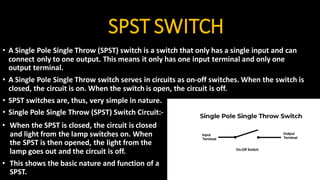
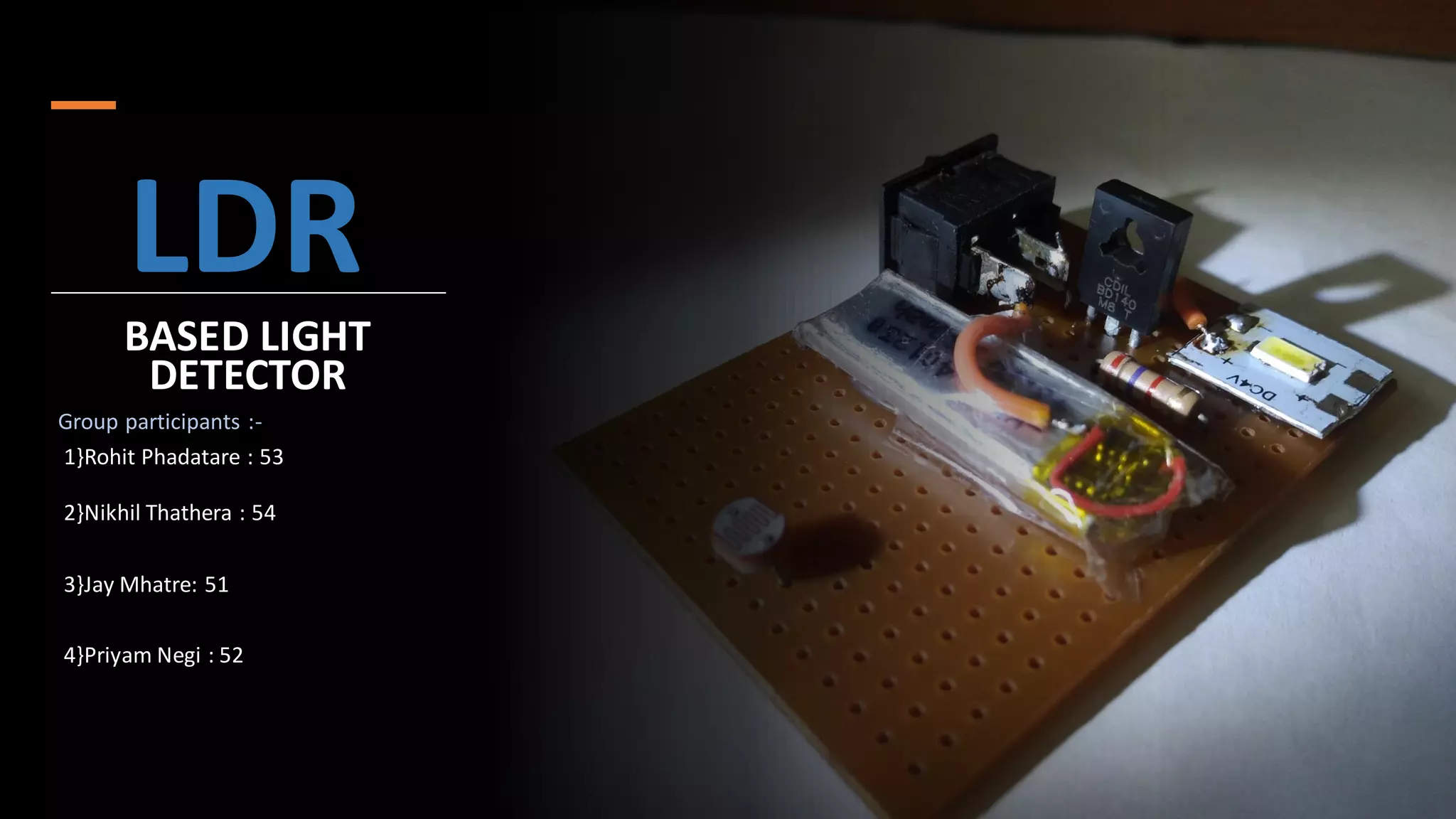
1) A group of 4 students created an LDR based light detector circuit using components like an LDR light sensor, 2.7k resistor, BD140 transistor, 3.7V battery, SPST switch, and 4V LED.
2) The circuit functions by using an LDR light sensor to generate a signal based on light intensity which is then amplified using a BD140 transistor to power a 4V LED, creating a light-detecting circuit.
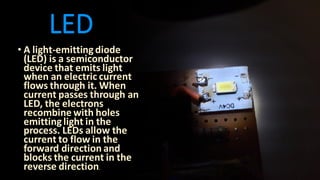
3) Key components like the LDR, resistors, transistors, batteries, switches, and LEDs are described in terms of their electrical properties and functions within circuits.




![BATTERY
• Batteries are classified into primary and
secondary forms:
• Primary batteries are designed to be used
until exhausted of energy then discarded. Their
chemical reactions are generally not reversible,
so they cannot be recharged. When the supply of
reactants in the battery is exhausted, the battery
stops producing current and is useless.[28]
• Secondary batteries can be recharged; that is,
they can have their chemical reactions reversed
by applying electric current to the cell. This
regenerates the original chemical reactants, so
they can be used, recharged, and used again
multiple times.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronicsldrproject-230129172647-ab5e8962/85/LDR-PROJECT-7-320.jpg)