This document provides an introduction to JavaScript including:
- JavaScript is the most popular programming language for adding interactivity to web pages.
- It is embedded directly into HTML and is case-sensitive.
- JavaScript can change HTML content, attributes, styles, validate data, and display pop-ups.
- The <script> tag is used to insert JavaScript into HTML. Scripts can go in the head or body.
- External JavaScript files allow code reuse across pages and improve performance.
- JavaScript outputs can be written to alerts, the page, elements, and the console.
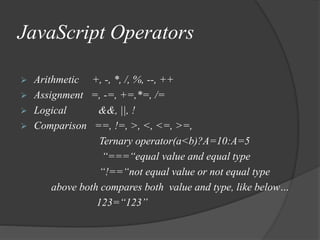
- Variables, data types, operators, functions, conditional statements, loops, arrays and events are also introduced.










![JavaScript Data Types
JavaScript variables can hold many data types.
String, Number, Boolean, Array, Object and more.
Used to be able to operate on variables.
Examples:
var length = 16; // Number
var lastName = "Johnson"; // String
var cars = [“Skoda", "Volvo", "BMW"]; // Array
var x = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe"}; // Object
var z= true; //Boolean](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-160216062449/85/Javascript-11-320.jpg)





![Arrays
Arrays are used to store multiple values in a single variable.
Array creation :
1. var team=new Array();
team[0]=“FTD";
team[1]=“Mercury";
2. var team=new Array(“FTD",“Mercury");
3. var team=[“ftd",“Mercury“];
Access an Array: we can access array elements by using name of
the array and index value.
Array methods : length, sort and etc …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-160216062449/85/Javascript-19-320.jpg)








