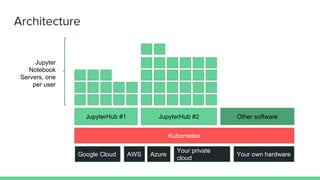
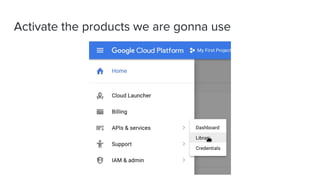
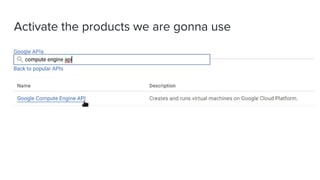
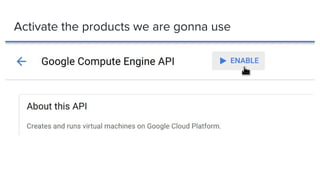
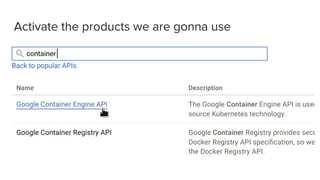
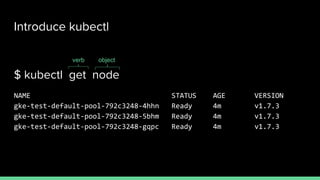
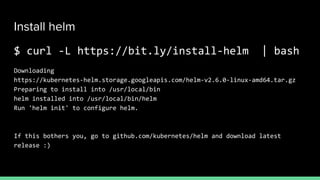
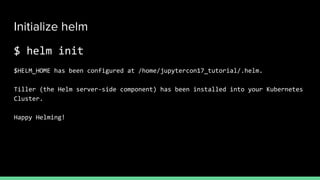
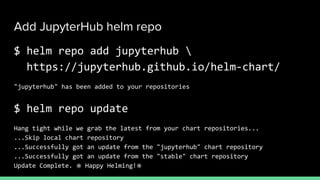
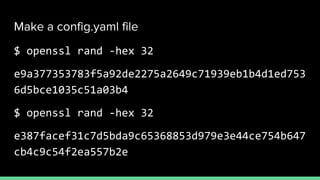
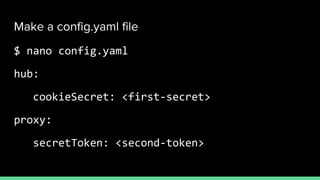
This document introduces Zero to JupyterHub, which allows for scalable JupyterHub deployments on Kubernetes. It provides instructions on setting up a JupyterHub instance on Google Cloud using Kubernetes and Helm. The tutorial goals are to launch a JupyterHub on Google Cloud using free credits, understand allocated resources for users, perform basic debugging, and tear down the deployment. Key steps include signing up for Google Cloud, activating products, installing Kubernetes components like kubectl and Helm, adding the JupyterHub Helm chart repository, generating configuration files, and installing JupyterHub using Helm.