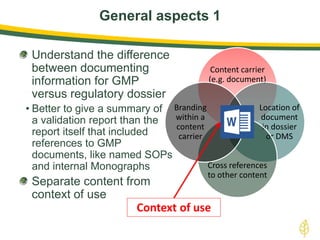
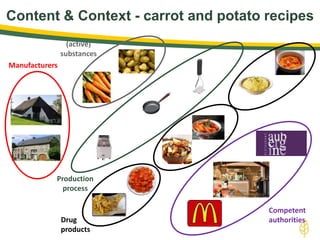
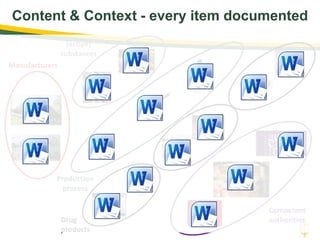
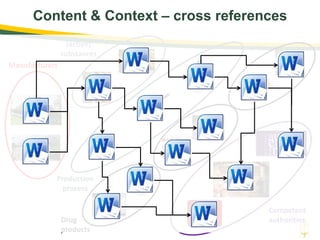
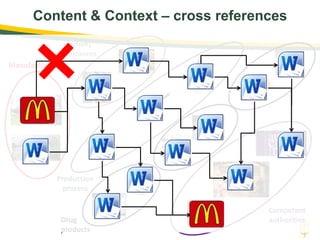
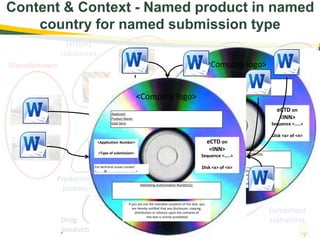
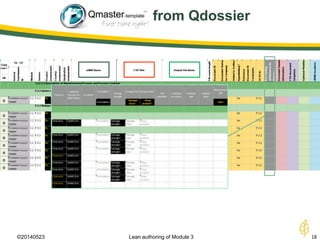
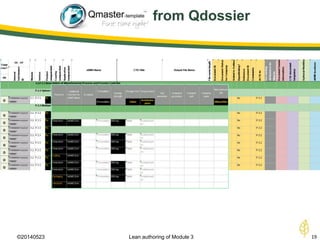
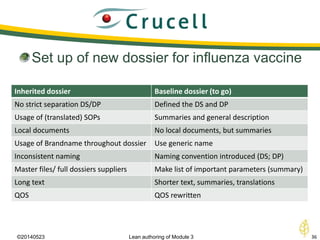
The document discusses lean authoring in the context of regulatory dossiers, emphasizing the importance of efficient documentation to enhance traceability and reduce redundancy. It outlines the principles of lean authoring, including separating content from context, using consistent terminology, and applying document reuse across submissions. The benefits include improved communication, ease of updates, and reduced risk of regulatory rejection.