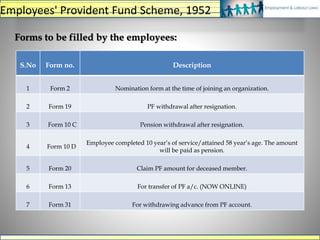
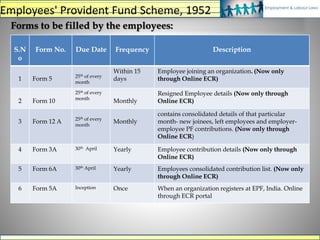
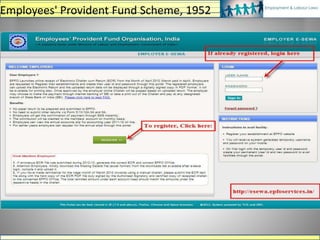
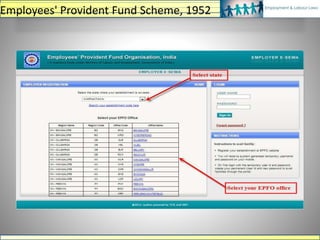
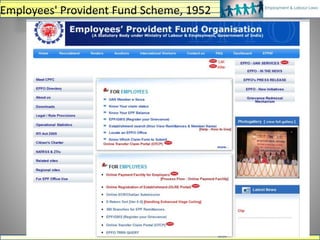
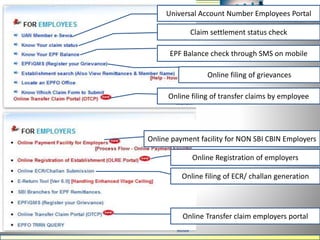
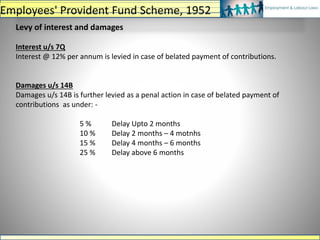
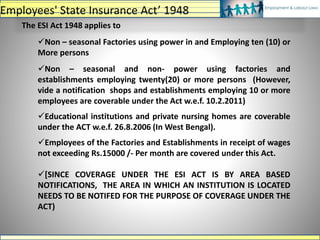
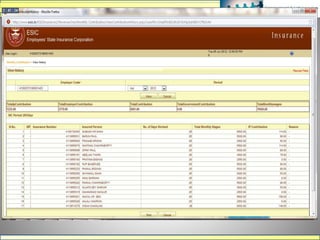
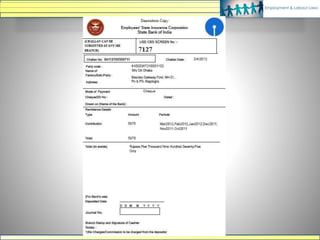
The document discusses various labour laws in India including those related to wages, social security, and industrial relations. It provides details about the Payment of Wages Act, Minimum Wages Act, Employees' Provident Fund & Miscellaneous Provisions Act, and Employees' State Insurance Act. These laws govern issues like minimum wages, working hours, social security benefits, and compliance requirements for employers like maintaining proper records and making timely contributions. The document also categorizes different labour laws and outlines the purpose, applicability and key compliance aspects of the aforementioned acts.













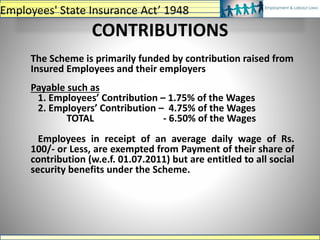
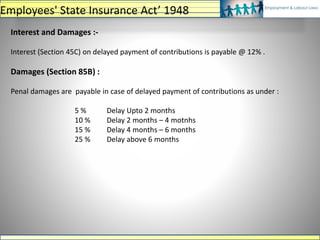
![Rate of Contribution
• Employee: 12% on Basic + DA + CVFA
• Employer: 13.36% on Basic + DA + CVFA
• [(PF-3.67% + 0.85%) + (EDLI-0.5% + 0.01%) + (Pension-8.33%)]
• * 0.85% Is PF Administrative charges payable in A/c 2 (subject to minimum of Rs
75/- per month for non-functional establishment and Rs 500 per month for other
establishments,
• 0.01 % is ELDI Adm. Charges payable in A/c 22 (subject to minimum of Rs 25/- per
month for non-functional establishment and Rs 200/- per month for other
establishments.
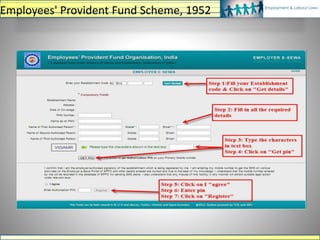
Monthly Remittance of Contribution & Return of employees
• Remittance of Contribution (PF Challan), for the previous month, on or before
15th of following month
• ECR copy with details of the employees deployed
Employees' Provident Fund Scheme, 1952](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labourlawsppt-191125171143/85/Labour-laws-ppt-16-320.jpg)