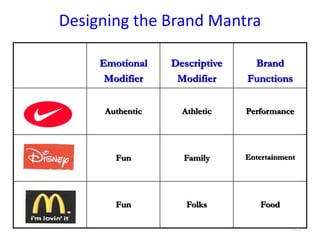
This document discusses brand positioning and provides guidelines for effective brand positioning. It covers the following key points:
1. Brand positioning involves designing the brand's offer and image to occupy a distinct place in customers' minds. It requires understanding customers, competitors, and how the brand is similar or different.
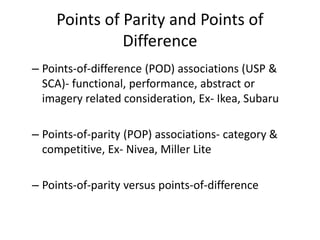
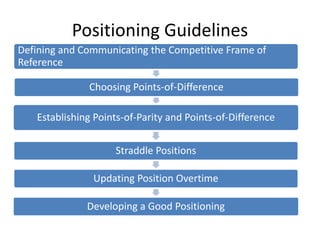
2. Effective positioning chooses points-of-parity (shared attributes) and points-of-difference (unique attributes) versus competitors. It also clearly defines the competitive frame of reference.
3. A brand audit examines a brand's health, equity sources, and ways to improve equity. It assesses brand elements, programs, perceptions, and provides recommendations.