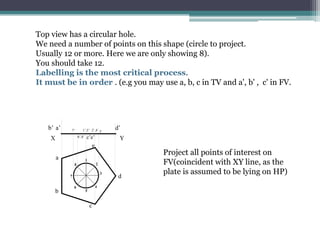
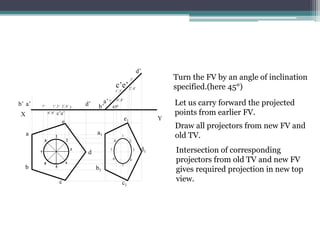
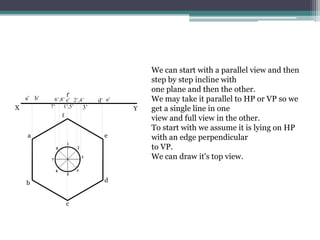
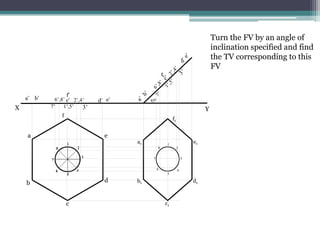
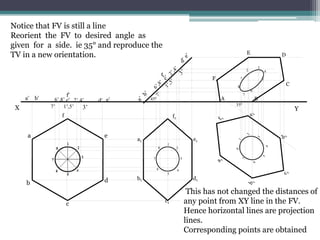
The document discusses the process of projecting planes in engineering drawings. It provides examples of projecting a pentagonal lamina with a circular hole and a regular hexagonal lamina with a central hole. The key steps are: 1) Drawing the top view with the plane parallel to the horizontal plane; 2) Projecting points of interest onto the front view; 3) Rotating the front view to the specified inclination angle; 4) Drawing new projectors from the rotated front view to the original top view to obtain the inclined top view.