The document discusses key aspects of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). It covers:
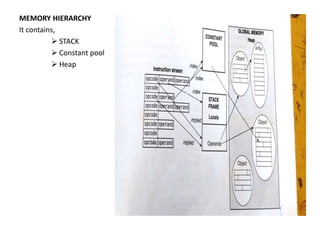
1) Data types and storage on the JVM including primitive types, objects, arrays, stacks, and heaps.
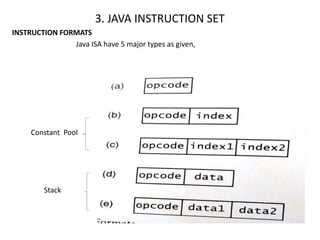
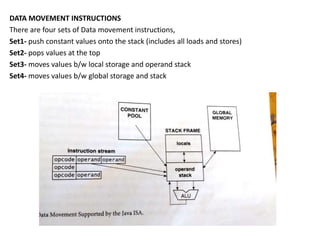
2) The Java instruction set which includes data movement, type conversion, control flow, and exception handling instructions.
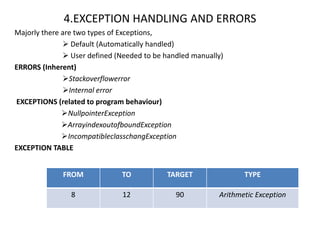
3) How exceptions and errors are handled on the JVM through an exception table.
4) How classes are stored as binary classes in class files for efficient loading.
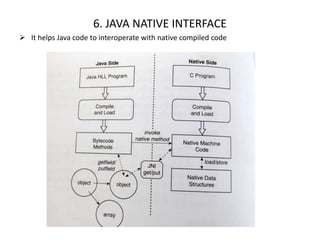
5) The Java Native Interface which allows Java code to interact with native compiled code.