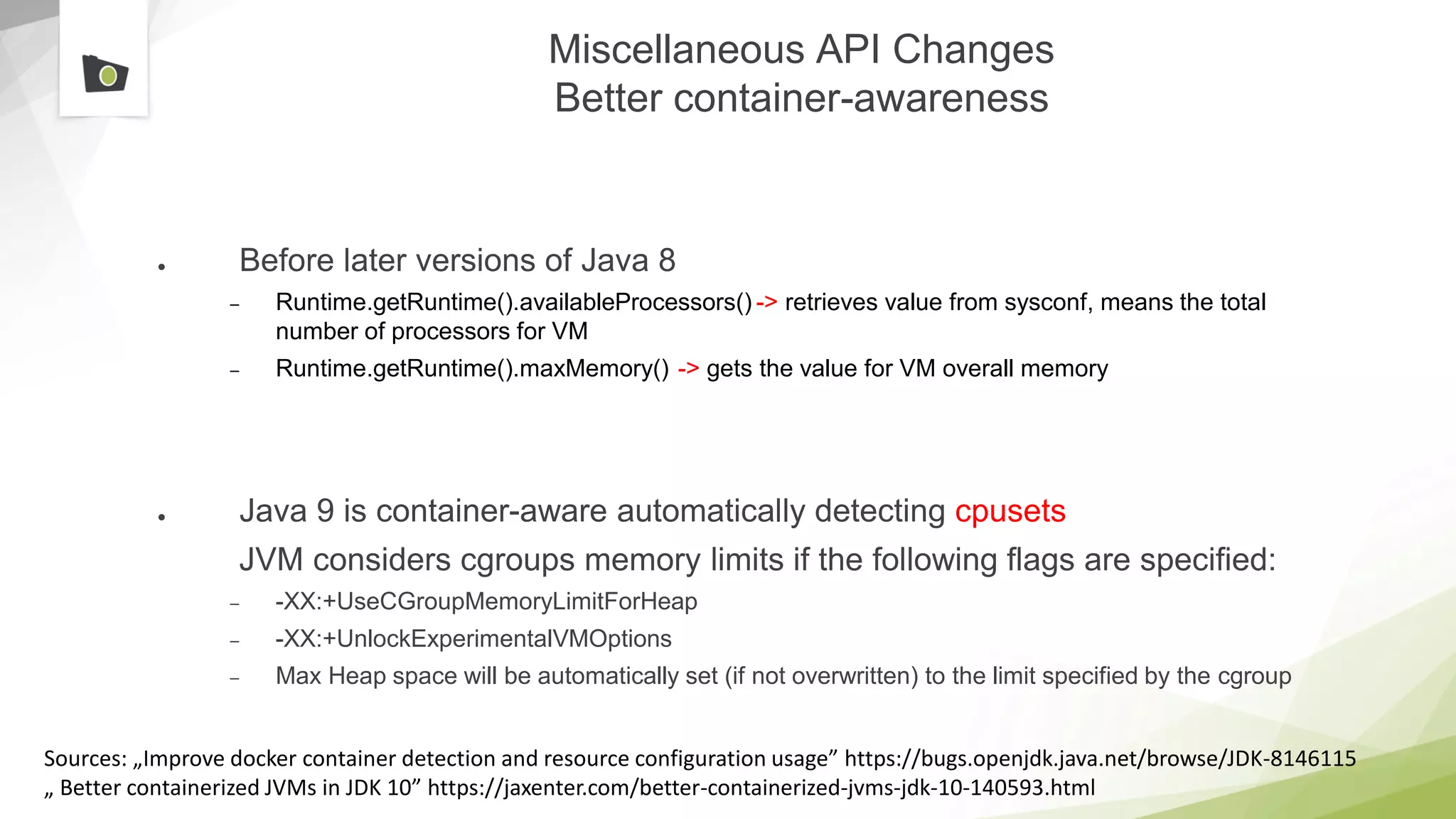
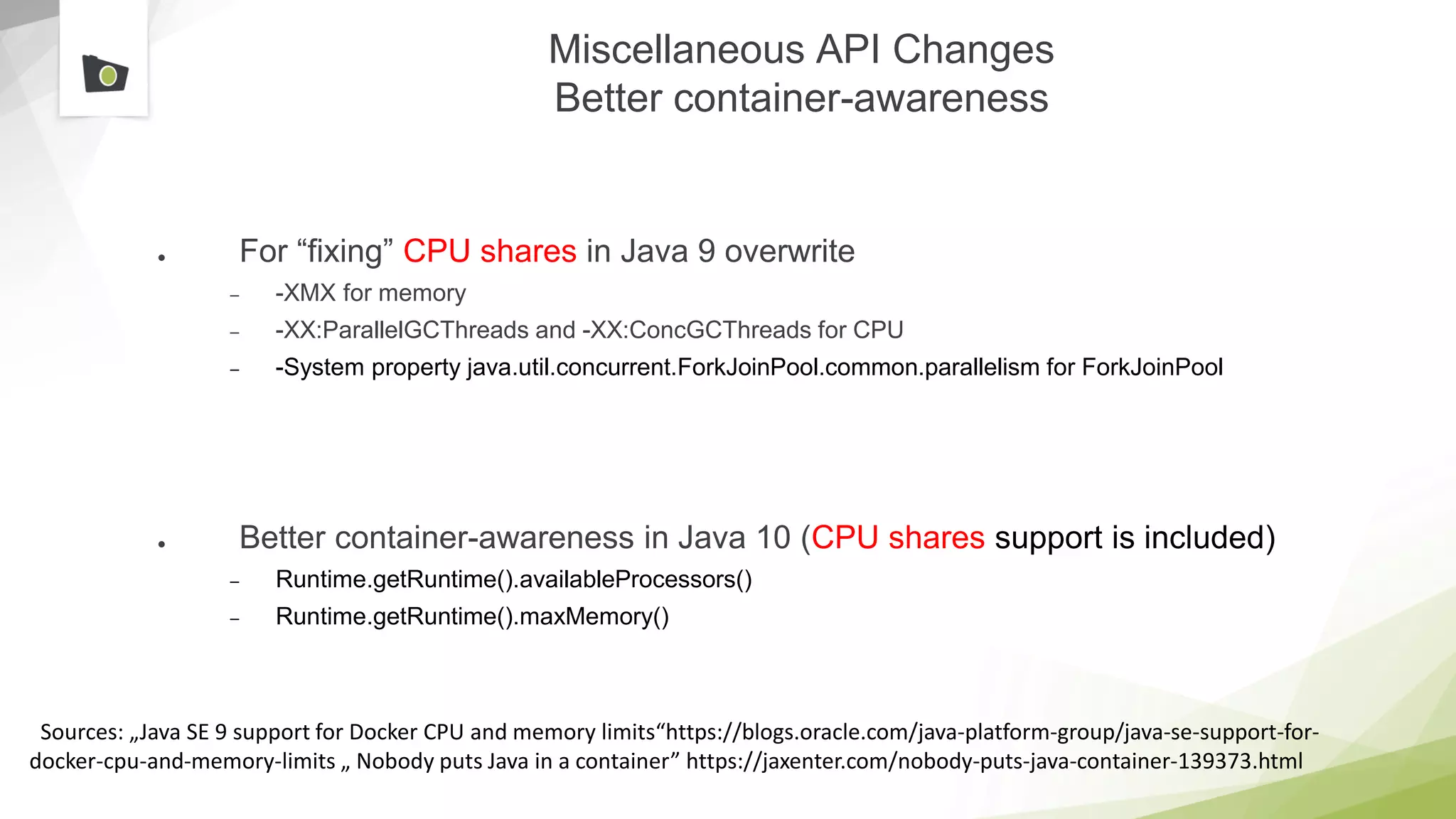
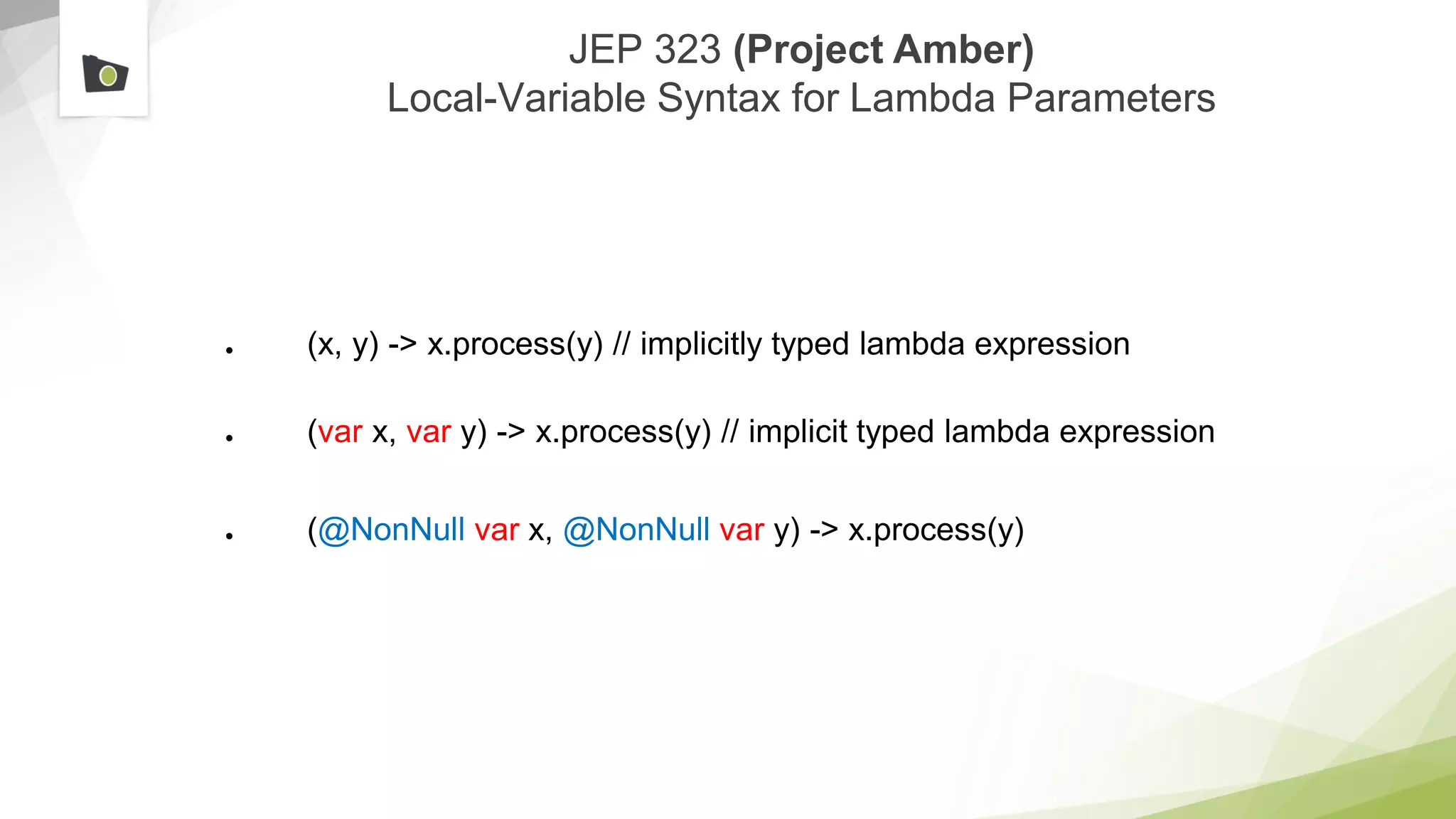
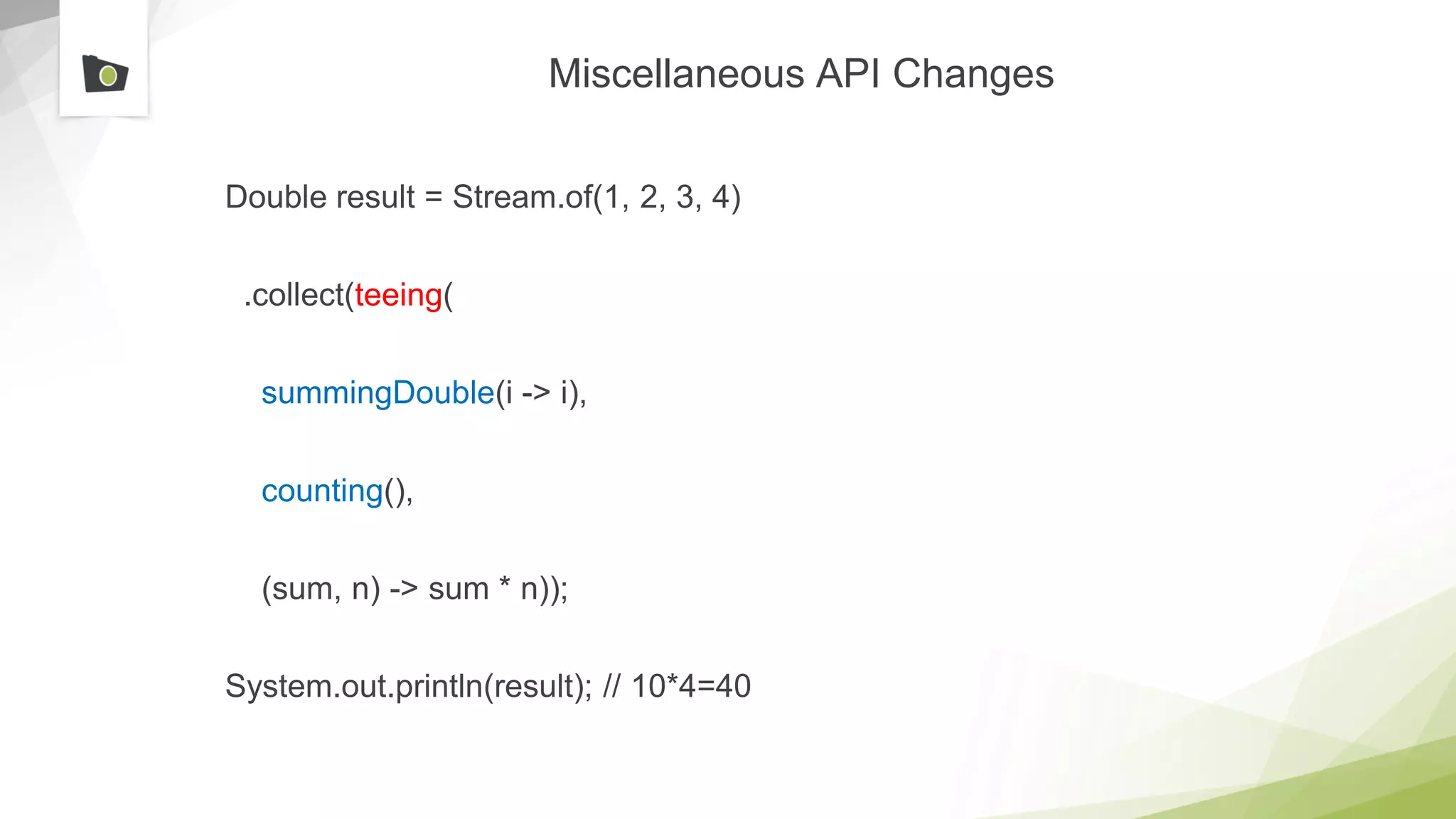
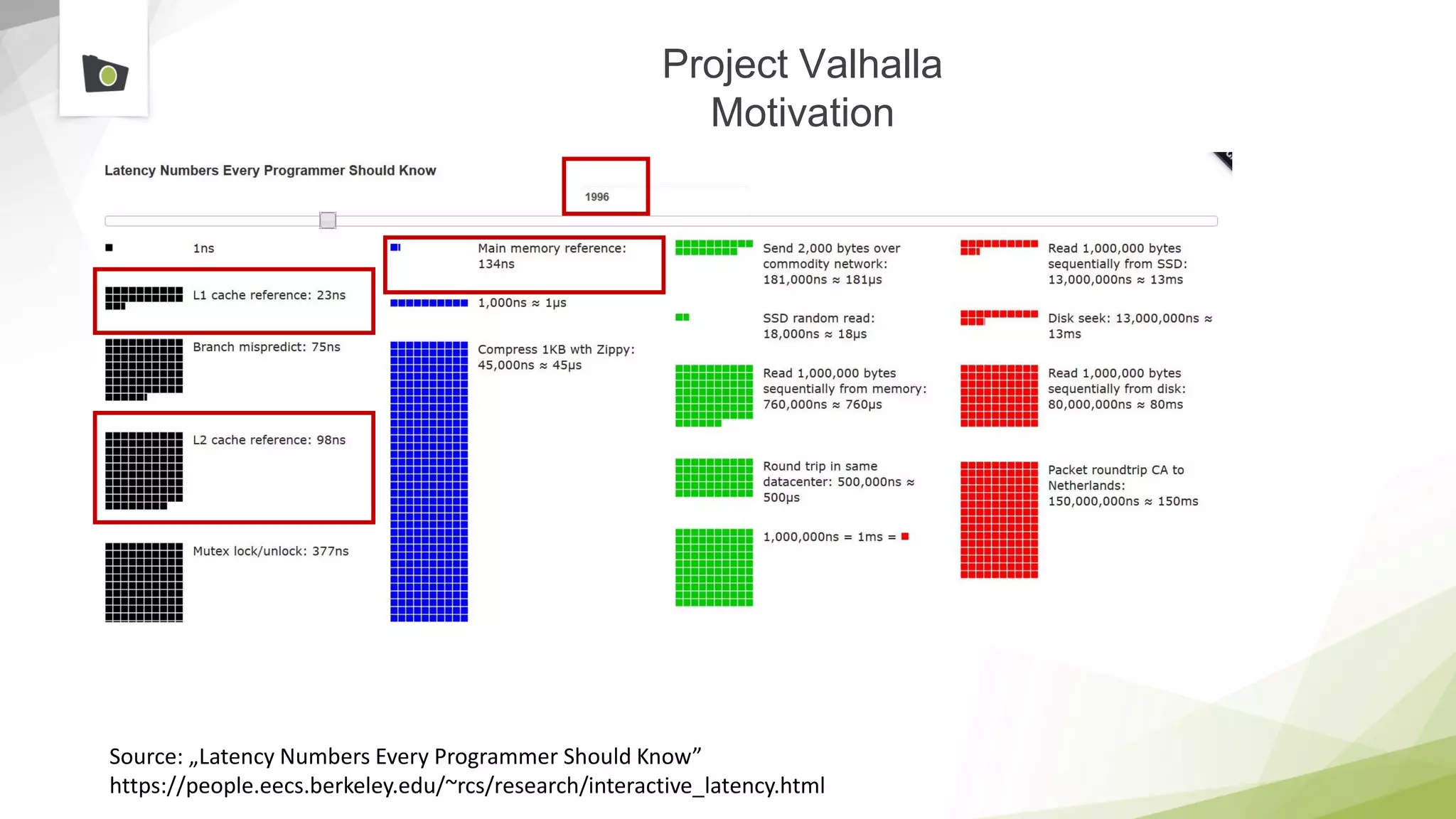
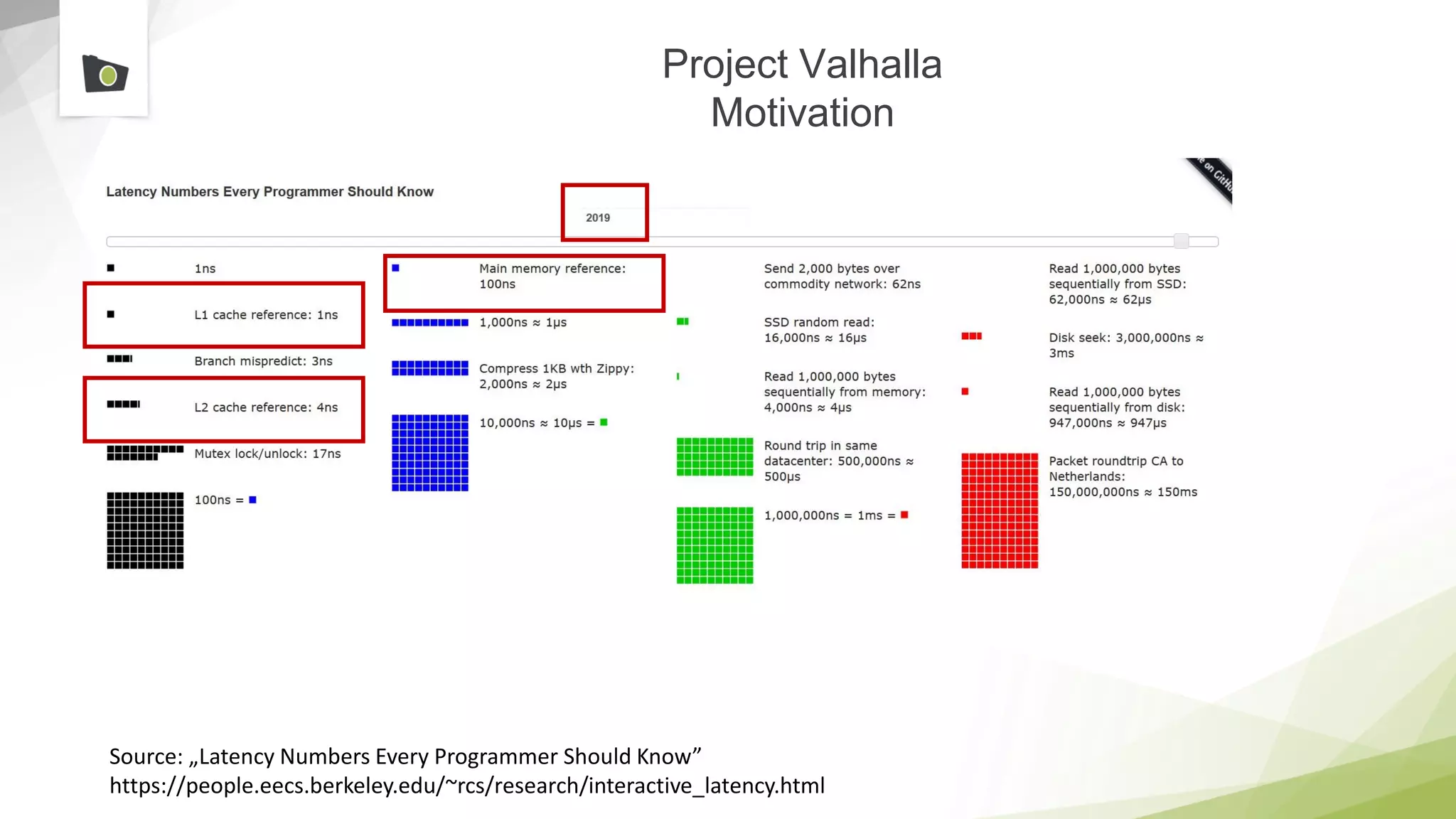
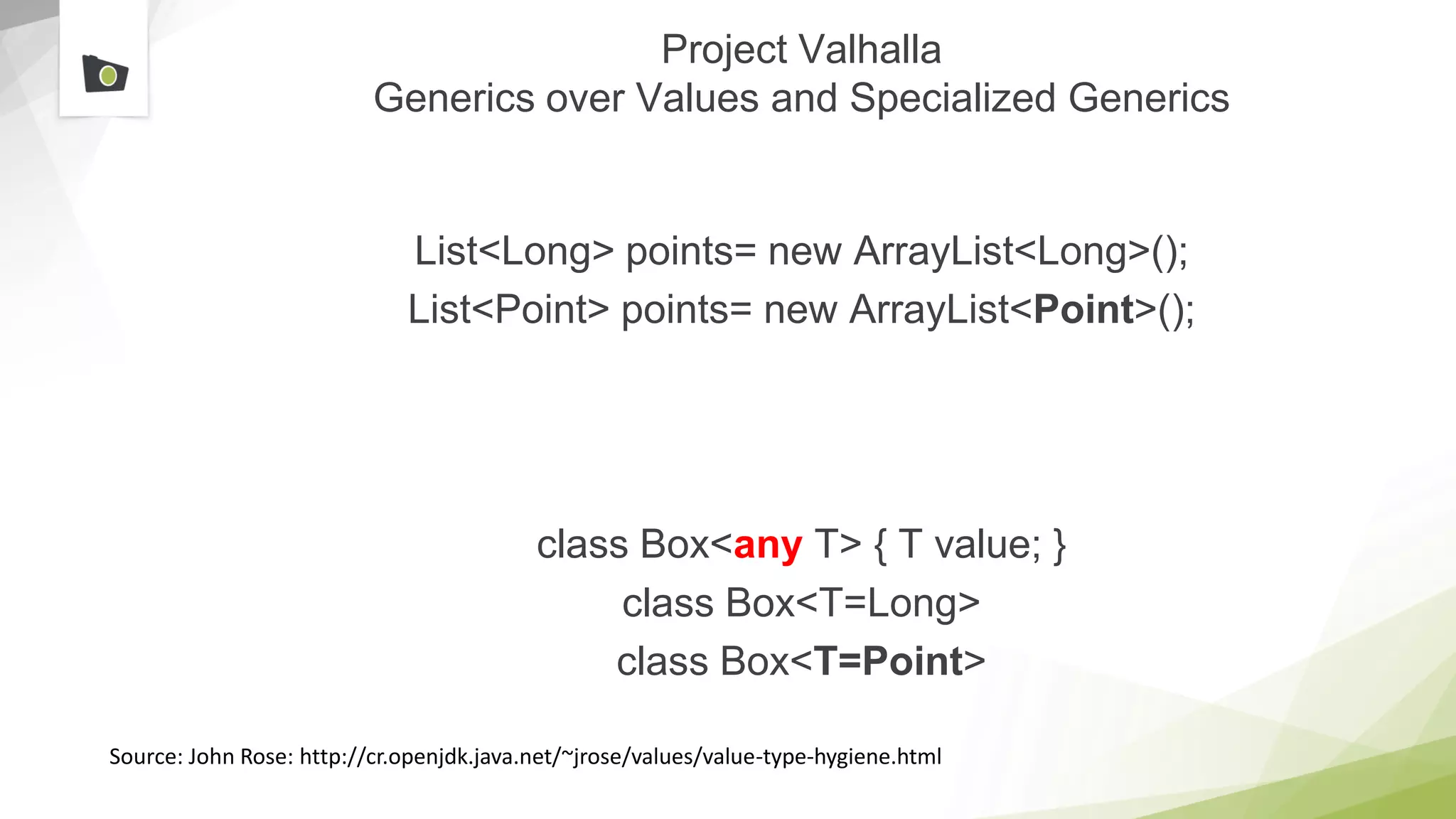
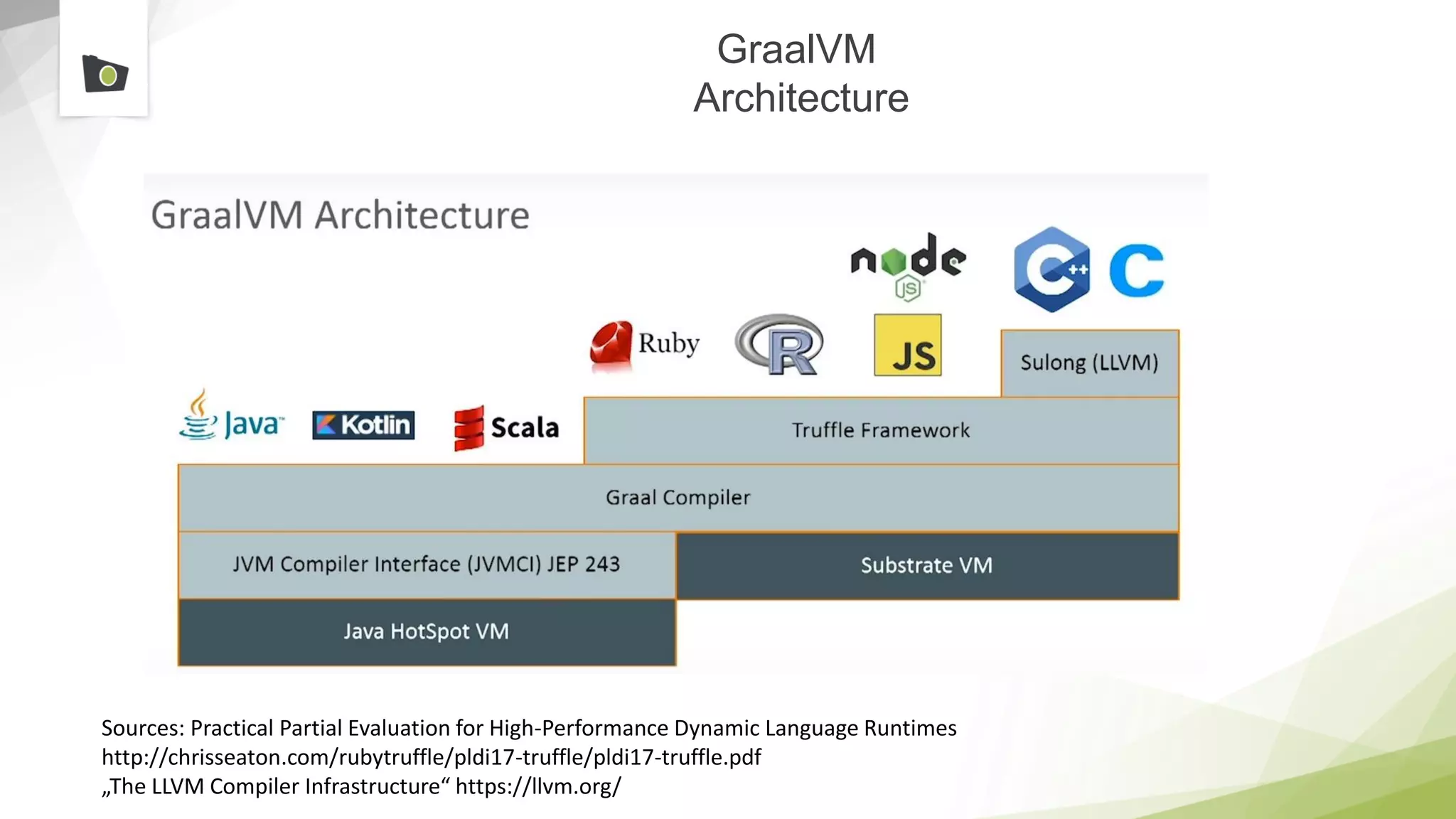
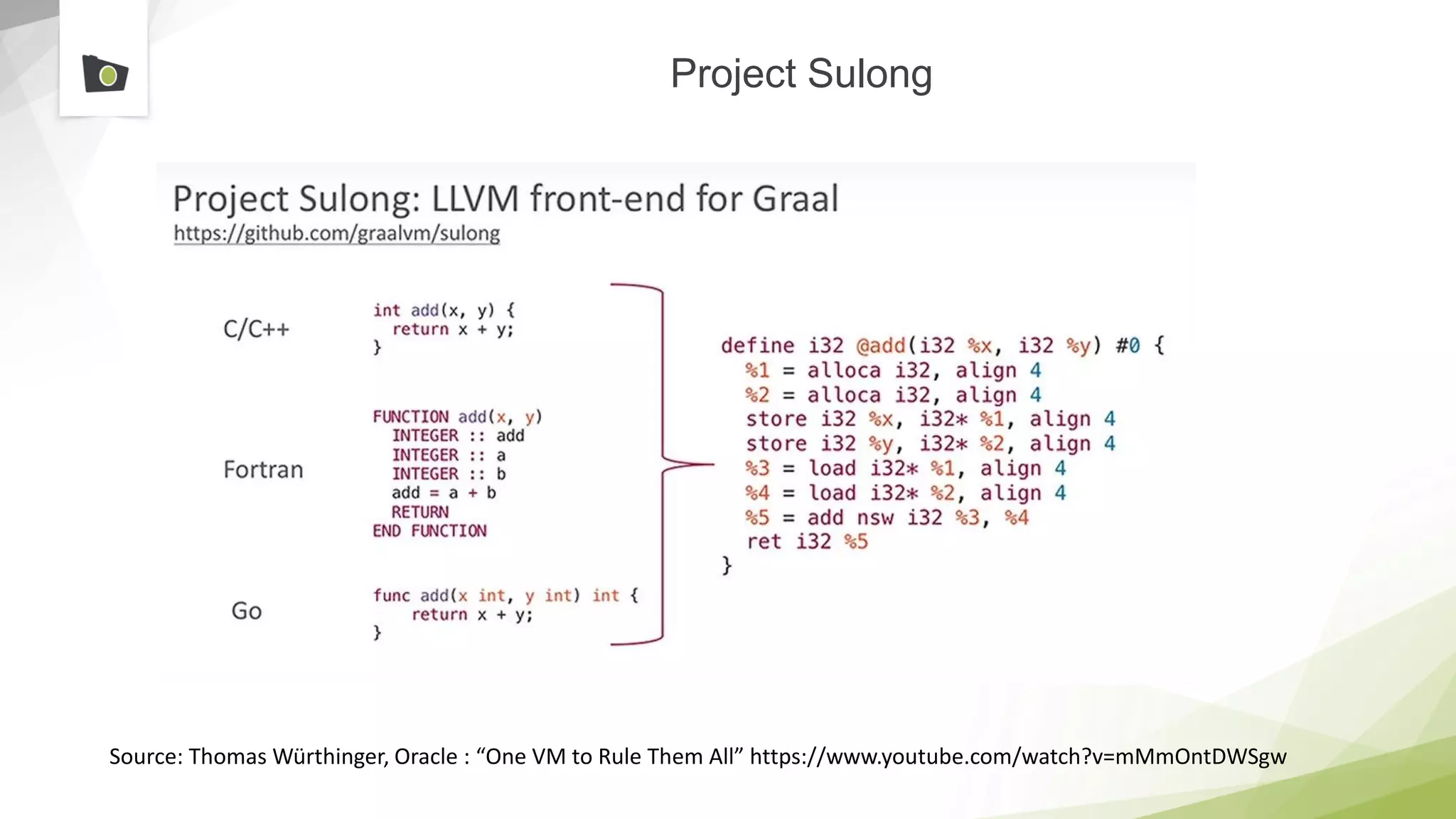
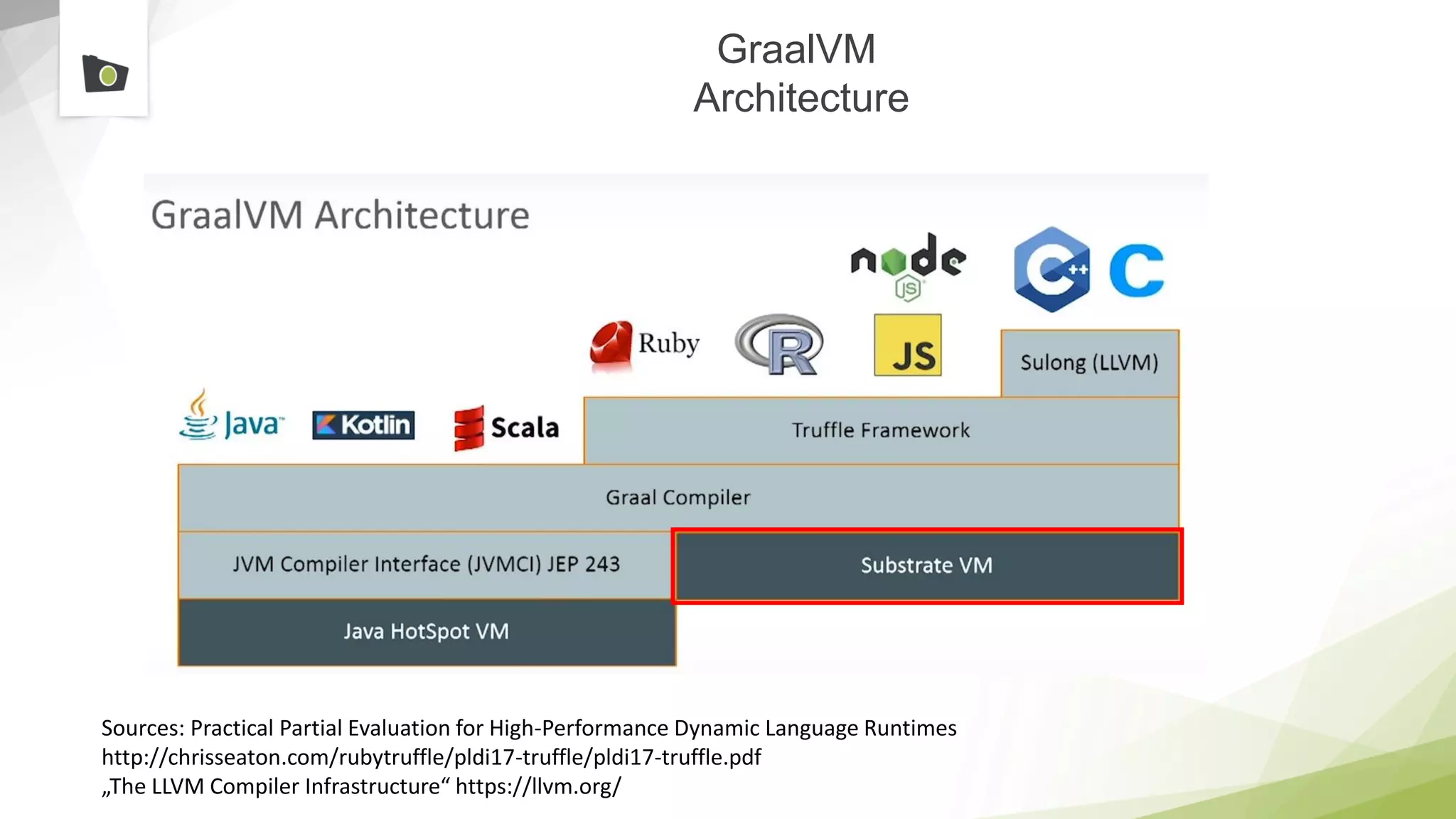
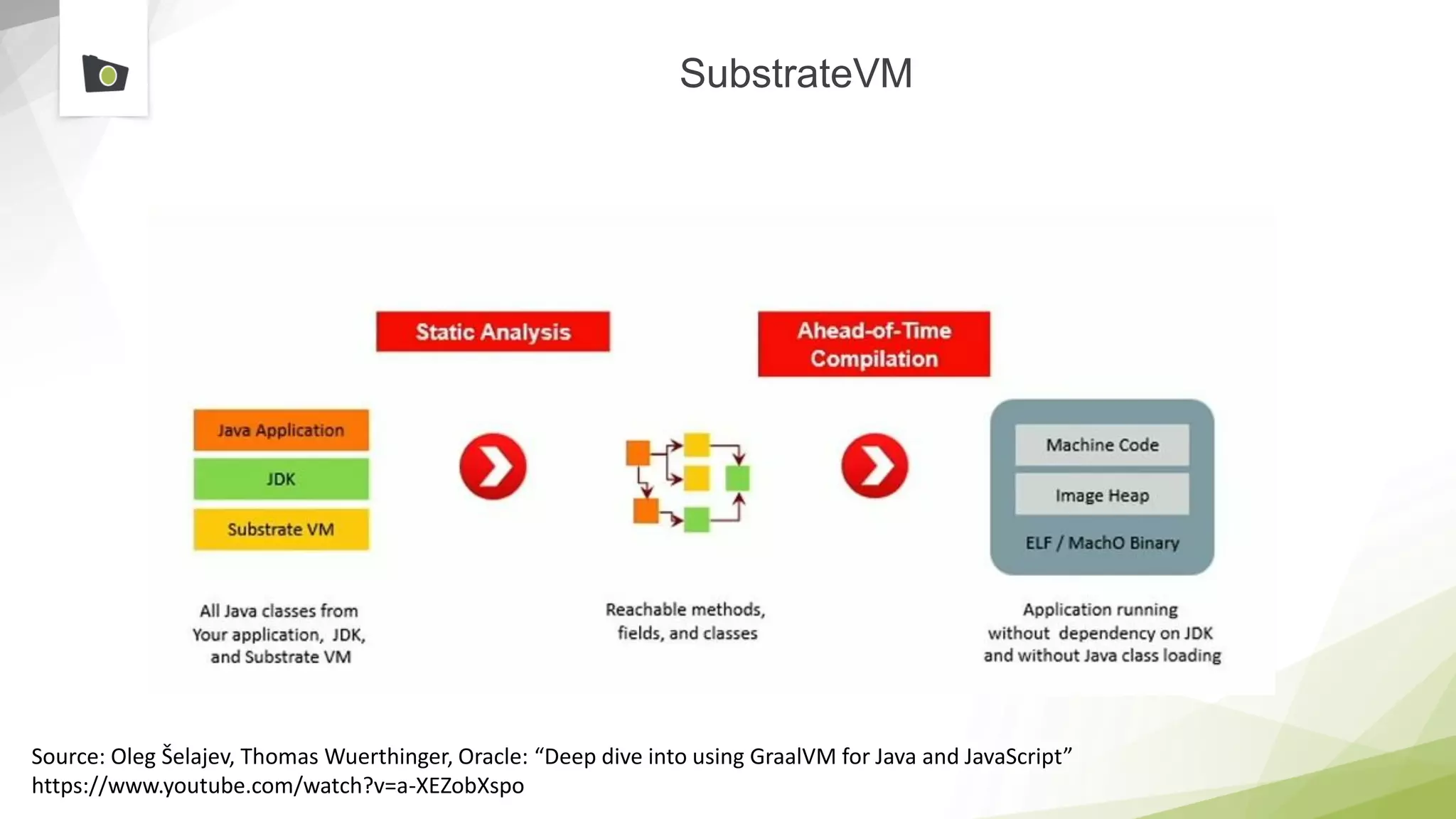
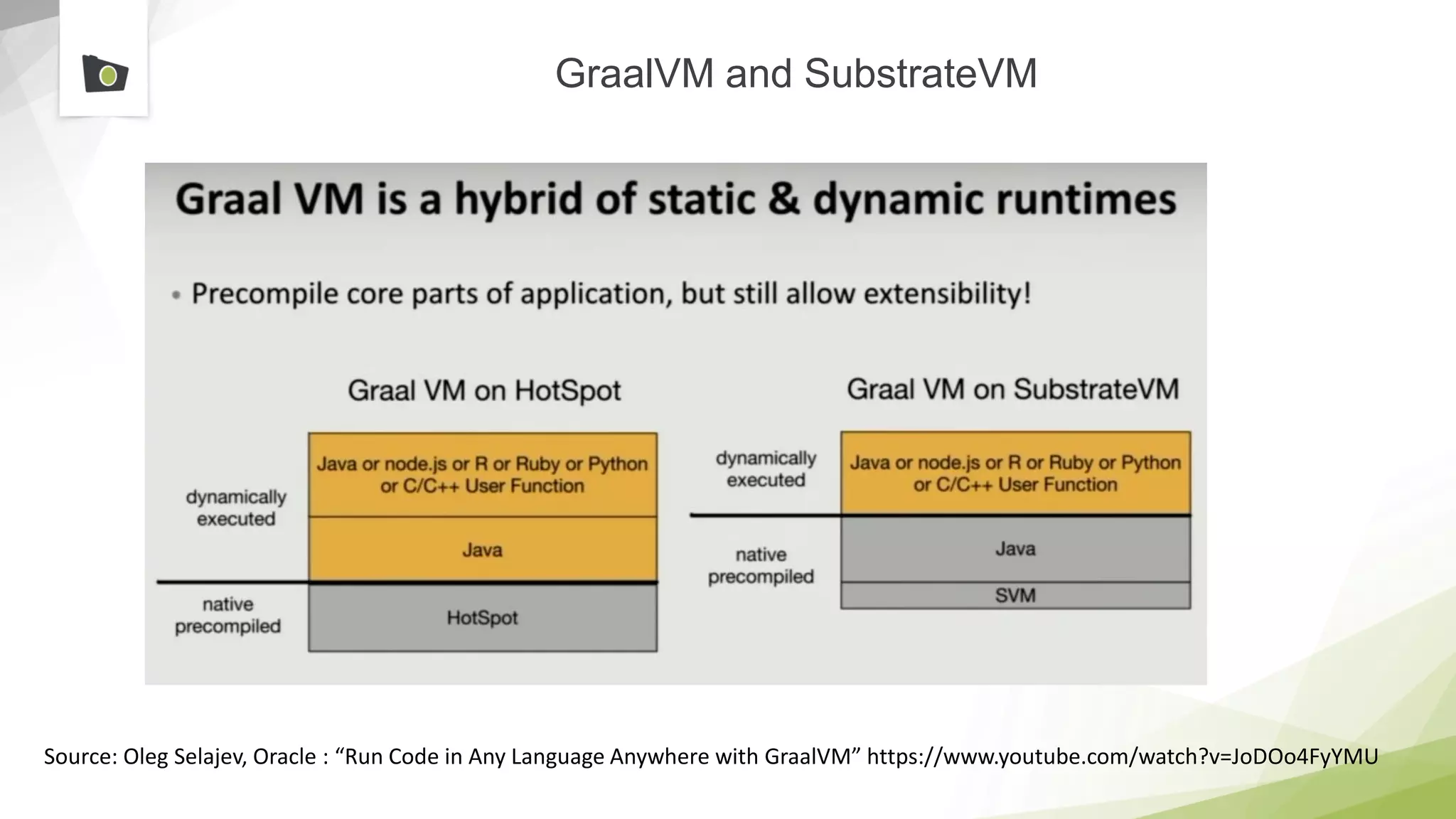
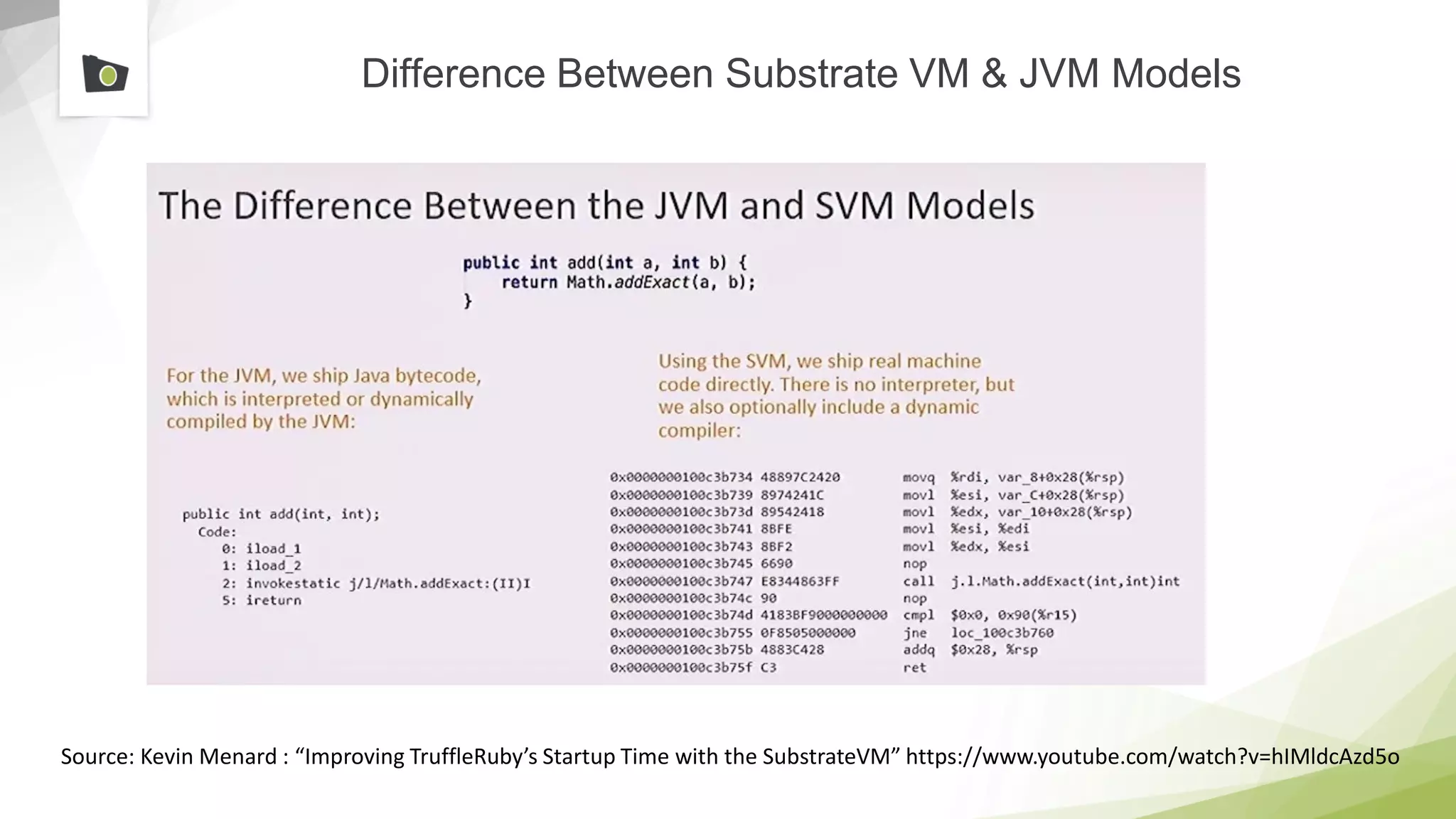
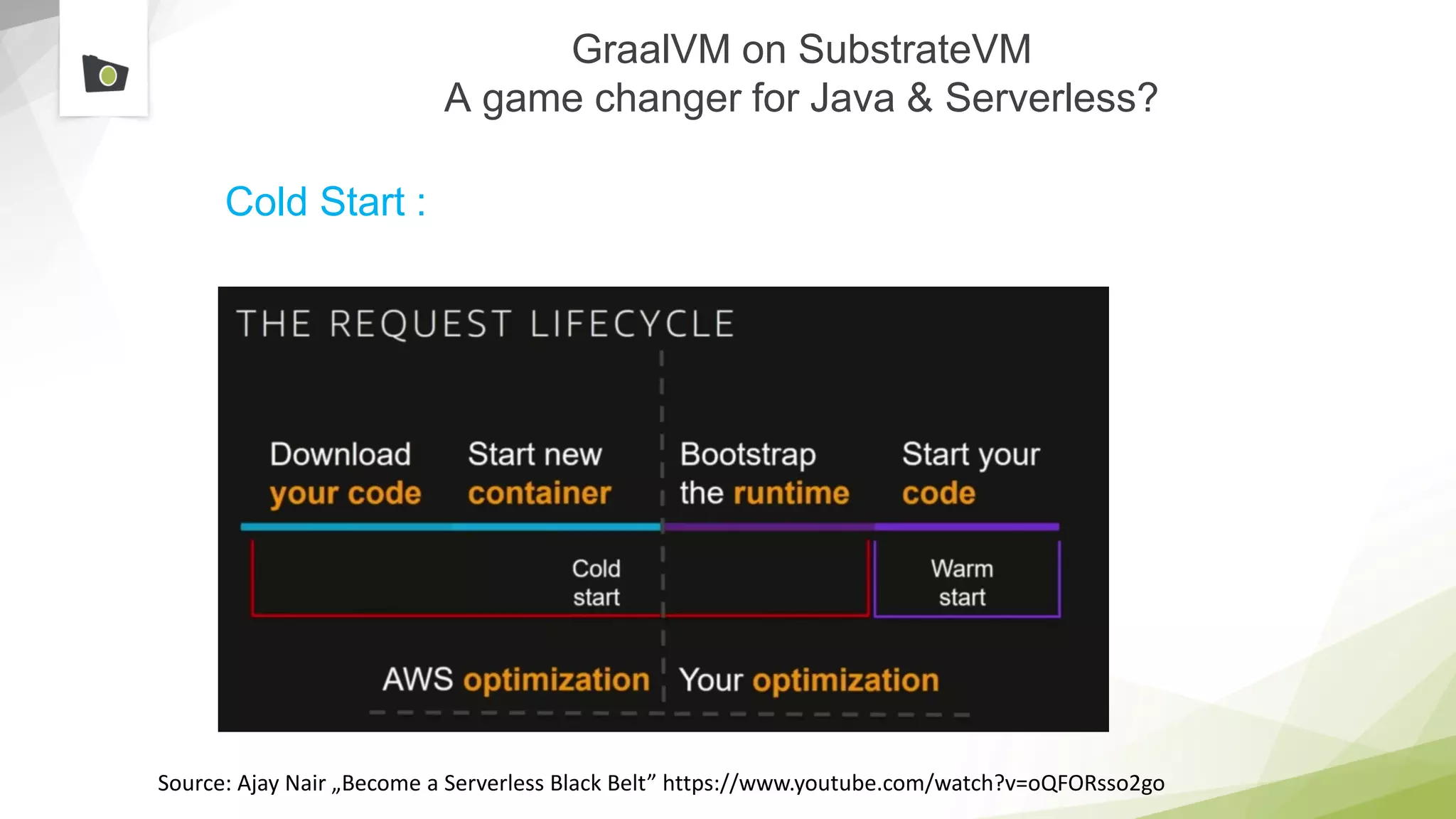
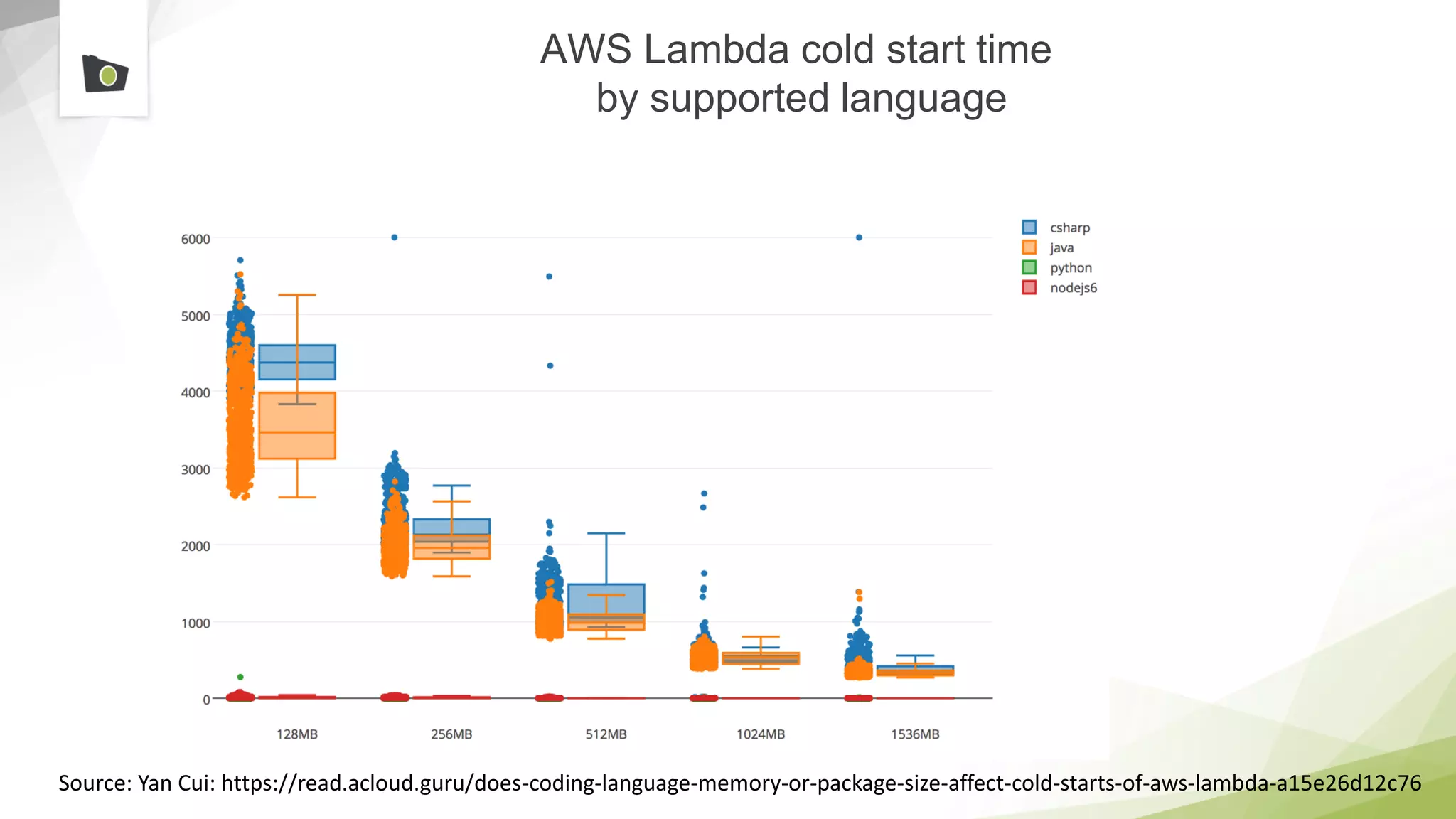
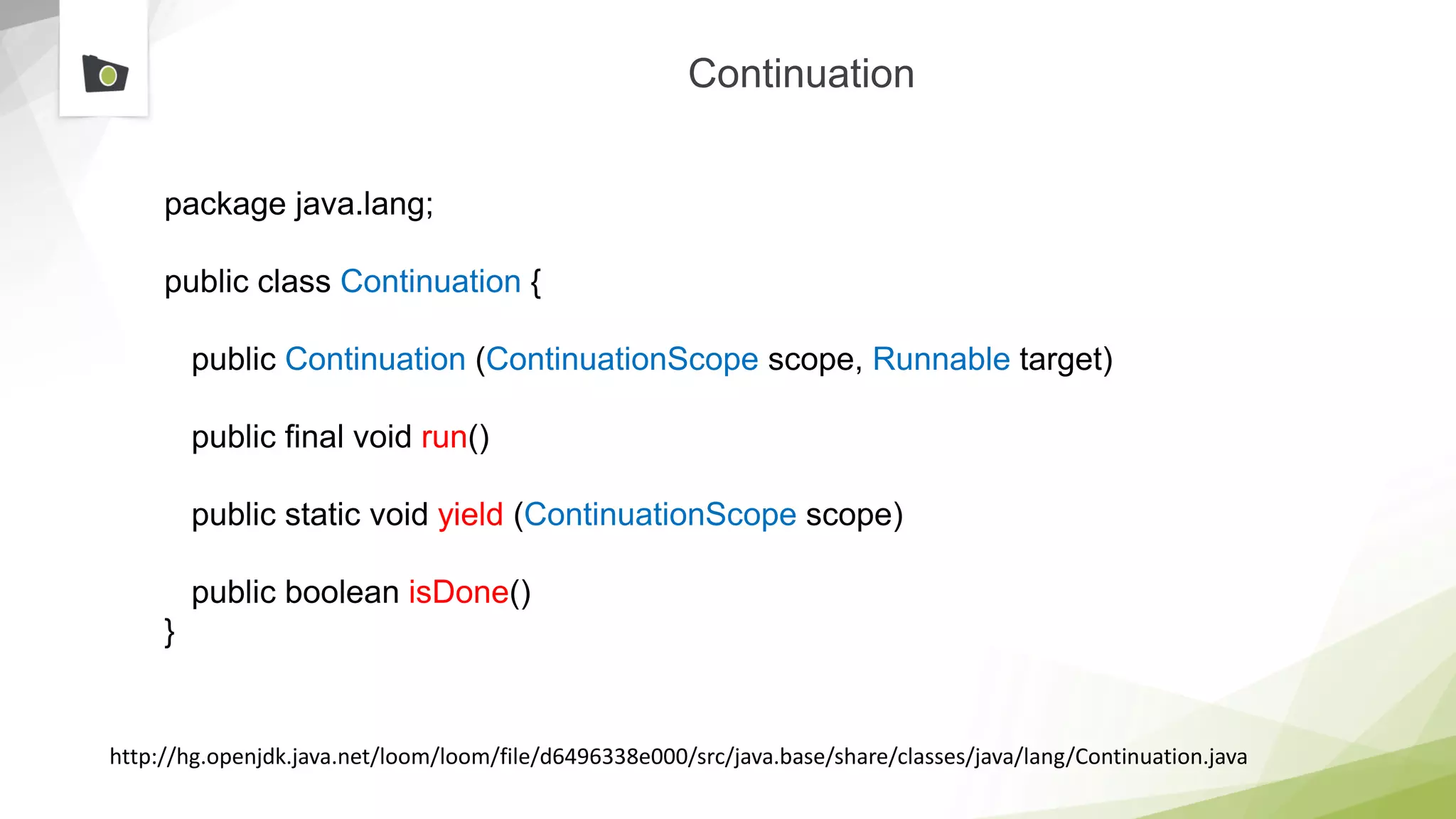
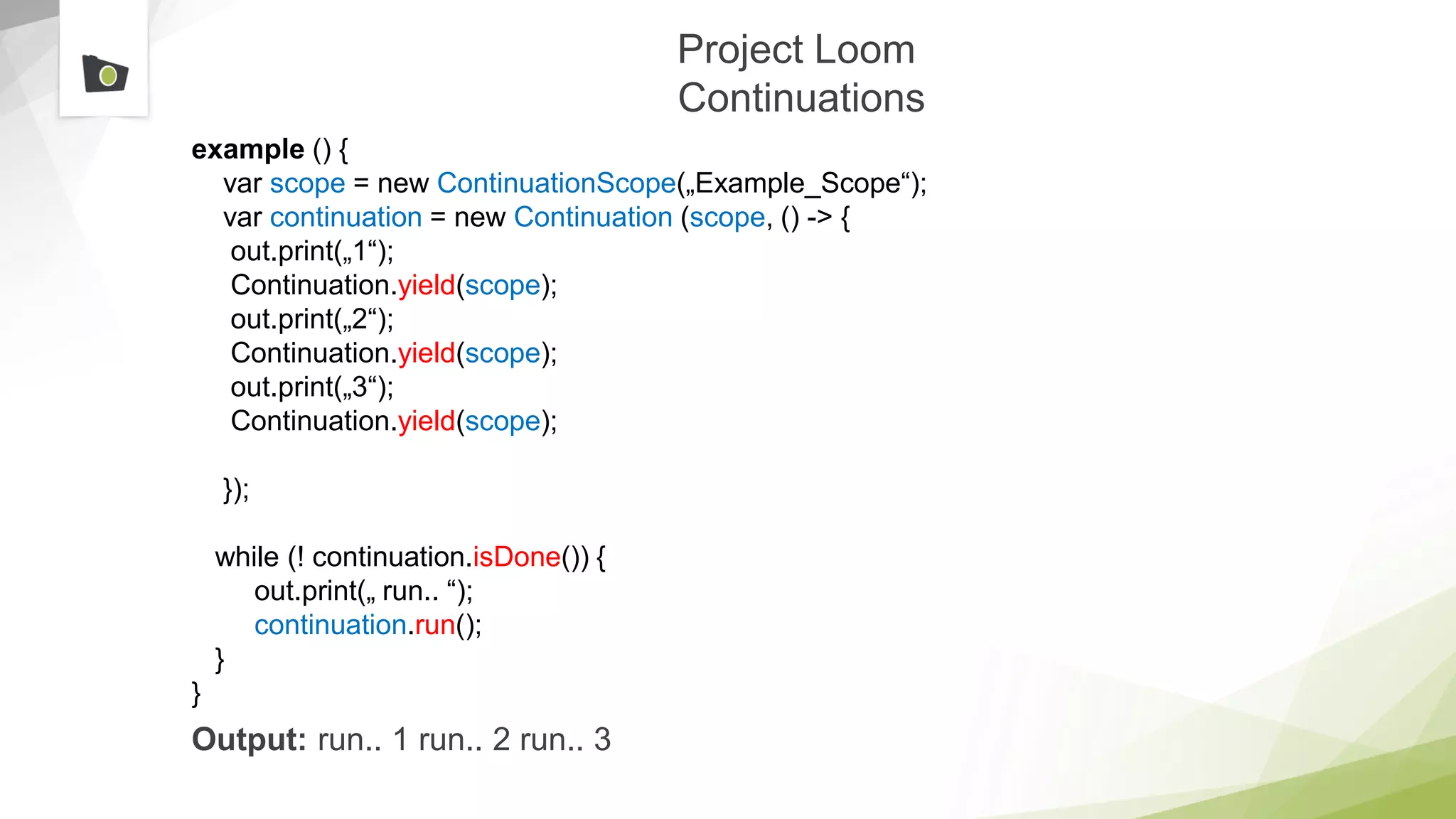
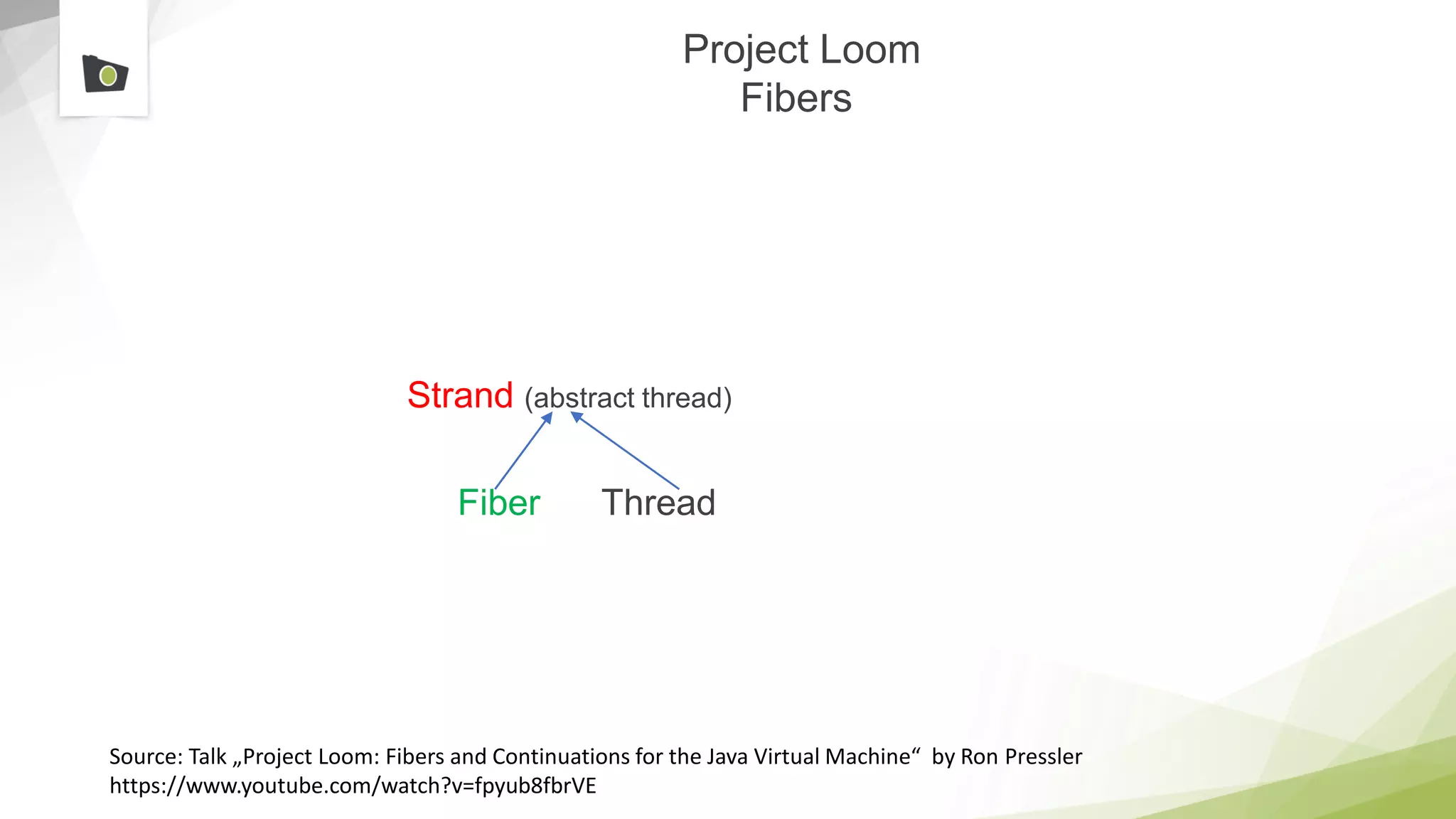
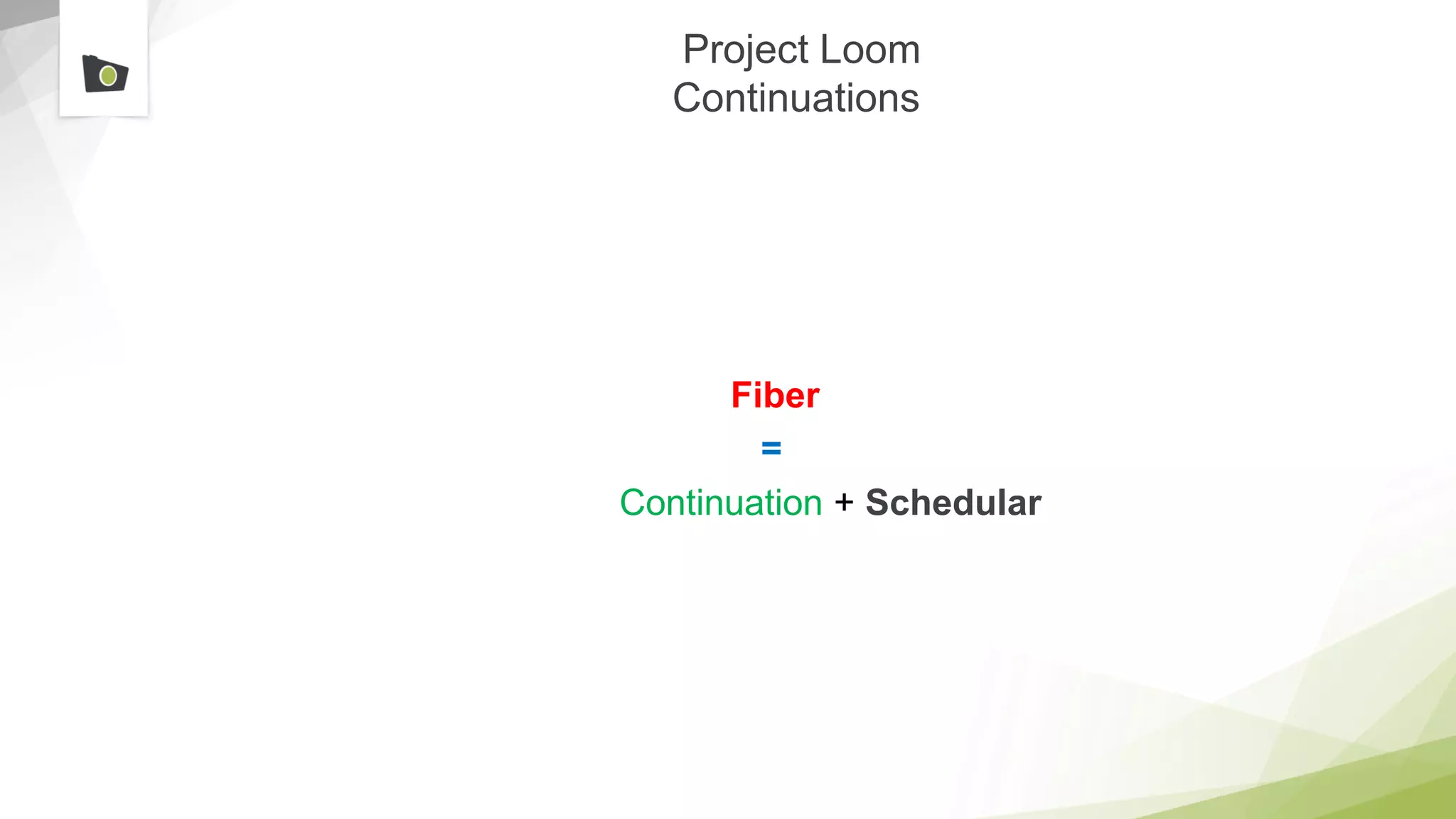
The document outlines the highlights and features introduced in Java versions 10, 11, and 12, along with future developments planned in Java, such as Project Amber, Project Valhalla, and Project Loom. It covers new syntax simplifications, updates to the garbage collector, enhancements to the HTTP client API, and experimental garbage collectors like Shenandoah. Additionally, it discusses the motivations and goals behind upcoming projects aimed at improving Java's efficiency, interoperability, and usability.