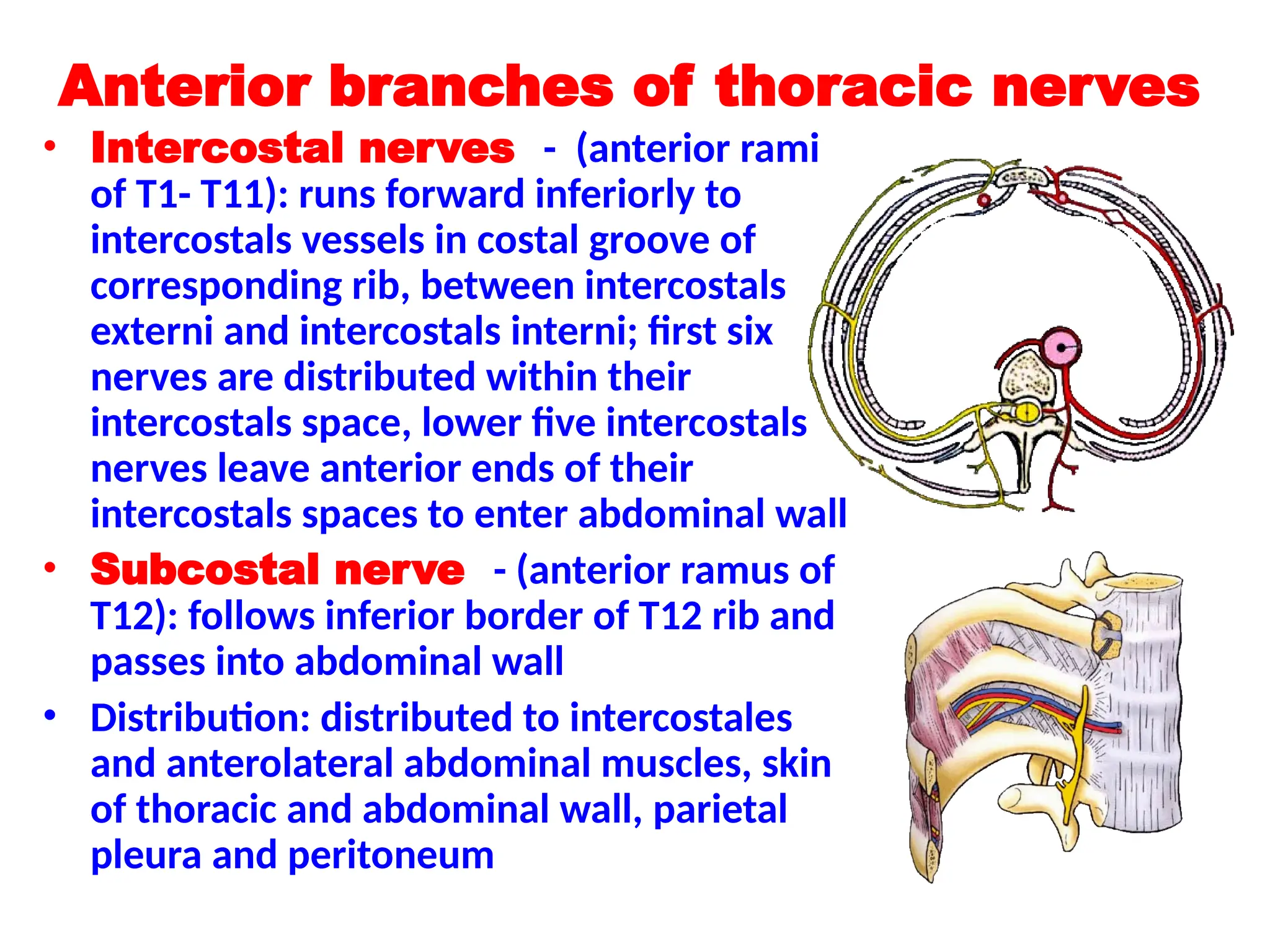
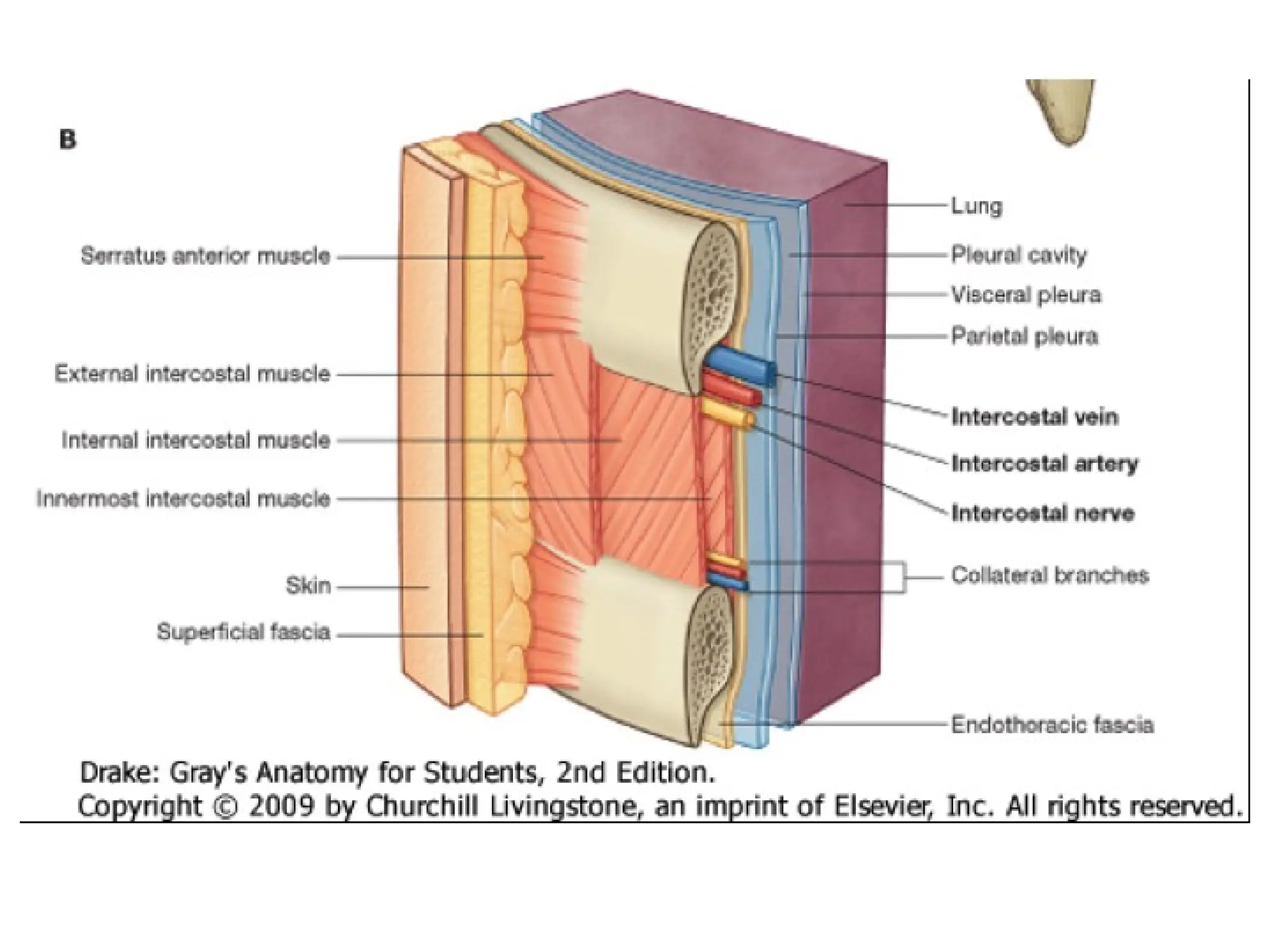
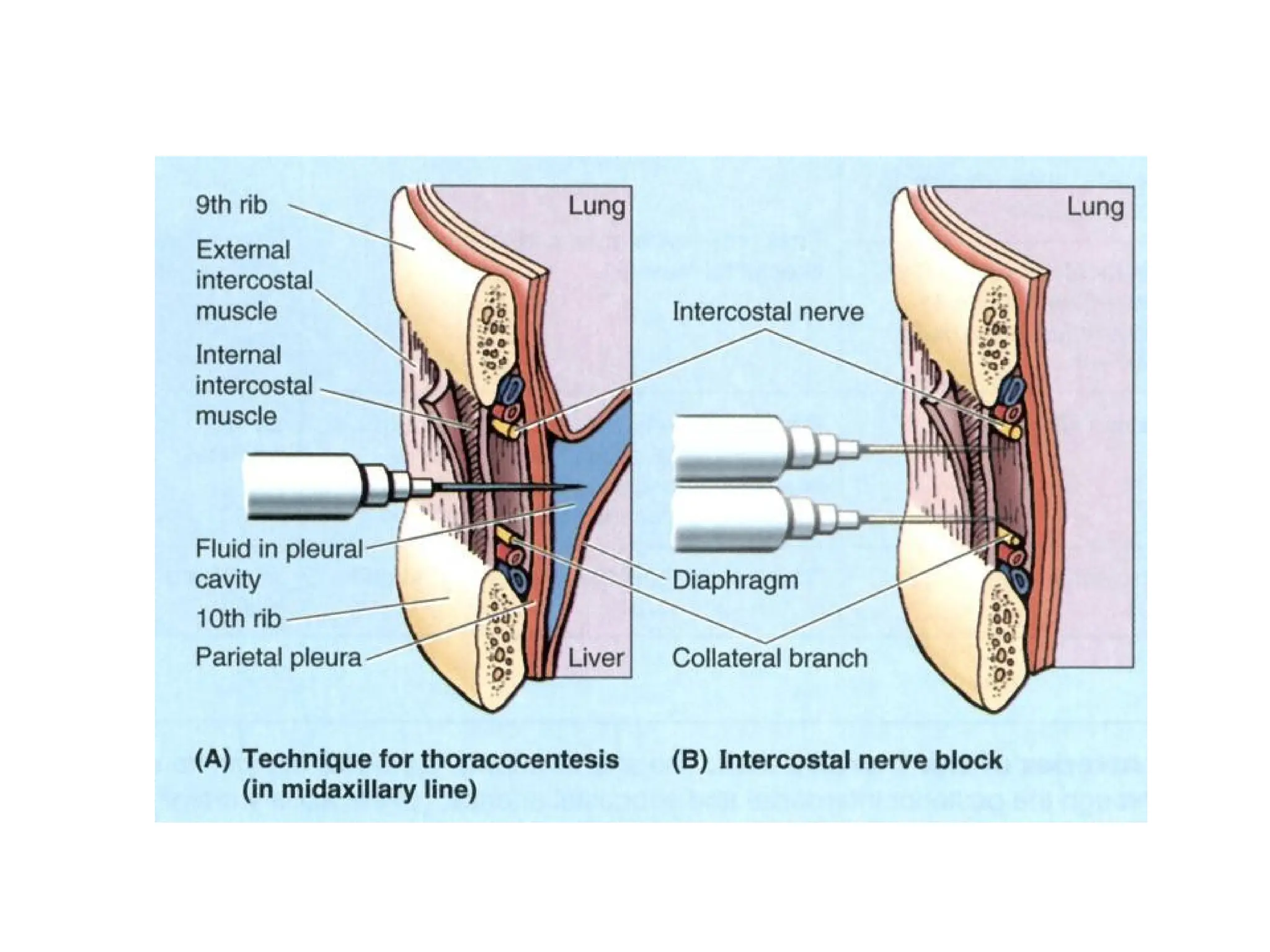
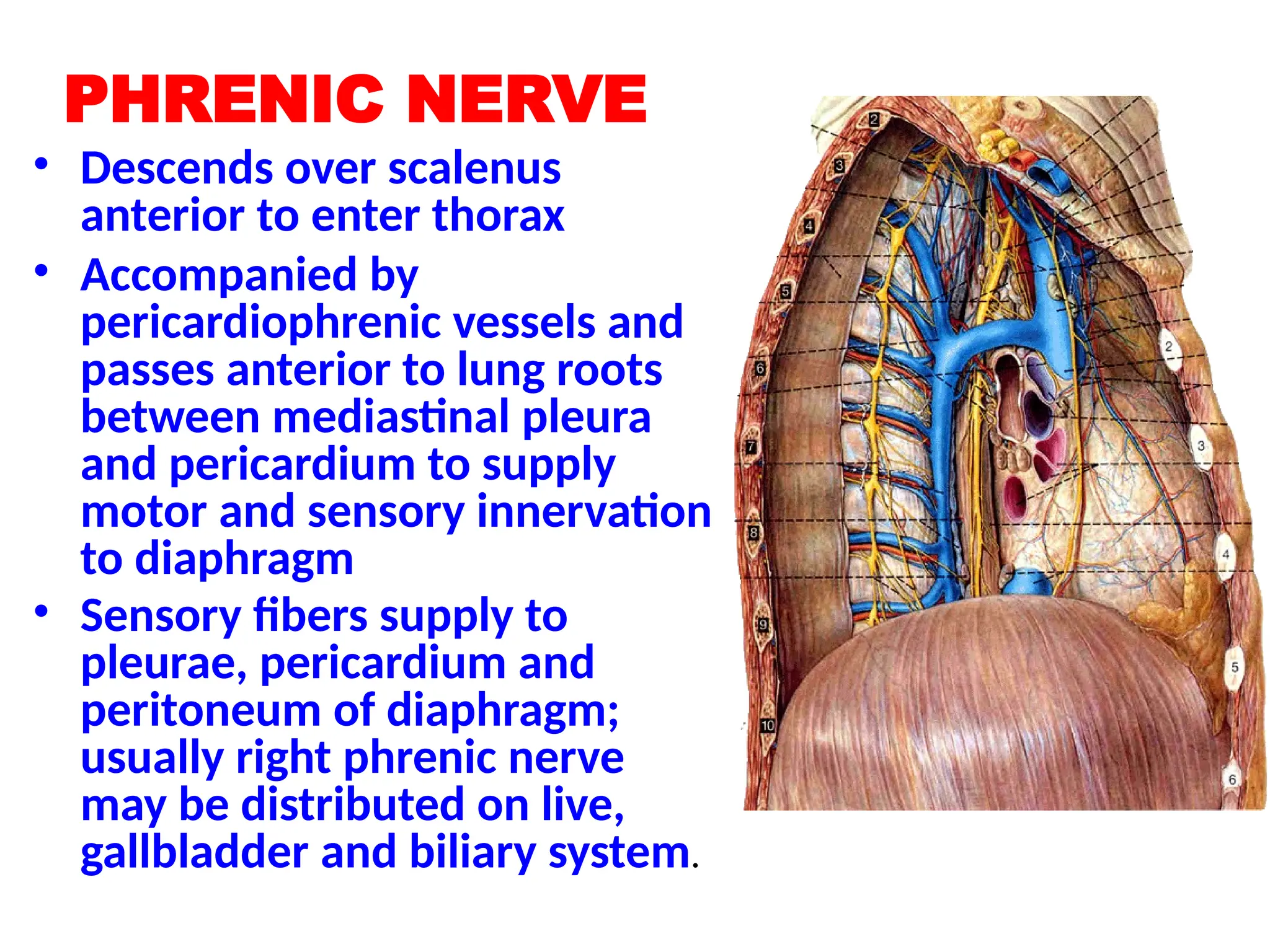
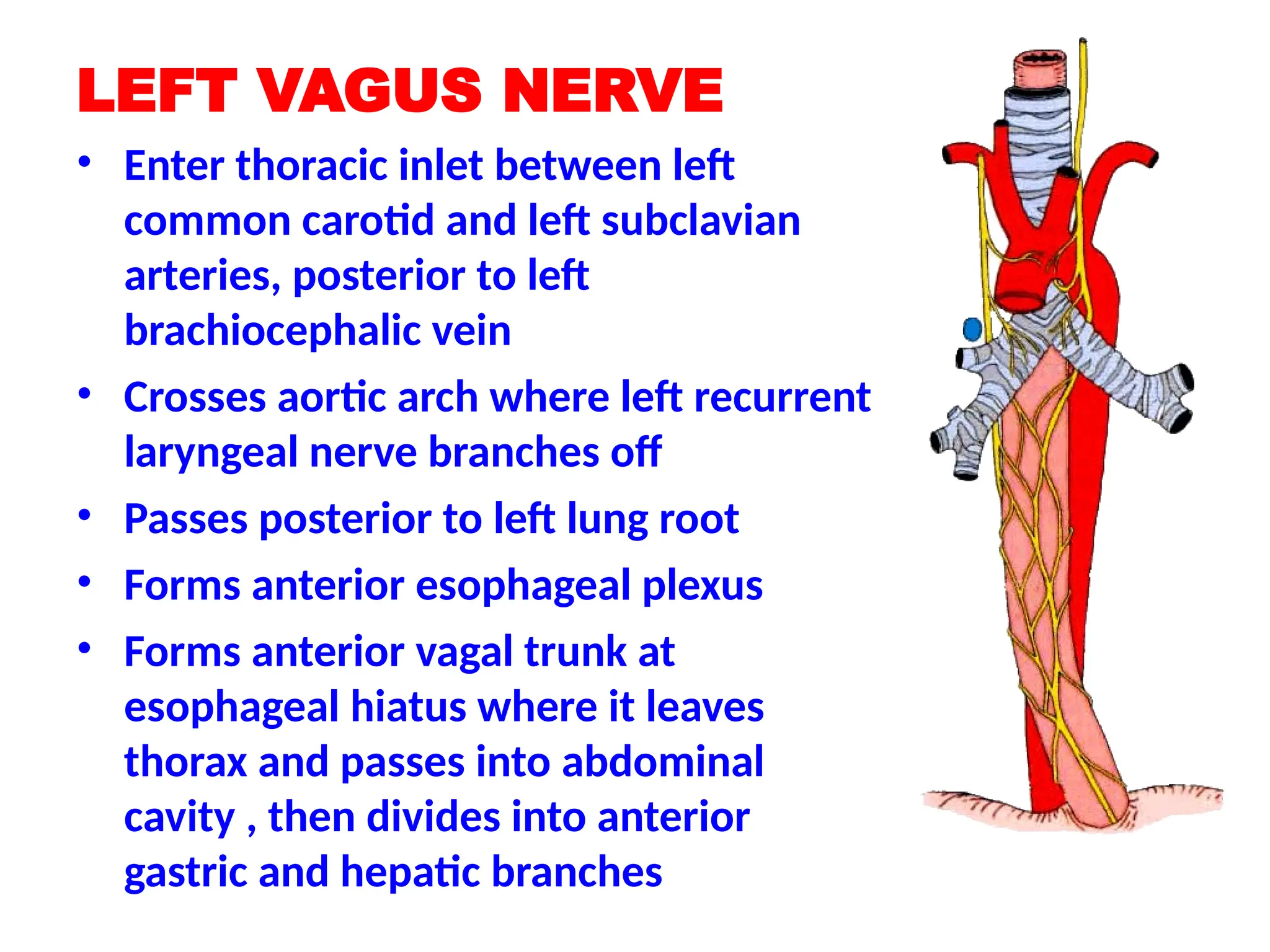
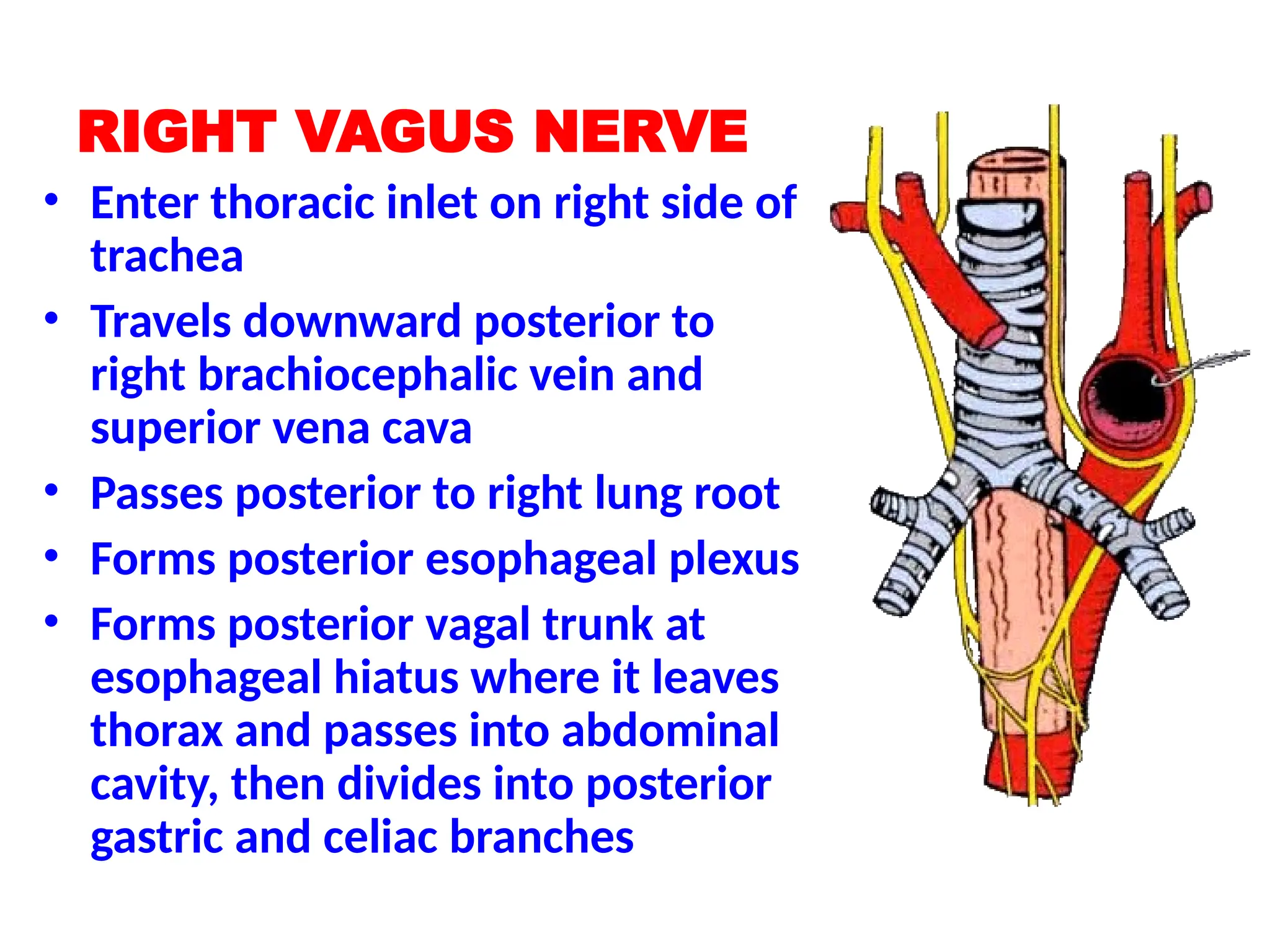
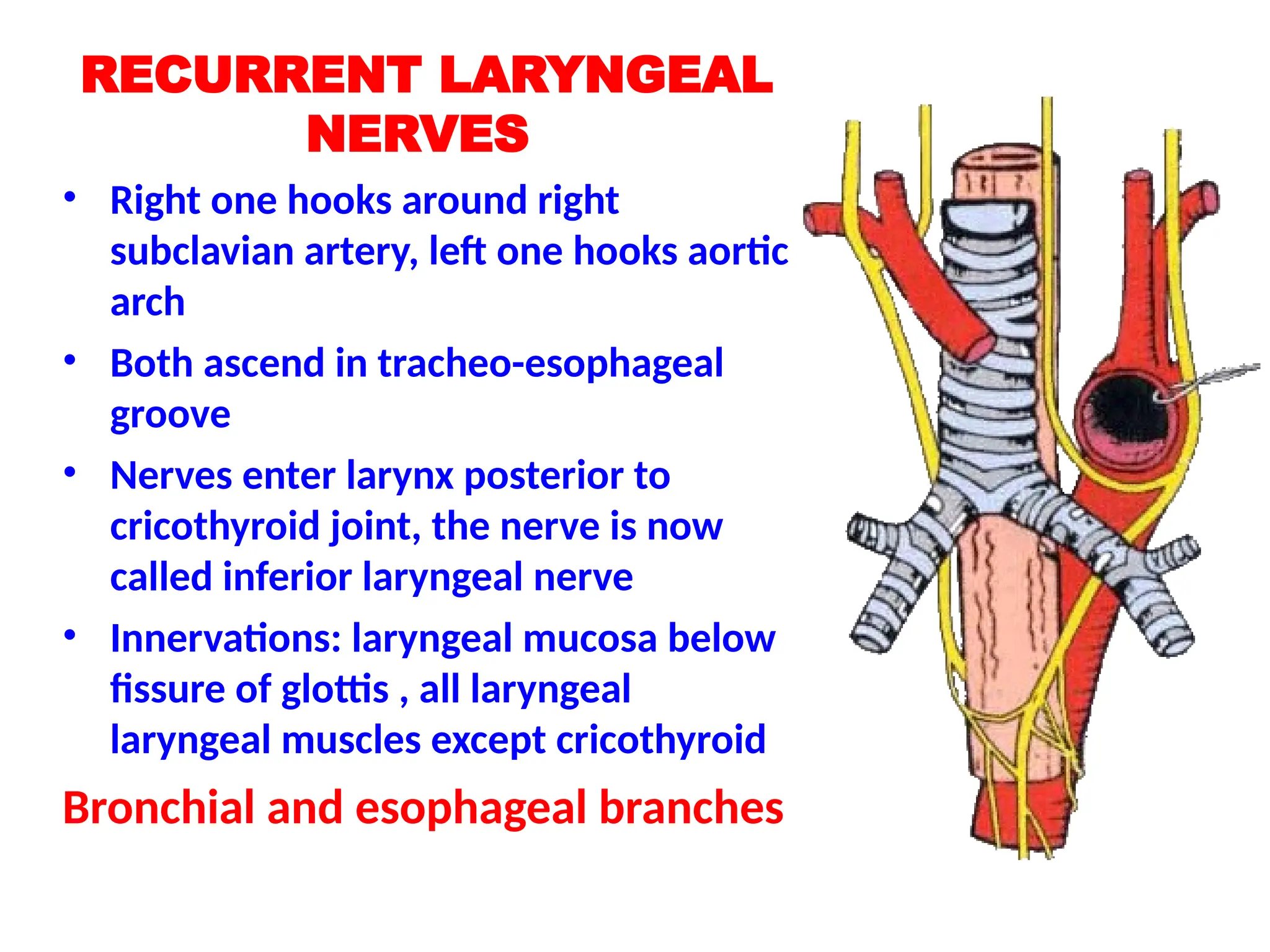
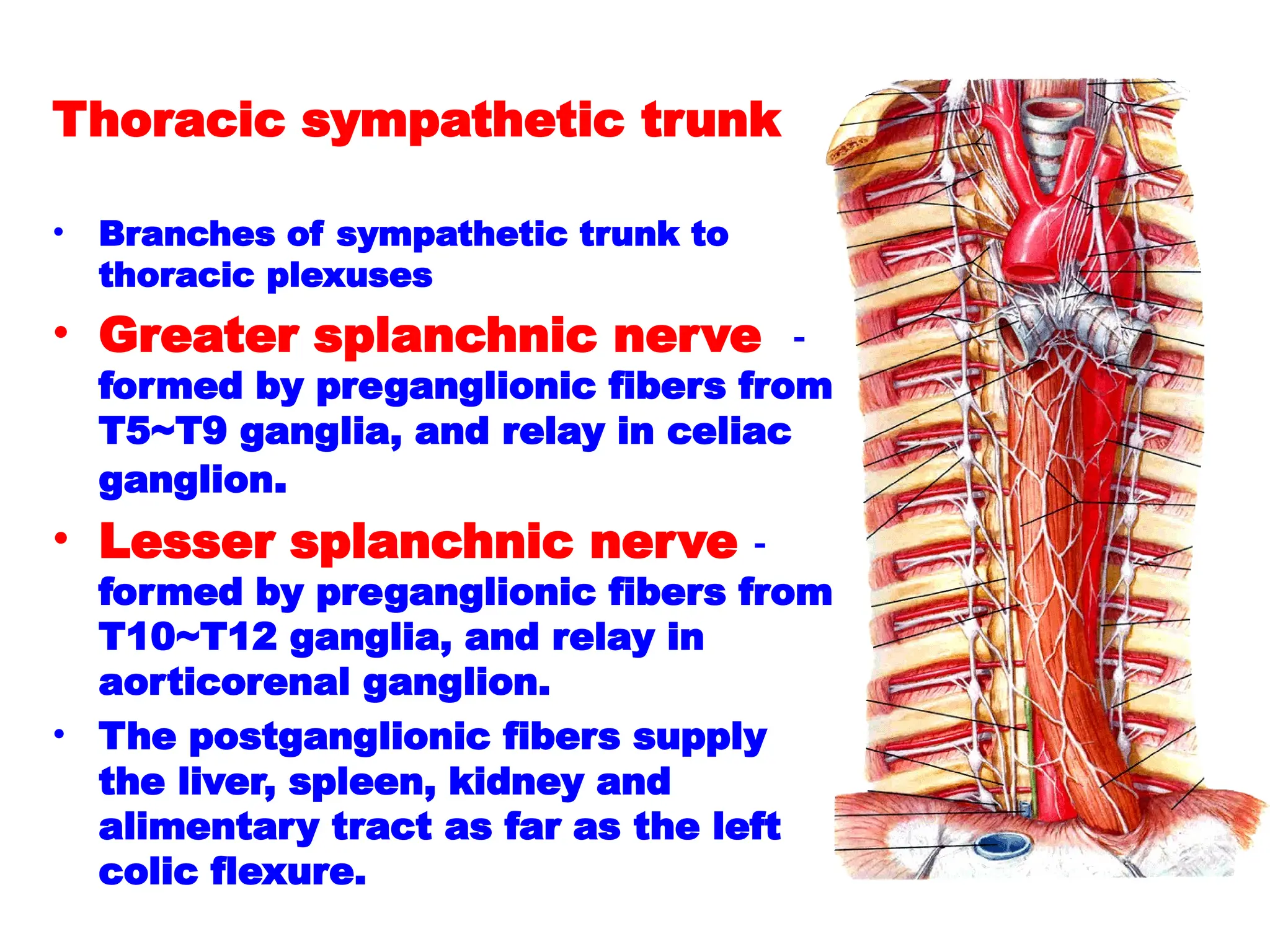
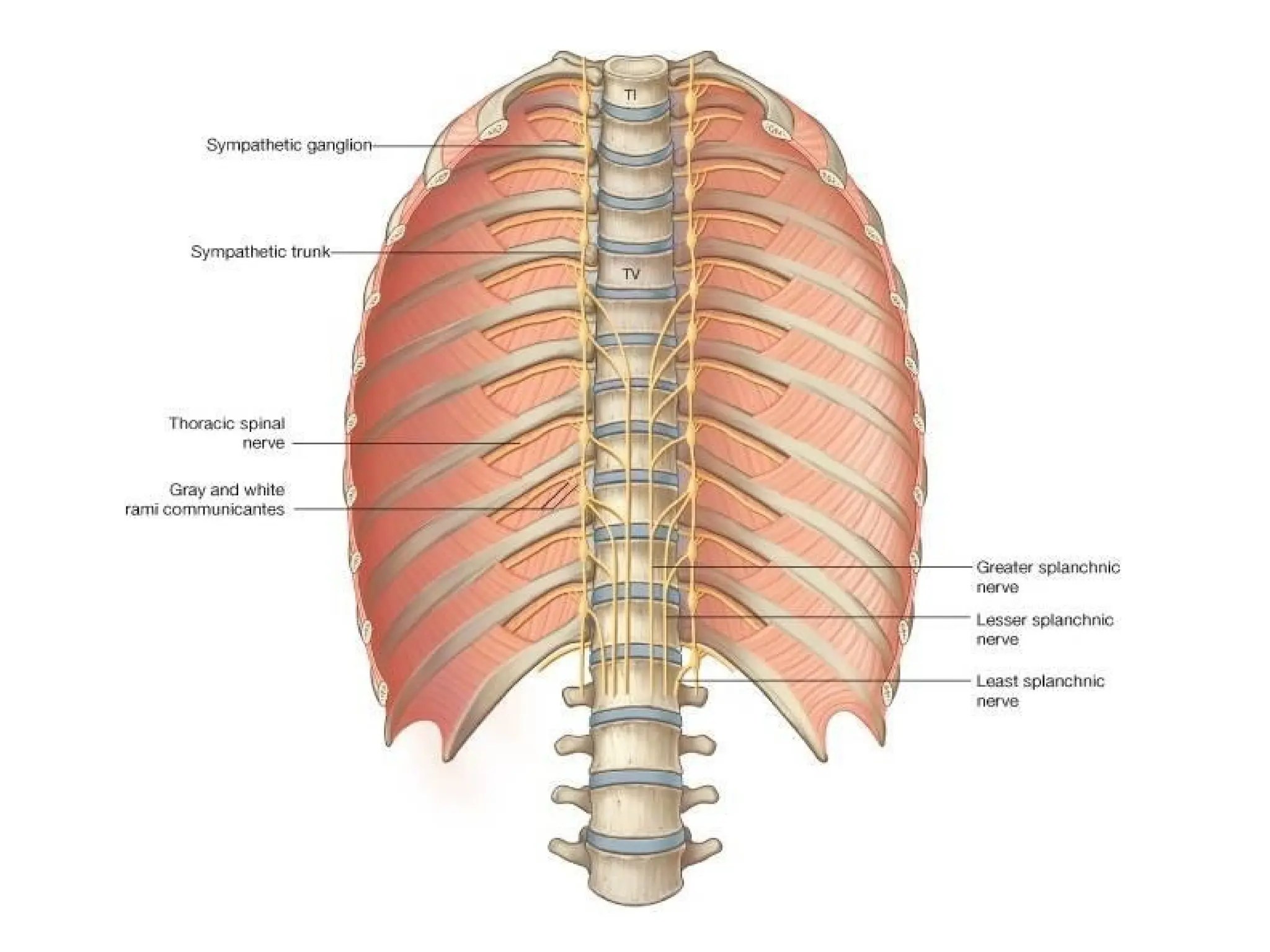
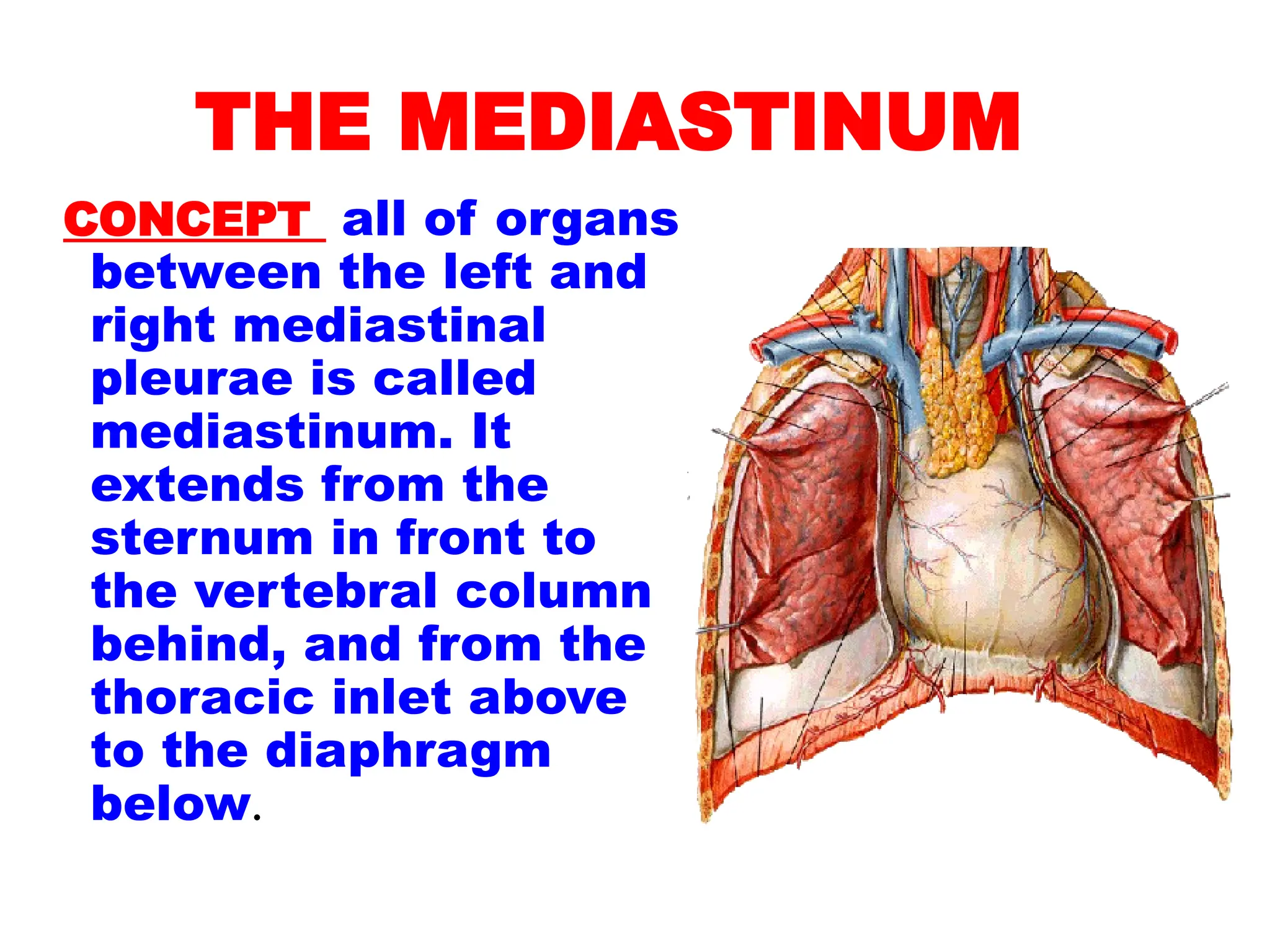
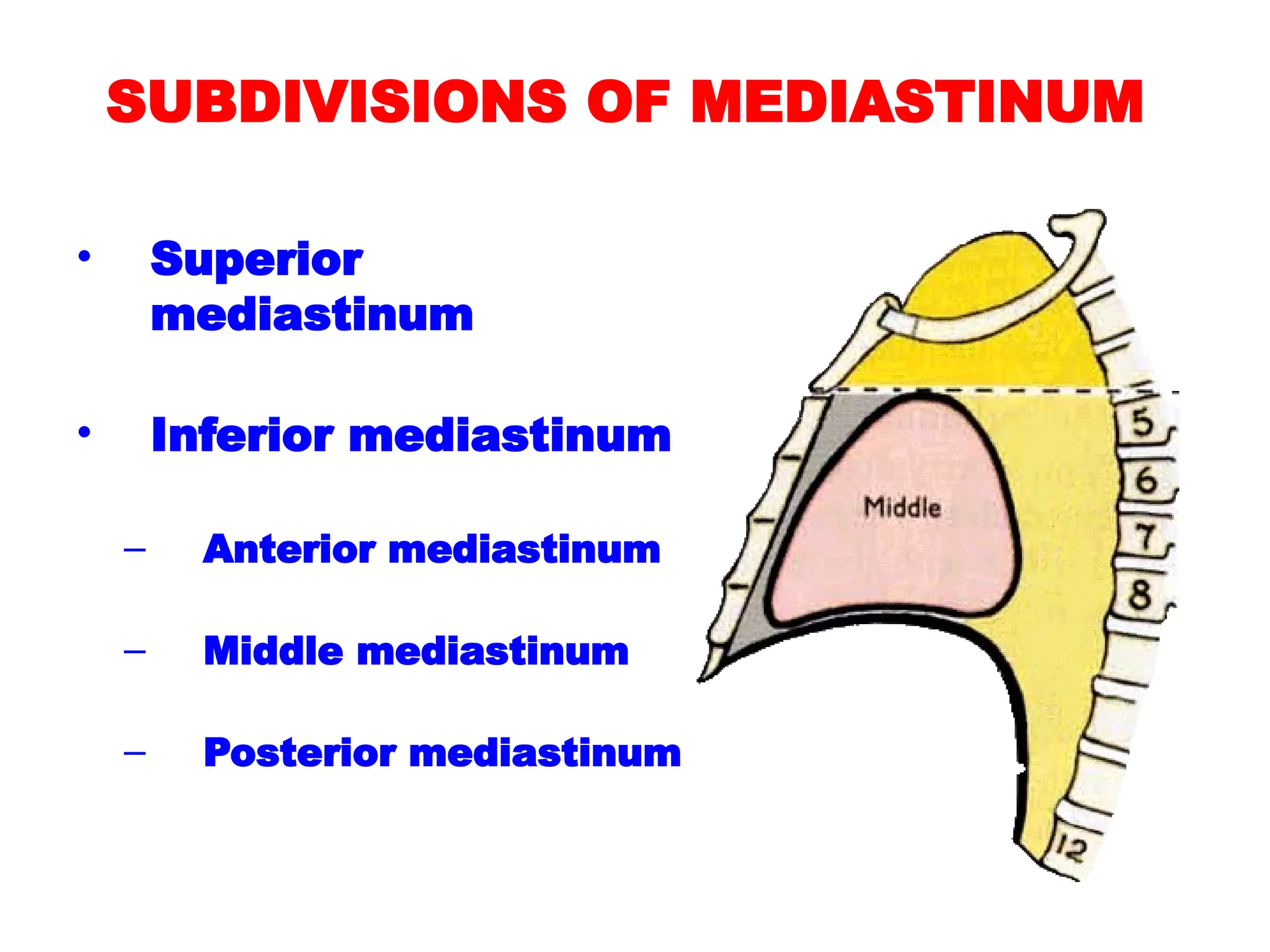
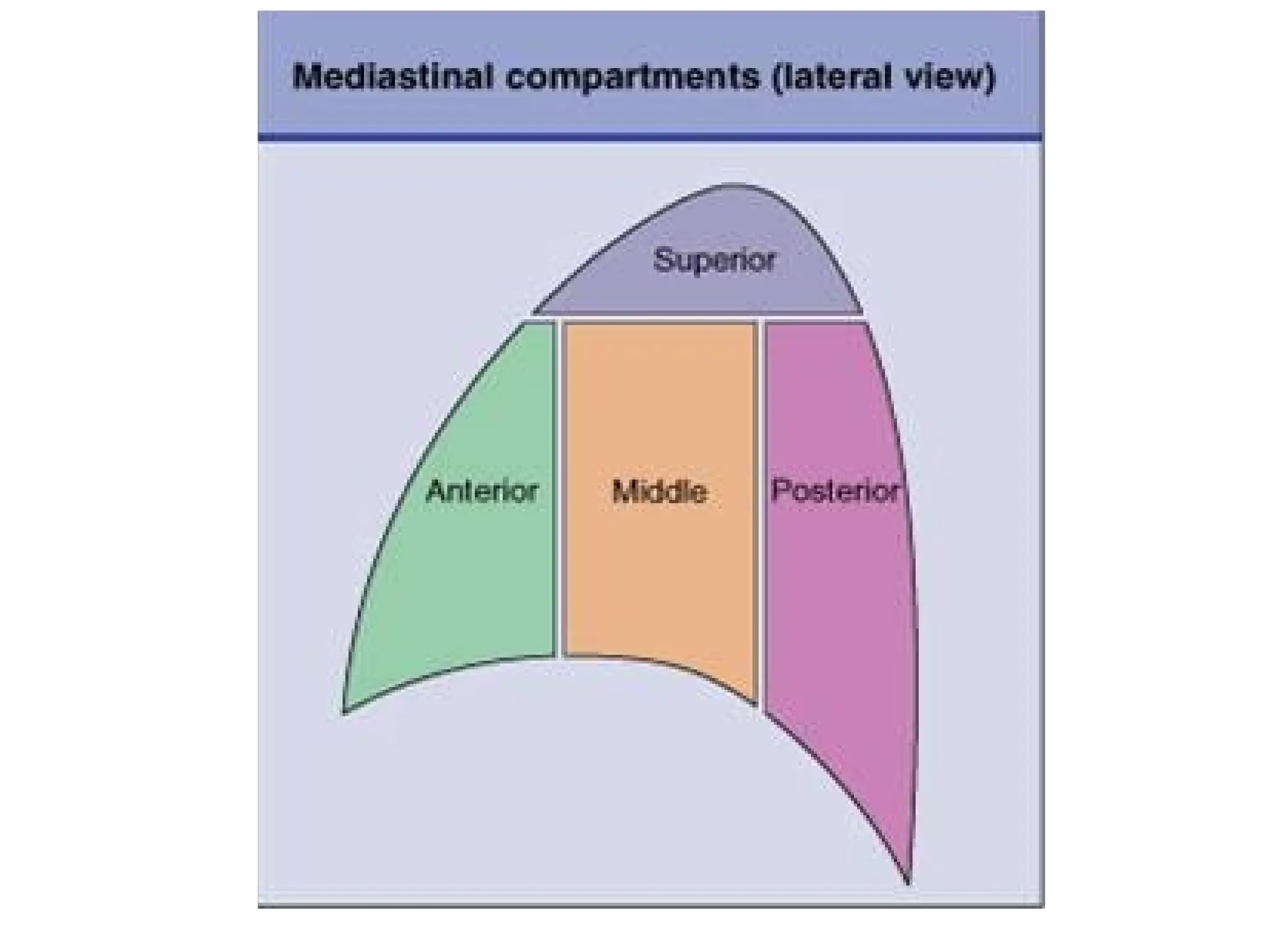
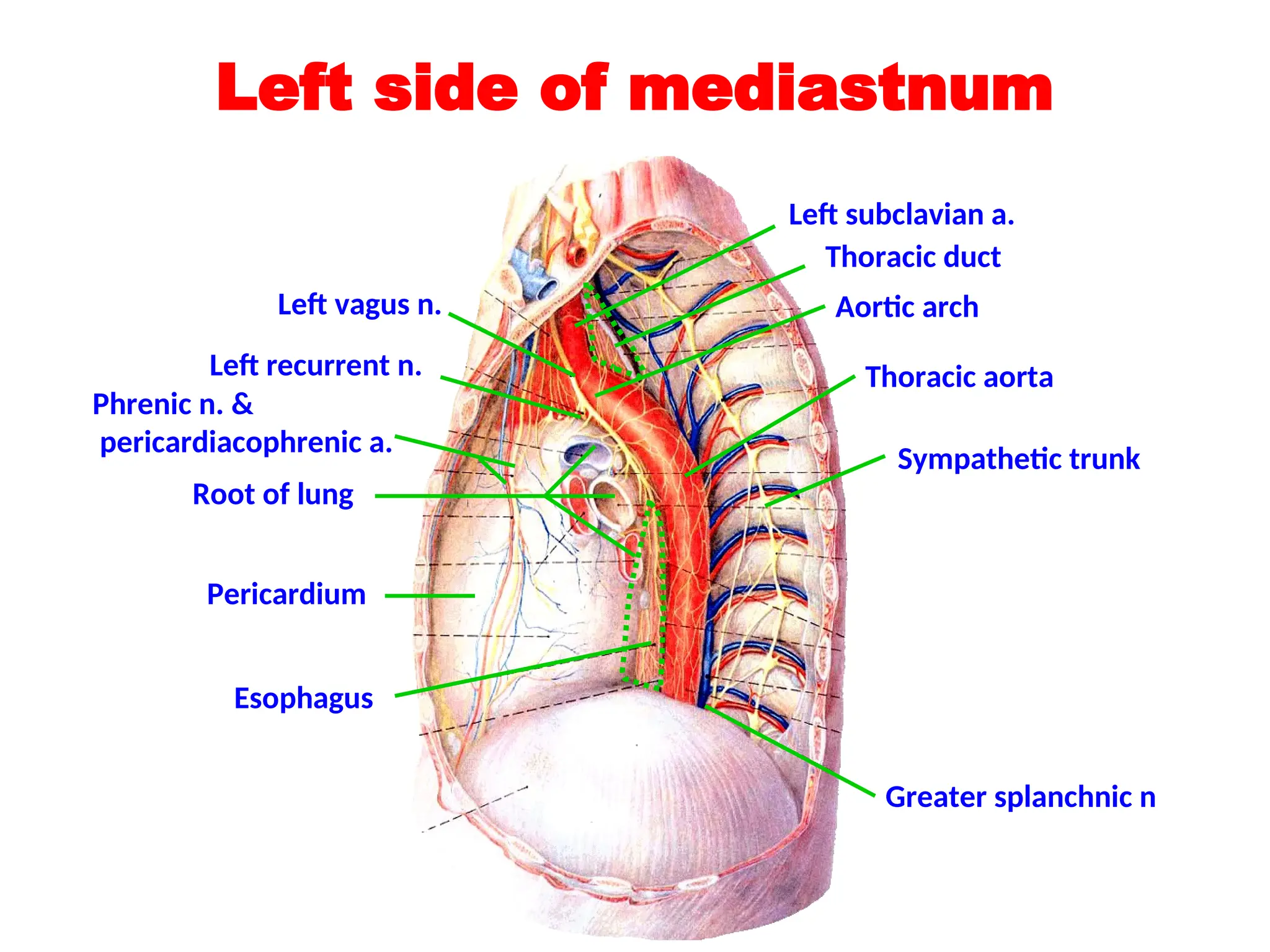
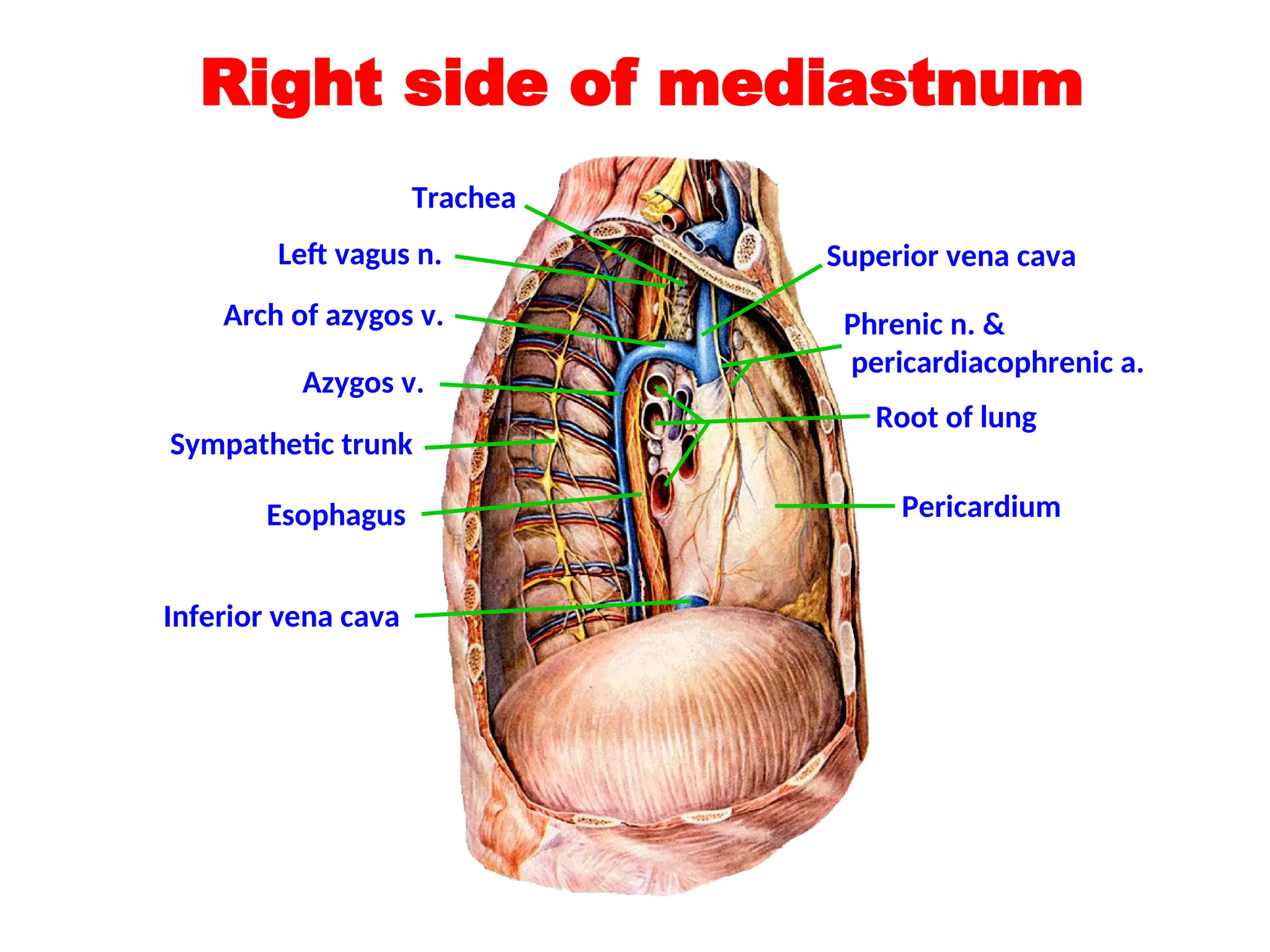
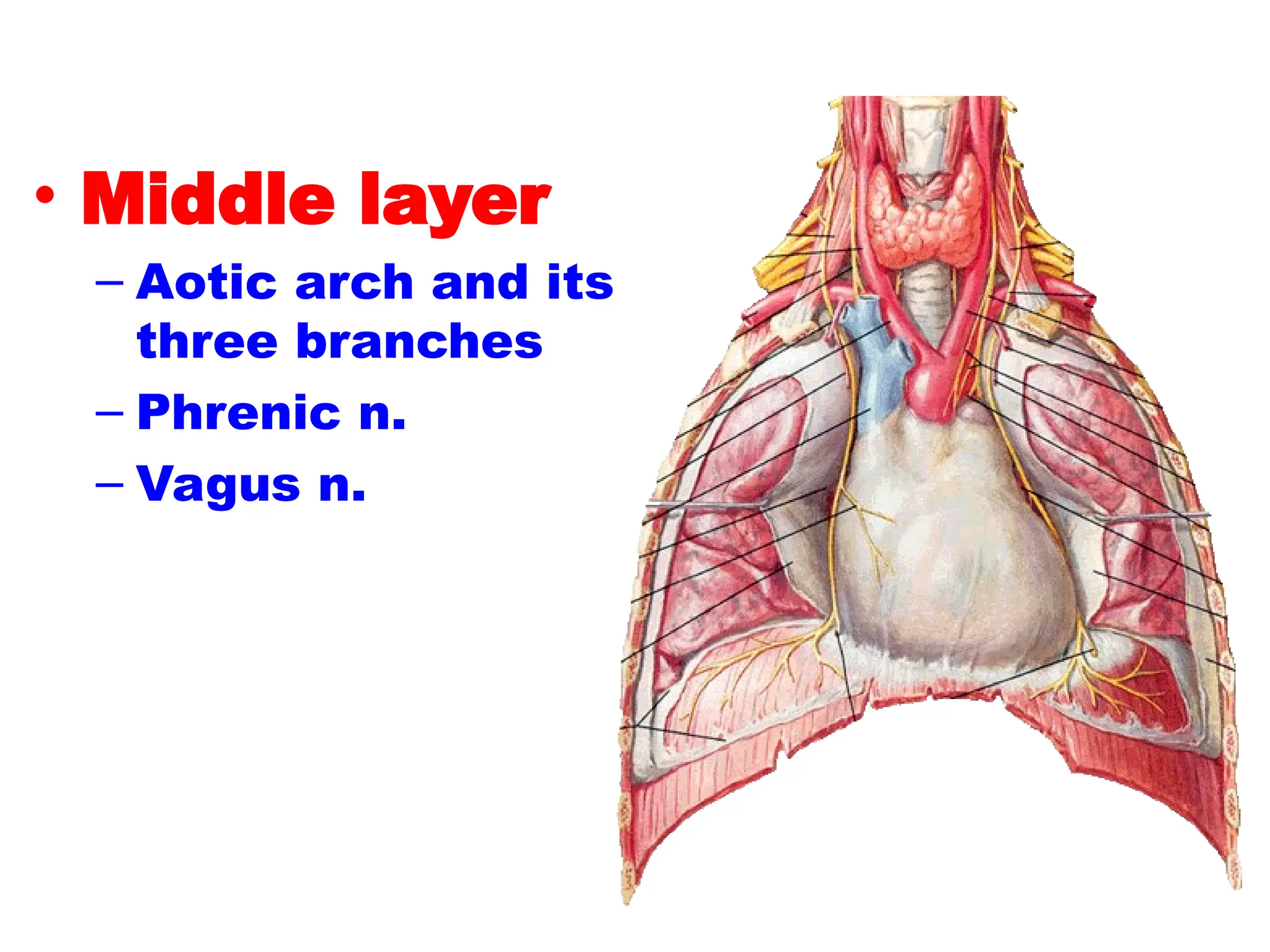
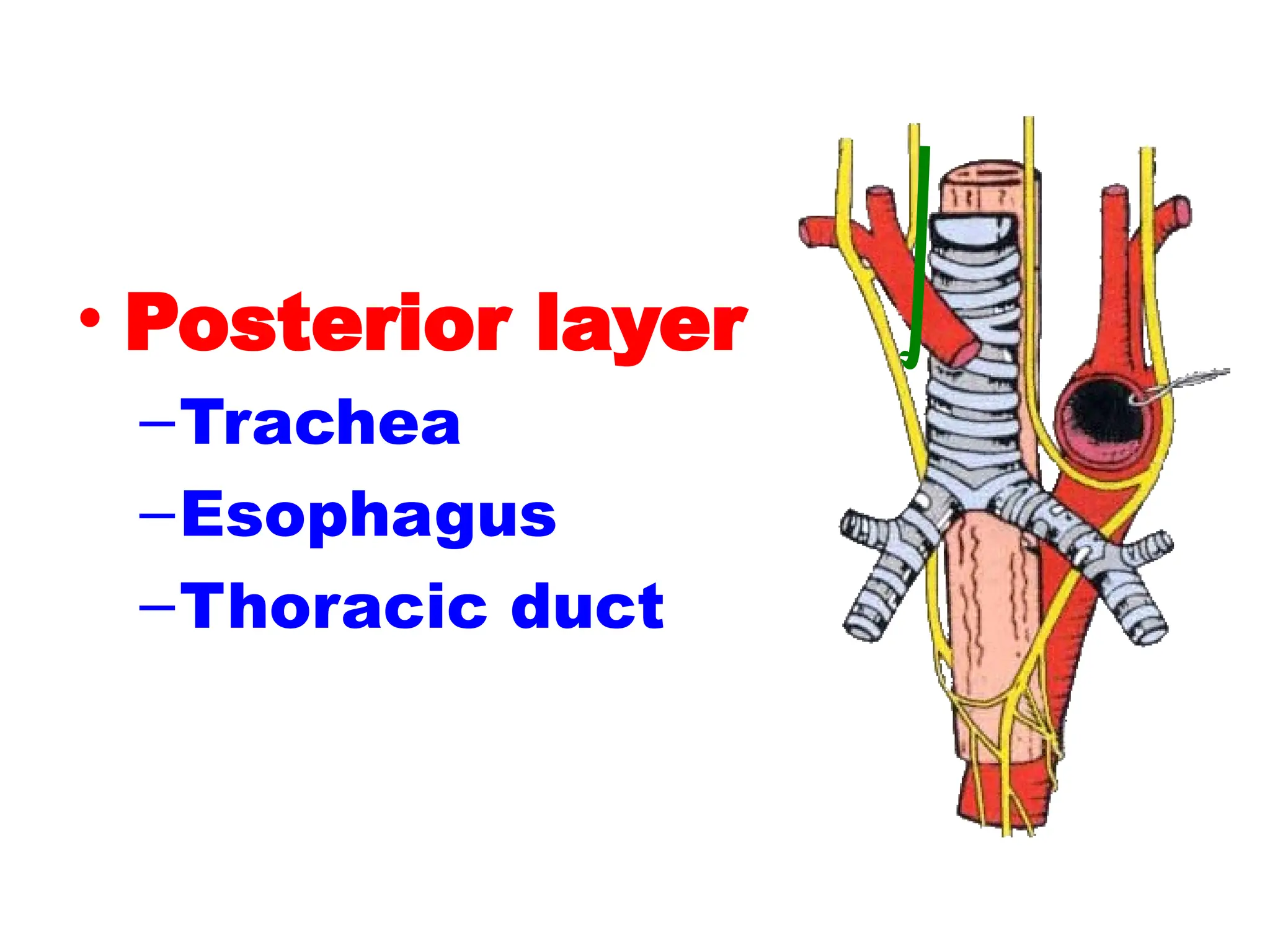
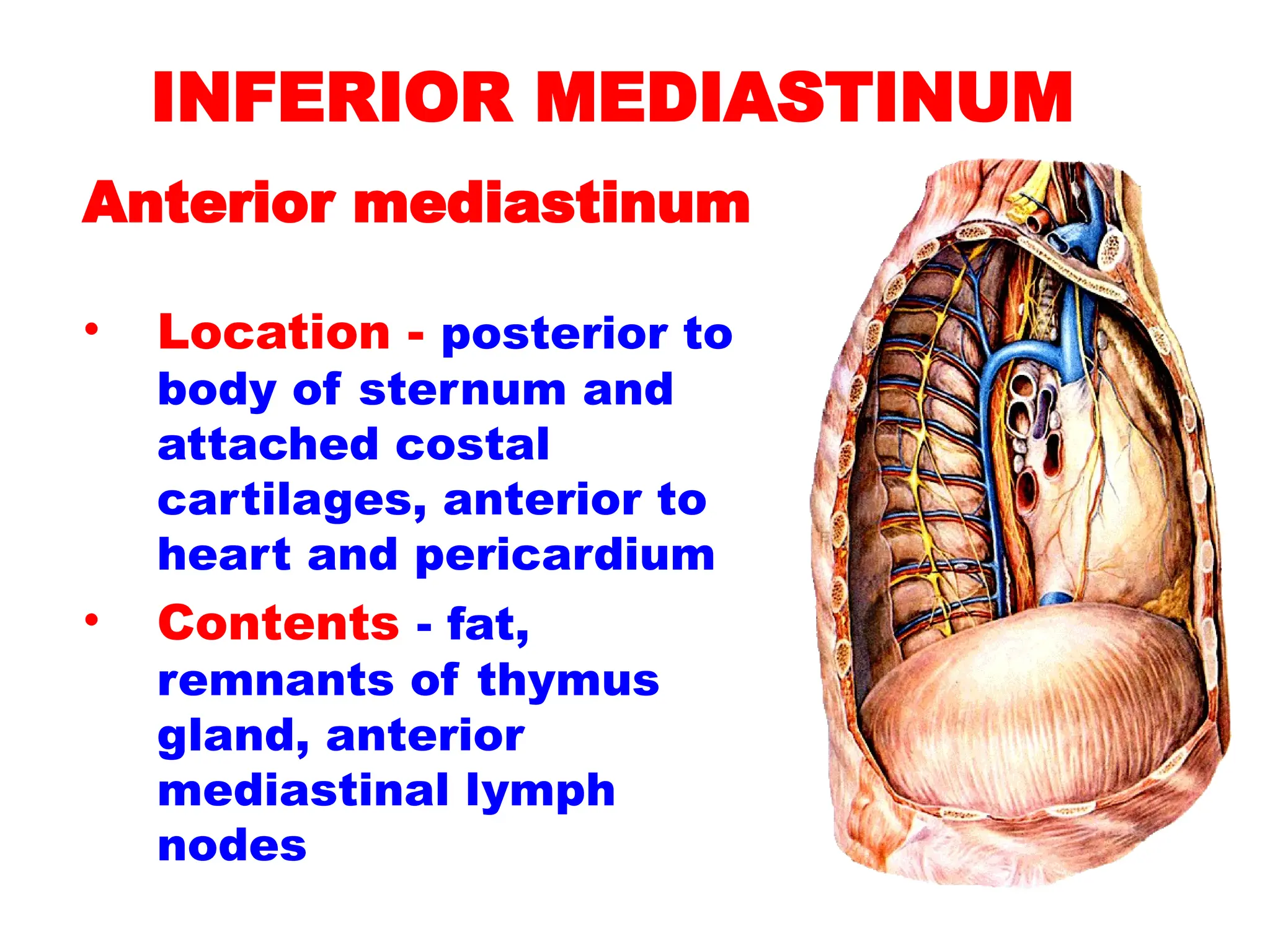
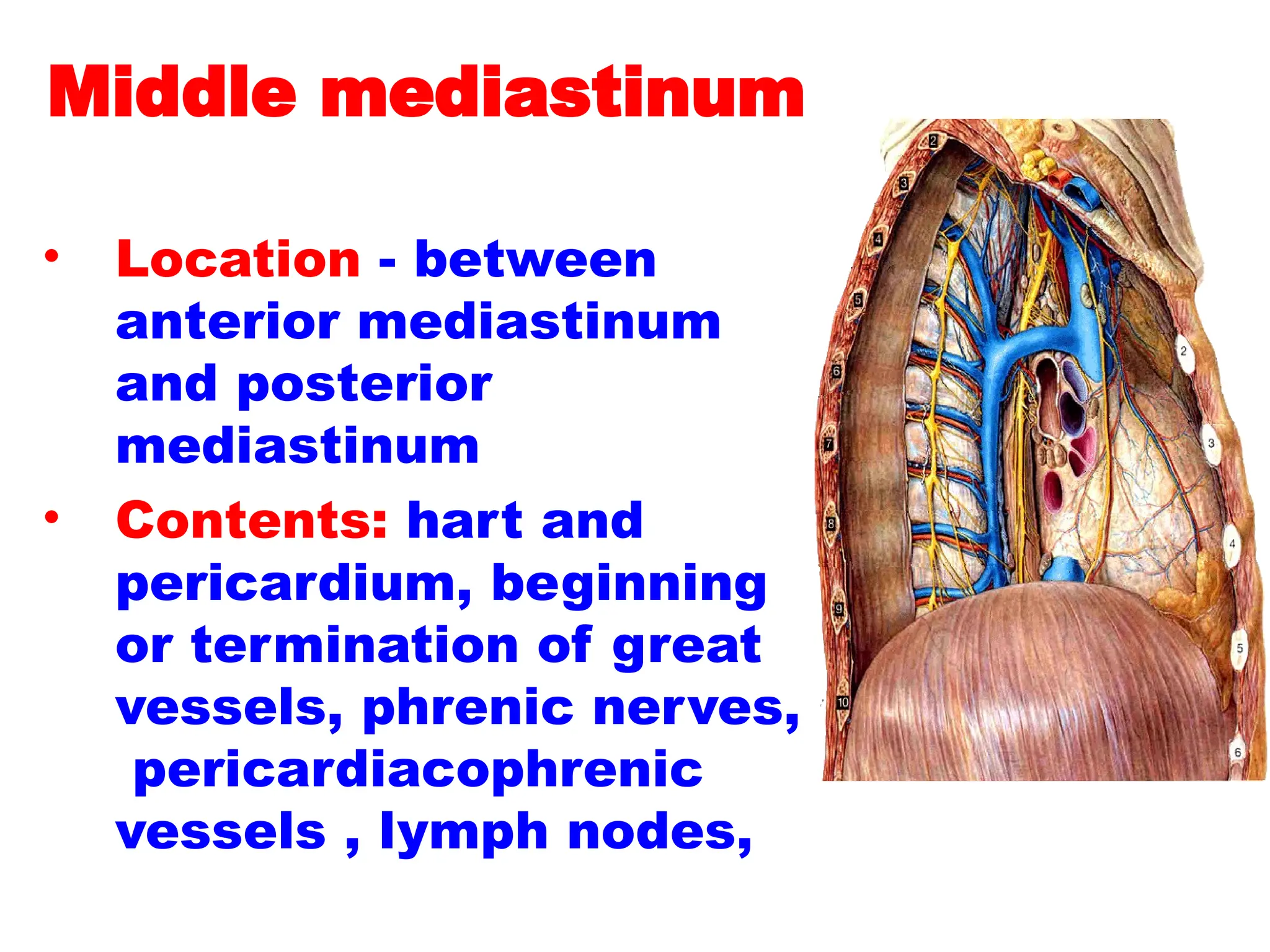
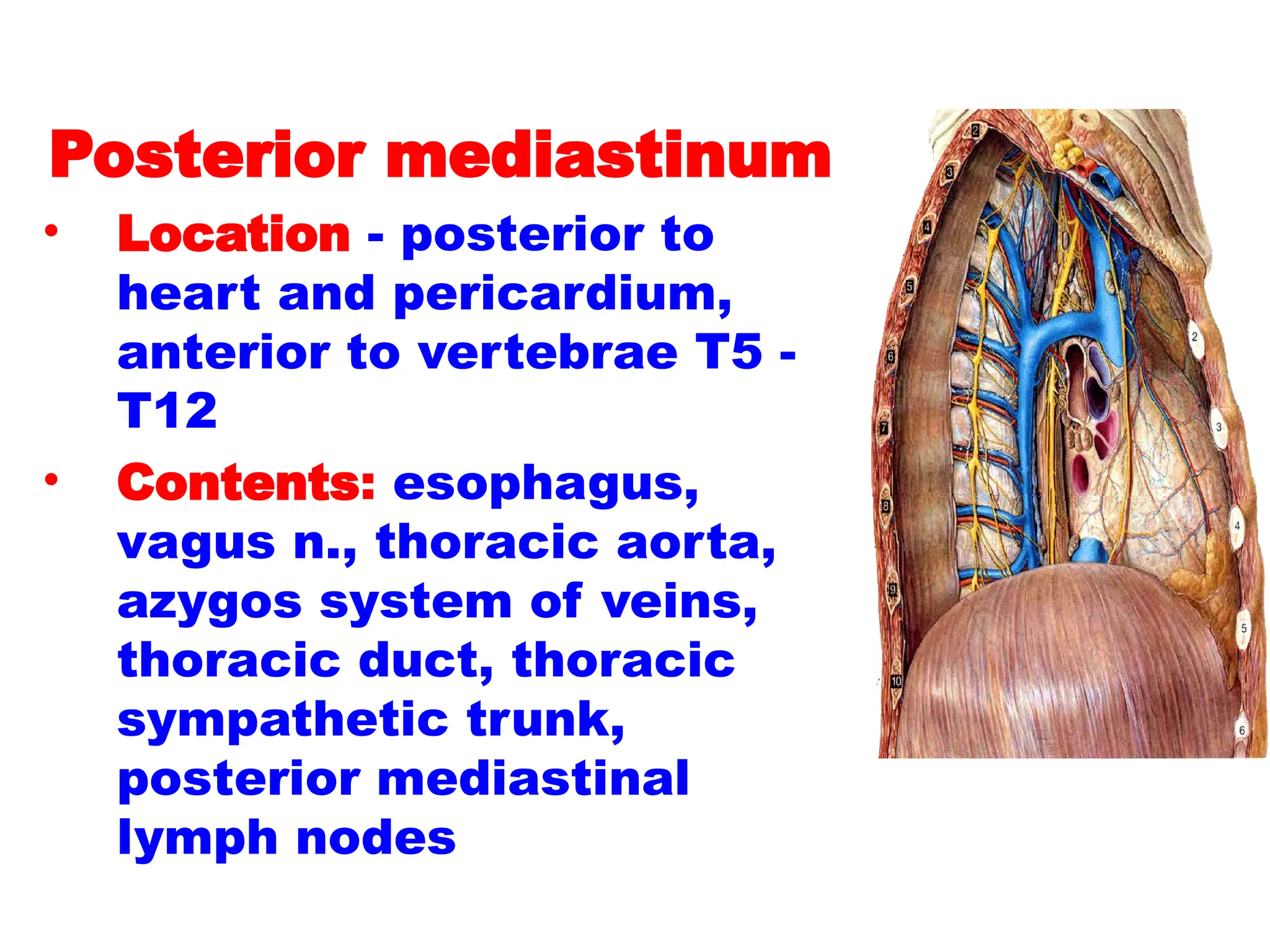
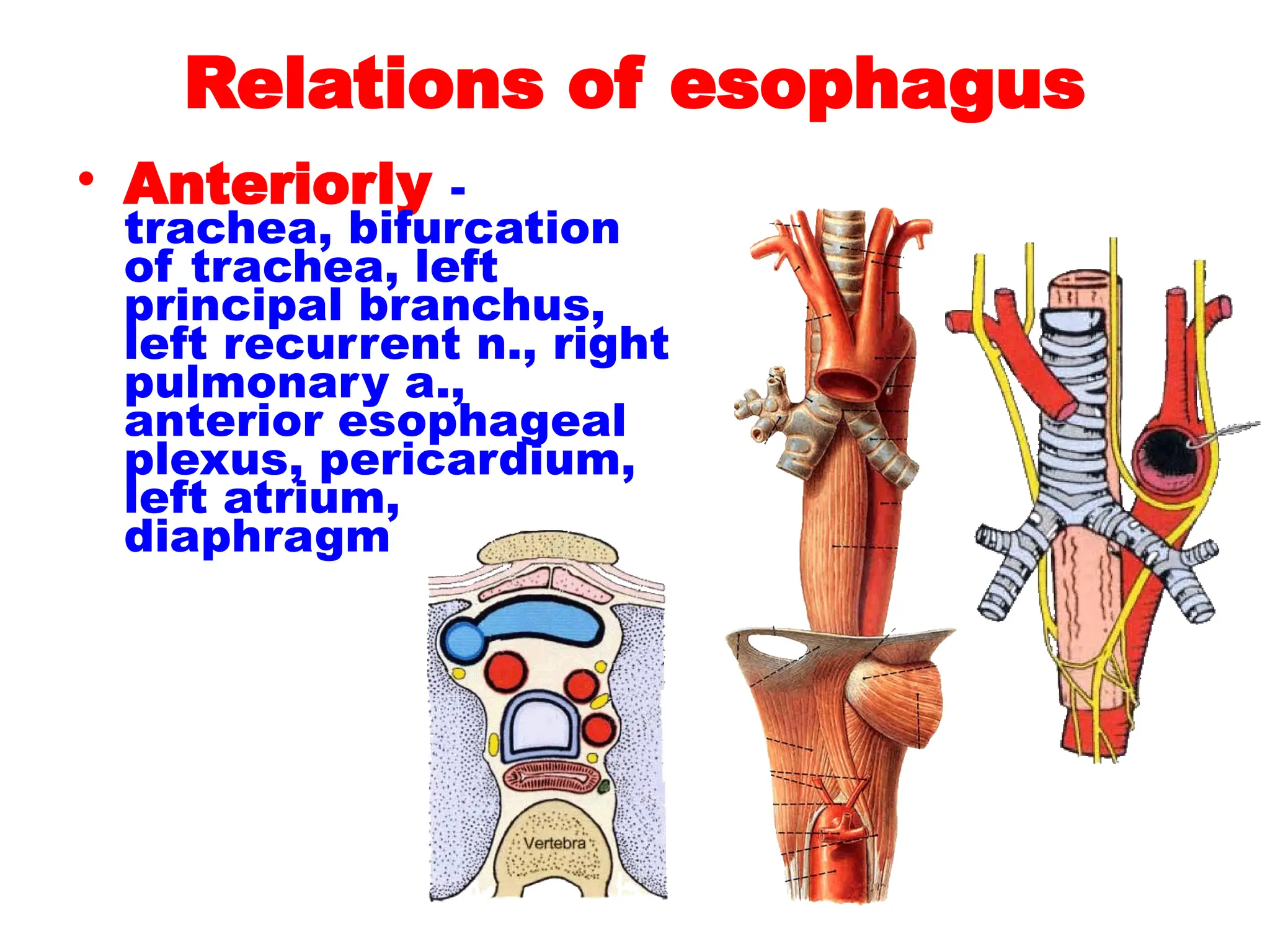
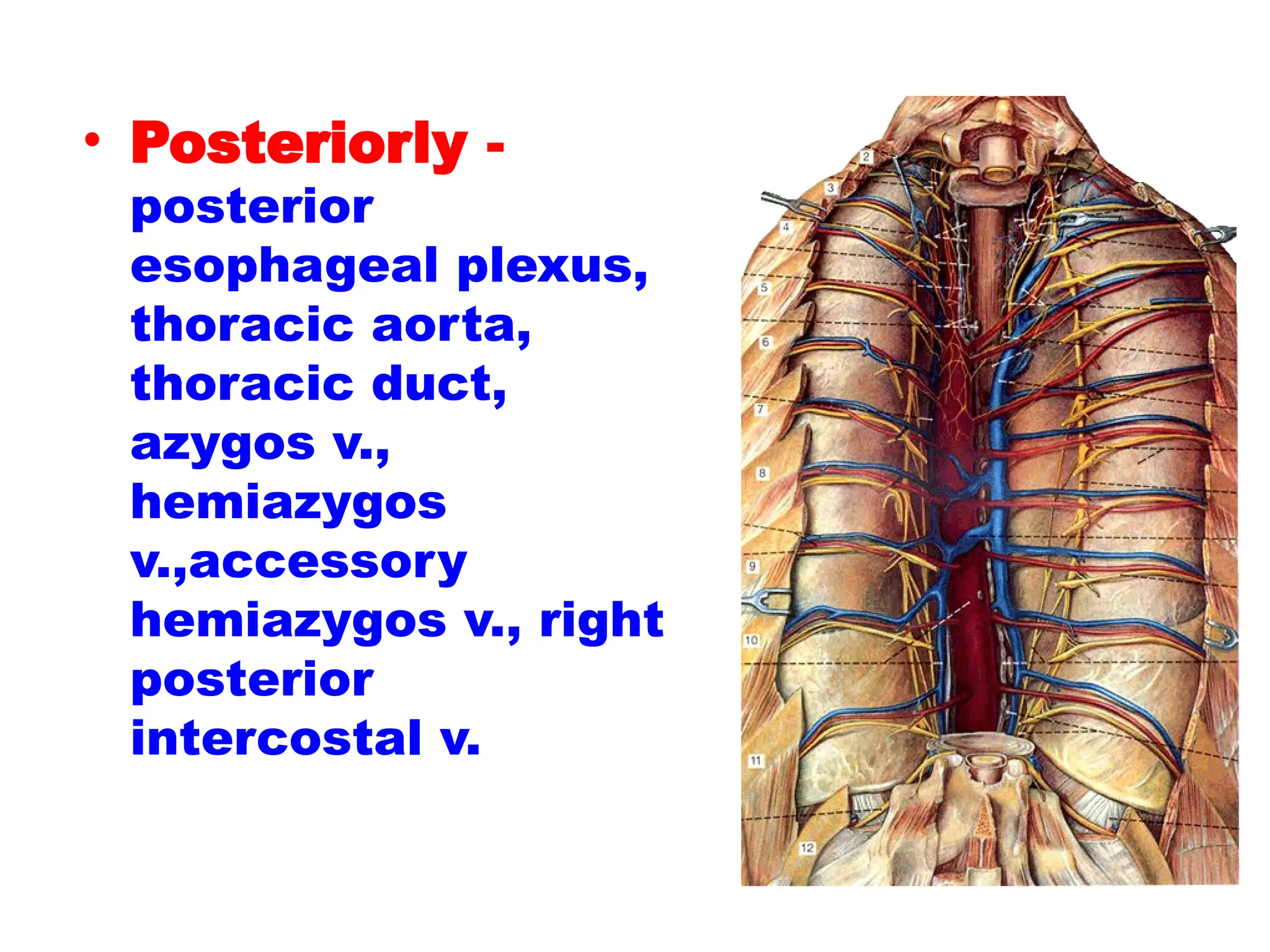
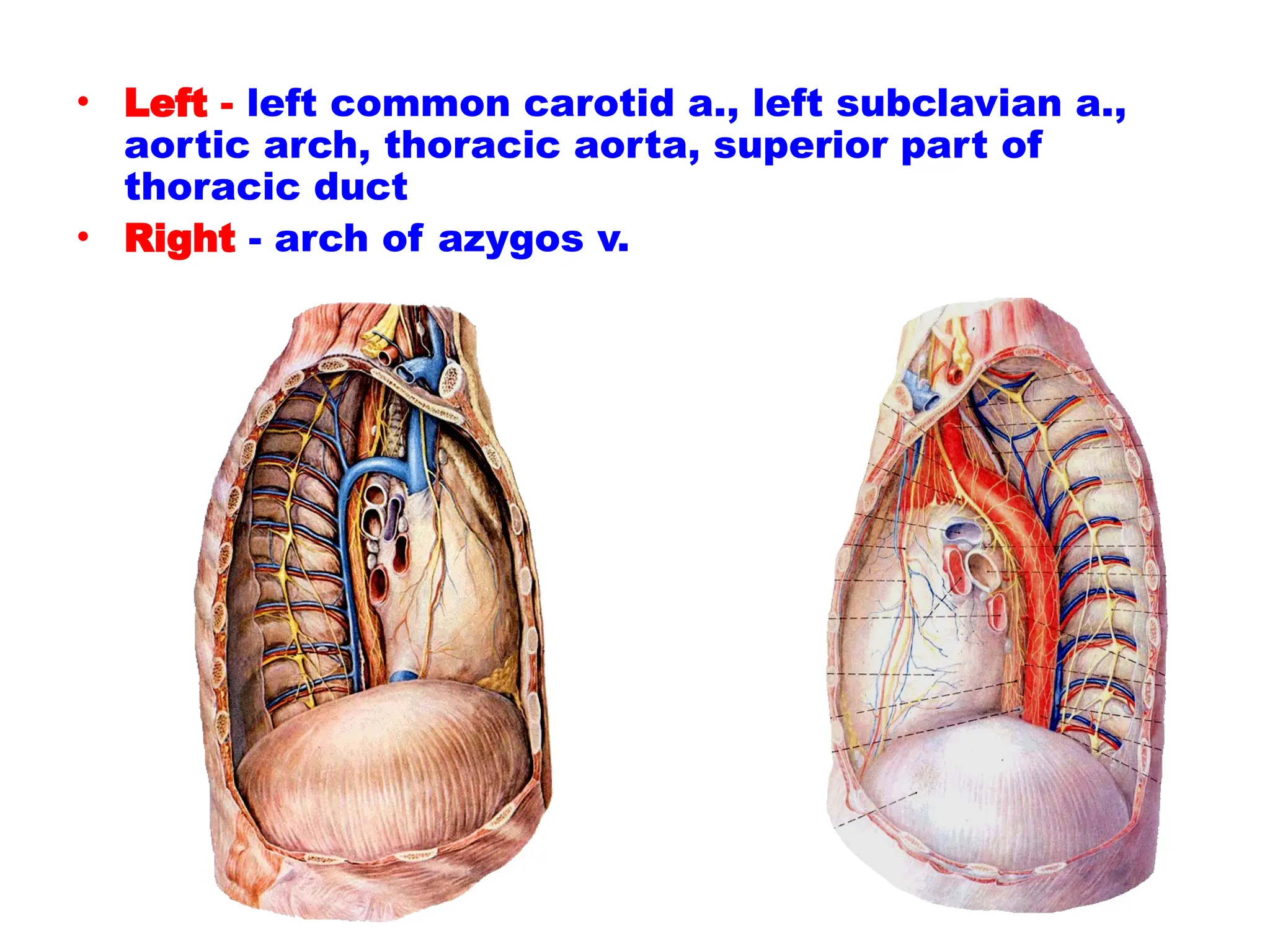
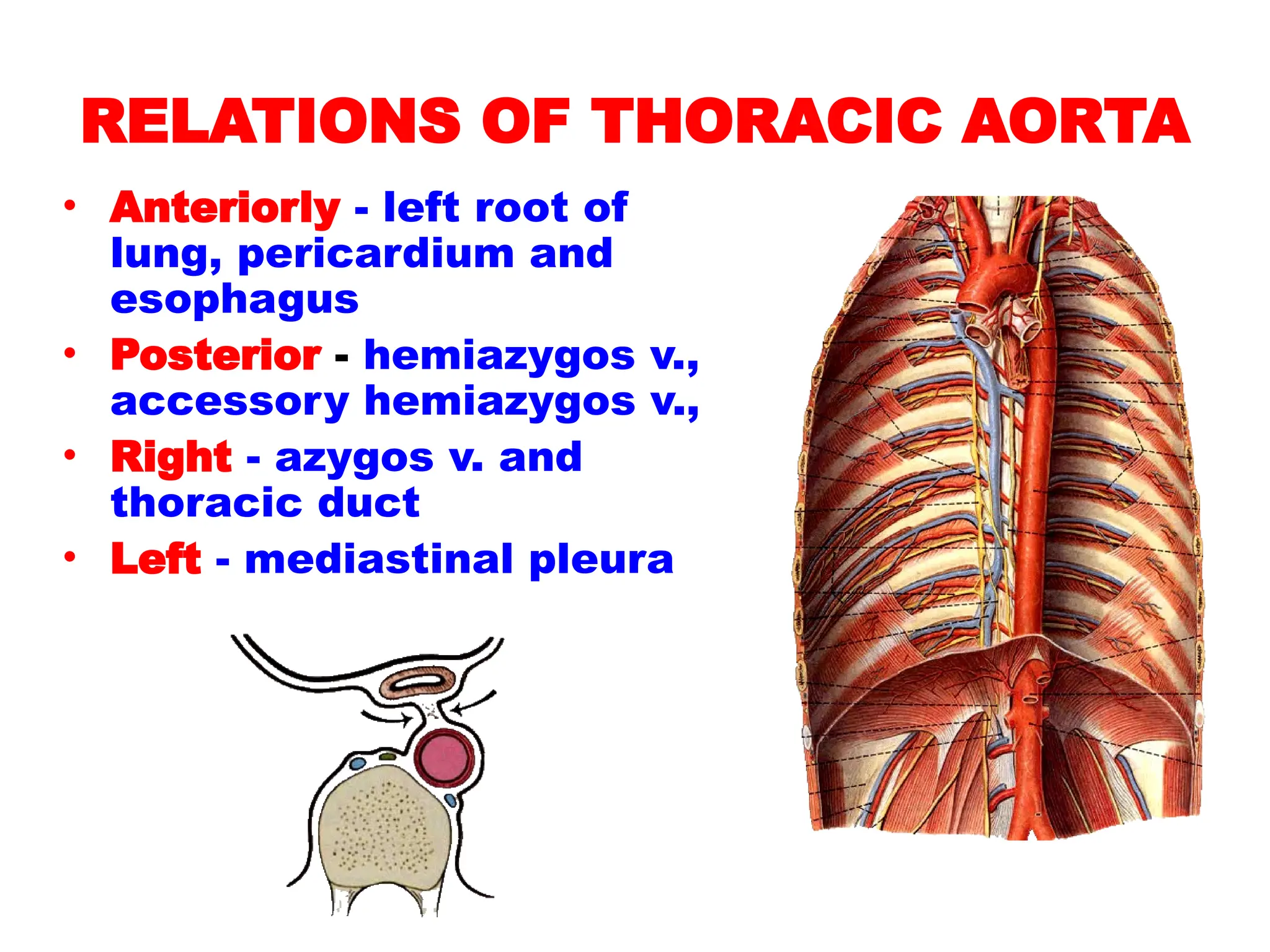
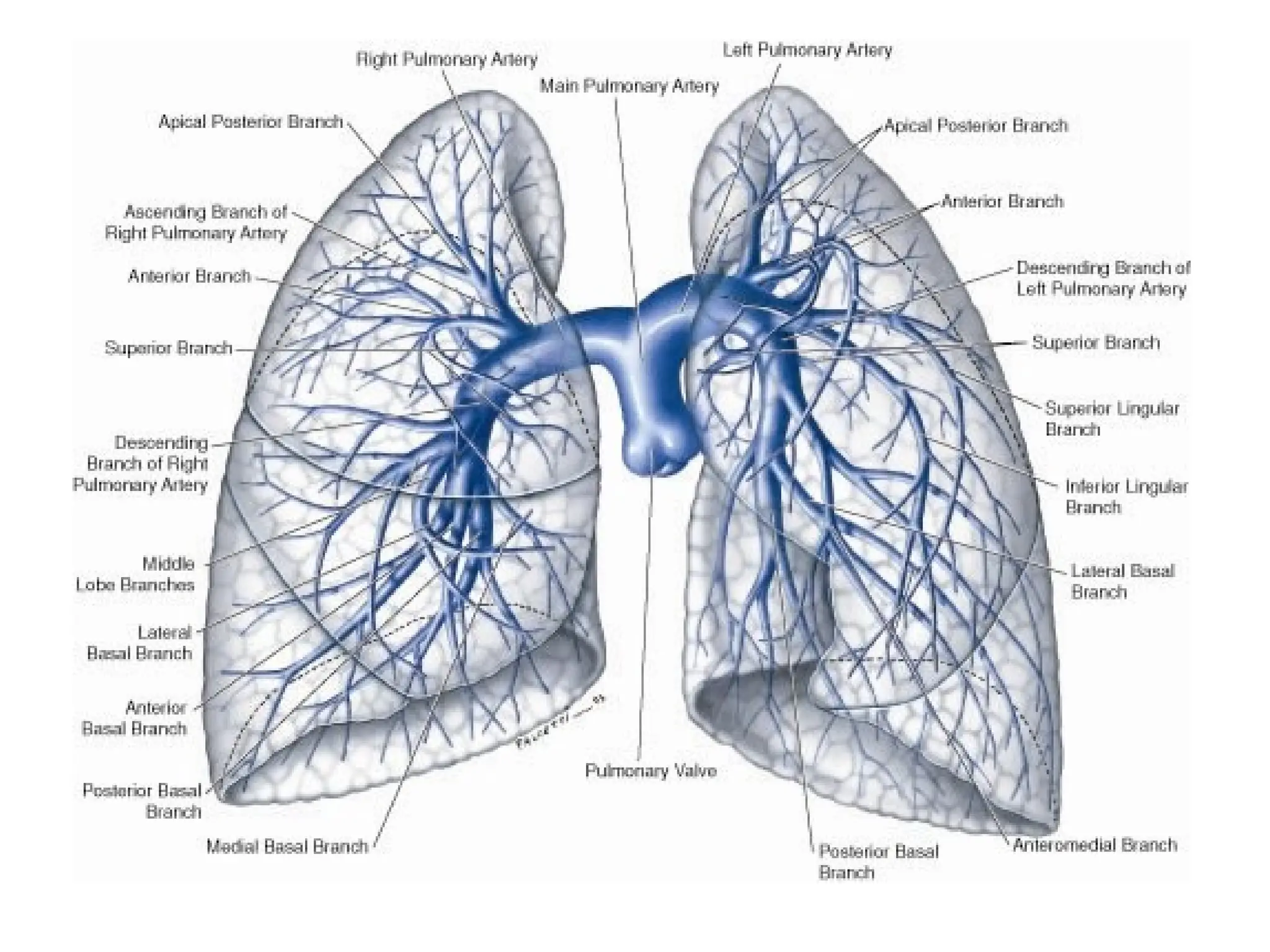
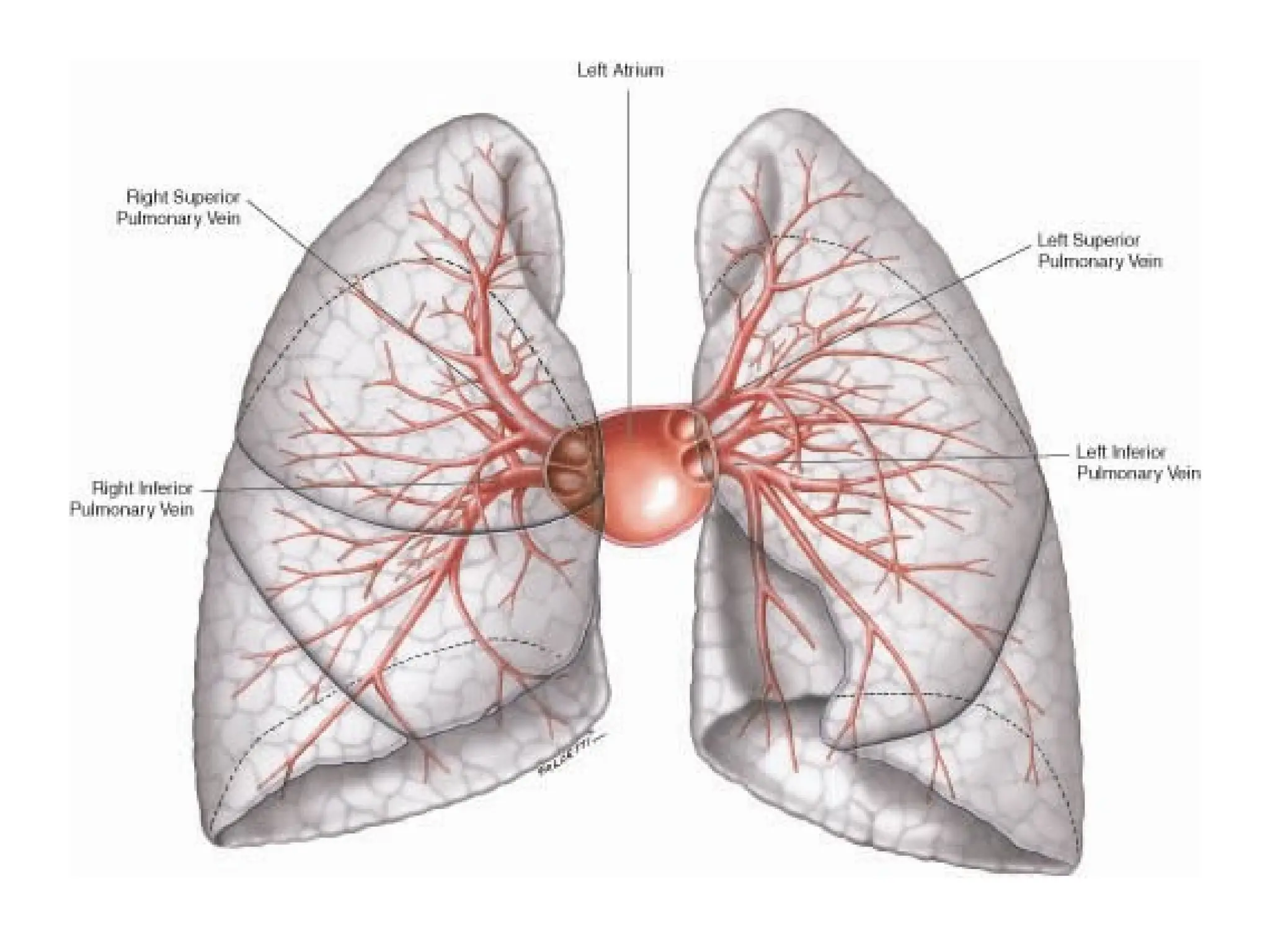
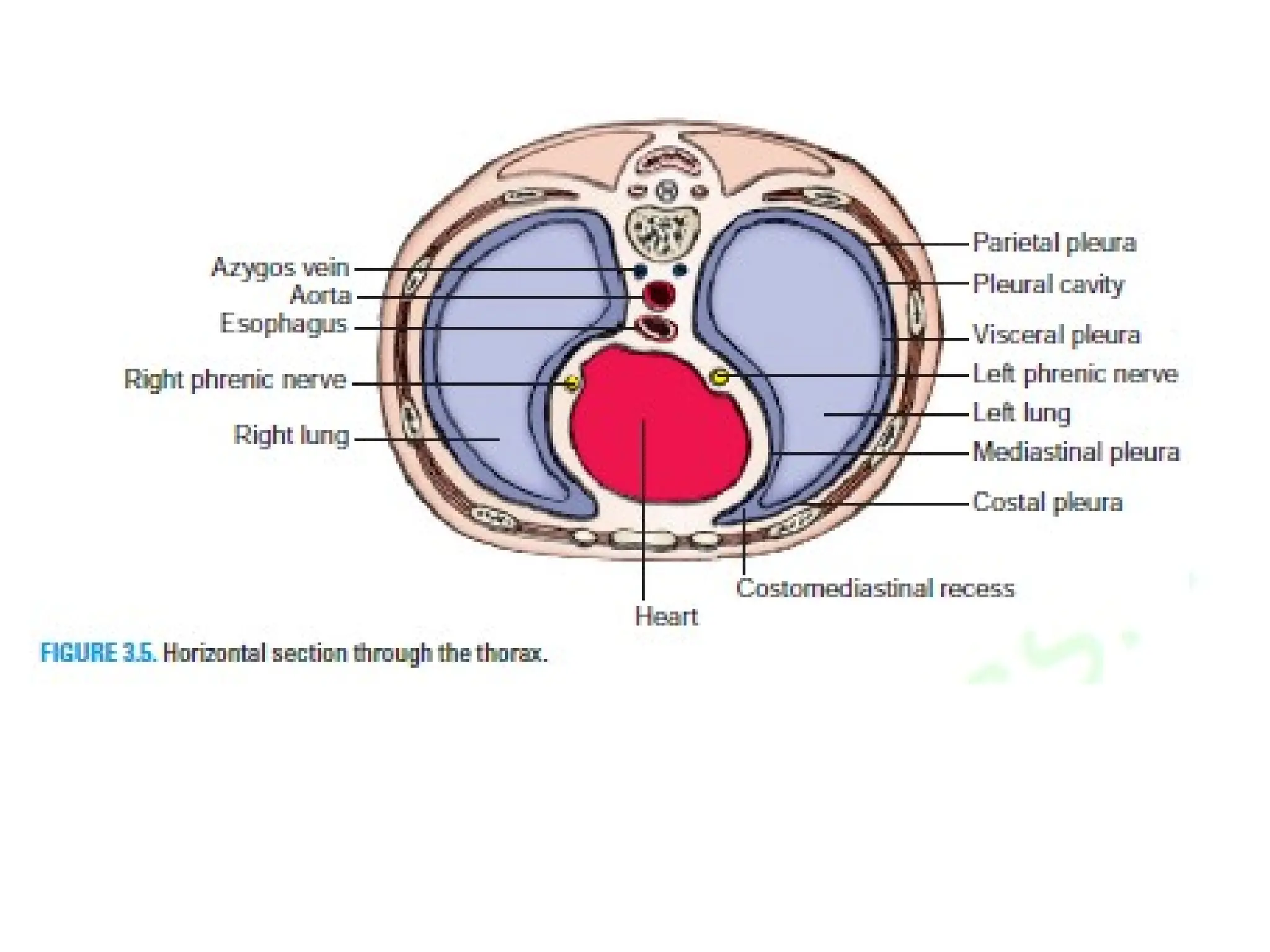
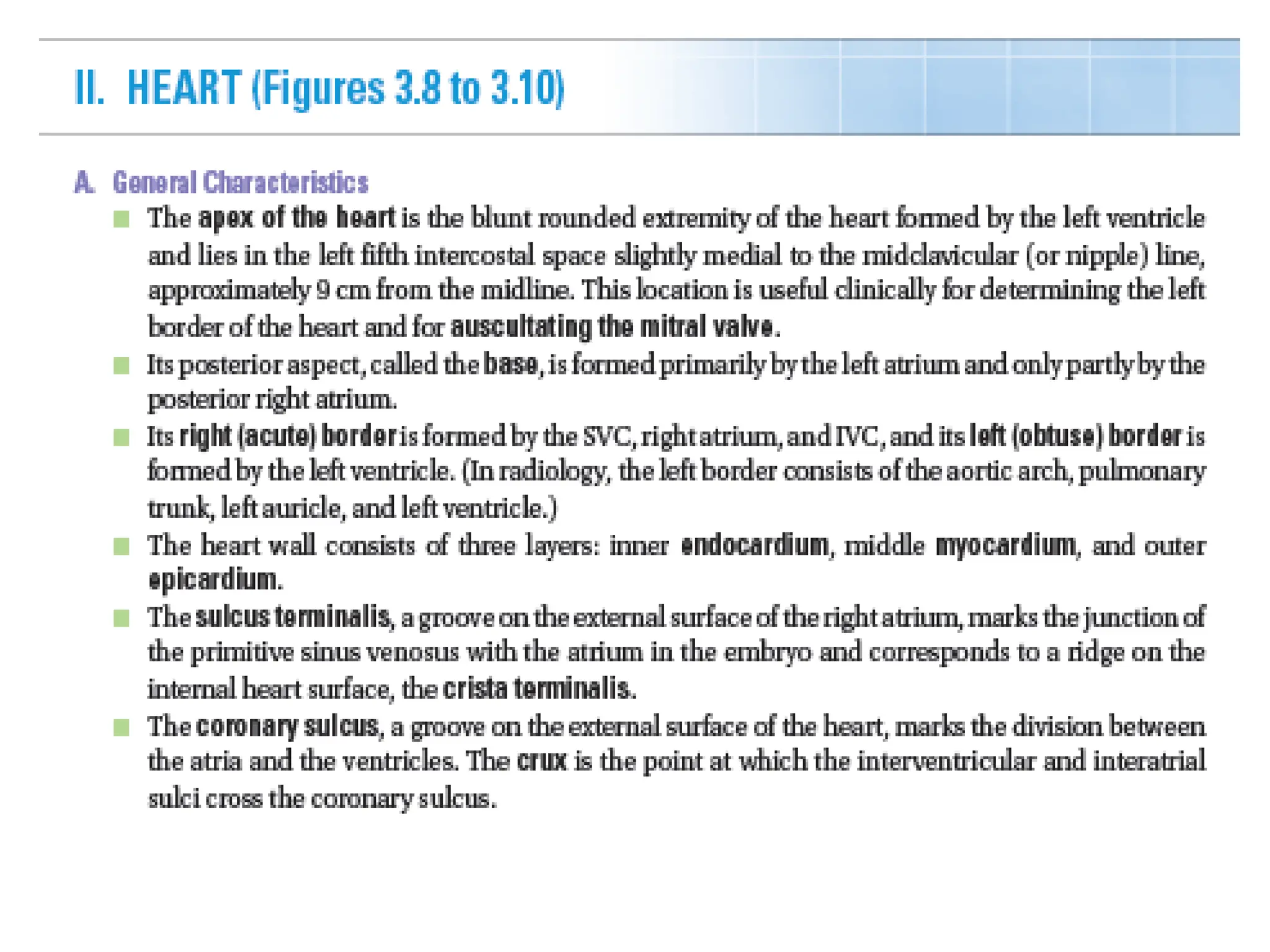
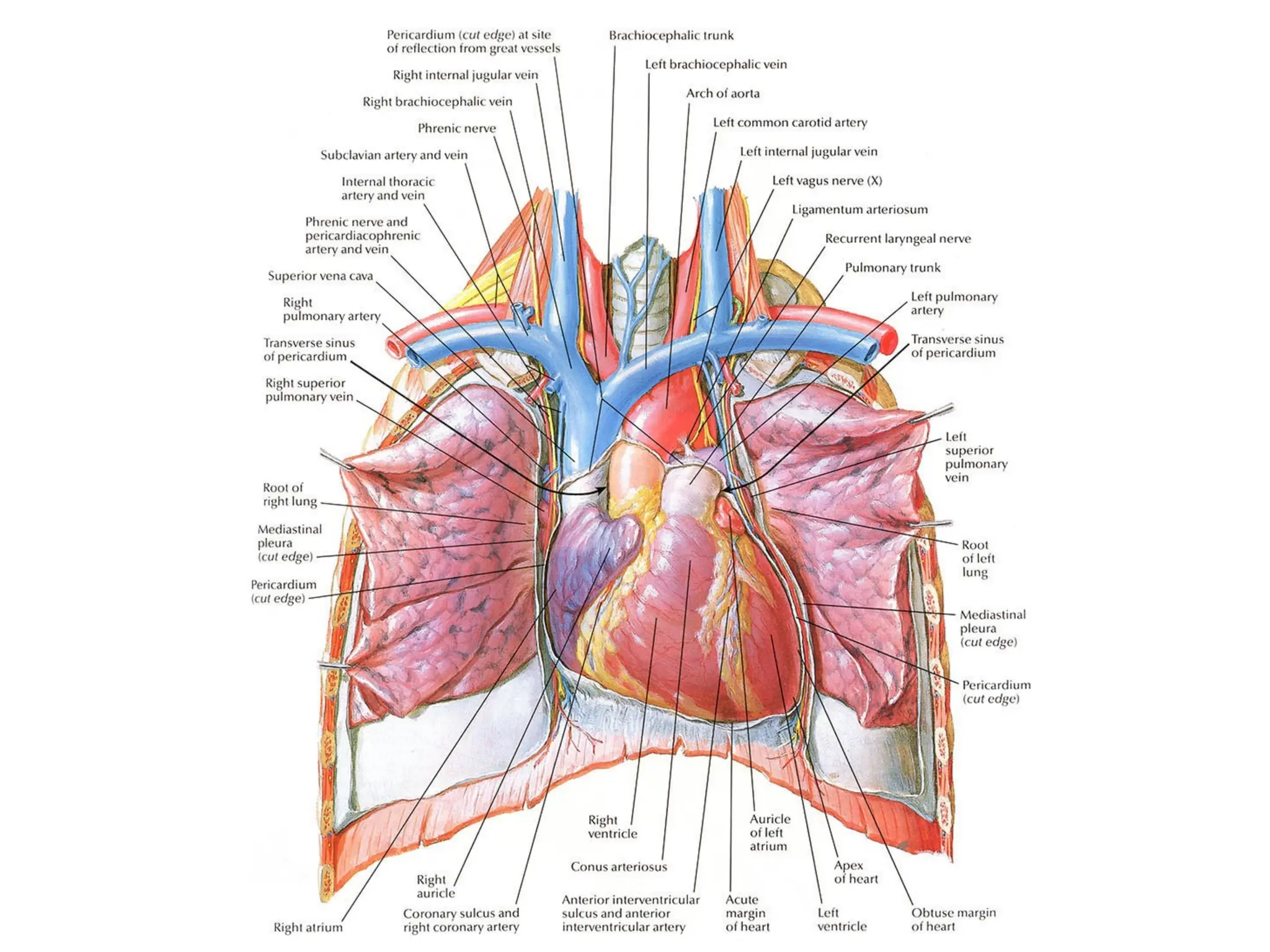
The document discusses the anatomy and topography of the thorax, detailing its borders, regions, and contents such as the thoracic wall, cavities, vessels, and nerves. It describes the mediastinum's subdivisions and the relations of critical structures, including the esophagus and thoracic aorta. Additionally, the document outlines the distribution and function of major nerves and vessels associated with the thoracic area.