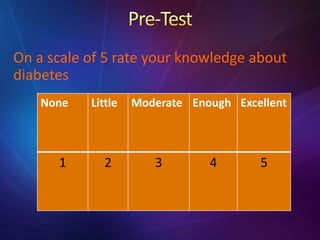
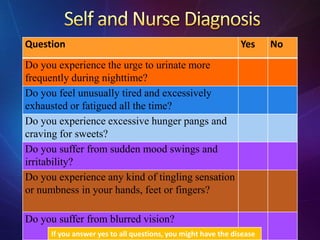
The document provides information about diabetes, including:
1) It defines diabetes as a disease resulting from the body's inability to properly regulate blood sugar levels, either due to not producing enough insulin or not responding properly to the insulin produced.
2) It describes the three main types of diabetes - Type 1 caused by lack of insulin production, Type 2 caused by insulin resistance or lack of insulin, and gestational diabetes during pregnancy.
3) It emphasizes the importance of eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and monitoring blood sugar levels in managing diabetes to prevent or delay health complications.