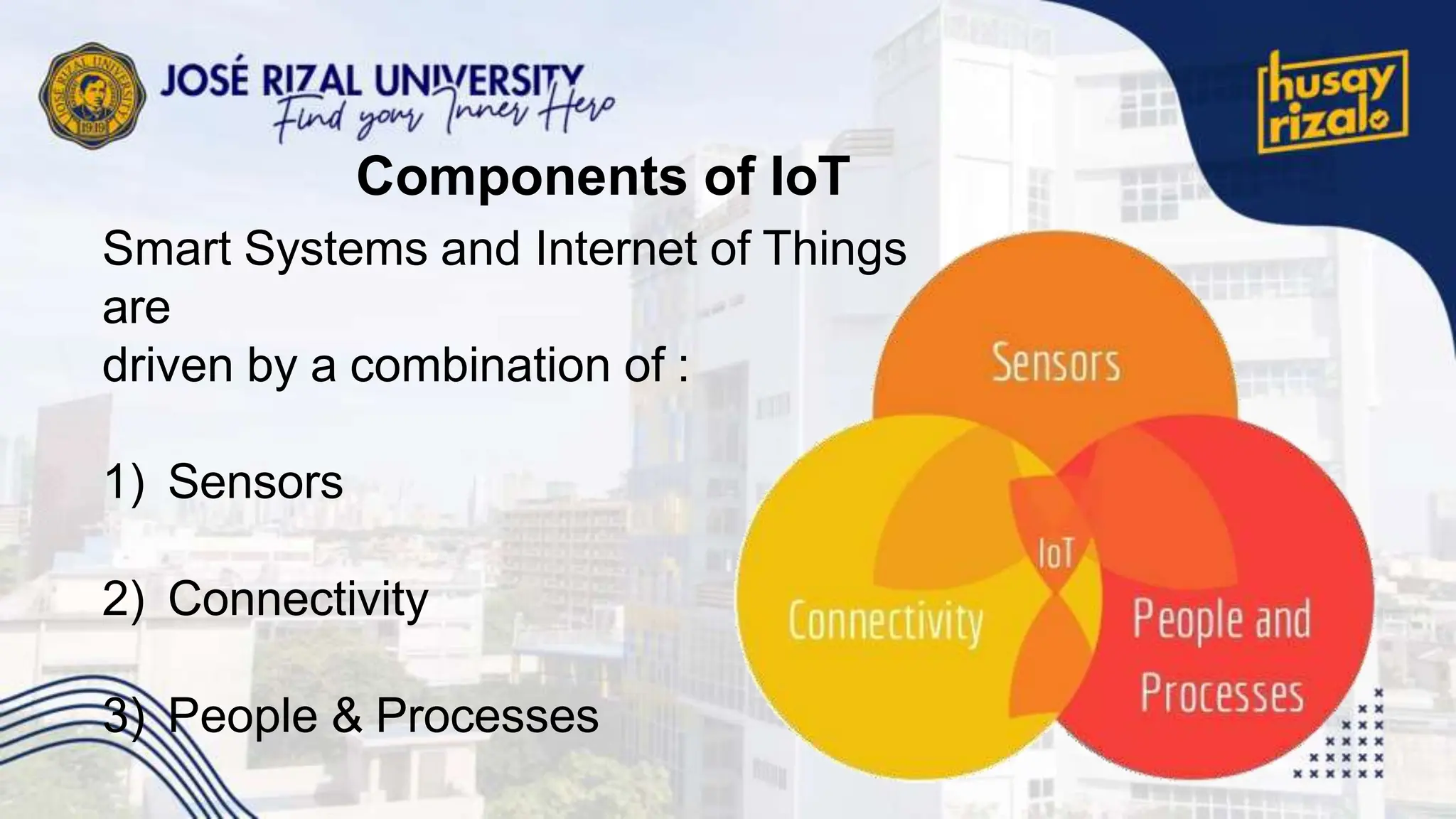
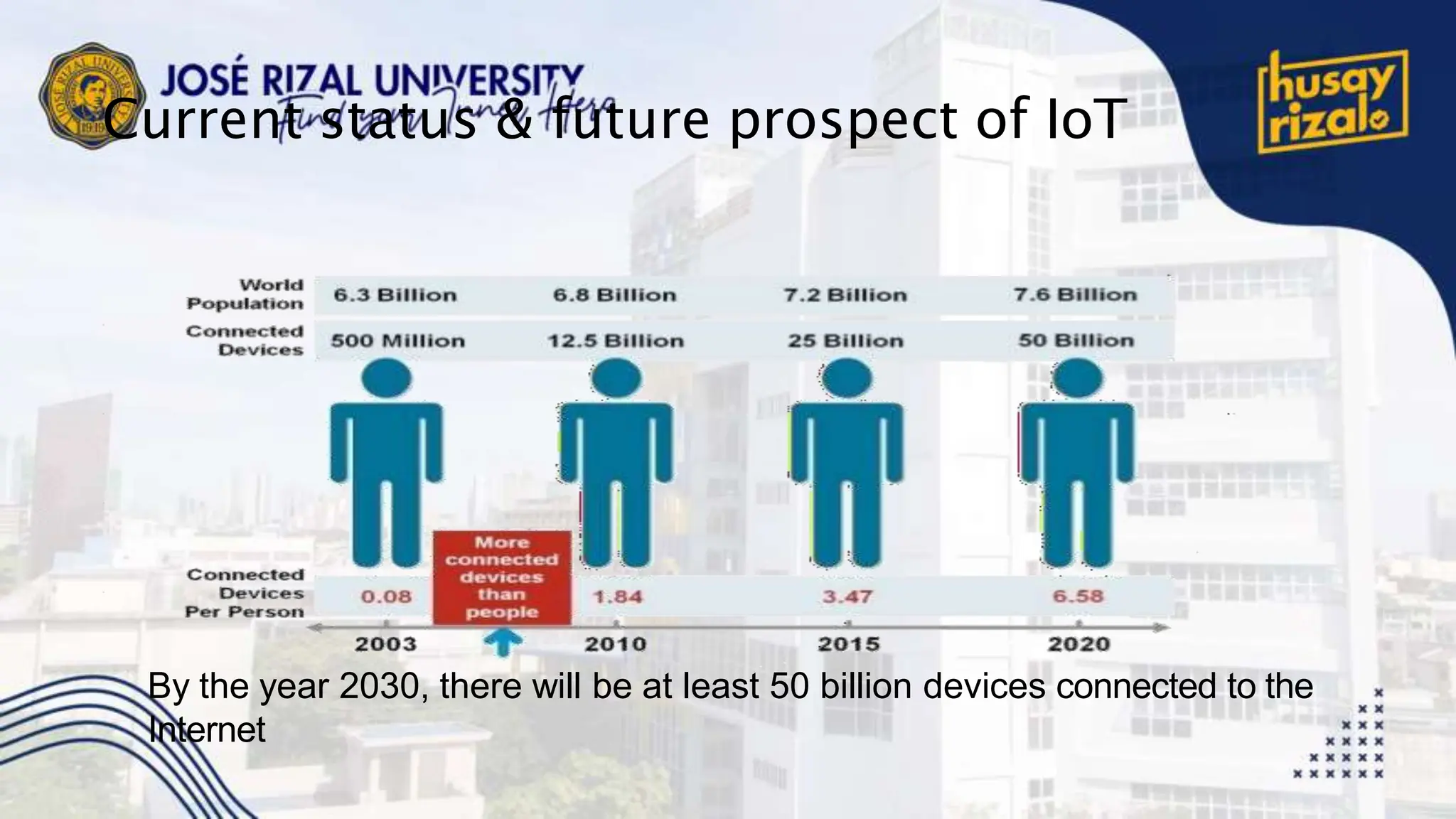
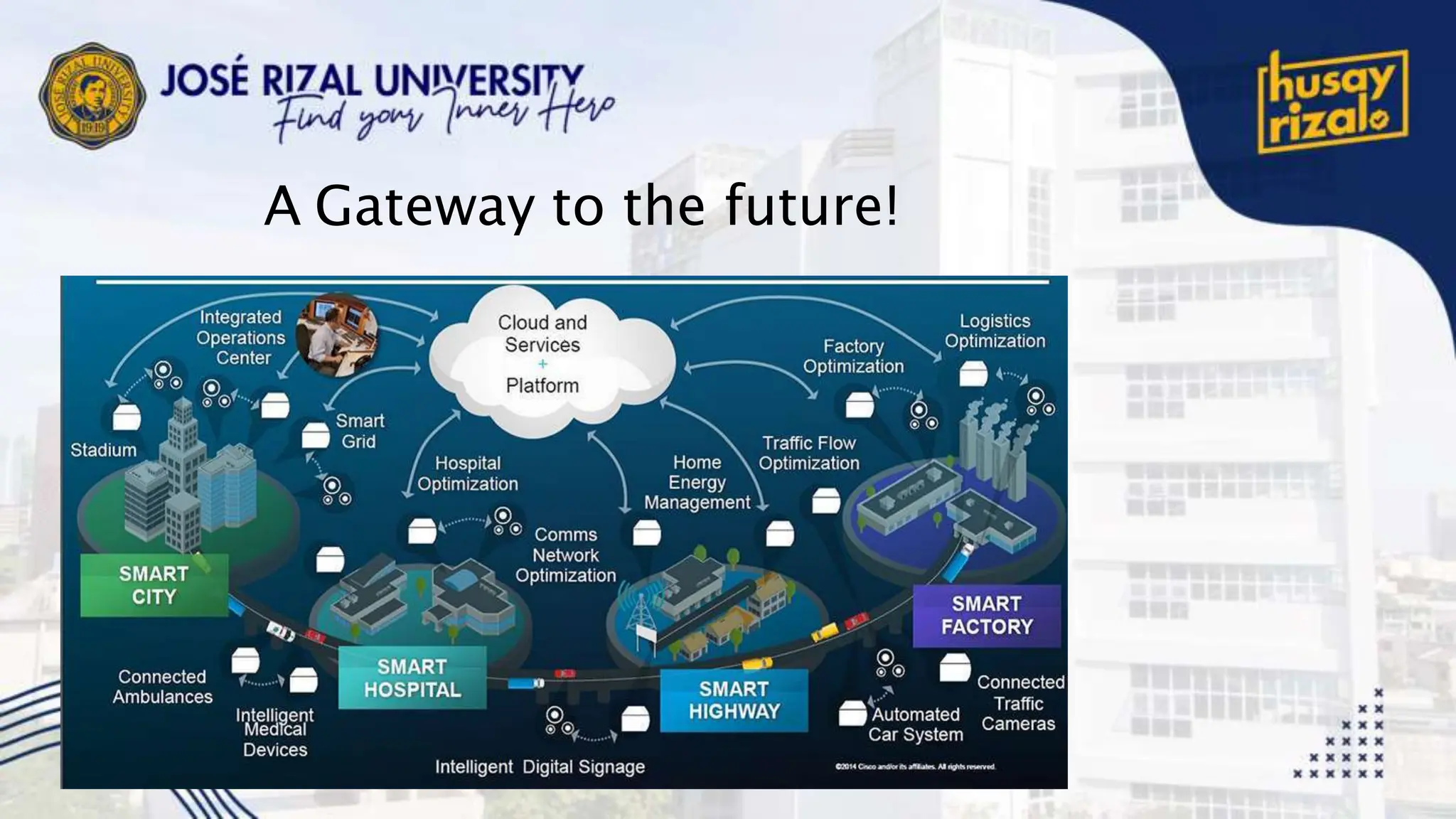
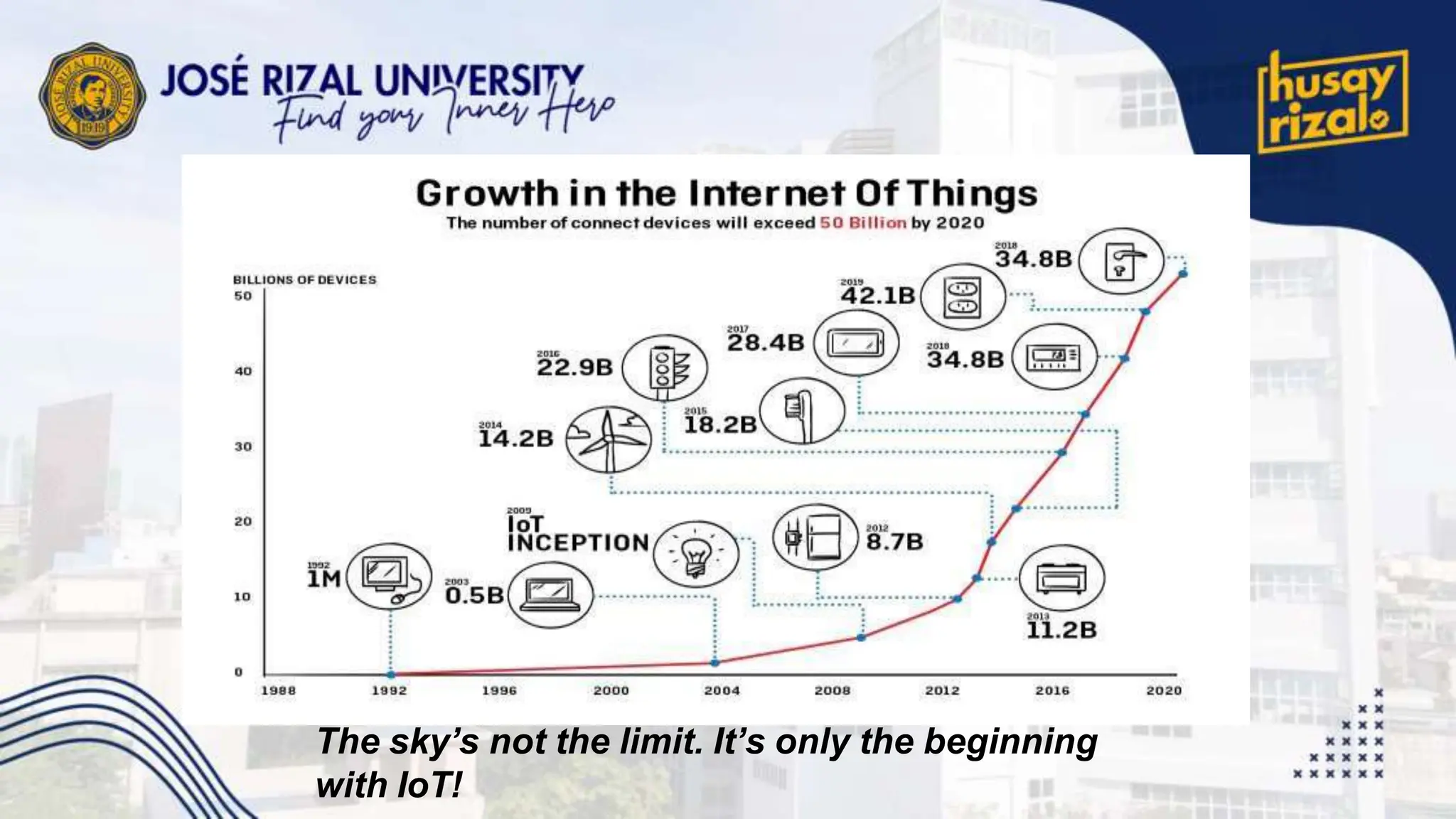
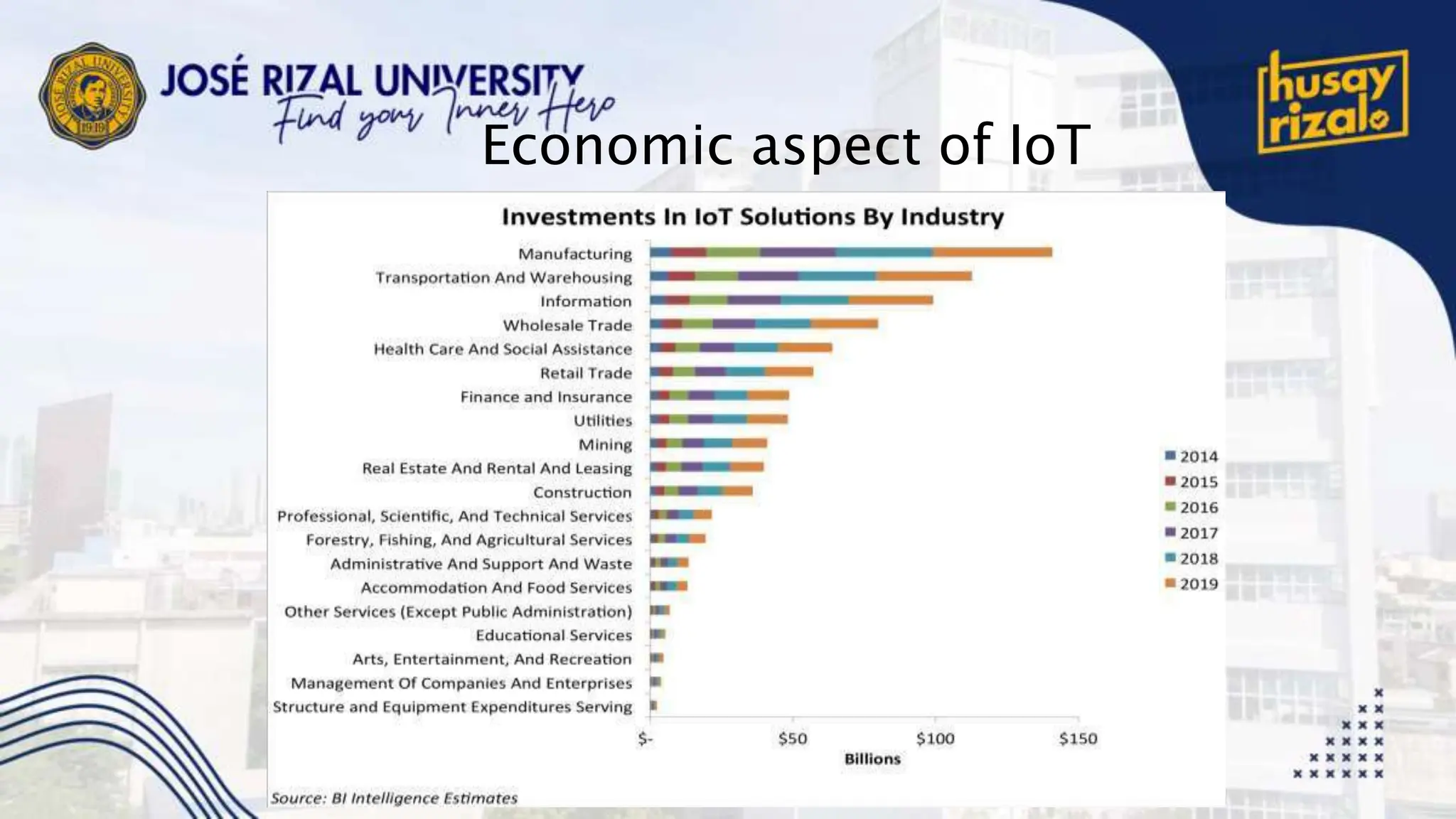
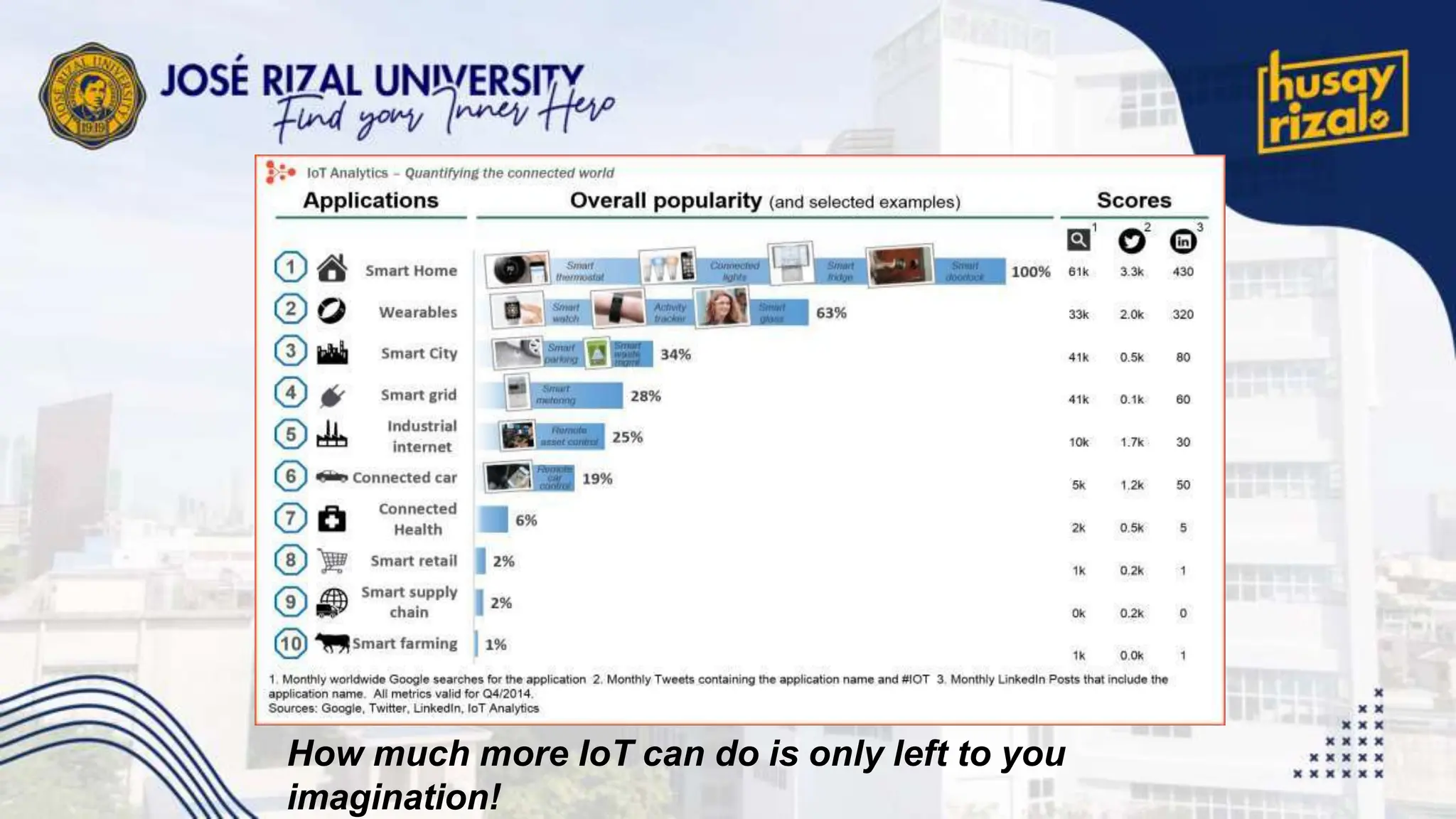
The Internet of Things (IoT) encompasses a network of connected devices that communicate over the internet, improving efficiency and resource utilization across various industries. IoT presents opportunities for transformational change in sectors like manufacturing and transportation, but faces challenges such as scalability and security. Projections suggest significant growth, with up to 100 billion connected devices by 2025 and a potential economic impact exceeding $11 trillion.