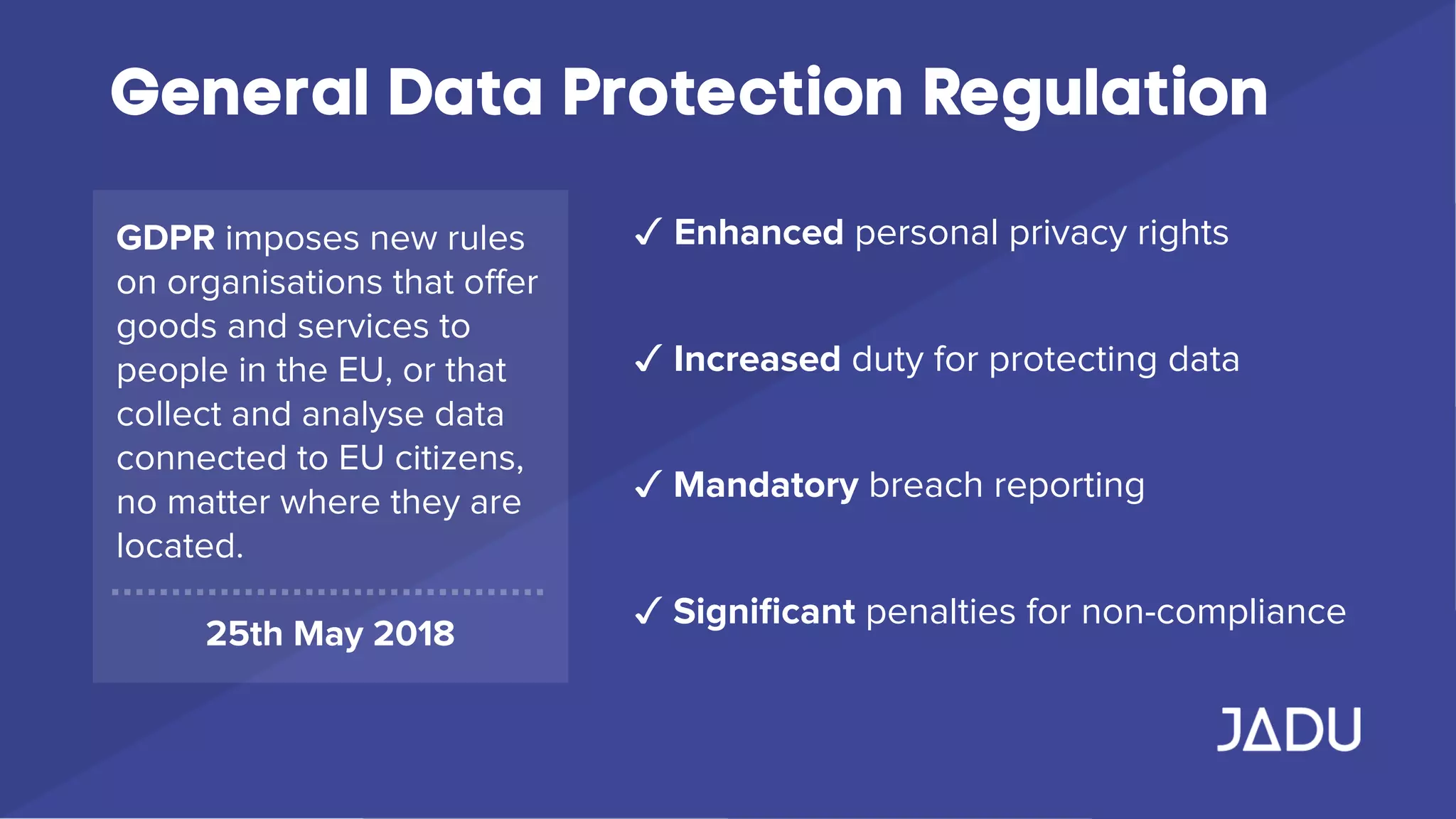
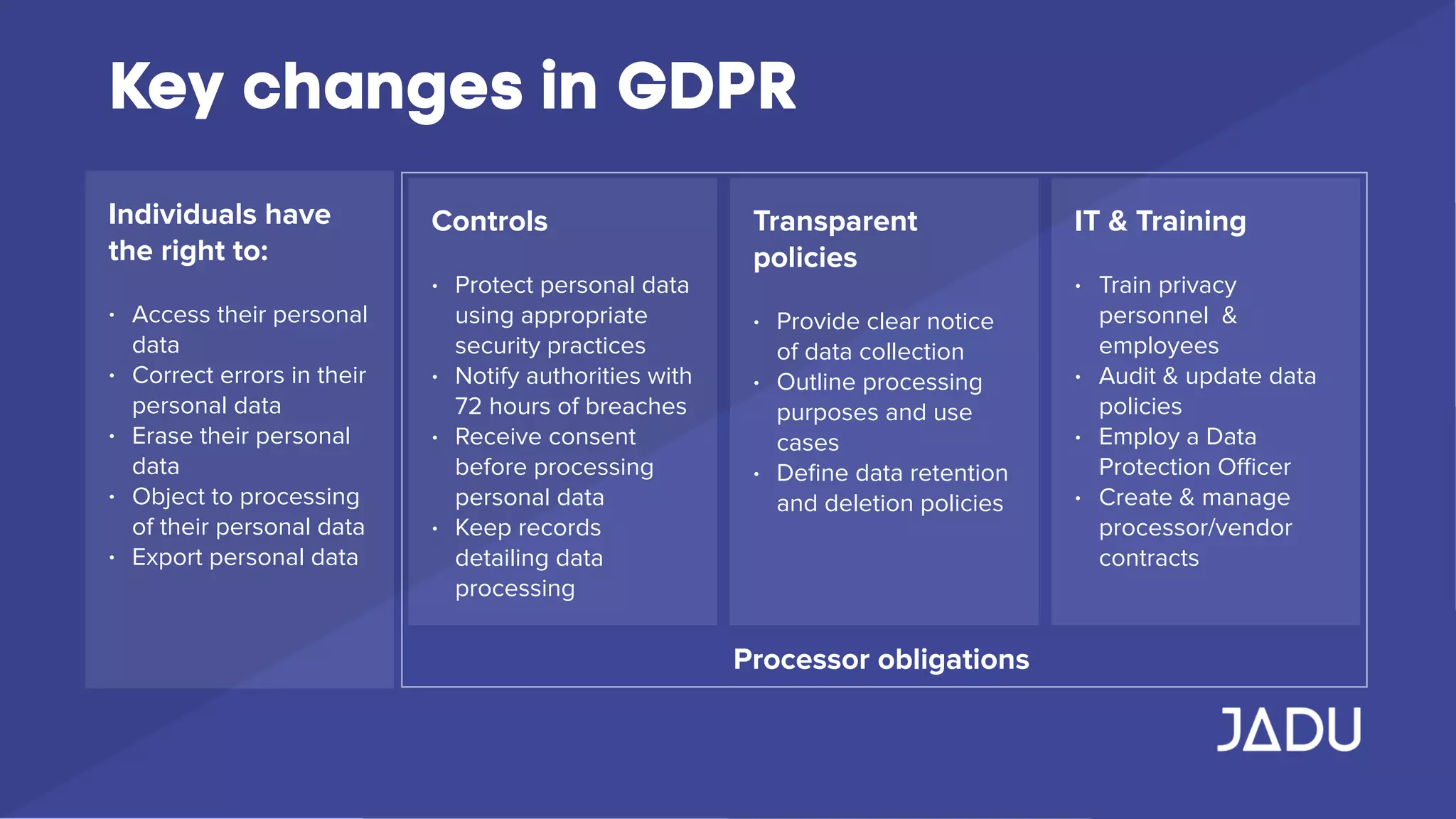
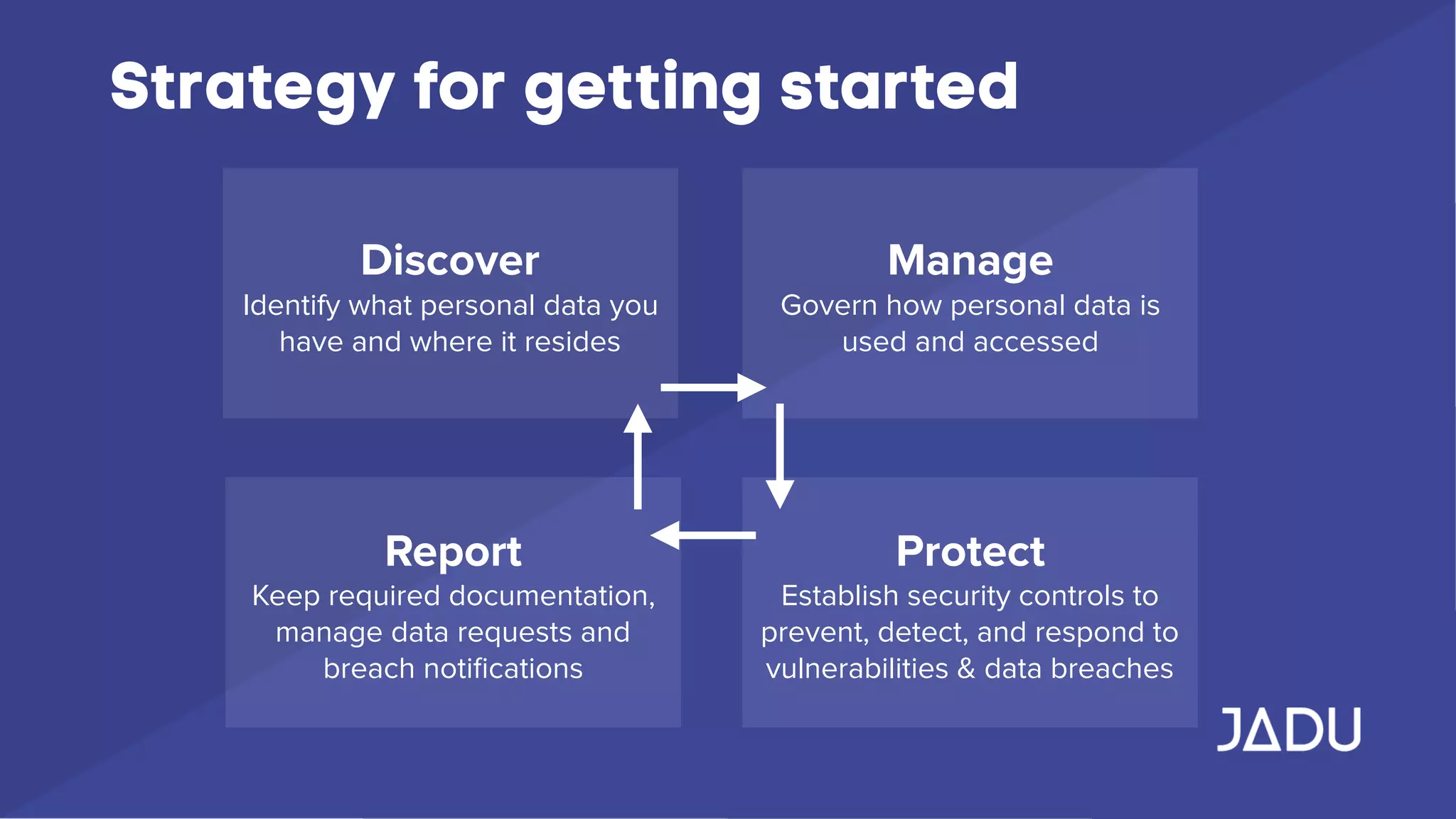
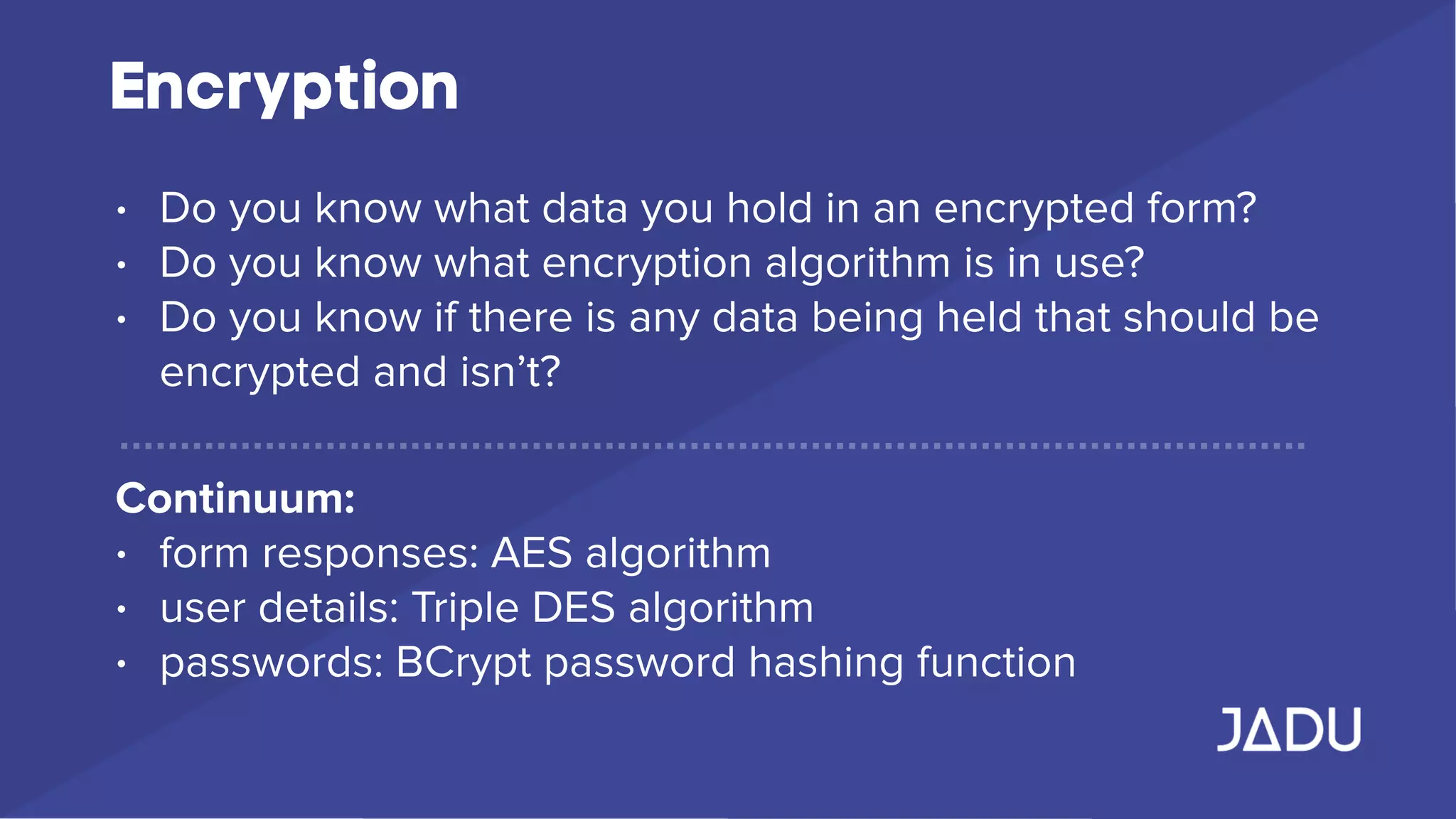
The document outlines the requirements of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), effective May 25, 2018, which mandates enhanced privacy rights for EU citizens and increased responsibilities for organizations handling personal data. Key measures include data access rights for individuals, mandatory breach reporting, and stringent data management protocols, with specific focus on consent and security practices. Organizations are advised to audit their data practices, ensure compliance, and establish clear privacy policies to protect personal data.