This document outlines the principles of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java, detailing key concepts such as objects, classes, inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation. It explains the differences between object-oriented and object-based programming languages, provides naming conventions for various components, and discusses methods, constructors, and their features including method and constructor overloading. The document also elaborates on how objects are created and the roles of classes in Java programming.








![Annonymous object
⚫ Annonymous simplymeans nameless.An object that have no reference is
known asannonymous object.If you haveto use an object only once,
annonymous object is agood approach.
class Calculation{
void fact(int n){
int fact=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
fact=fact*i;
}
System.out.println("factorial is "+fact);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
new Calculation().fact(5);/ / calling method with annonymous object
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapptoops-240712111756-79545003/85/Java-PPT-OOPS-prepared-by-Abhinav-J-pptx-12-320.jpg)


![WhyMethodOverloadingisnot possible bychangingthe
return type of method?
⚫In java,method overloading is not possible bychanging the
return type of the method becausethere mayoccur ambiguity
.
Let's seehowambiguitymayoccur: becausethere was
problem:
⚫ class Calculation{
int sum(int a,int b){System.out.println(a+b);}
double sum(int a,int b){System.out.println(a+b);}
public static void main(String args[]){
Calculation obj=new Calculation();
int result=obj.sum(20,20);//CompileTime Error
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapptoops-240712111756-79545003/85/Java-PPT-OOPS-prepared-by-Abhinav-J-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![Can we overload main() method?
⚫Yes, by method overloading.You can have any number of main
methods in aclass by method overloading. Let's see the simple
example:
class Simple{
public static void main(int a){
System.out.println(a);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("main() method invoked");
main(10);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapptoops-240712111756-79545003/85/Java-PPT-OOPS-prepared-by-Abhinav-J-pptx-16-320.jpg)
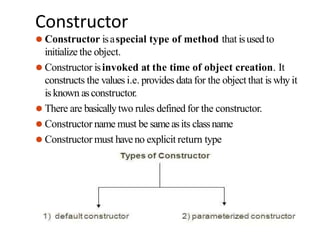

![Constructor Overloading
class Student{
int id;
String name;
int age;
Student(int i,String n){
id = i;
name = n;
}
Student(int i,String n,int a){
id = i;
name = n;
age=a;
}
void display(){System.out.println(id+" "+name+" "
+age);}
public static void main(String args[]){
Student s1 = new Student(111,“T
arif");
Student s2 = new Student(222,“Soheab",25);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}
Constructor overloadingisatechnique in Javain whichaclasscanhaveanynumber of
constructors that differ in parameter lists.The compiler differentiatesthese constructors by
taking into account the number of parametersin the list and their type.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapptoops-240712111756-79545003/85/Java-PPT-OOPS-prepared-by-Abhinav-J-pptx-19-320.jpg)