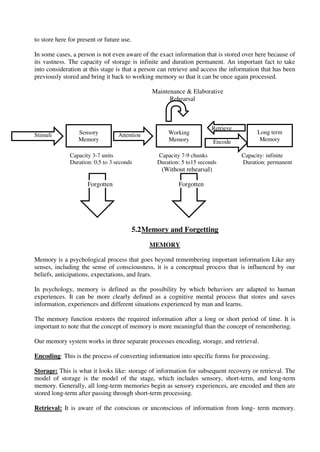
Information processing theory explains how the human mind processes, stores, and retrieves information in a manner similar to computers. There are four main steps in both human and computer information processing: input, storage, processing, and output. In psychology, the four steps are: attending to focus on information, encoding to process it, storing it in memory, and retrieving it when needed. The three stages of memory that work together are sensory memory, short-term/working memory, and long-term memory. Cognitive processes like attention, memory, problem-solving, decision-making, perception, reasoning, learning, creativity, thinking, comprehension, and metacognition are important mental functions studied in cognitive psychology.