The document discusses React patterns and hooks. It covers topics like inheritance, composition, mixins, render props, higher order components (HOCs), and React hooks. Some key points:
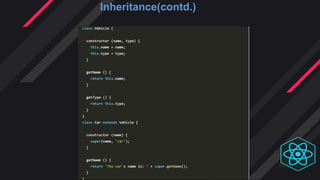
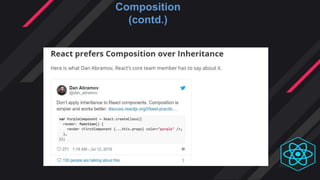
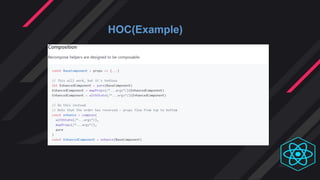
- Inheritance and composition are approaches to code reuse in object-oriented programming. React uses composition over inheritance.
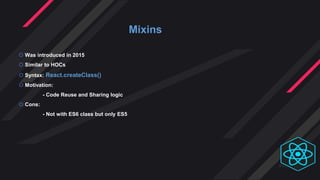
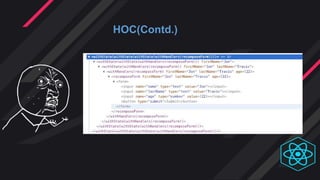
- Mixins were introduced in 2015 for code reuse but are now deprecated due to issues. Render props and HOCs are preferred patterns.
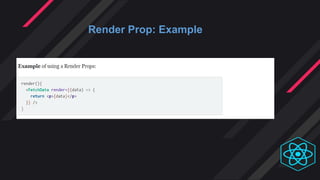
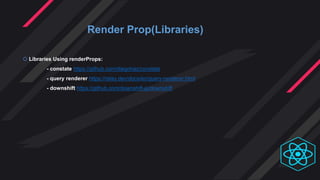
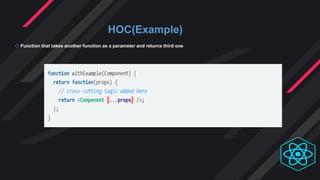
- Render props and HOCs allow code and state to be shared across components. Render props have fewer levels of nesting while HOCs are better for applying multiple concerns.
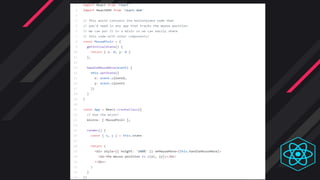
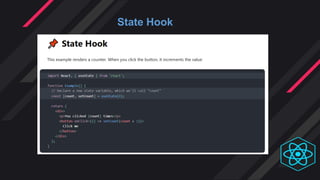
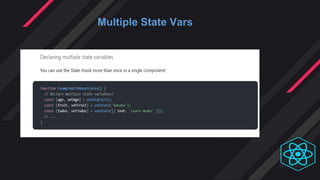
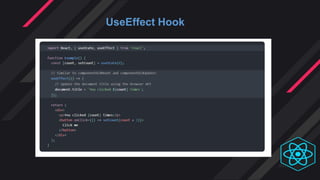
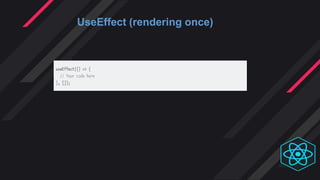
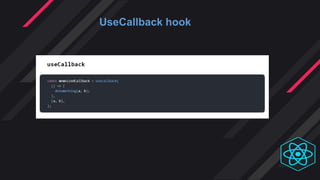
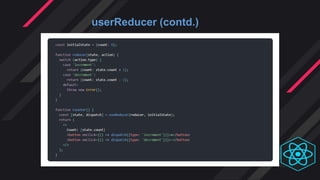
- Hooks were introduced to overcome class component limitations and support functional components with local state and lif