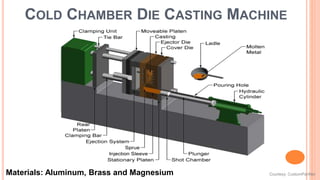
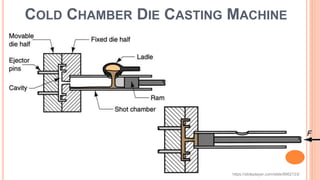
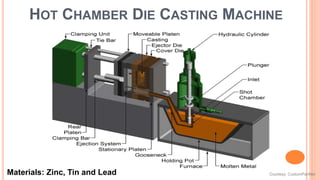
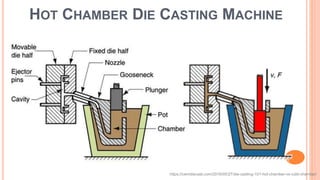
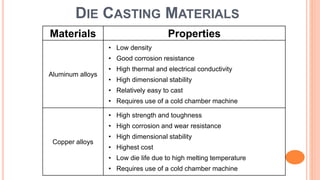
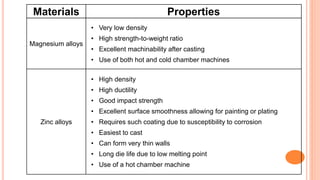
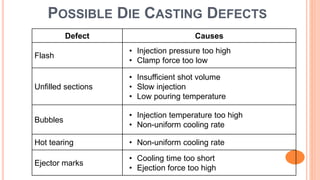
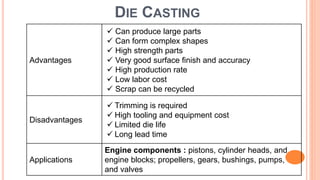
The document provides an overview of die casting, focusing on cold chamber and hot chamber processes used with various metal alloys such as aluminum, brass, magnesium, zinc, tin, and lead. It details the advantages and disadvantages of die casting, including production rates, part complexity, and potential defects during the casting process. Additionally, it highlights the application of die casting in manufacturing engine components and other mechanical parts.