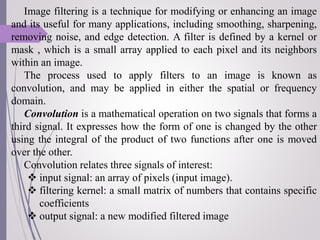
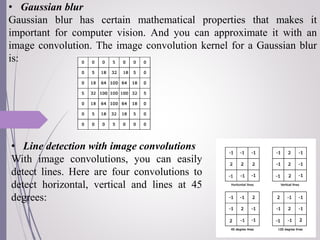
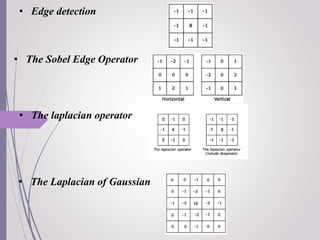
Image filtering is a technique for modifying or enhancing an image through the use of kernels or masks applied to each pixel and its neighbors. The process of applying filters to an image is called convolution, which can be done in either the spatial or frequency domain and relates the input, filtering kernel, and output signals. Convolution expresses how the input signal is changed by the filtering kernel and can be represented as the image convolved with the mask. Common filters include box blur for smoothing, Gaussian blur with important mathematical properties, and edge detection filters.