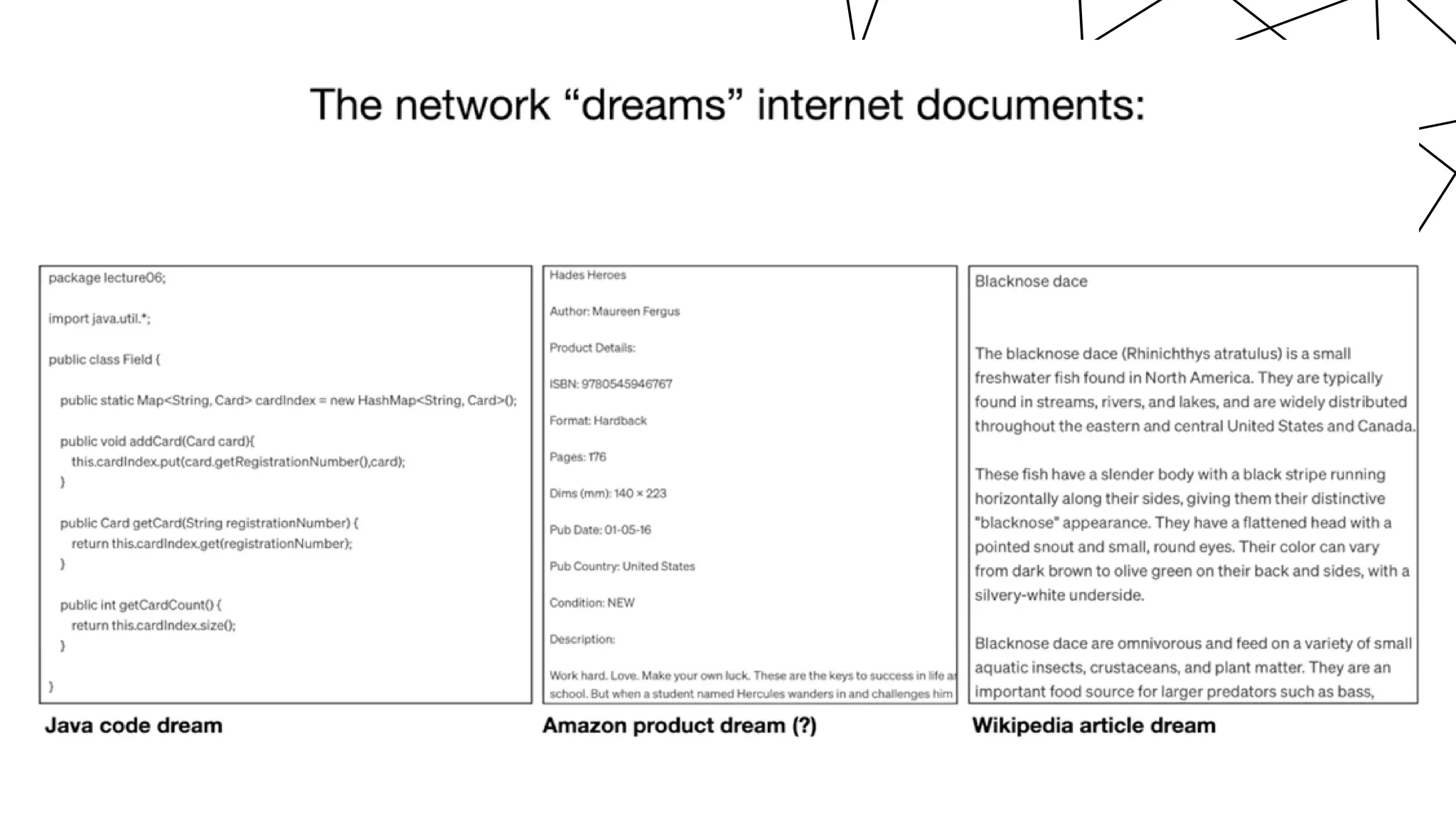
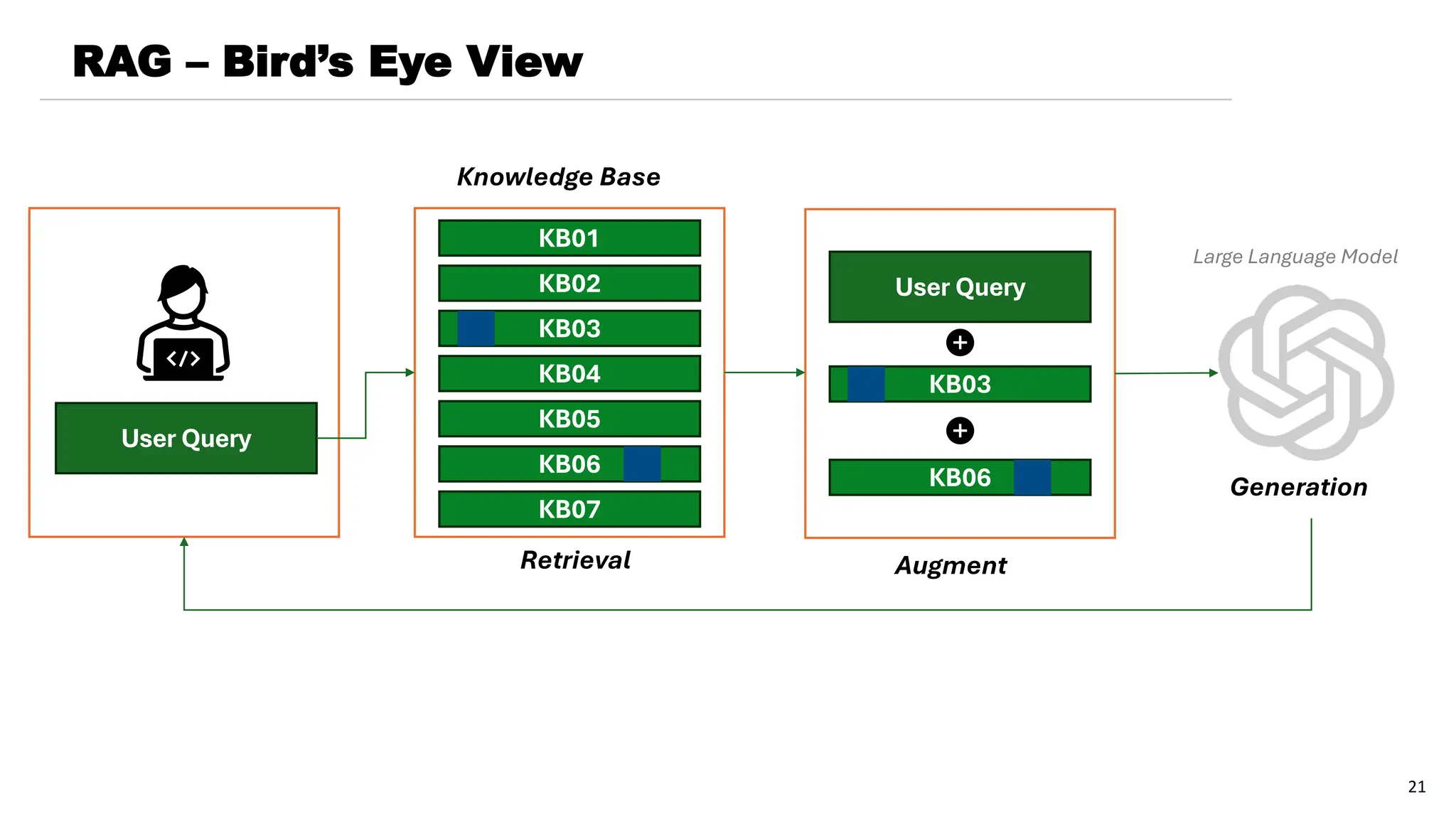
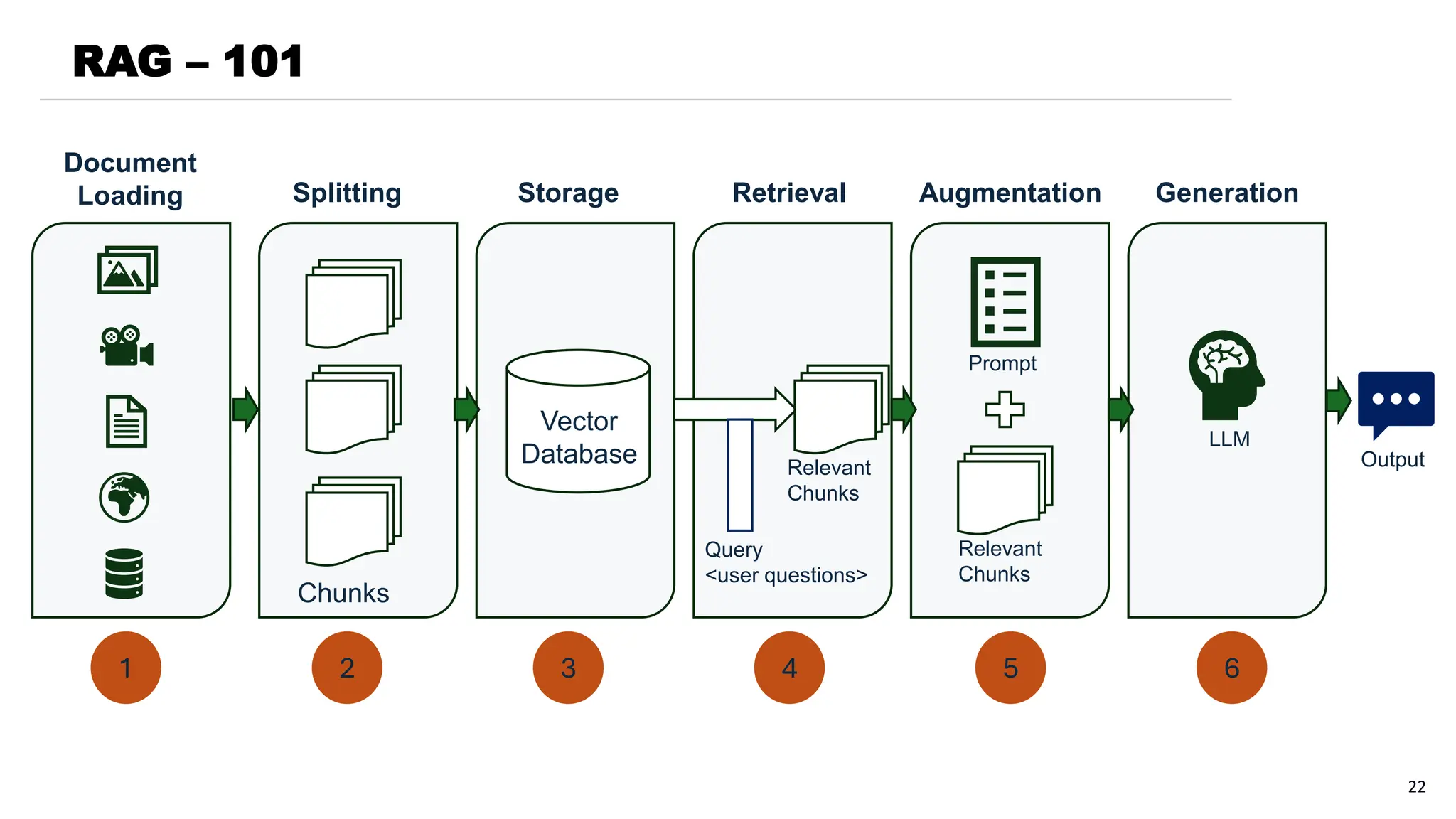
The document provides a comprehensive overview of generative AI and large language models (LLMs), covering their historical development, capabilities in text generation, and various applications across fields such as natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics. It details how LLMs work, the training processes involved, and the significance of natural language generation techniques like extractive and abstractive summarization. Additionally, the document discusses the state of technologies for generating text-to-image and text-to-video content, alongside the challenges and future prospects of these advancements.