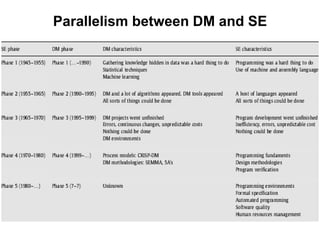
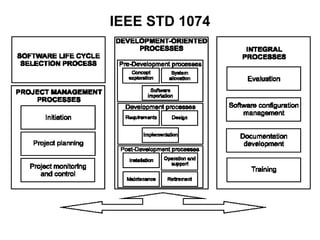
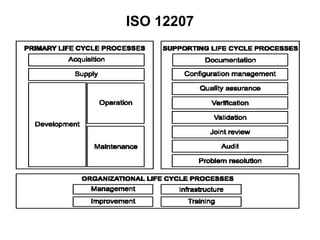
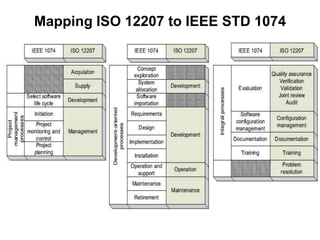
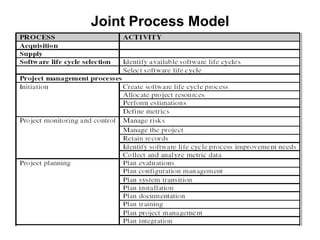
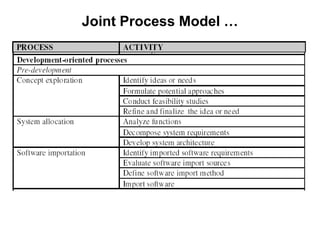
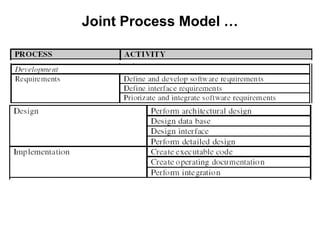
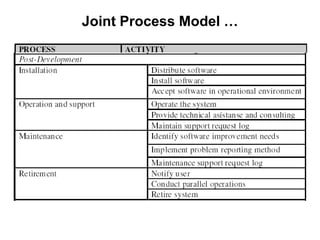
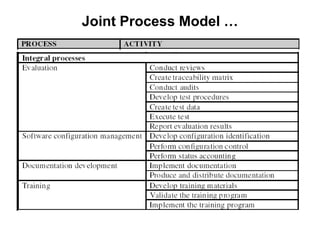
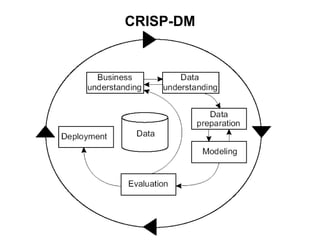
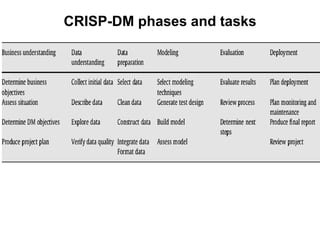
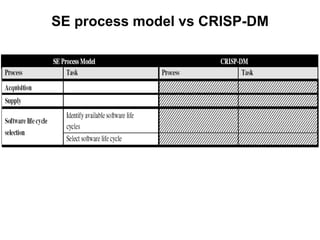
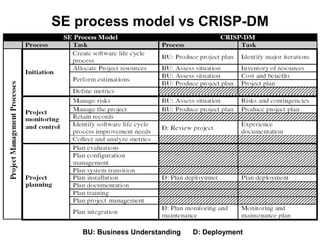
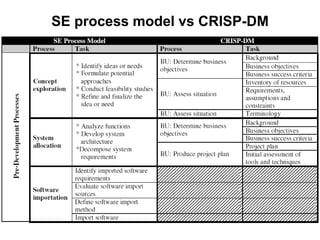
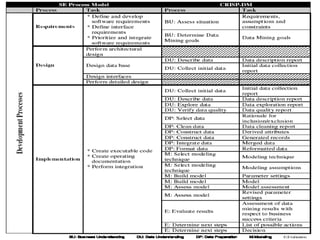
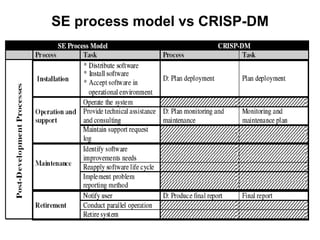
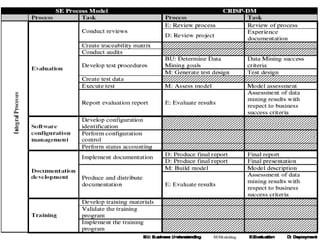
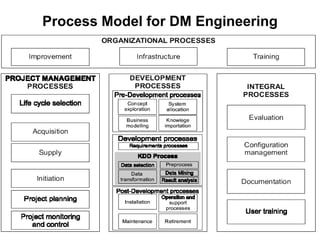
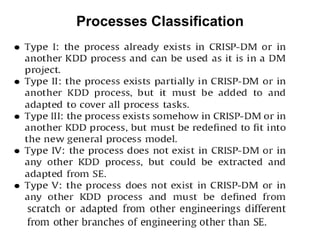
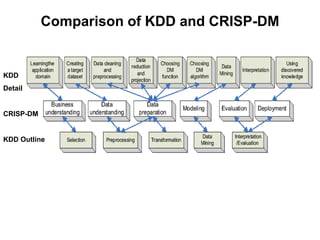
The document discusses process models for data mining engineering. It outlines software engineering process models like IEEE STD 1074 and ISO 12207, and compares them to the CRISP-DM process model for data mining. CRISP-DM is presented as a standard process consisting of 6 phases: business understanding, data understanding, data preparation, modeling, evaluation, and deployment. The document also proposes a process model for data mining engineering that adapts concepts from software engineering process models and CRISP-DM.