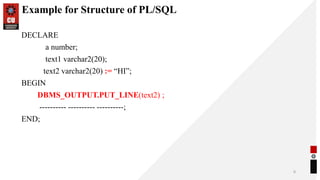
This document provides an overview of a Database Management Systems course. It outlines the course objectives which are to understand database concepts, implement SQL statements, and understand transaction processing and recovery techniques. It also lists an expected course outcome of being able to apply relational algebra and calculus to query databases. The document then discusses control structures in PL/SQL including conditional controls like IF-THEN-ELSE statements and iterative controls like loops. It provides examples of PL/SQL code using these structures to find even numbers and determine the largest of three numbers.