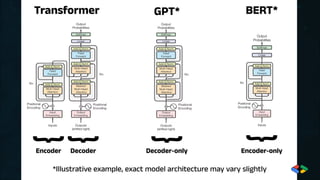
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) enhances LLMs (Large Language Models) by combining retrieval mechanisms with generative AI. Here's how it works:
- LLM Limitations: LLMs generate text based on training data but often lack specific context or up-to-date info.
- RAG Solution: It retrieves relevant documents or data and feeds them to the LLM, improving response accuracy and relevance.
- Use Cases: Better question-answering, summarization, and context-rich content generation.
At THINKX, you'll learn to implement RAG with LLMs for smarter AI applications .