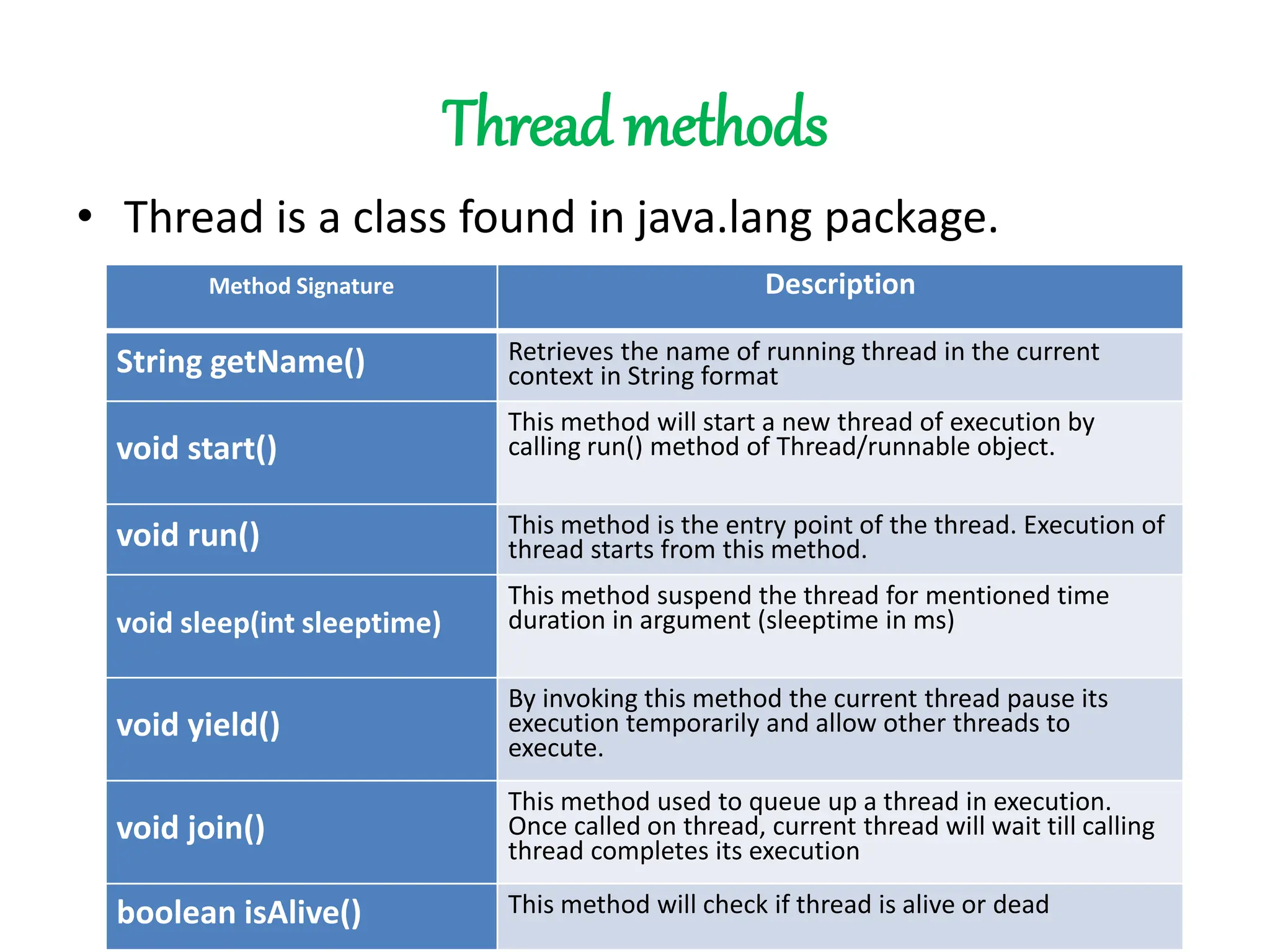
This document discusses multithreading in Java. It covers the creation of threads by extending the Thread class or implementing the Runnable interface. The life cycle of a thread is described including states like newborn, runnable, running, blocked, and dead. Common thread methods like start(), run(), sleep(), yield(), join(), isAlive() are outlined. Finally, ways to stop a thread using stop() and block a thread using sleep(), suspend(), and wait() are explained.





![CREATINGTHREAD
1. By Extending Thread class
class Multi extends Thread // Extending thread class
{
public void run() // run() method declared
{
System.out.println("thread is running...");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Multi t1=new Multi(); //object initiated
t1.start(); // run() method called through start()
}
}
Output: thread is running…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javatheoryppt-240320134123-d7ef49f0/75/JAVA-THEORY-PPT-pptx-on-based-up-on-the-transaction-7-2048.jpg)

![CREATINGTHREAD
2. By implementing Runnable interface
class Multi3 implements Runnable // Implementing Runnable interface
{
public void run()
{
System.out.println("thread is running...");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Multi3 m1=new Multi3(); // object initiated for class
Thread t1 =new Thread(m1); // object initiated for thread
t1.start();
} }
Output: thread is running…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javatheoryppt-240320134123-d7ef49f0/75/JAVA-THEORY-PPT-pptx-on-based-up-on-the-transaction-9-2048.jpg)