This document summarizes a JavaScript workshop that covers the fundamentals of JavaScript including:
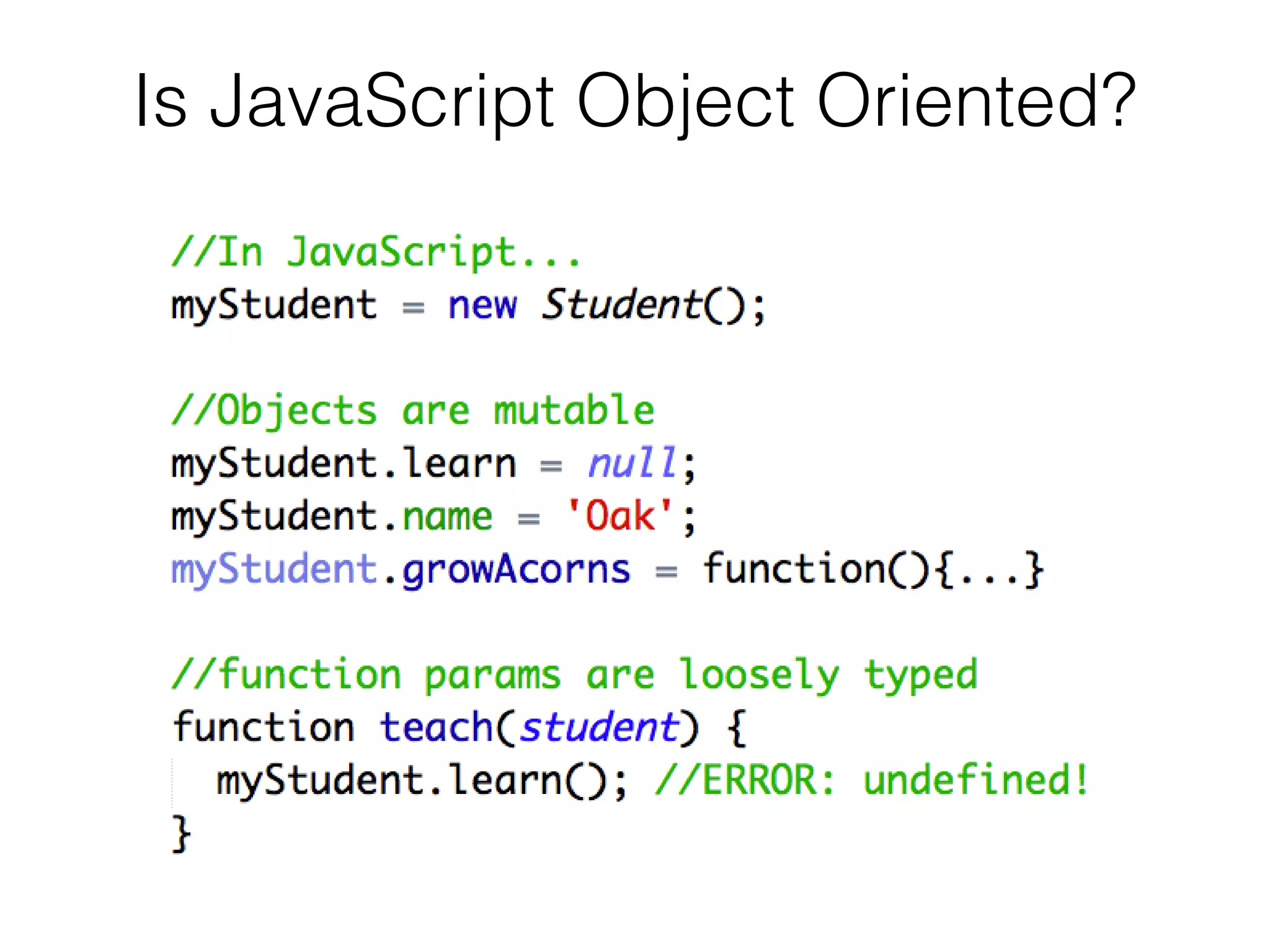
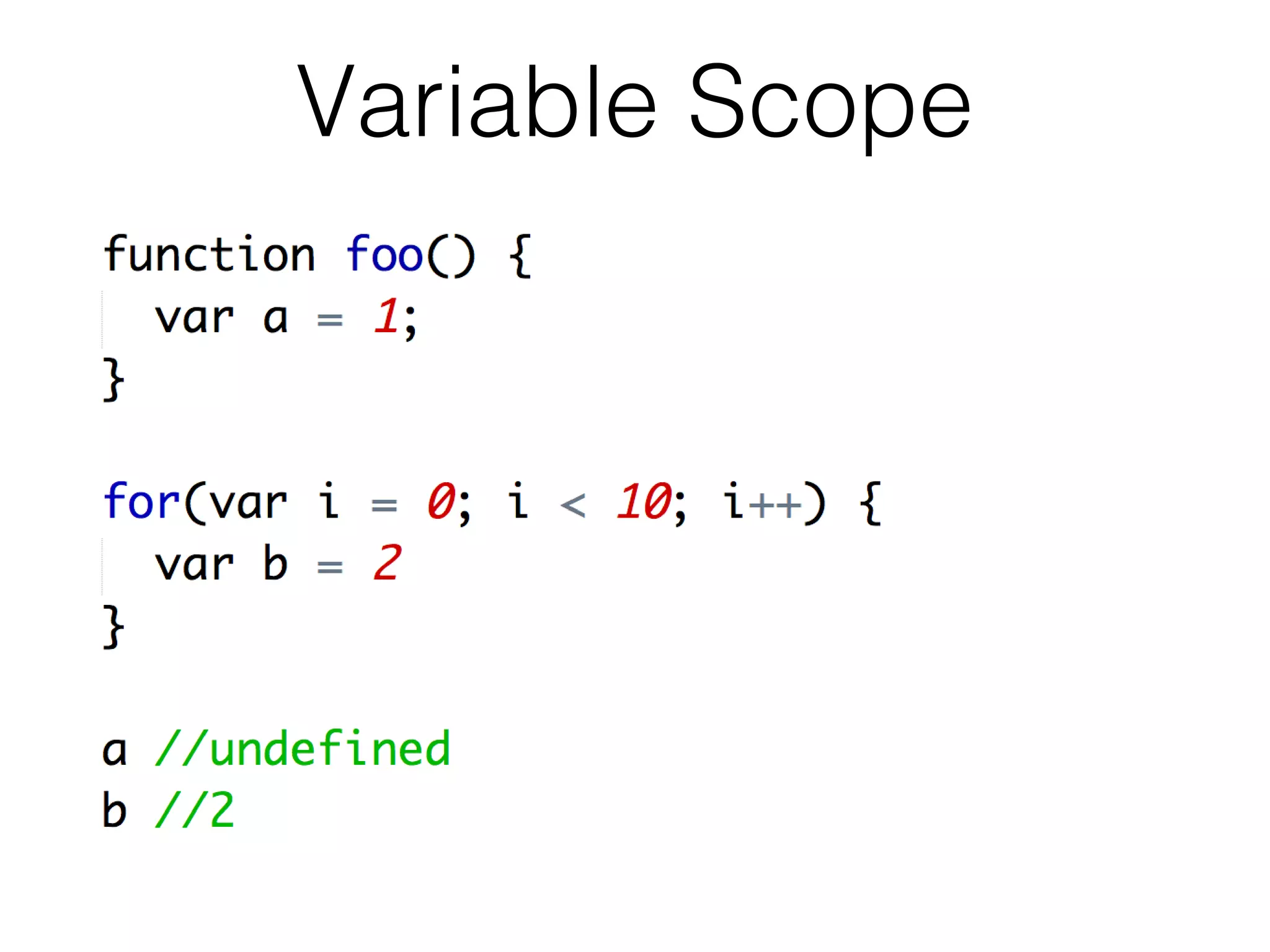
- JavaScript is loosely typed, uses mutable objects, and is a functional language. Functions are objects that have access to variables in their scope using closures.
- The workshop includes exercises to create karate fighter objects that perform moves, and a fight function to simulate matches until a winner emerges after 3 rounds.
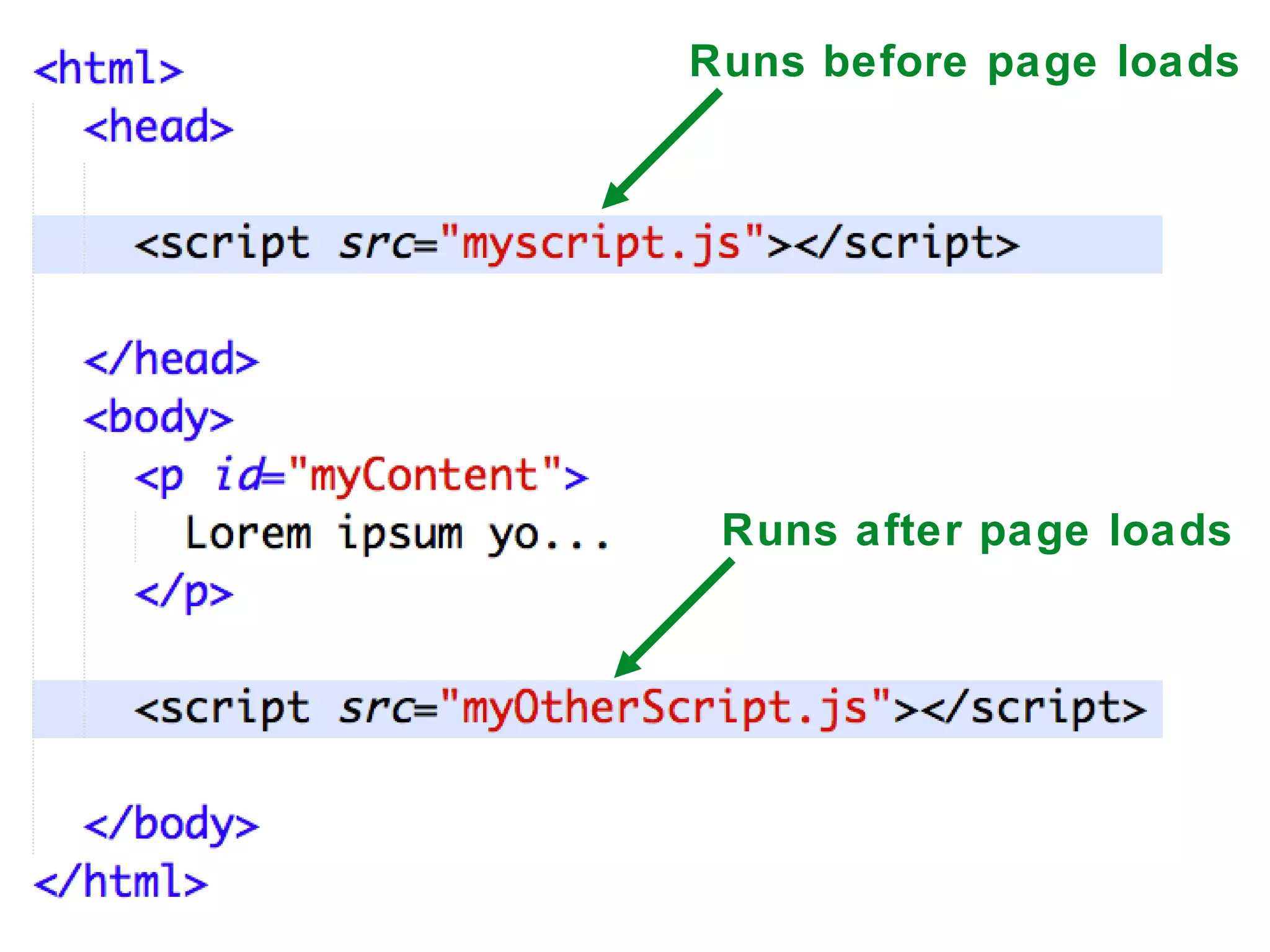
- The second part covers using JavaScript in the browser by manipulating the DOM through finding elements, attaching event handlers, and editing HTML. Exercises demonstrate outputting to the console, updating a paragraph on button click, and adding items to a list from user input.



























![Tournament Rules
1. Create an object to model a karate move. A move has a name (e.g. ‘karate chop’, ‘crane
kick”, etc.), and a strength score between 1 and 10. Output the move’s name to the console.
2. Create an array with at least 5 karate move objects. Output the name of the 3rd item in the
array to the console.
3. Create two objects to model karate fighters. Each fighter has a name, an array of moves,
and a function called “performMove” that returns a random move.
4. Create a function called “fight” that takes 2 fighter objects, gets a move from each of them,
and outputs a string “[fighter name] did [move name], [fighter 2 name] countered with [move
name 2].” to the console. Then return the winning fighter object with the higher strength
move. Null if tied.
5. Create a function that takes two fighters and makes them fight until one fighter has won 3
rounds, then outputs “[fightername] wins!” to the console
https://jsfiddle.net/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-workshop-150614151655-lva1-app6892/75/Javascript-Workshop-32-2048.jpg)