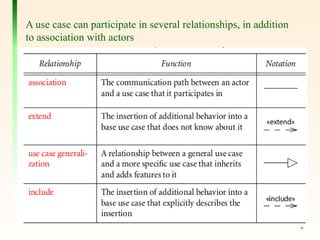
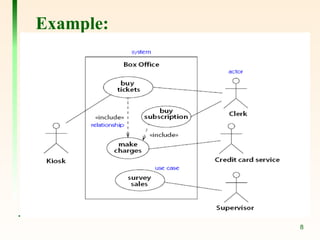
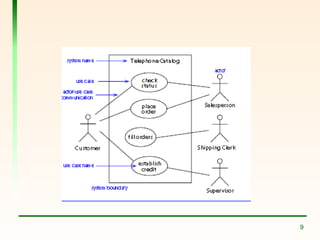
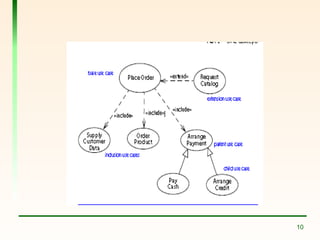
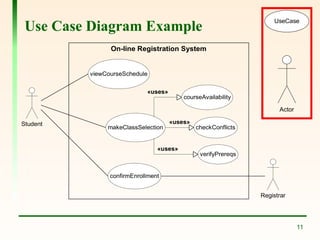
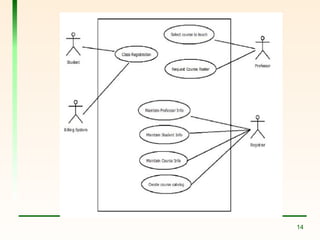
The document explains the concept of use cases in Unified Modeling Language (UML), detailing their role in representing interactions between business systems and their environments through formal scenarios. It covers types of relationships between use cases, such as 'include' and 'extend', which describe interactions between different use cases. An example is given featuring an online registration system, illustrating potential actors and tasks involved in the user registration process.