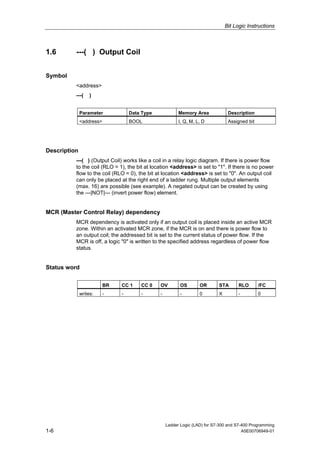
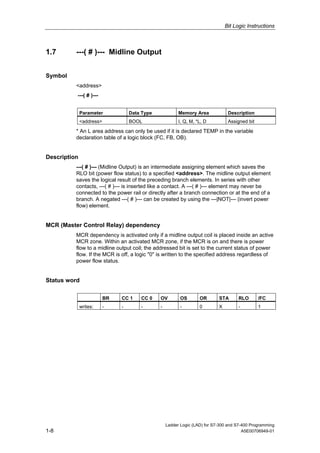
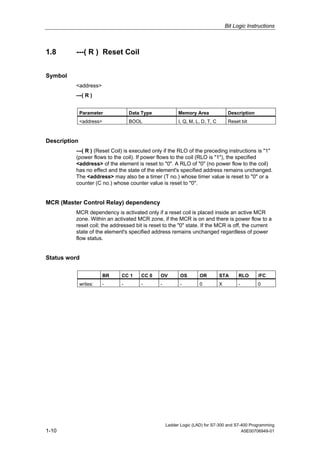
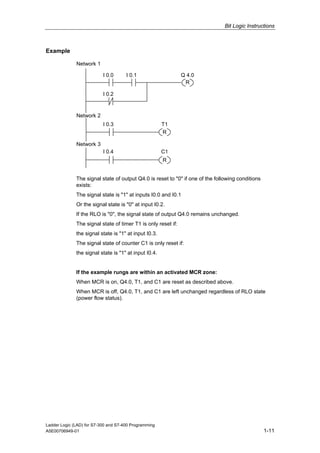
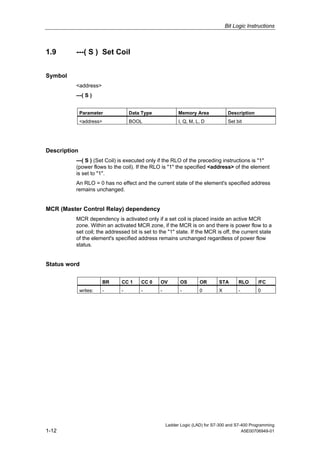
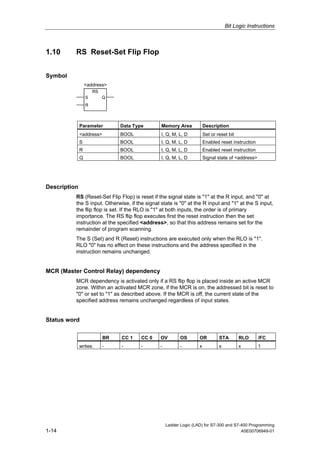
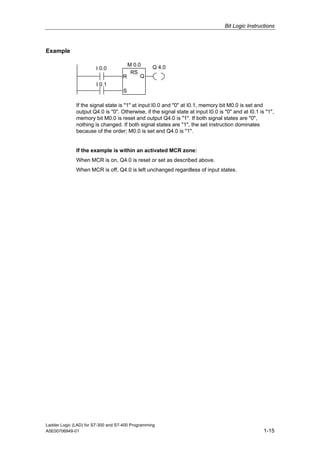
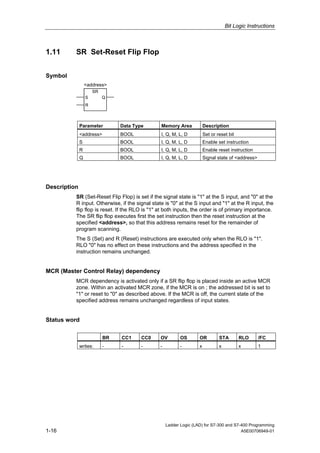
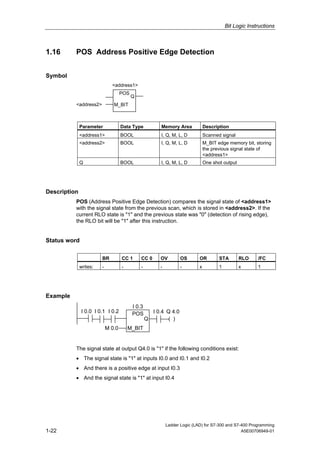
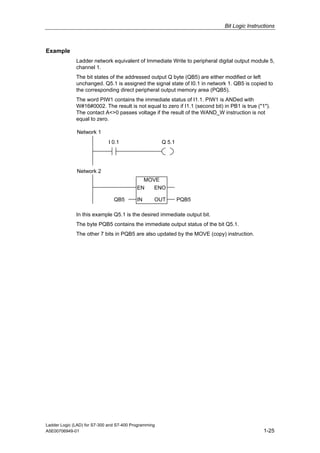
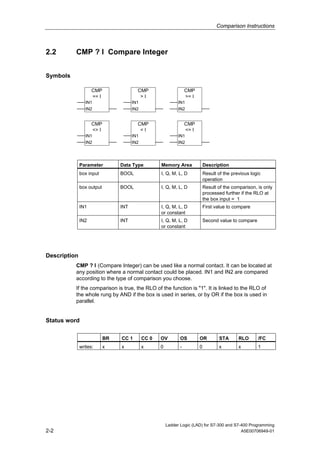
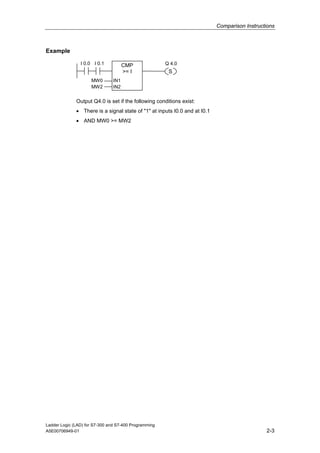
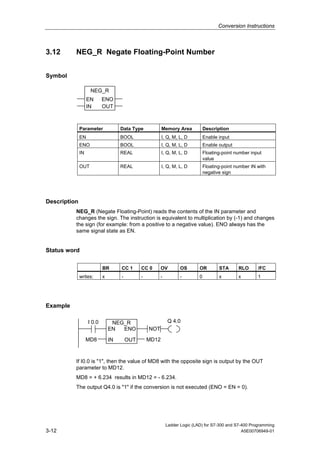
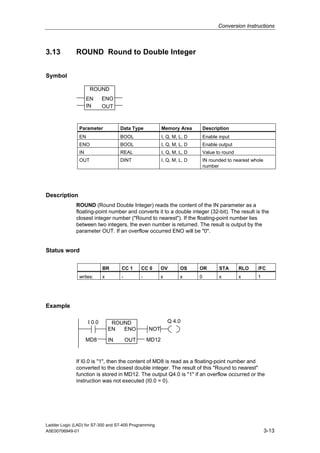
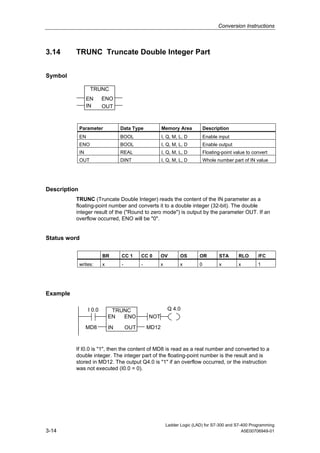
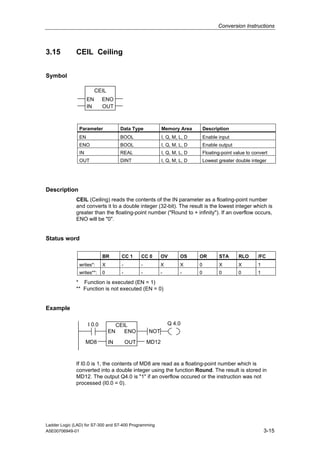
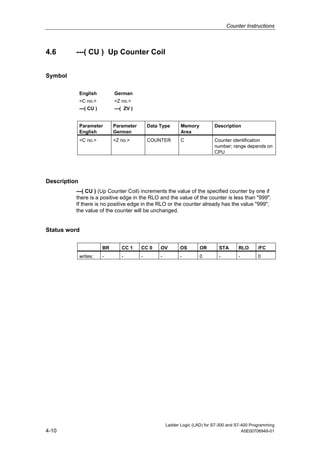
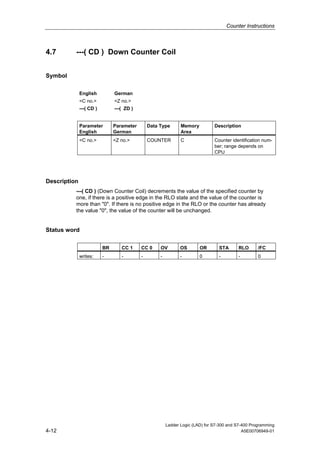
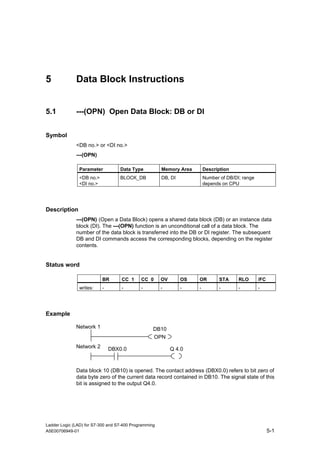
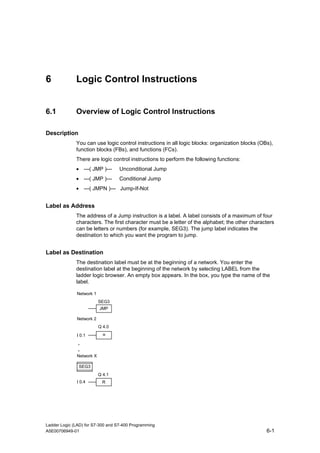
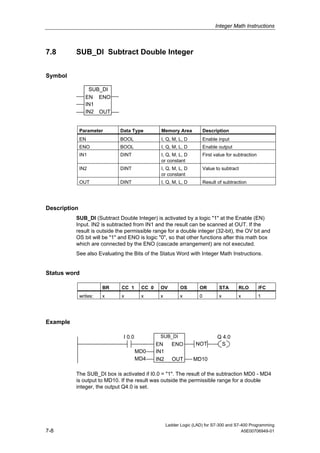
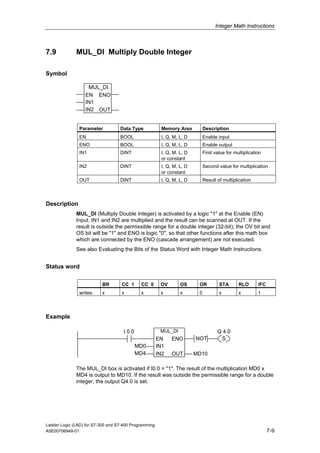
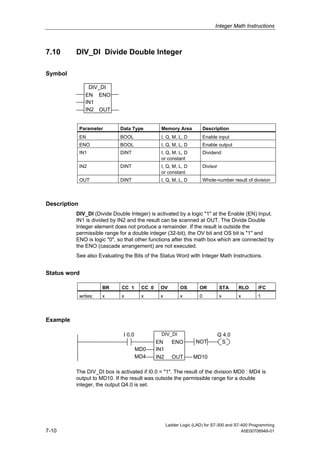
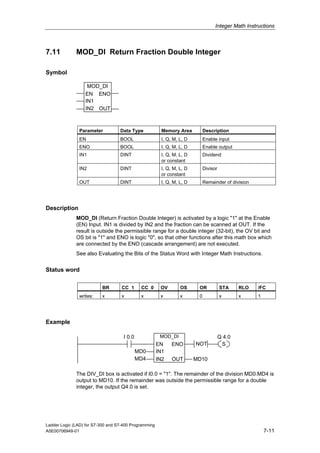
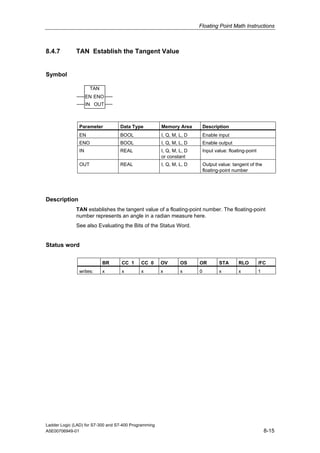
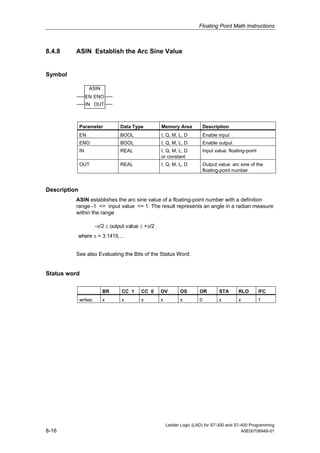
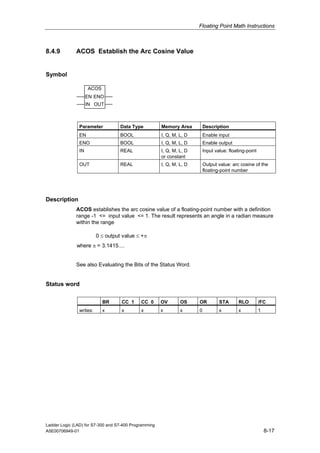
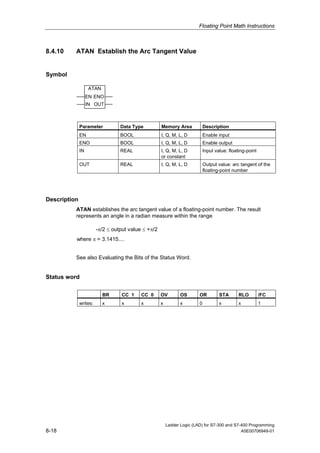
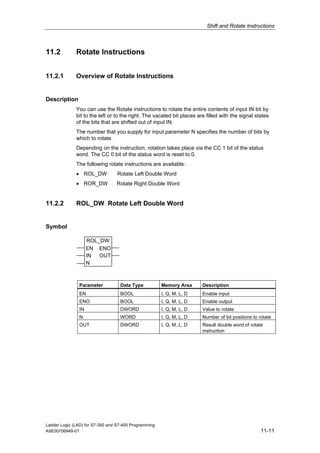
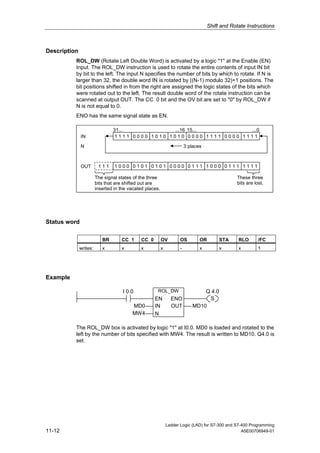
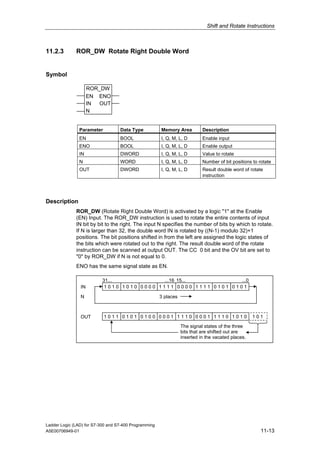
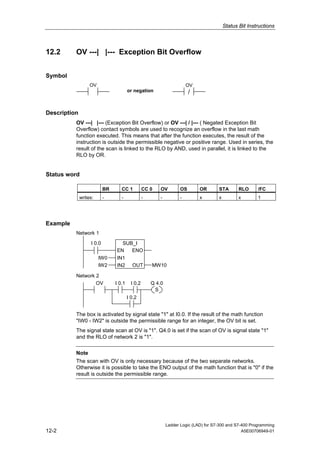
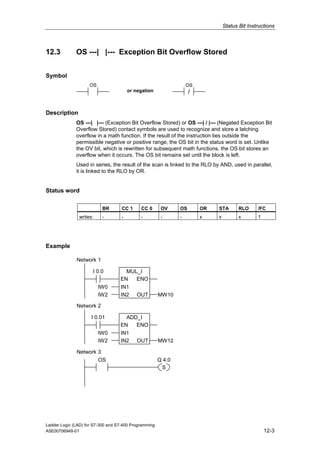
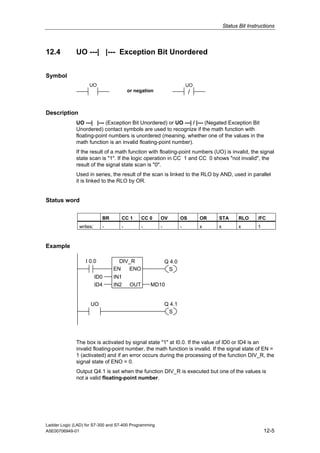
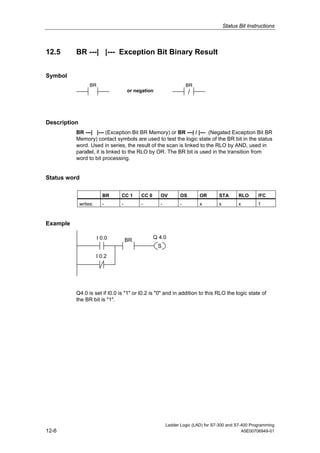
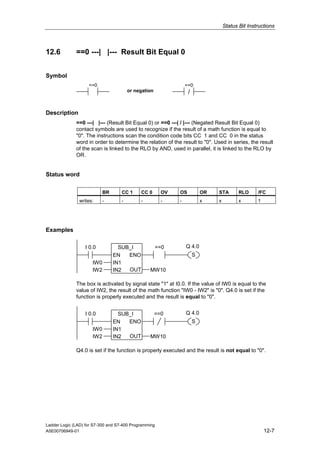
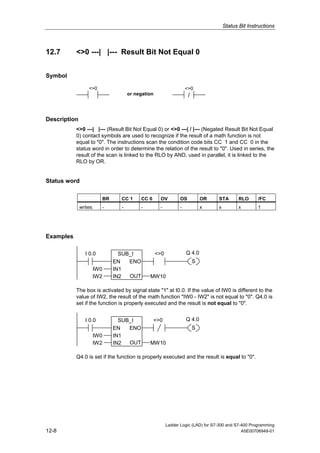
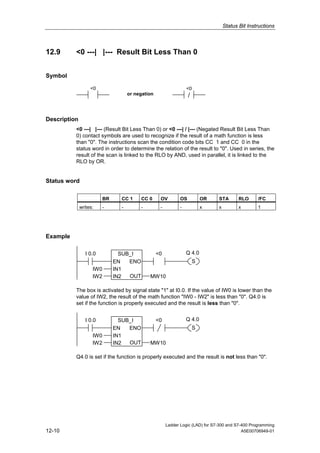
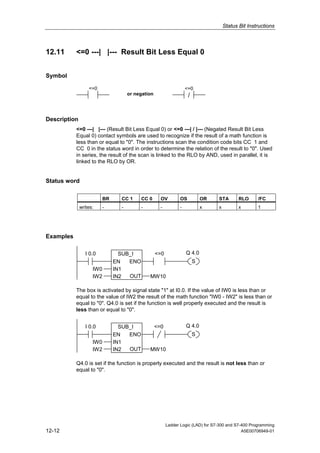
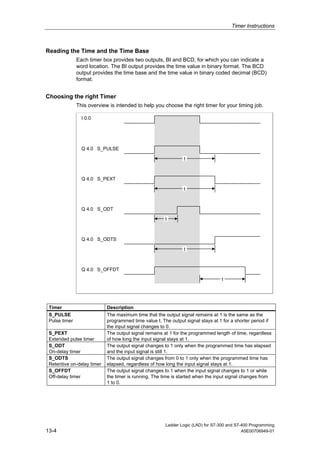
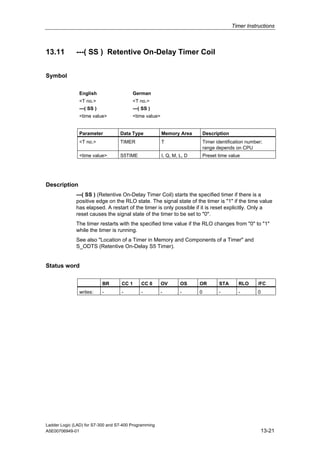
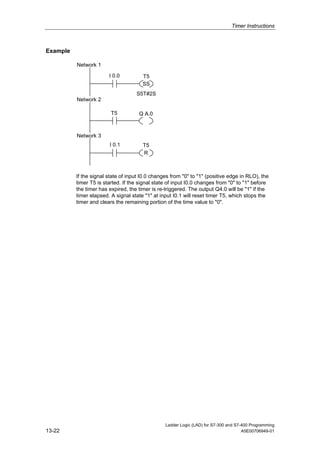
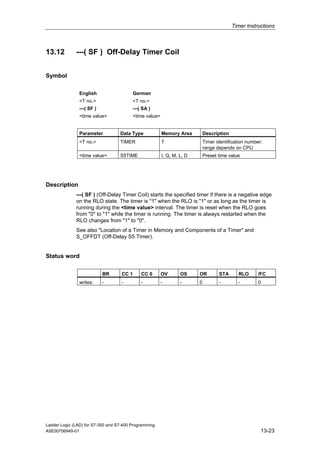
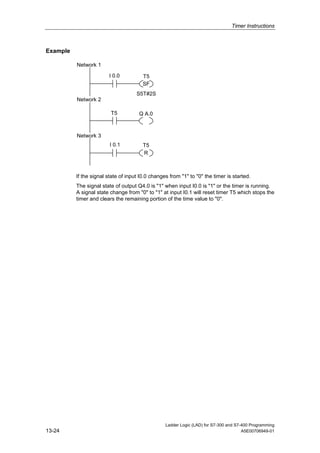
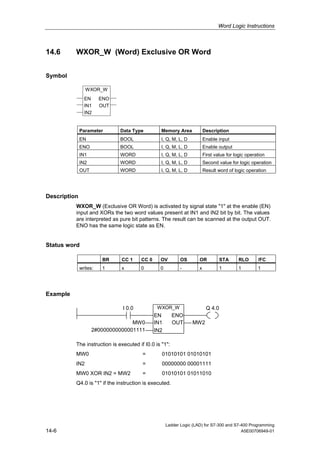
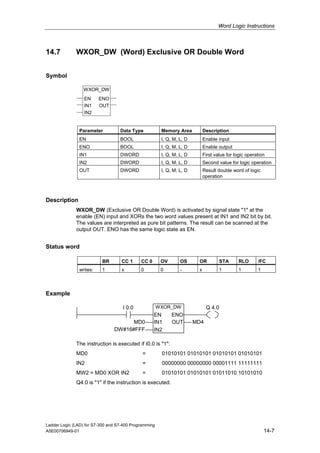
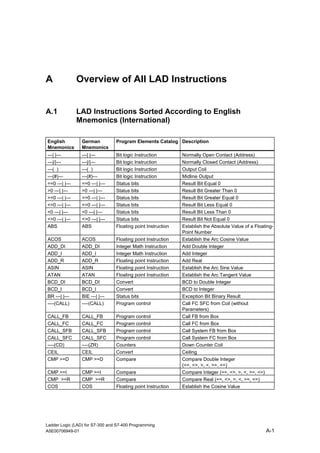
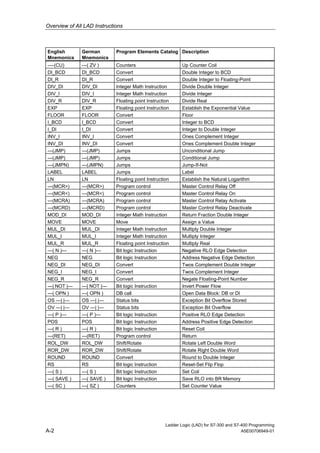
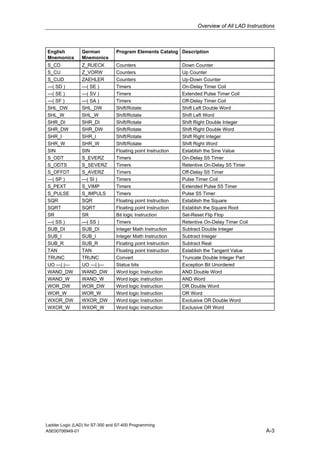
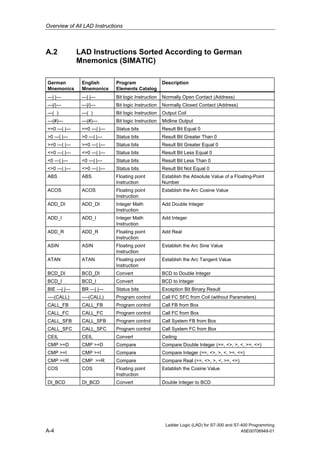
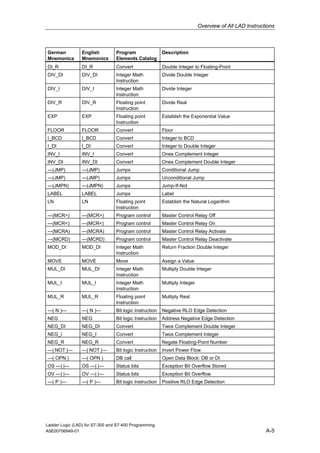
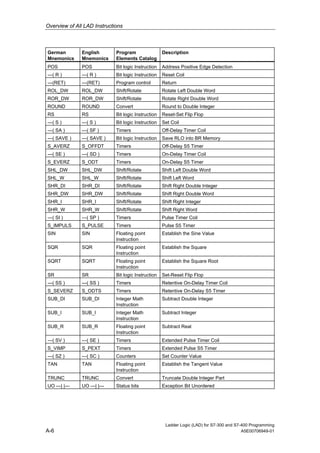
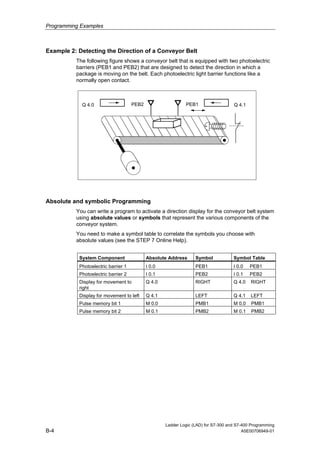
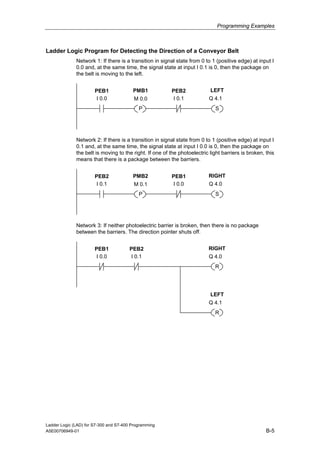
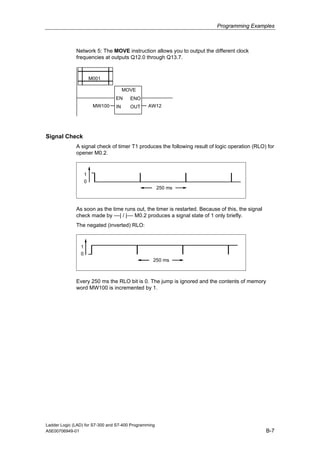
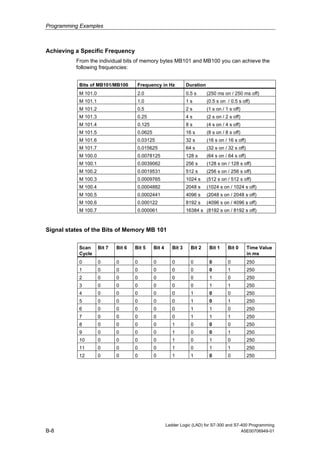
1) The manual is intended to guide users in creating LAD programs for S7-300 and S7-400 PLCs and provides a reference for LAD language elements.
2) Familiarity with automation technology, computer use, and STEP 7 software is required to understand the manual.
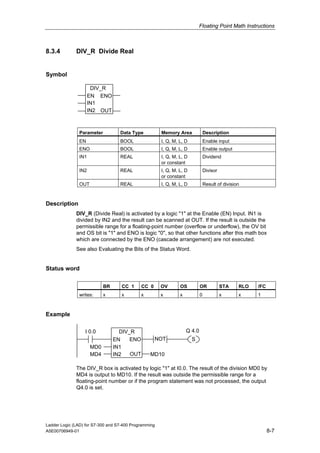
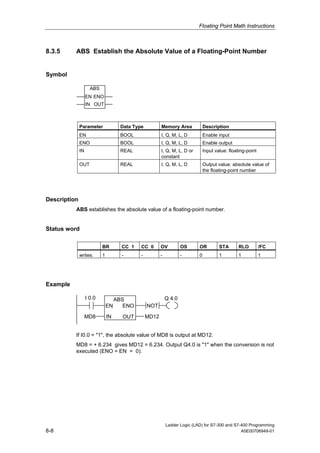
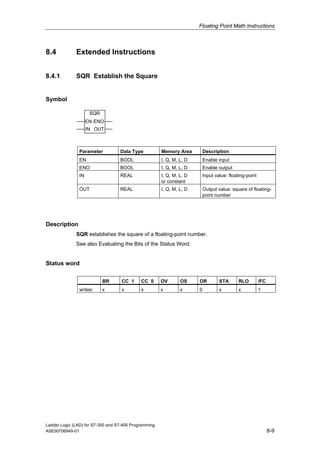
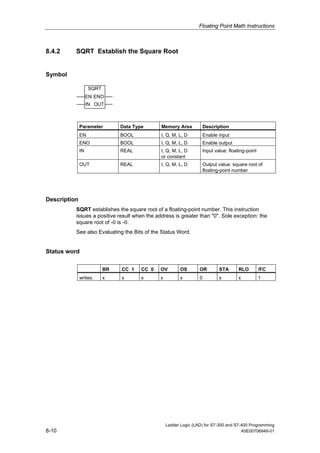
3) The manual complies with programming standard IEC 1131-3 and is valid for STEP 7 version 5.4.