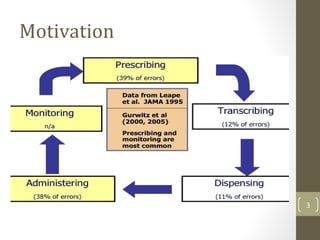
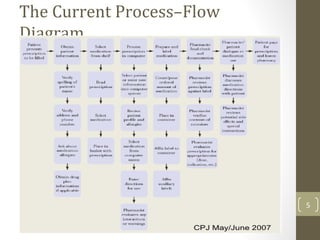
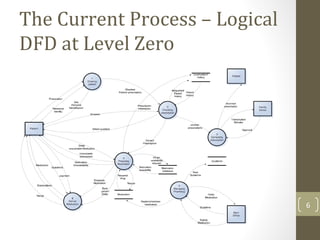
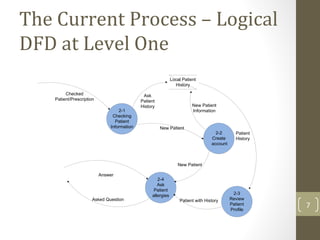
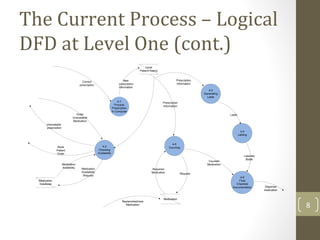
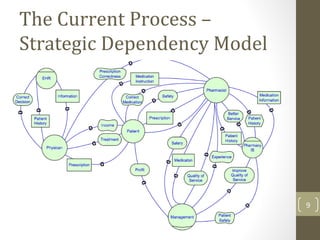
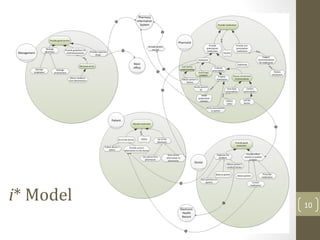
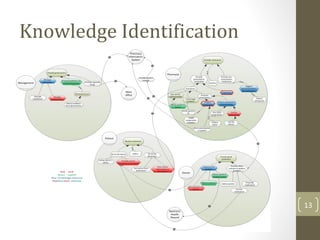
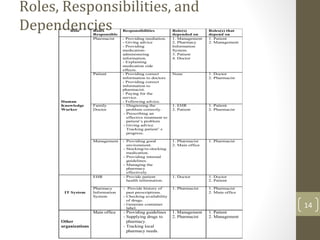
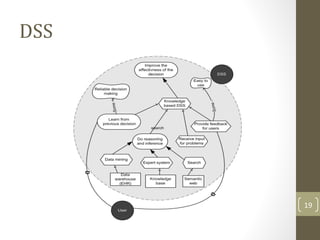
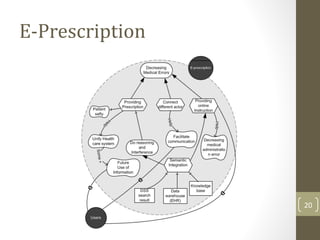
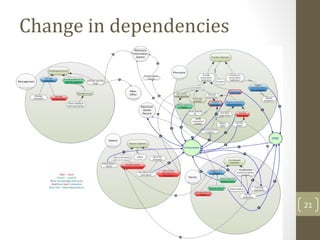
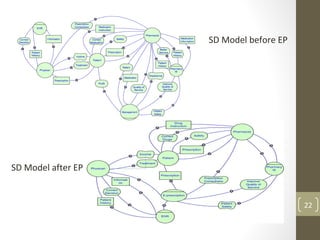
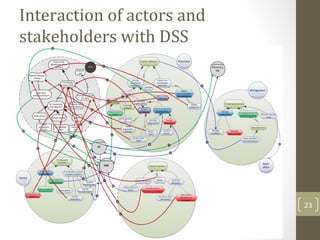
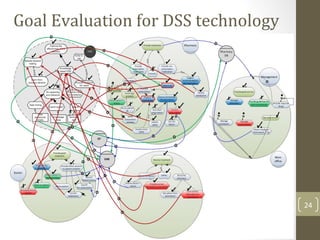
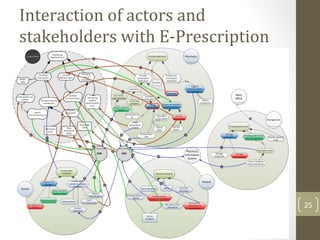
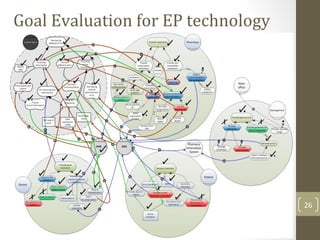
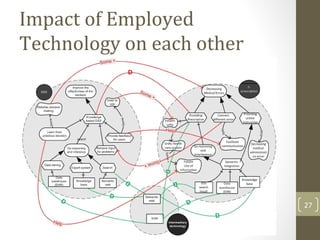
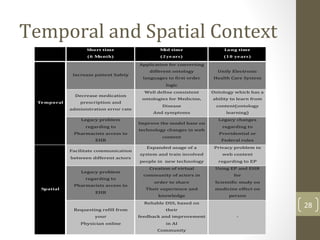
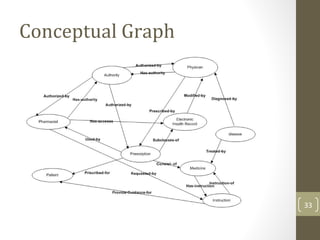
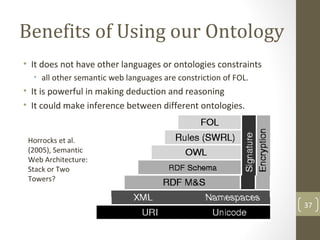
The document discusses knowledge management needs in the prescription medication process, highlighting current workflows, knowledge identification, and technology integration. It emphasizes the roles of pharmacists, doctors, and patients, and presents a portfolio of knowledge management systems, particularly decision support systems and e-prescribing. Additionally, the document explores the use of ontologies to improve medication safety and efficiency in the healthcare system.