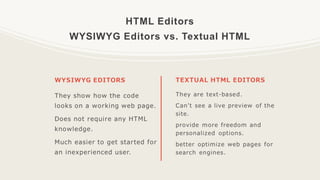
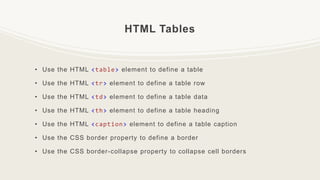
This document provides an introduction to HTML, including why it is used, common HTML elements and tags, how to format text and add images and links, and how to create tables, lists, and forms. It explains that HTML is the standard markup language for web pages and is easy to learn. It also lists some popular HTML editors that can be used to write HTML code.