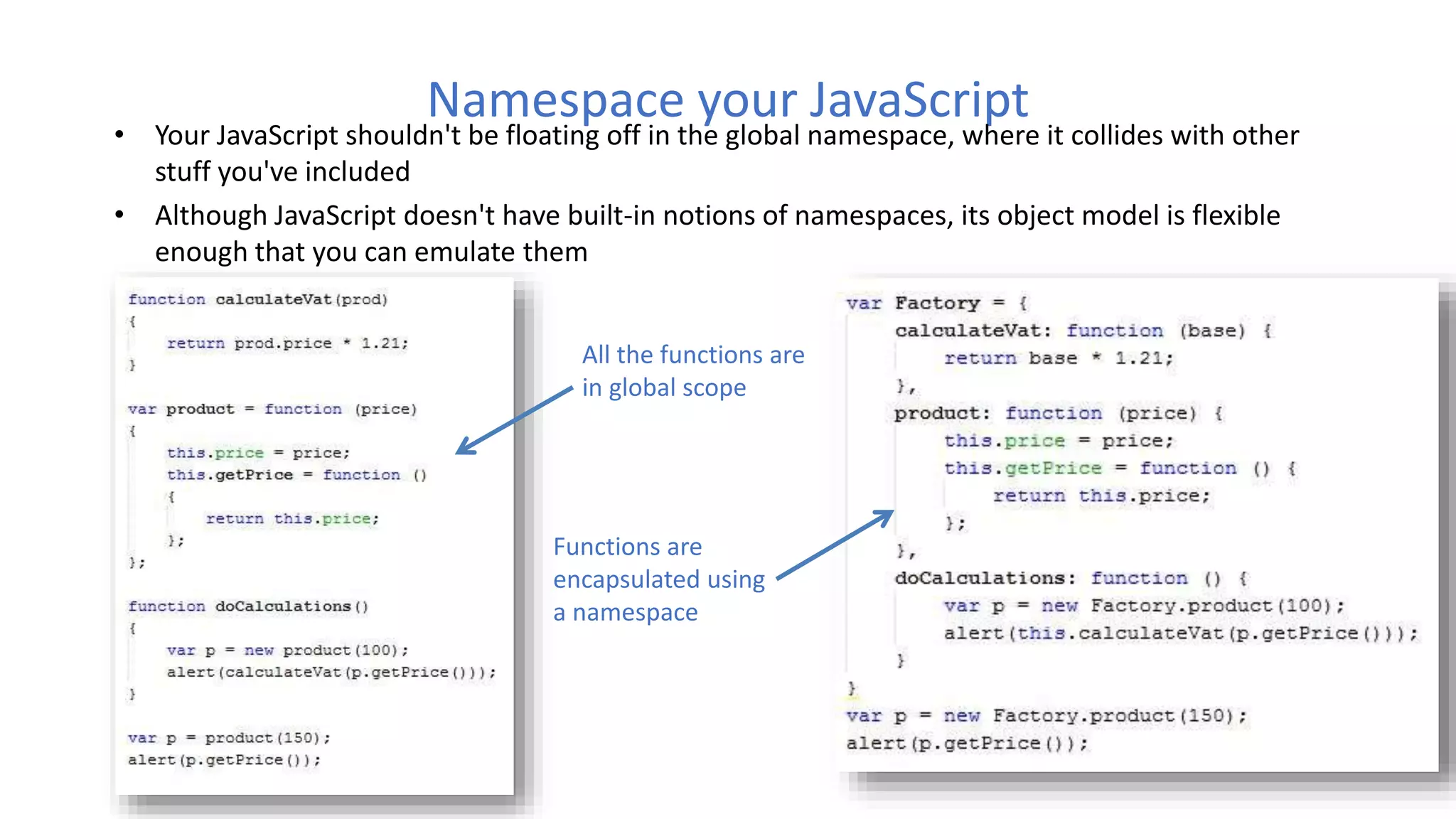
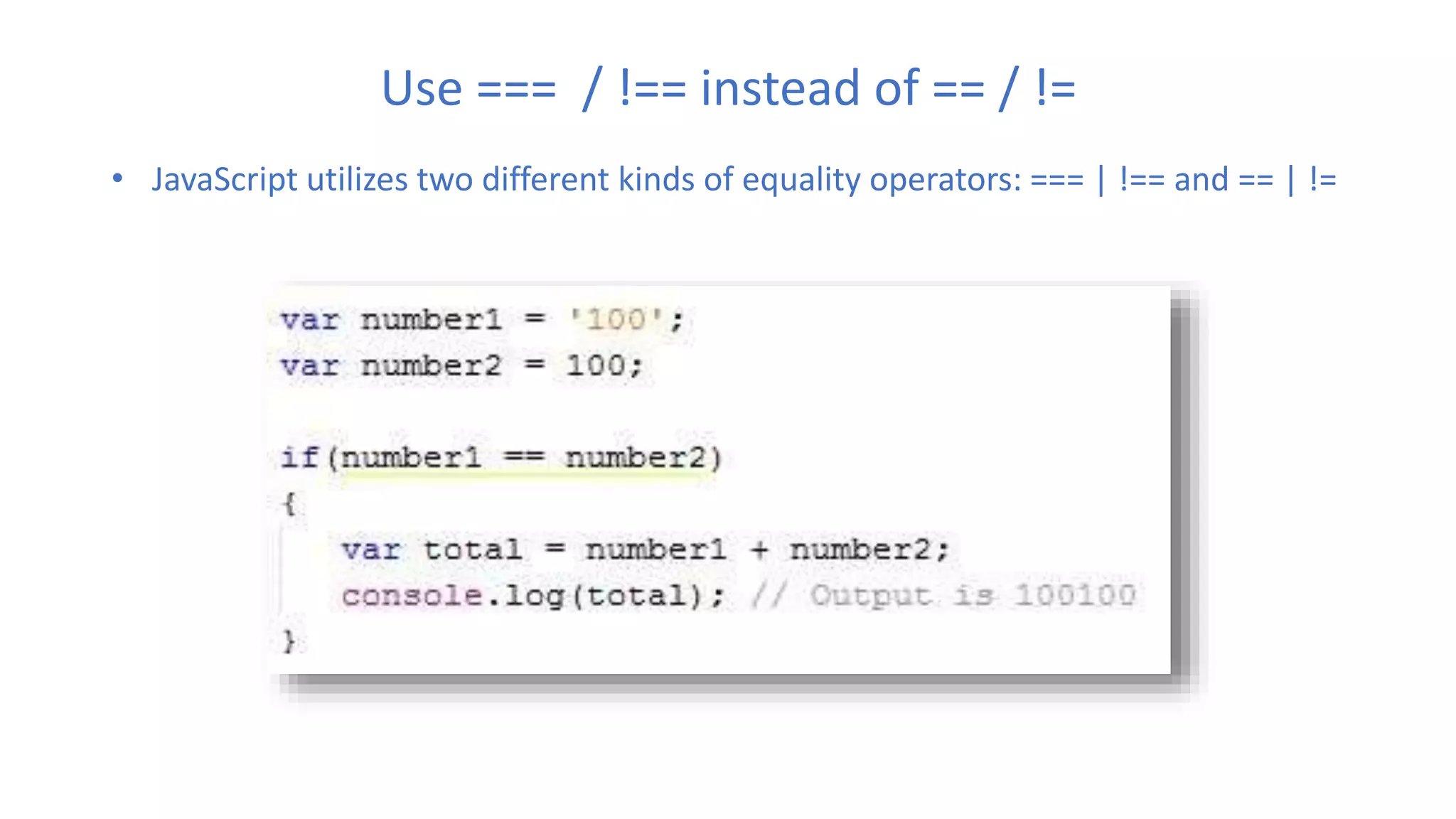
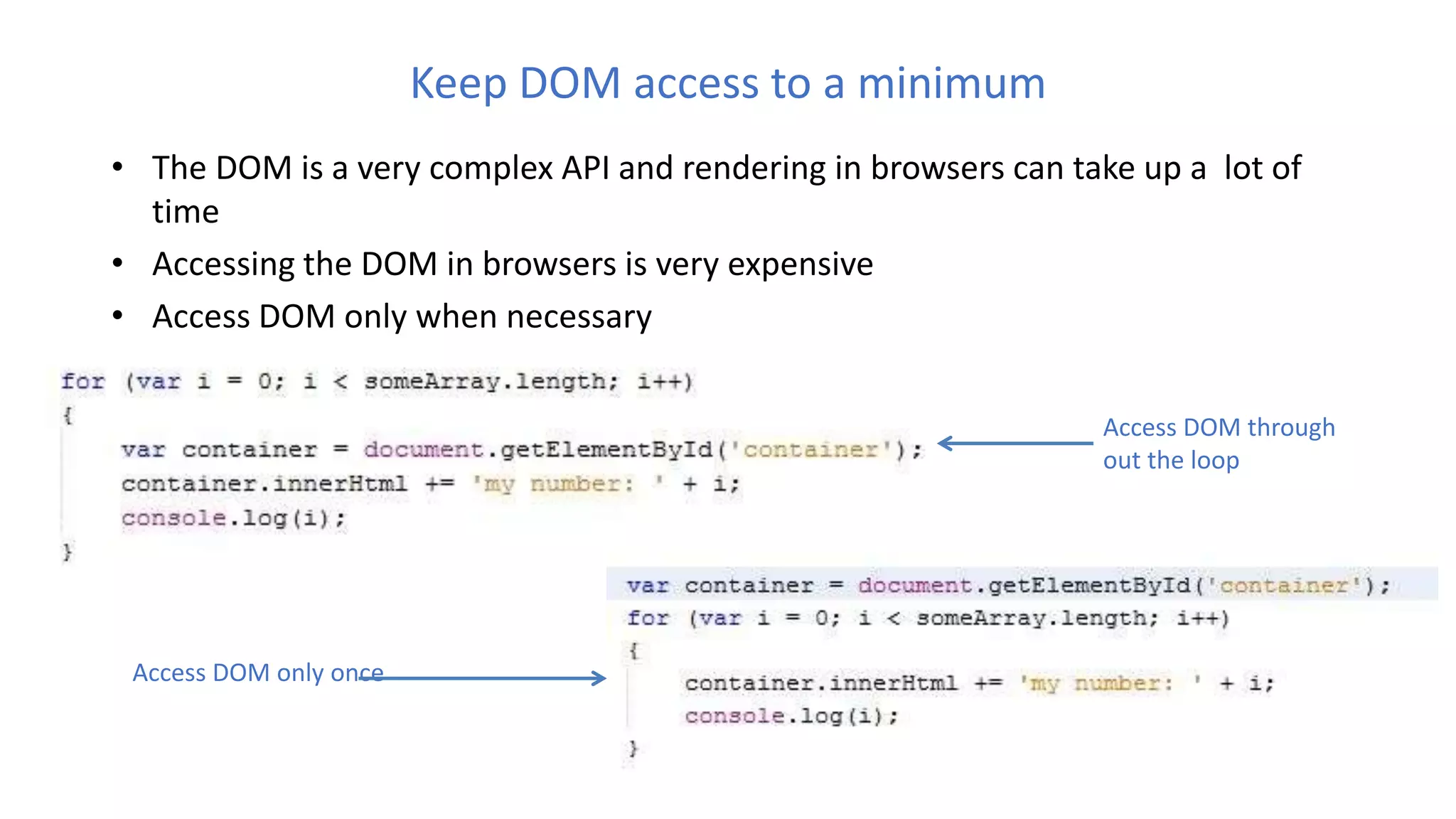
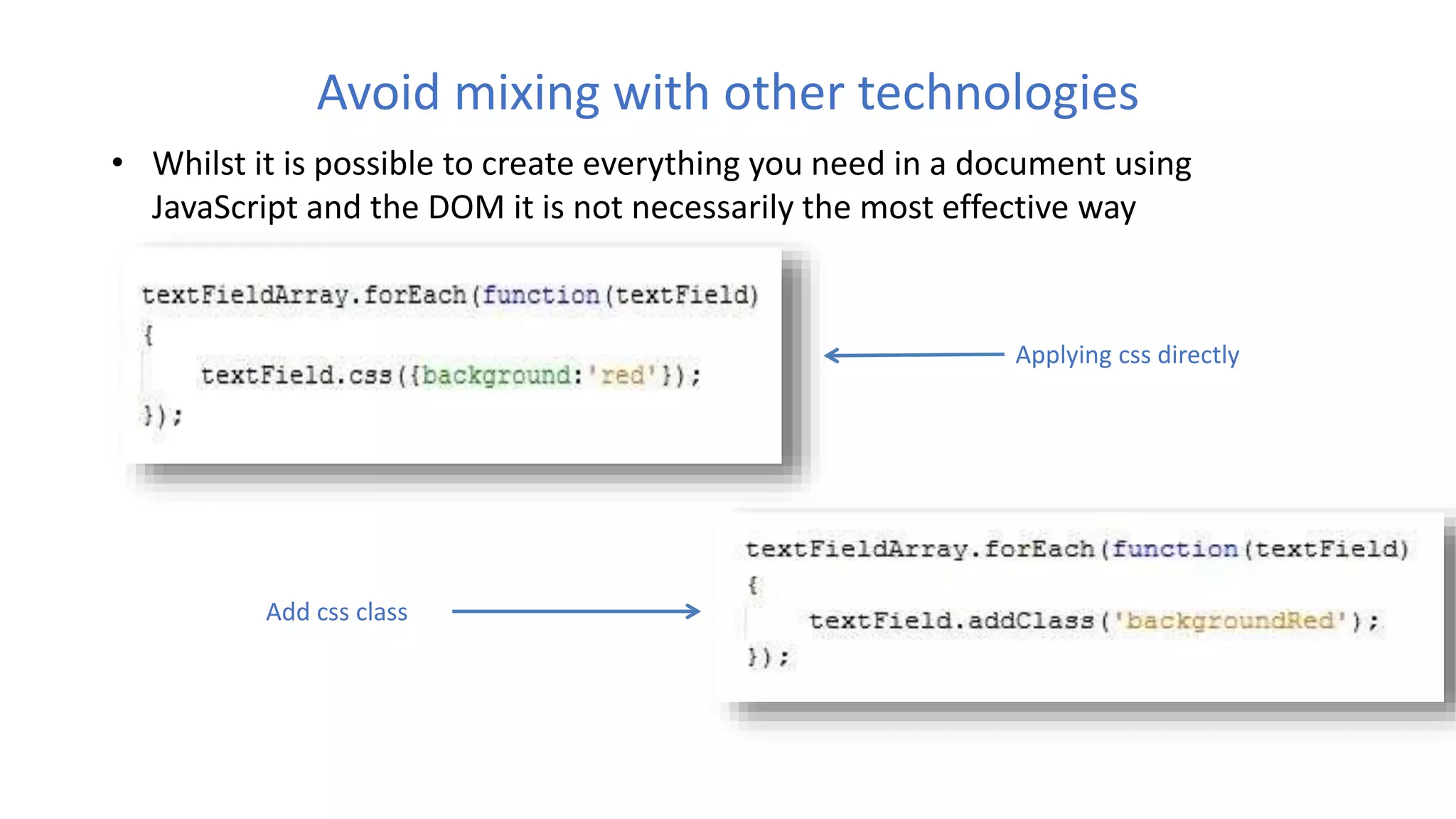
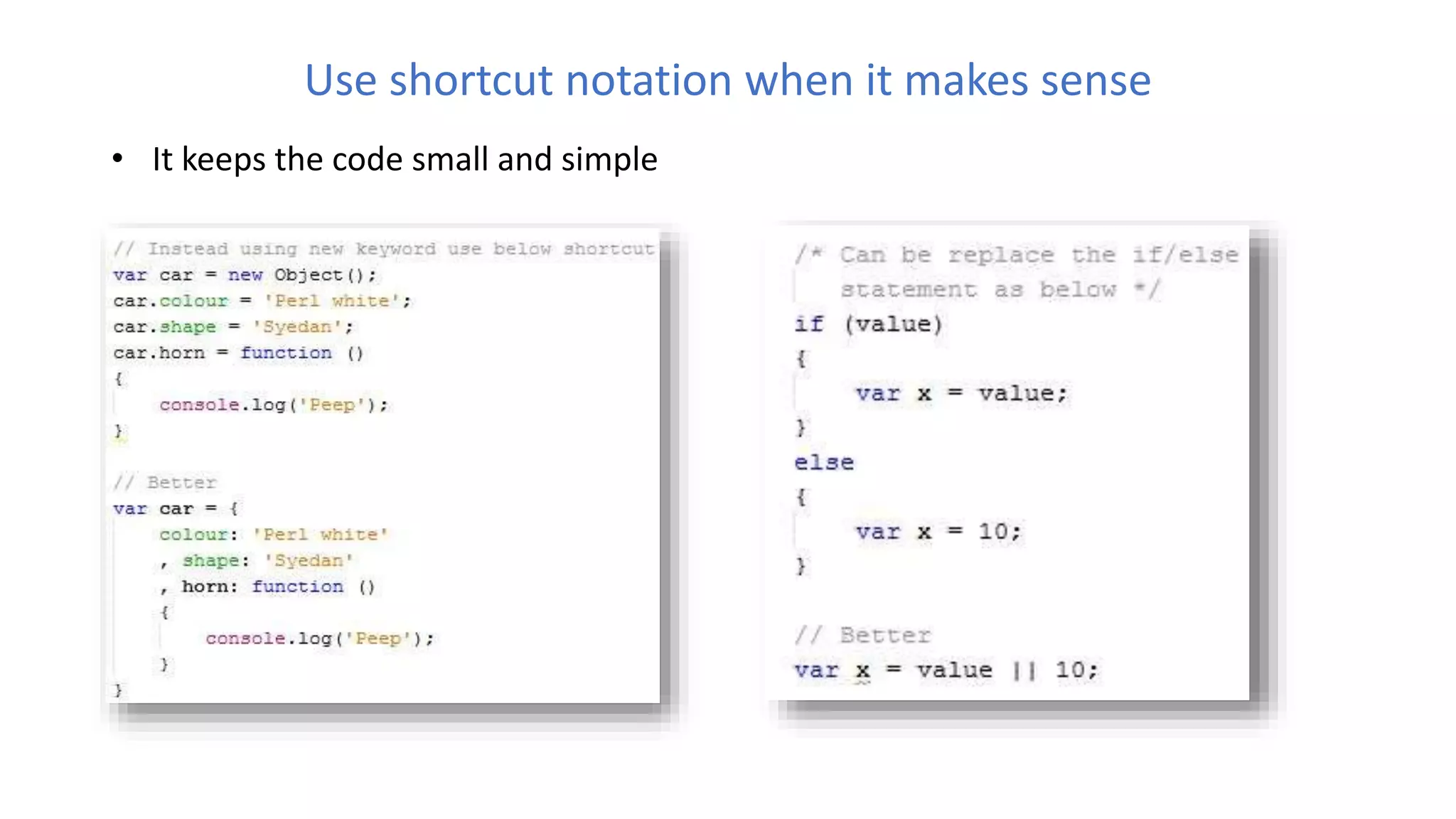
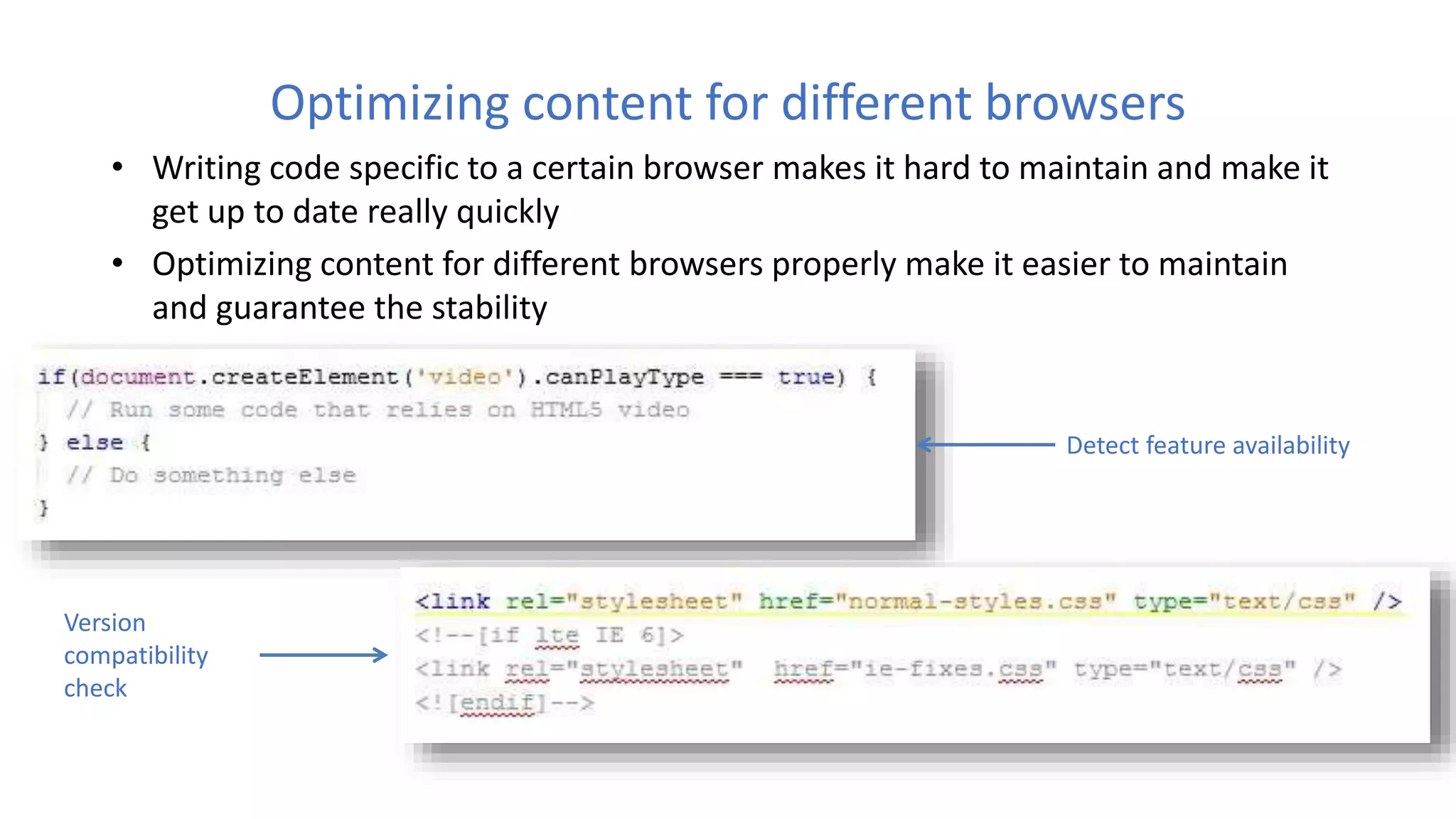
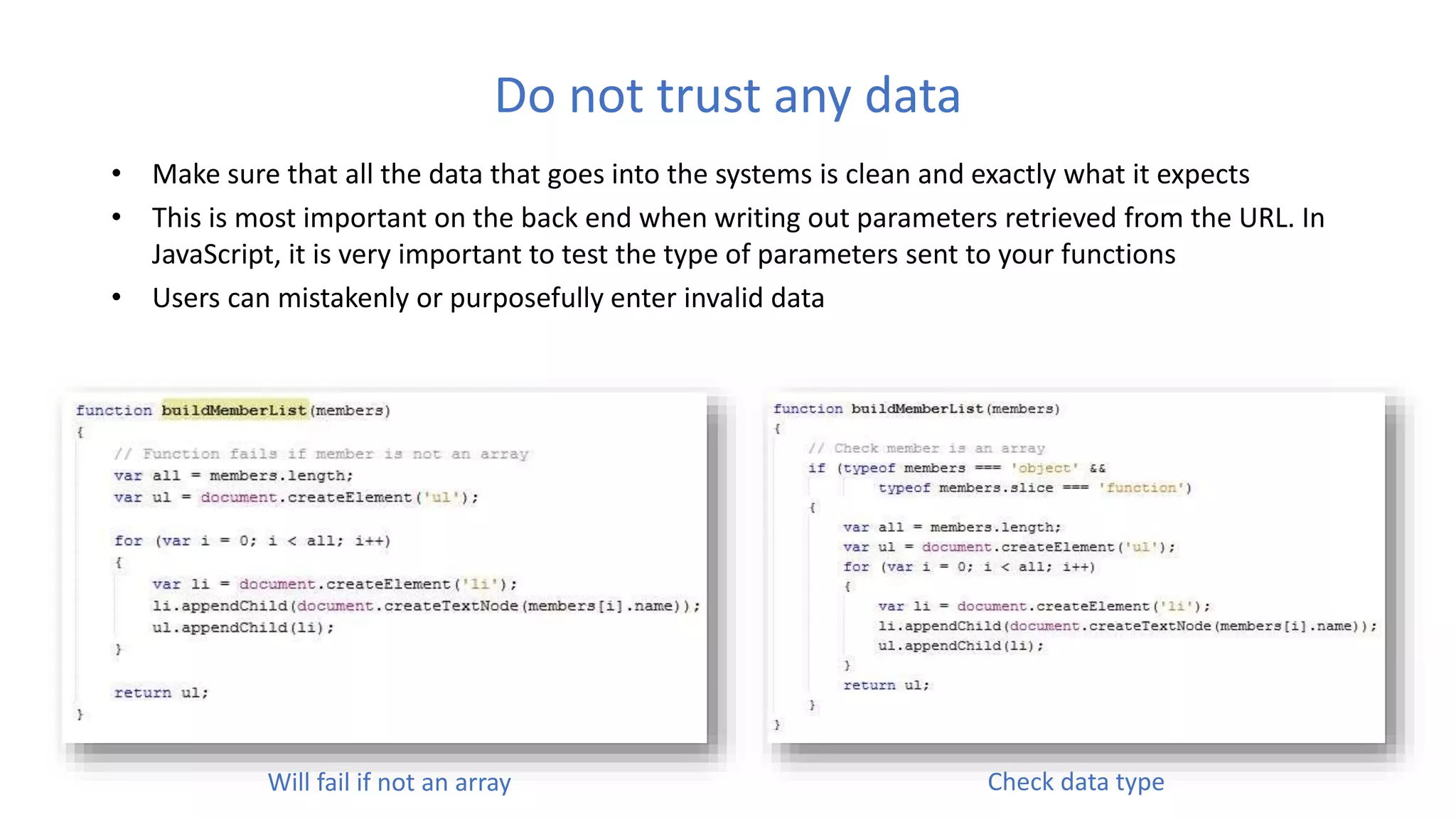
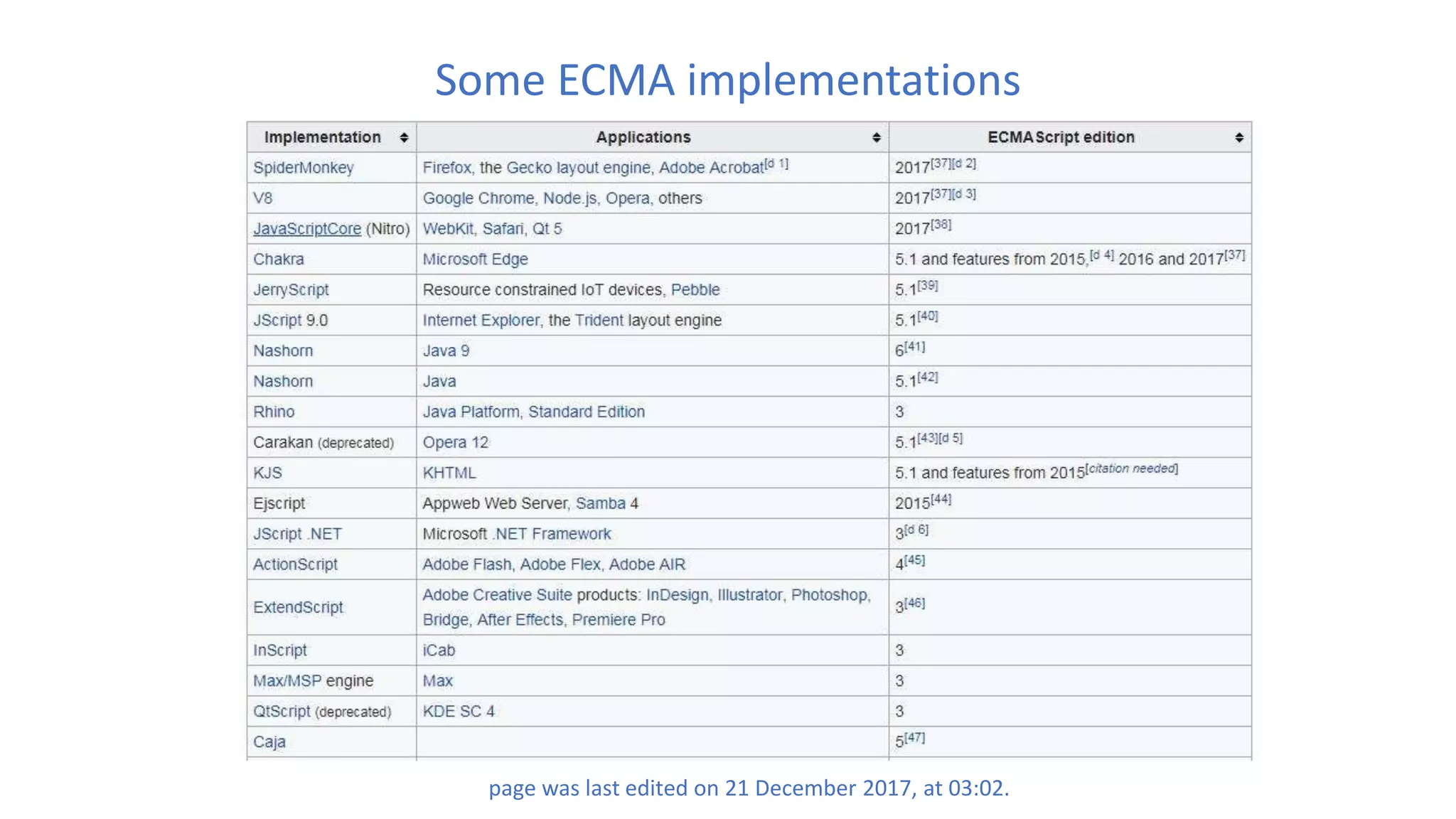
The document discusses various best practices for writing JavaScript code, including placing scripts at the bottom of pages, using meaningful variable and function names, avoiding global variables, and optimizing loops to minimize DOM access. It also covers JavaScript language features like namespaces, data types, and self-executing functions. Finally, it mentions tools for linting, minifying, and bundling code as well as popular integrated development environments for JavaScript development.