This document discusses several learning style models:
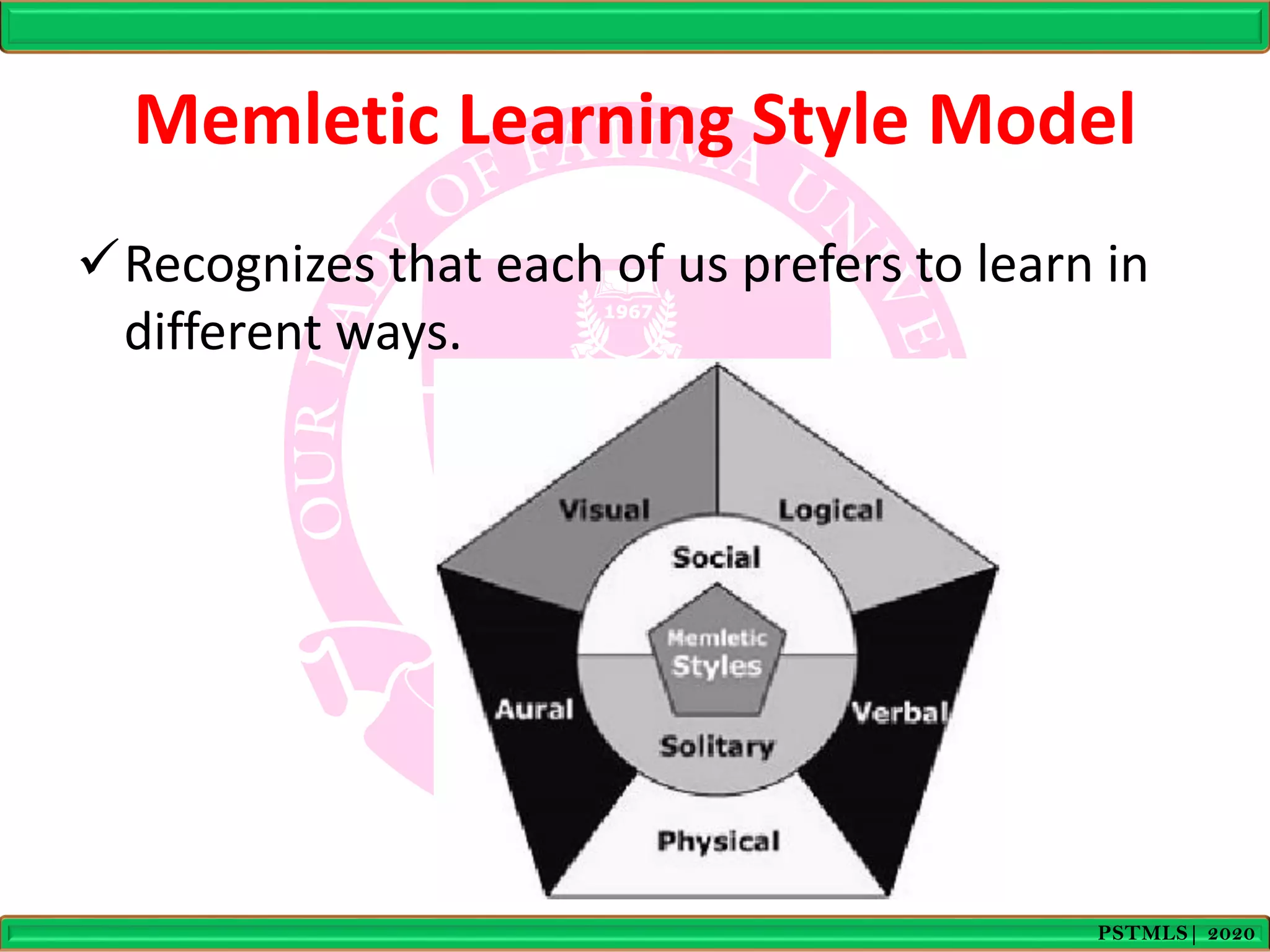
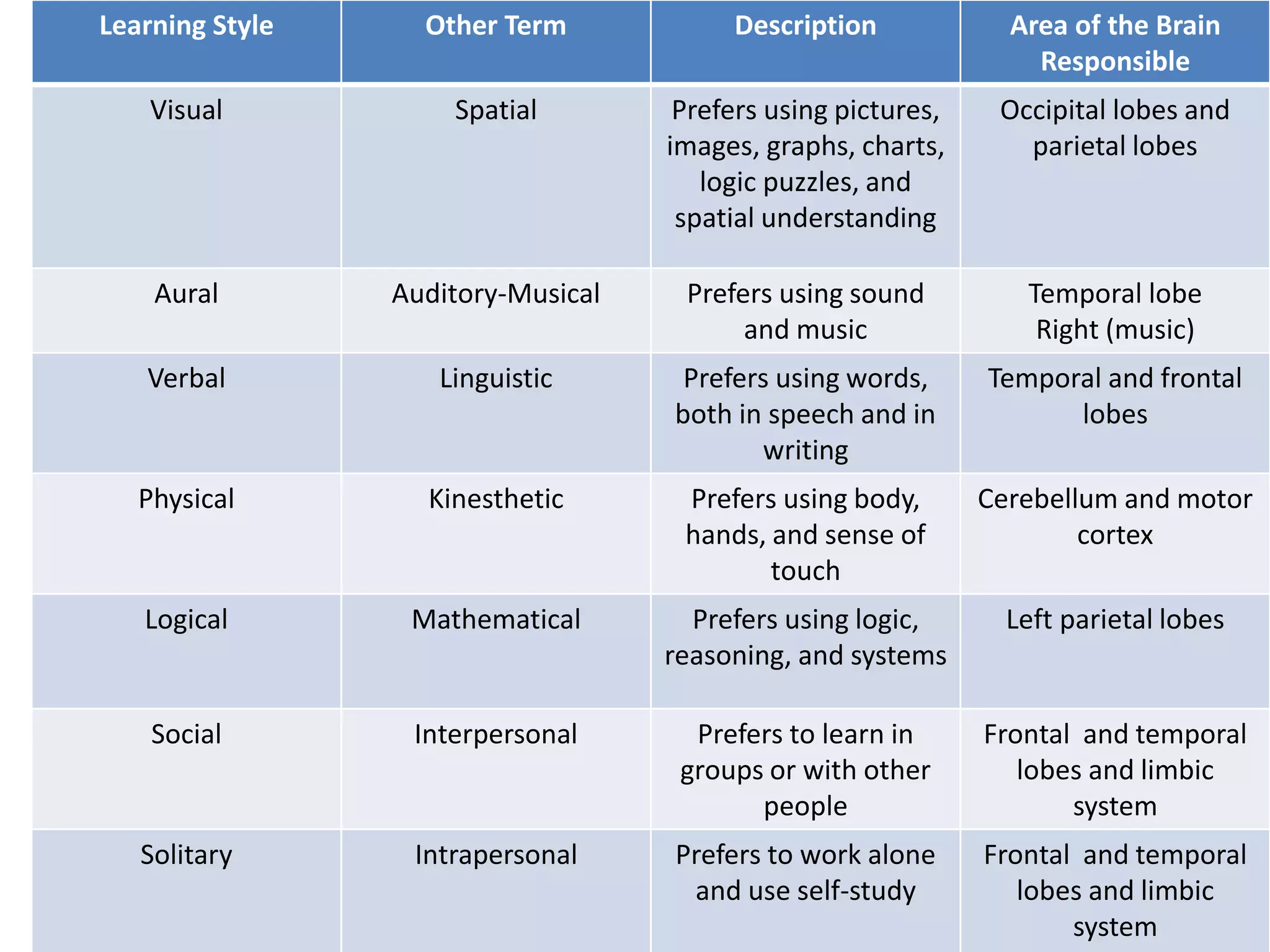
- The Memletic model recognizes that individuals prefer different ways of learning such as visual, auditory, verbal, physical, logical, social, or solitary styles.
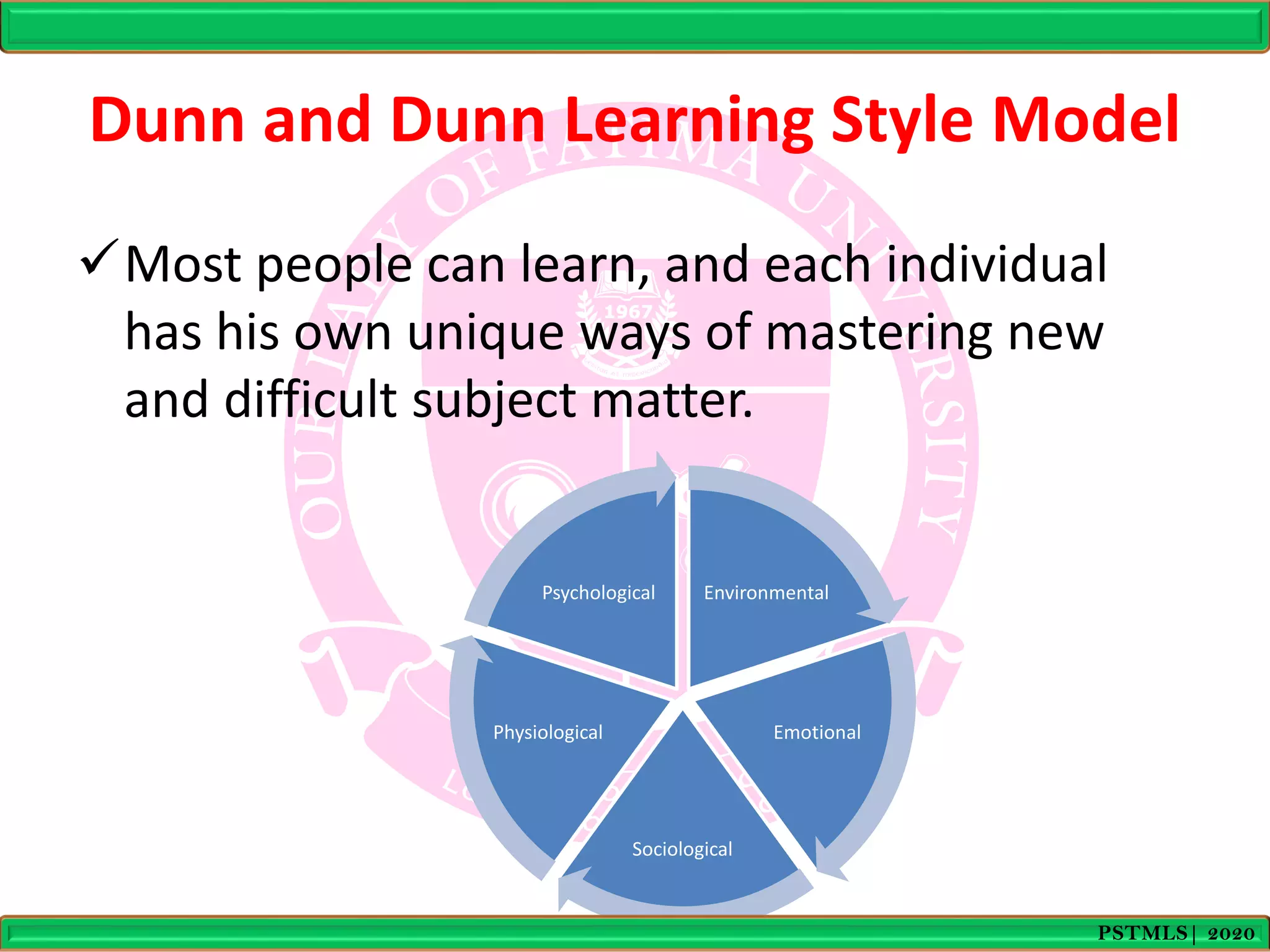
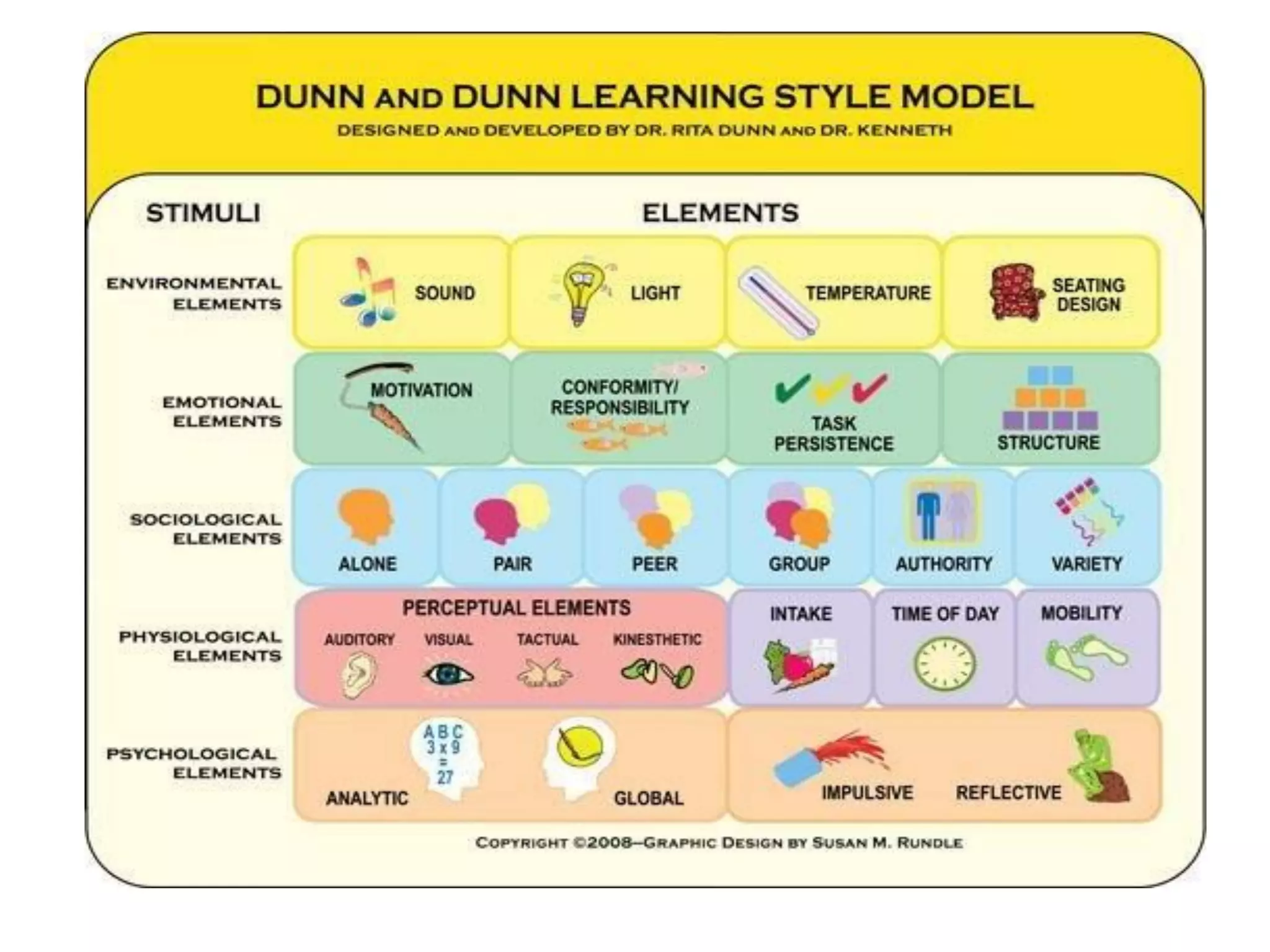
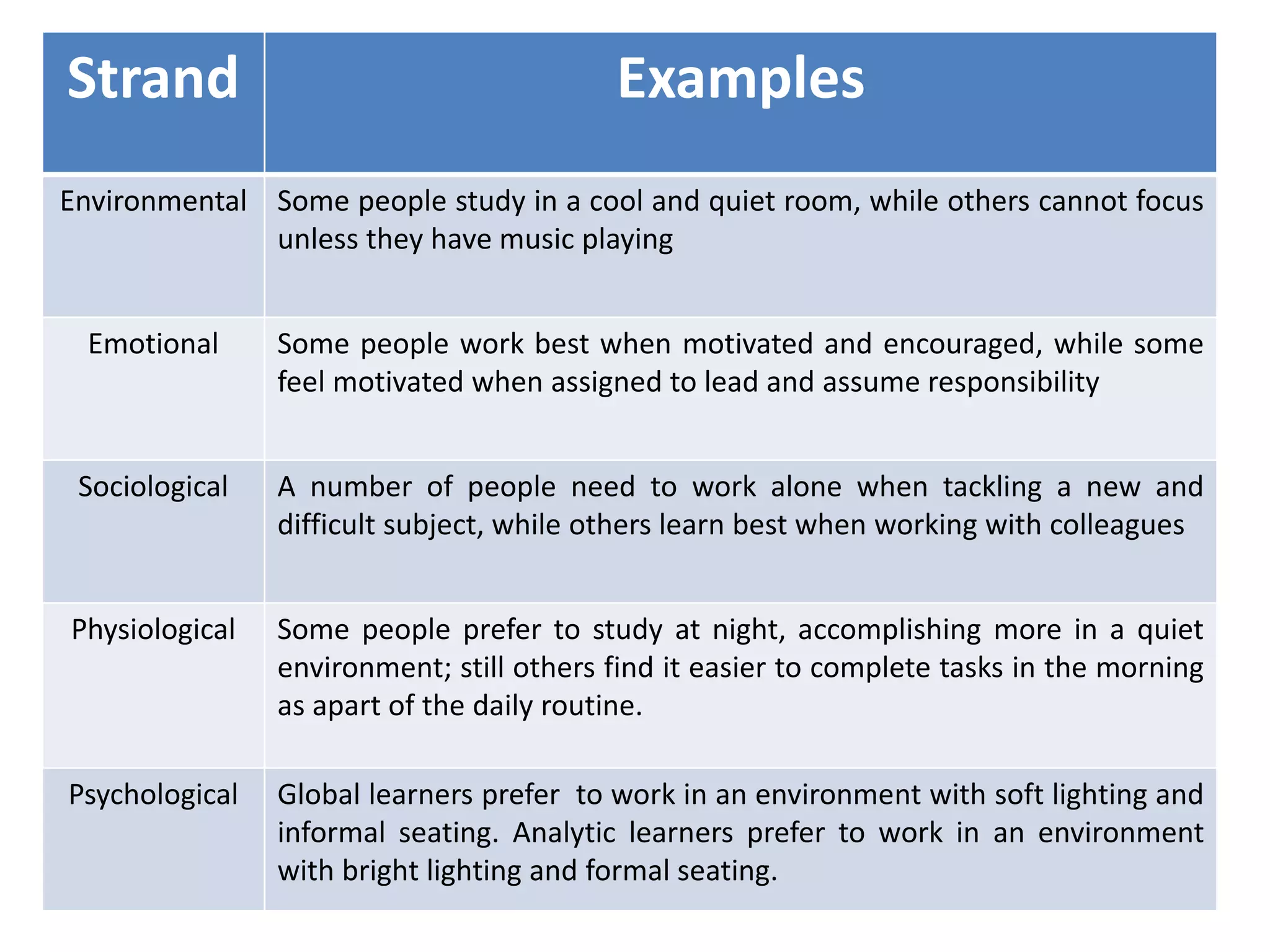
- The Dunn and Dunn model suggests that learning is influenced by environmental, emotional, sociological, physical, and psychological factors. It provides examples of how these factors can impact learning.
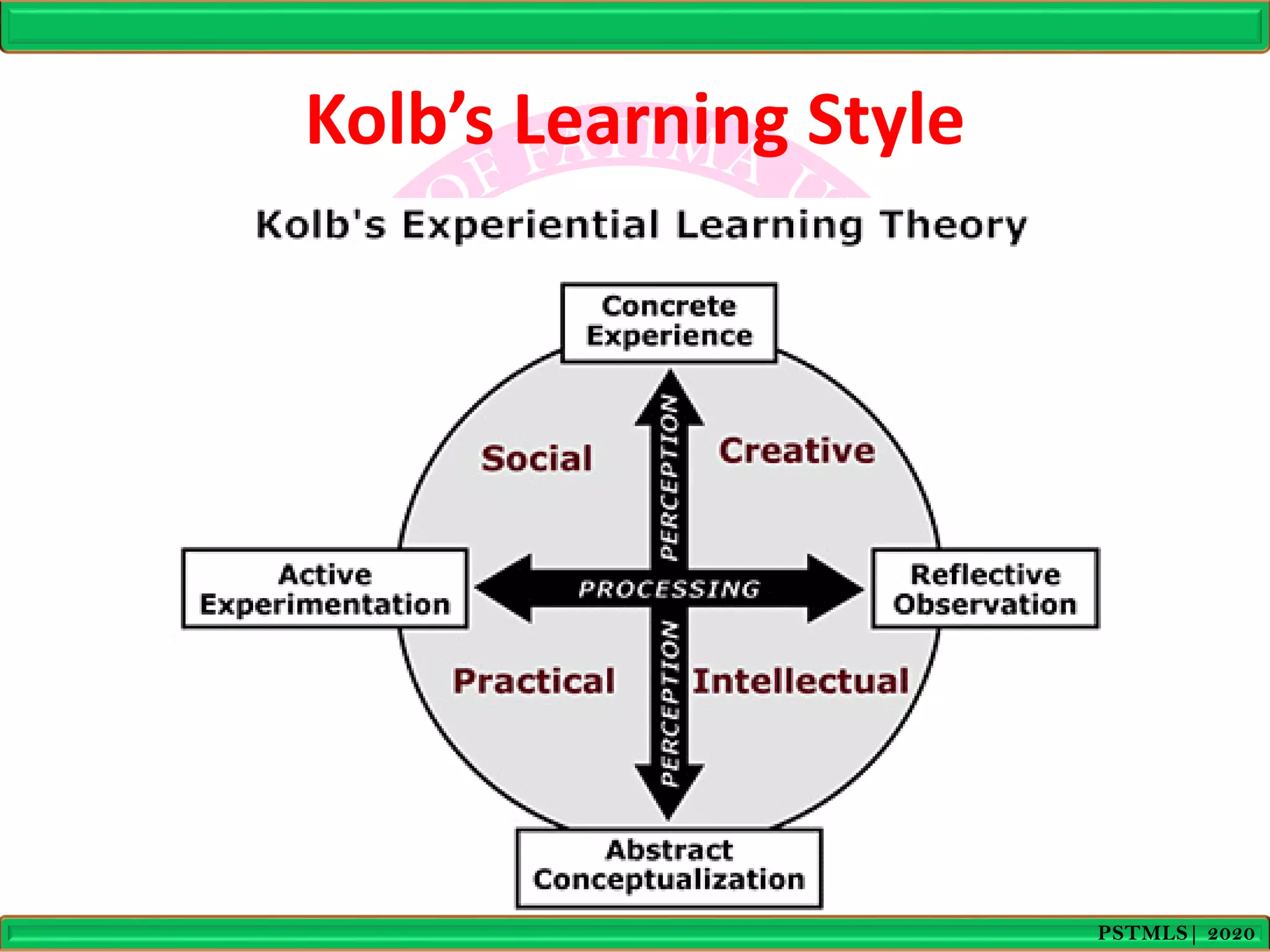
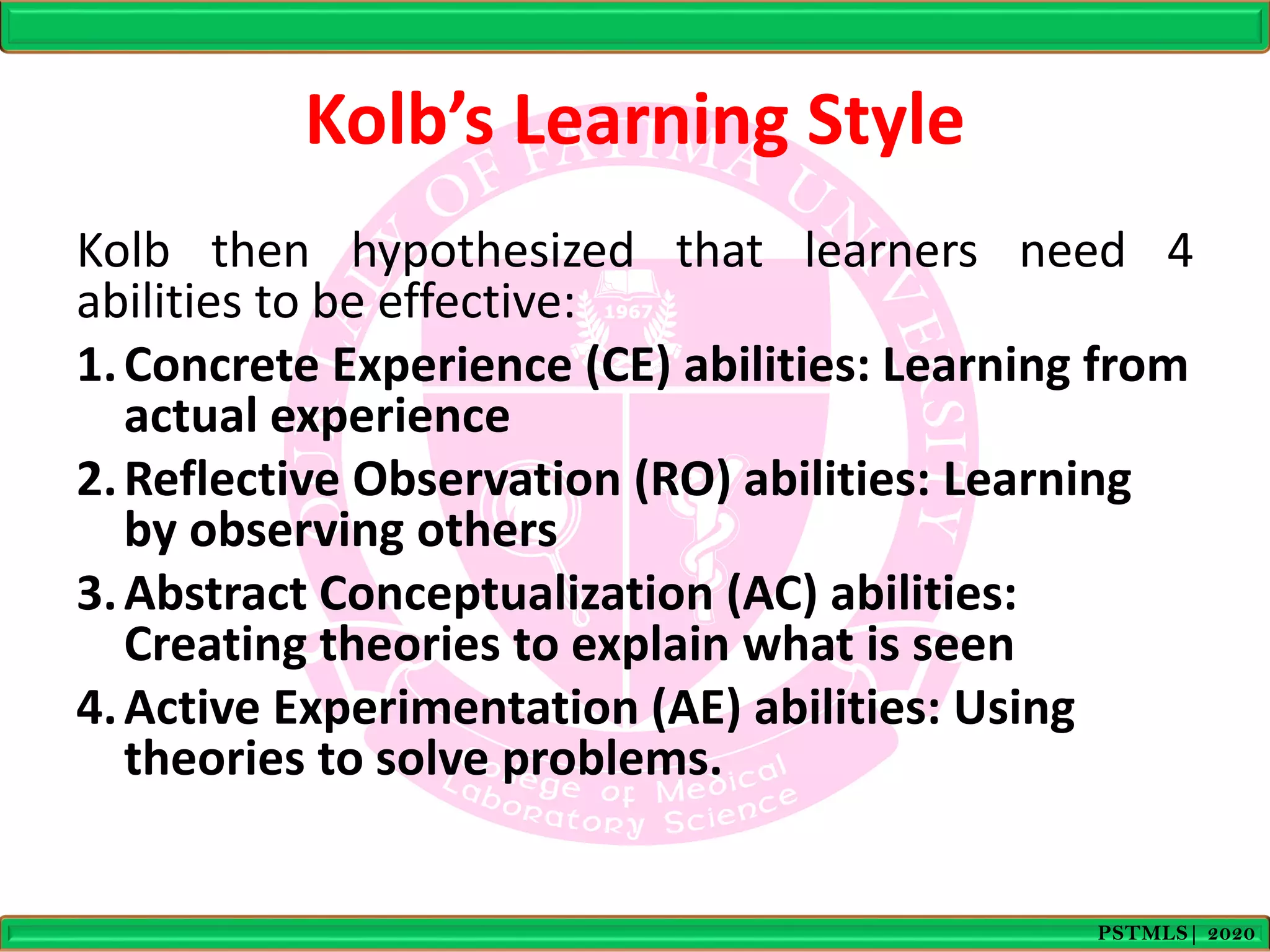
- Kolb's model depicts learning as a four stage cycle of concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. It identifies four learning styles - accommodating, diverging, assimilating, and converging - that correspond to abilities in these stages.
- The document describes the characteristics and