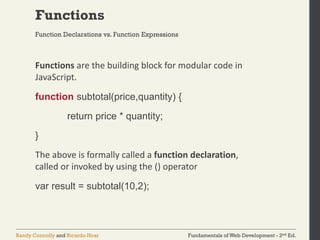
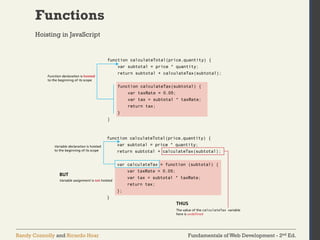
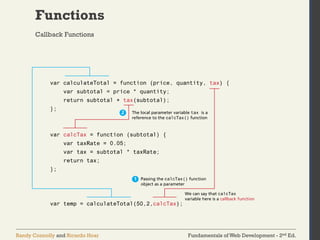
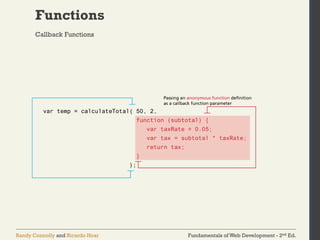
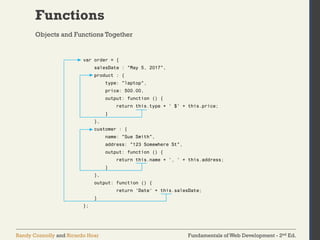
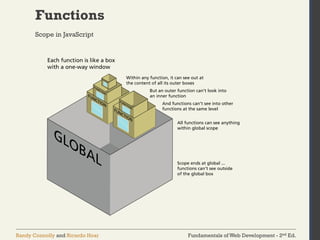
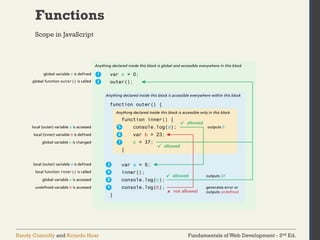
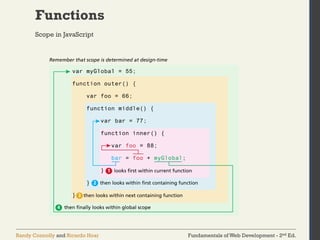
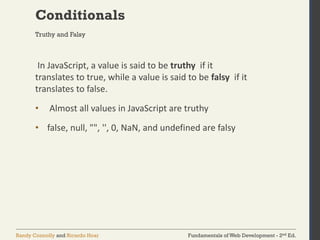
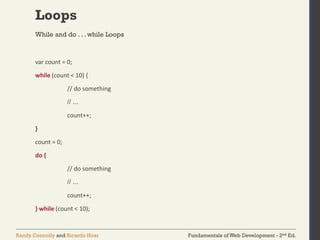
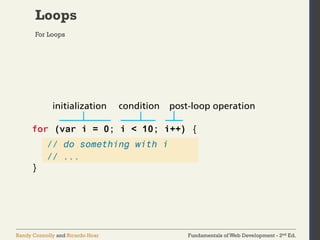
The document discusses the fundamentals of JavaScript, including its history, data types, output methods, control structures like conditionals and loops, and the use of arrays and objects. It covers different ways to include JavaScript in HTML, the distinctions between function declarations and expressions, as well as the concept of prototypes for object-oriented programming. The content serves as an introductory guide for understanding JavaScript in the context of web development.














![Fundamentals of Web Development - 2nd Ed.
Randy Connolly and Ricardo Hoar
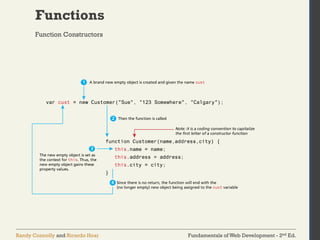
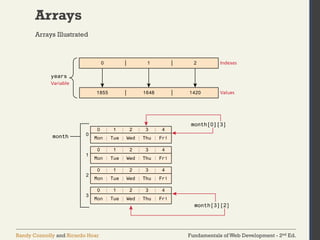
Arrays
The literal notation approach is generally preferred
since it involves less typing, is more readable, and
executes a little bit quicker
var years = [1855, 1648, 1420];
var countries = ["Canada", "France",
"Germany", "Nigeria",
"Thailand", "United States"];
var mess = [53, "Canada", true, 1420];
object literal notation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec7introductiontojavascriptlanguageandfundamentals-250131070256-8572a081/85/lec-7-Introduction-to-JavaScript-Language-and-Fundamentals-pdf-23-320.jpg)
![Fundamentals of Web Development - 2nd Ed.
Randy Connolly and Ricardo Hoar
Arrays
• arrays in JavaScript are zero indexed
• [] notation for access
• .length gives the length of the array
• .push()
• .pop()
• concat(), slice(), join(), reverse(), shift(), and sort()
Some common features](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec7introductiontojavascriptlanguageandfundamentals-250131070256-8572a081/85/lec-7-Introduction-to-JavaScript-Language-and-Fundamentals-pdf-24-320.jpg)

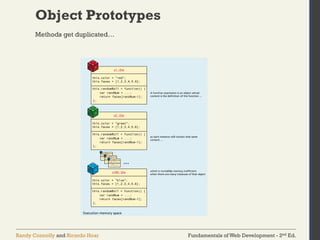
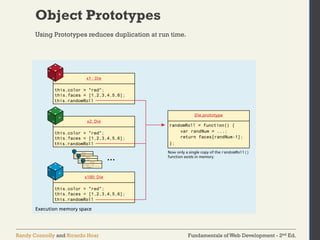
![Fundamentals of Web Development - 2nd Ed.
Randy Connolly and Ricardo Hoar
Objects
Access using either of:
• objName.name1
• objName["name1"]
Object Creation—Object Literal Notation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec7introductiontojavascriptlanguageandfundamentals-250131070256-8572a081/85/lec-7-Introduction-to-JavaScript-Language-and-Fundamentals-pdf-27-320.jpg)