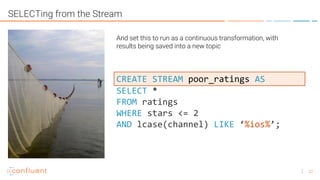
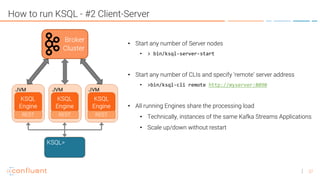
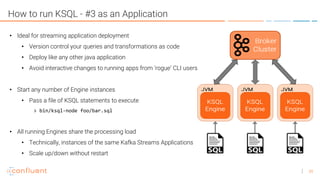
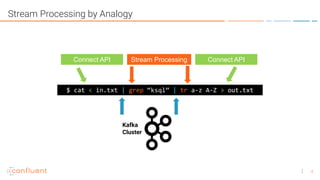
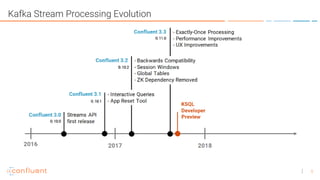
KSQL is an open-source streaming SQL engine for Apache Kafka that enables real-time stream processing with features like native integration, fault tolerance, and support for late data. It is particularly useful for tasks like streaming ETL, anomaly detection, and real-time monitoring, while having limitations in ad-hoc queries and lack of indexed lookup capabilities. KSQL supports continuous transformations, windowing for aggregation, and can be run in various modes, including local and client-server configurations.











![18
Schema and Format
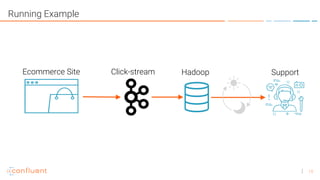
• A Kafka broker knows how to move <sets of bytes>
• Technically a message is ( ts, byte[], byte[] )
• SQL-like queries require a richer structure
• Start with message (value) format
• JSON
• DELIMITED (comma-separated in this preview)
• AVRO – requires that you supply a .avsc schema-file
• Pseudo-columns are automatically generated
• ROWKEY, ROWTIME](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ksqlintro201801-180112184313/85/KSQL-Intro-15-320.jpg)