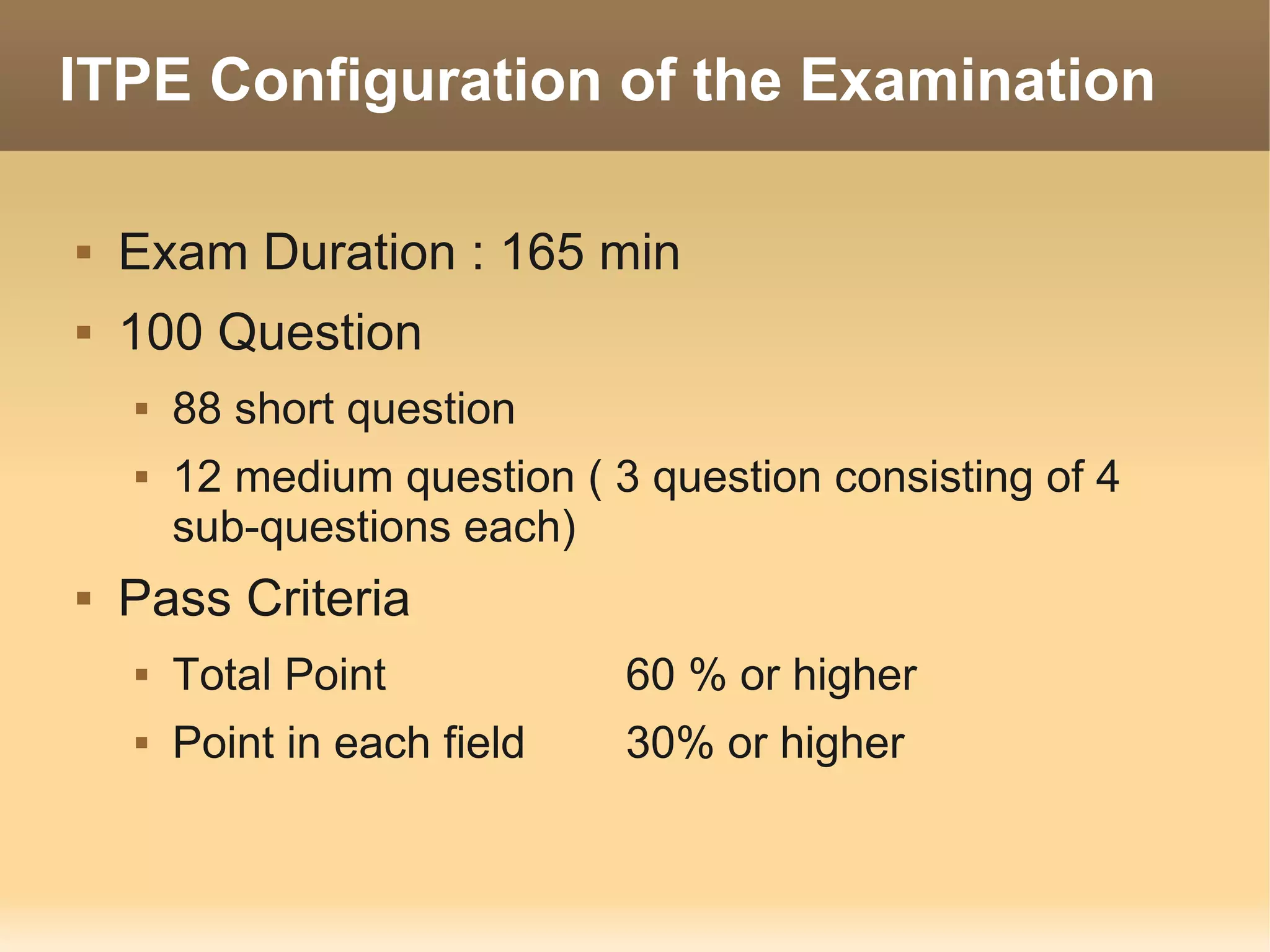
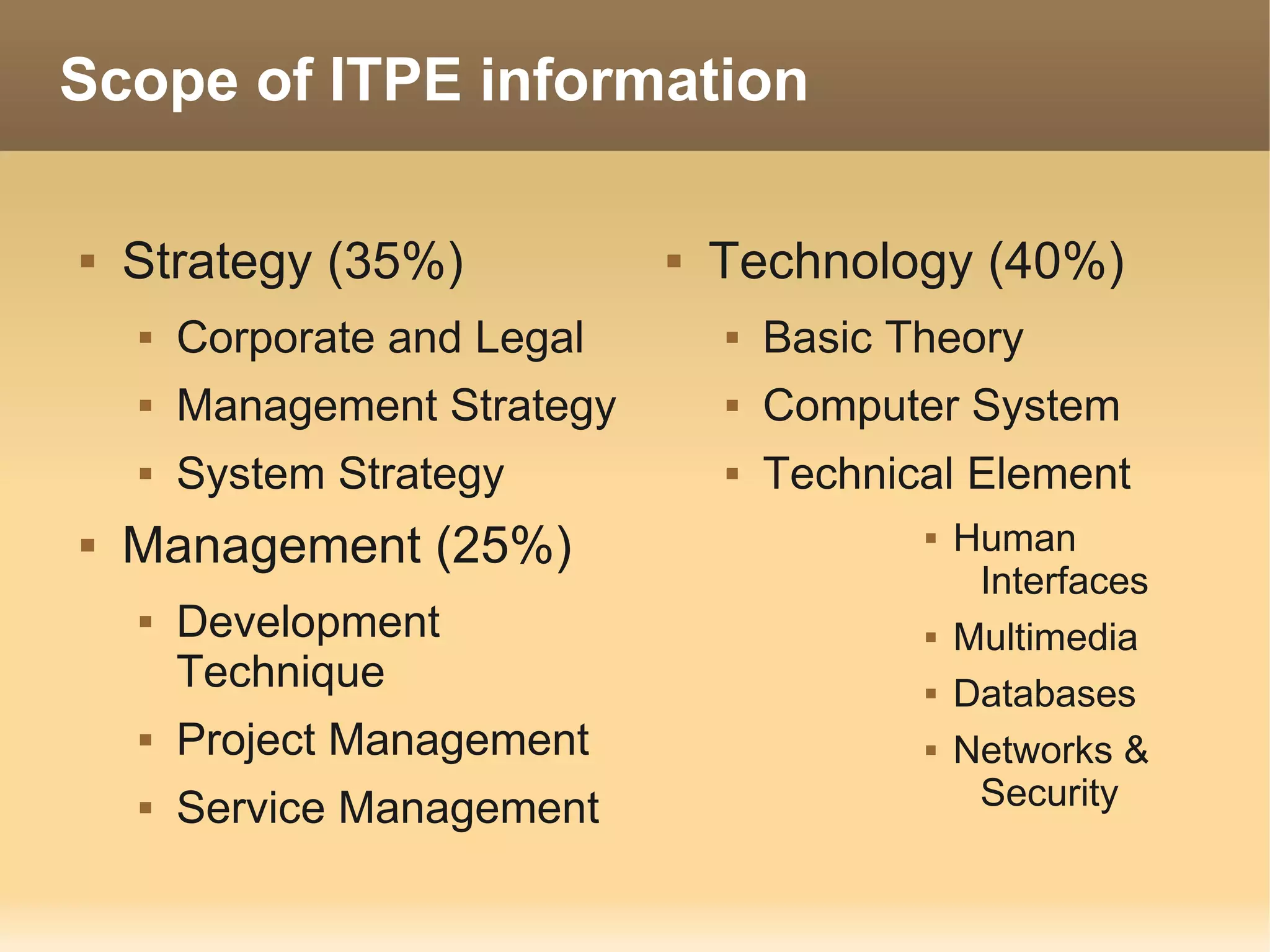
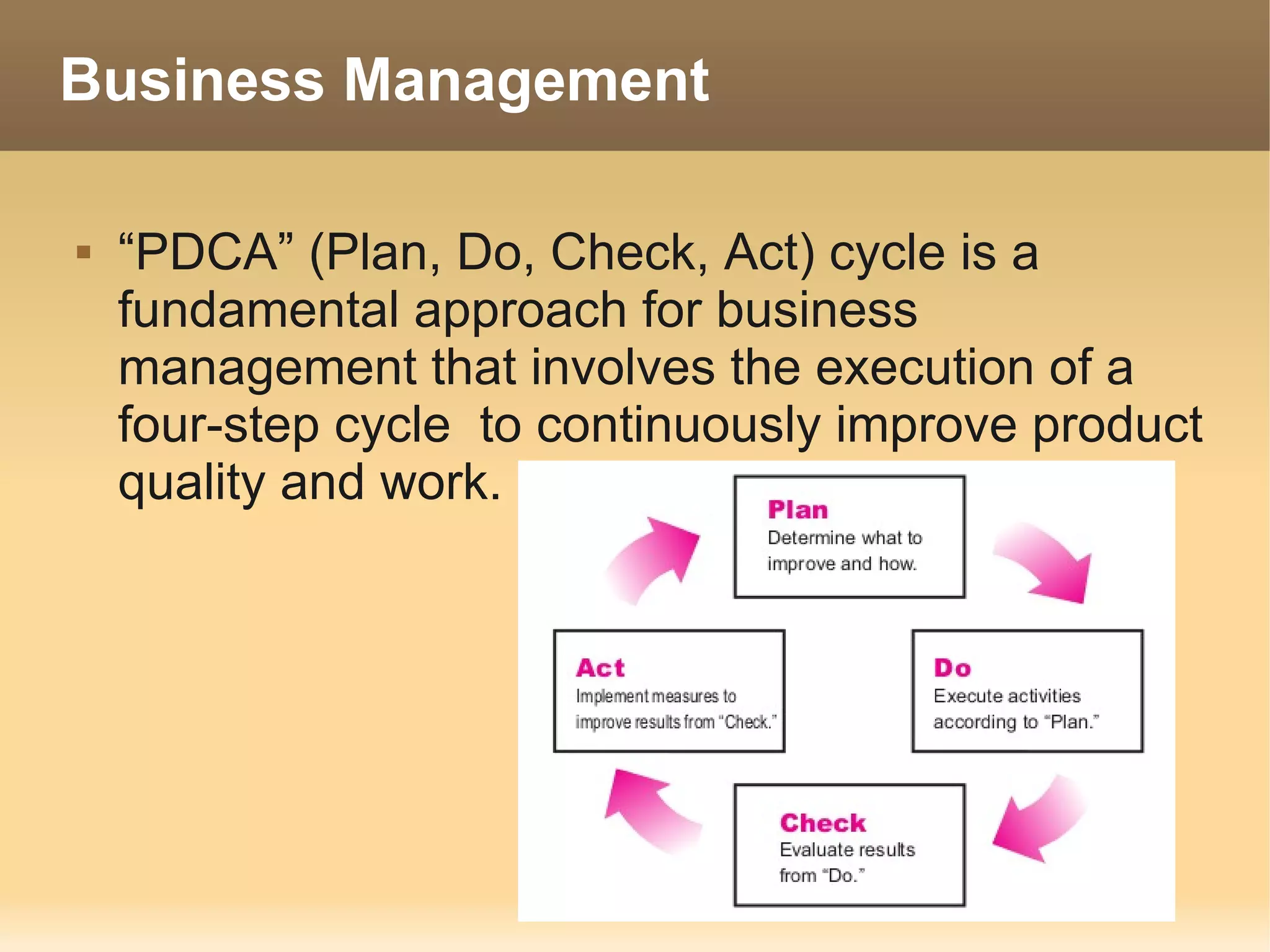
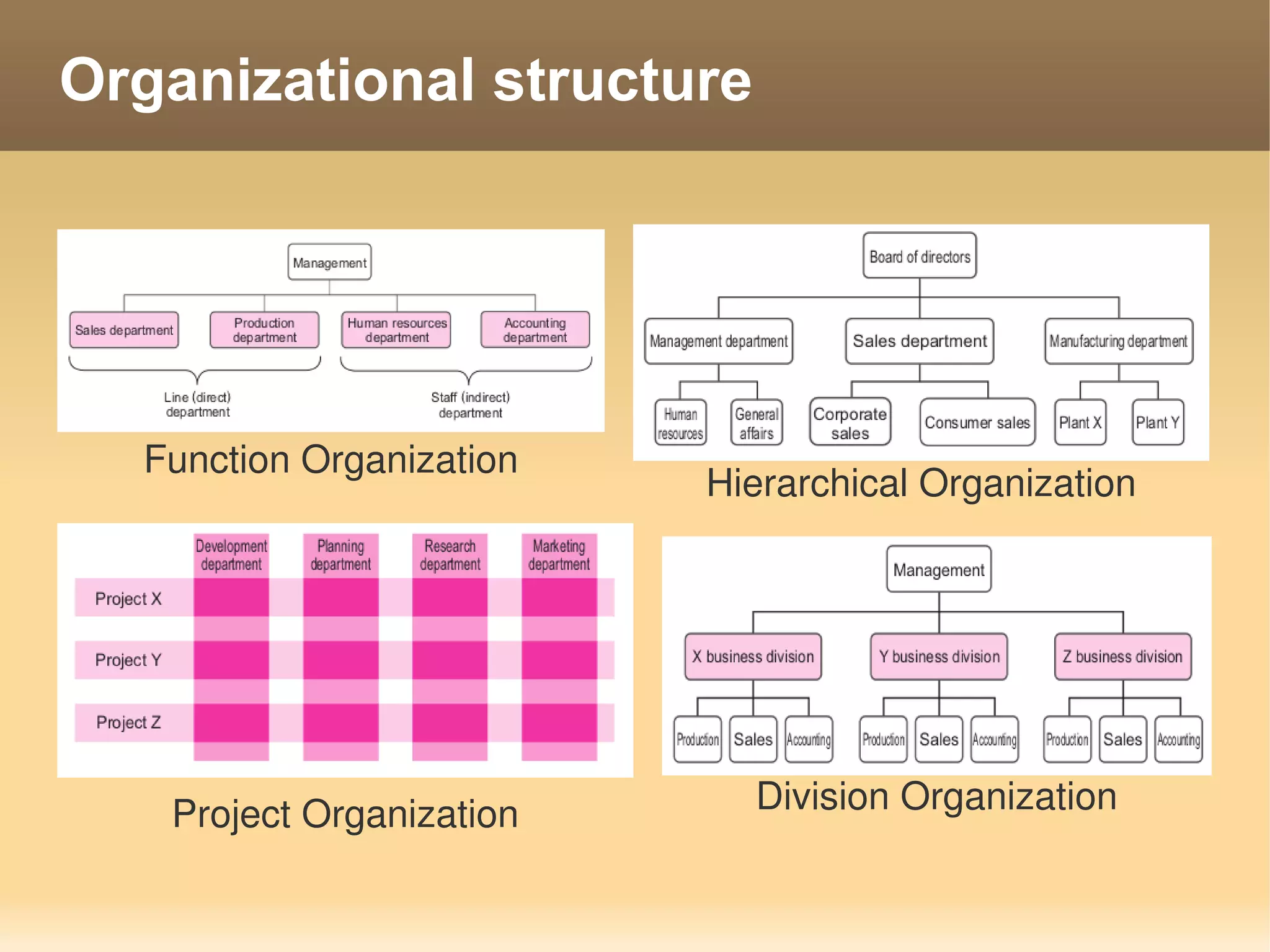
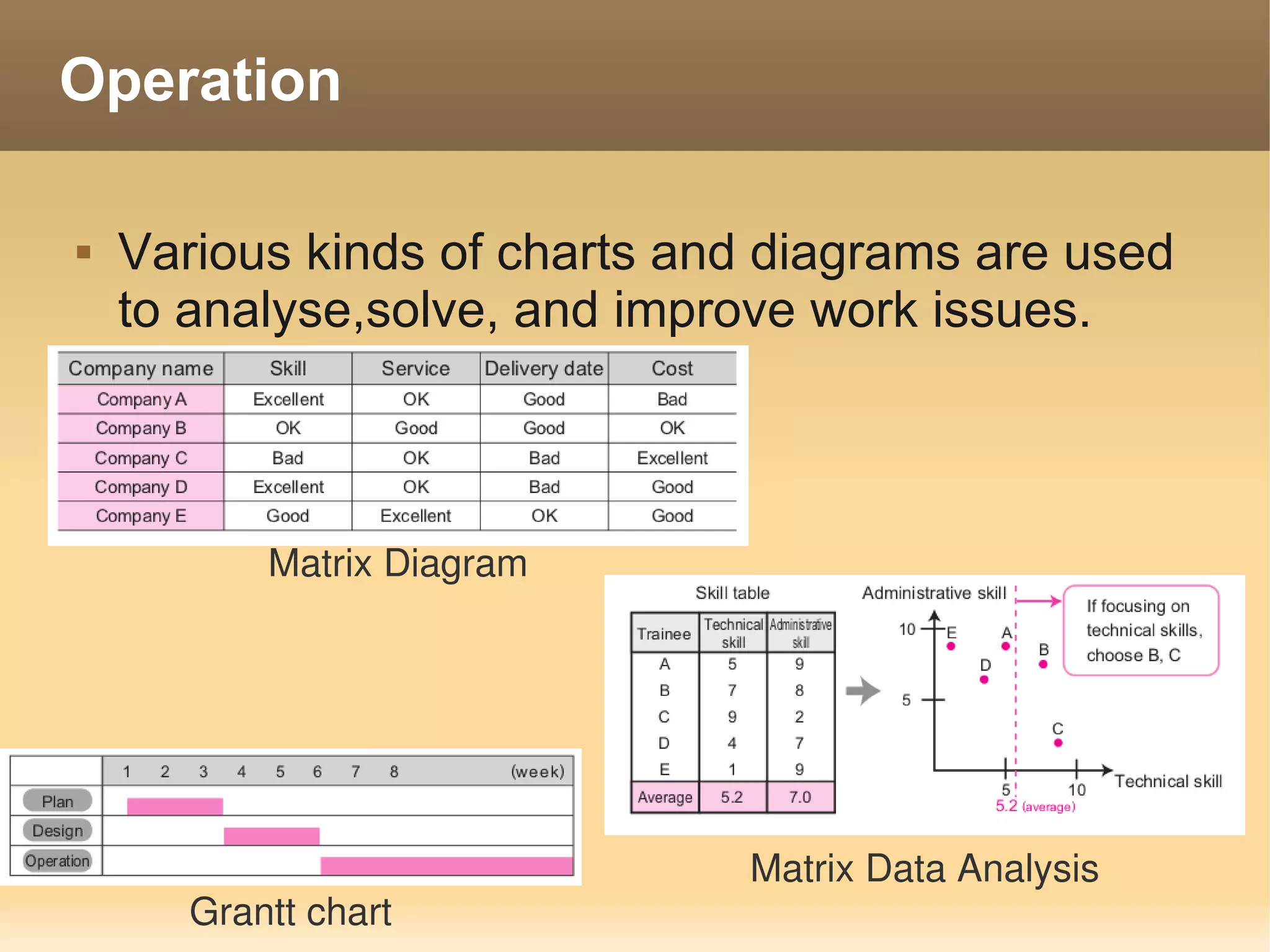
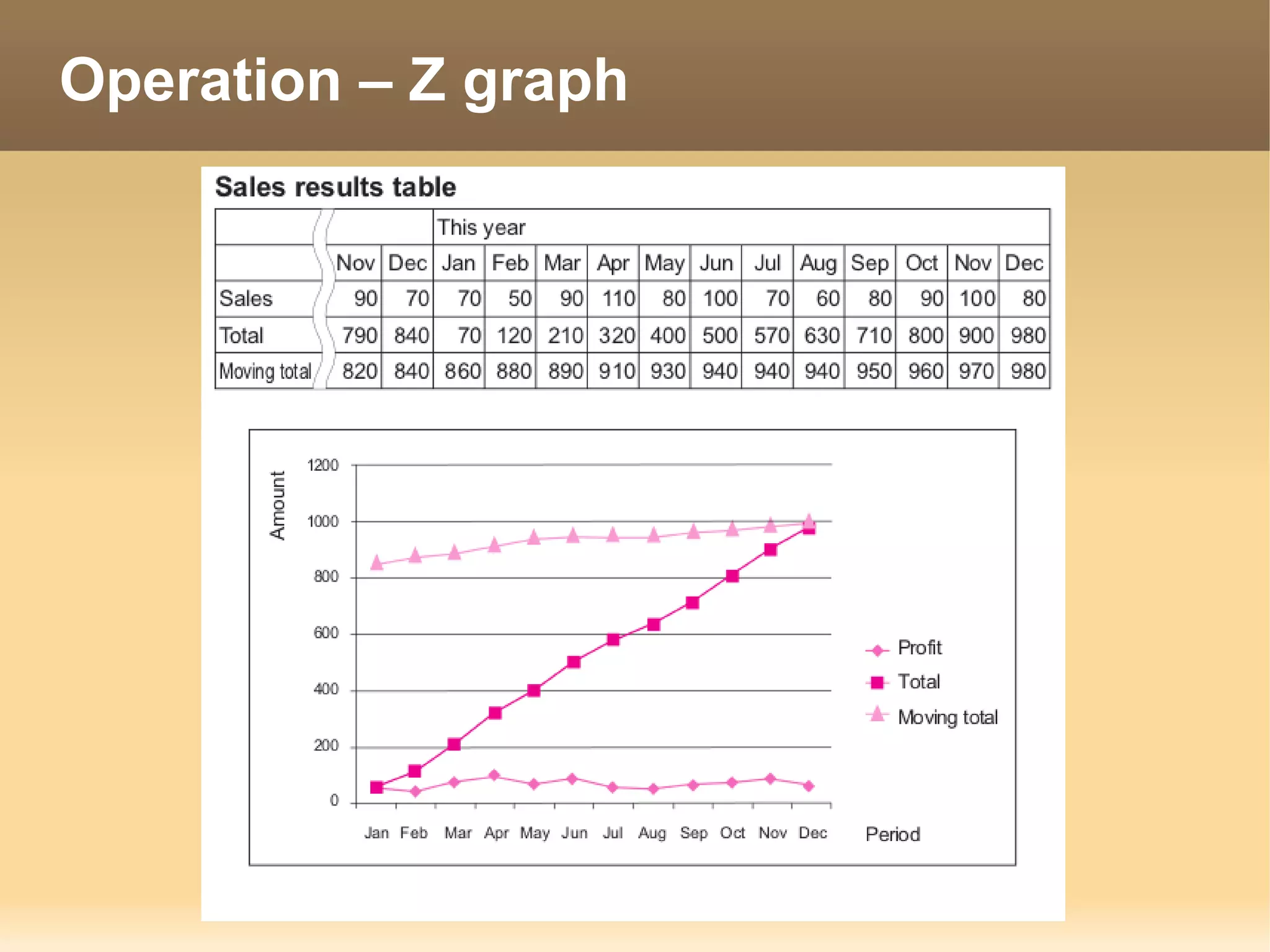
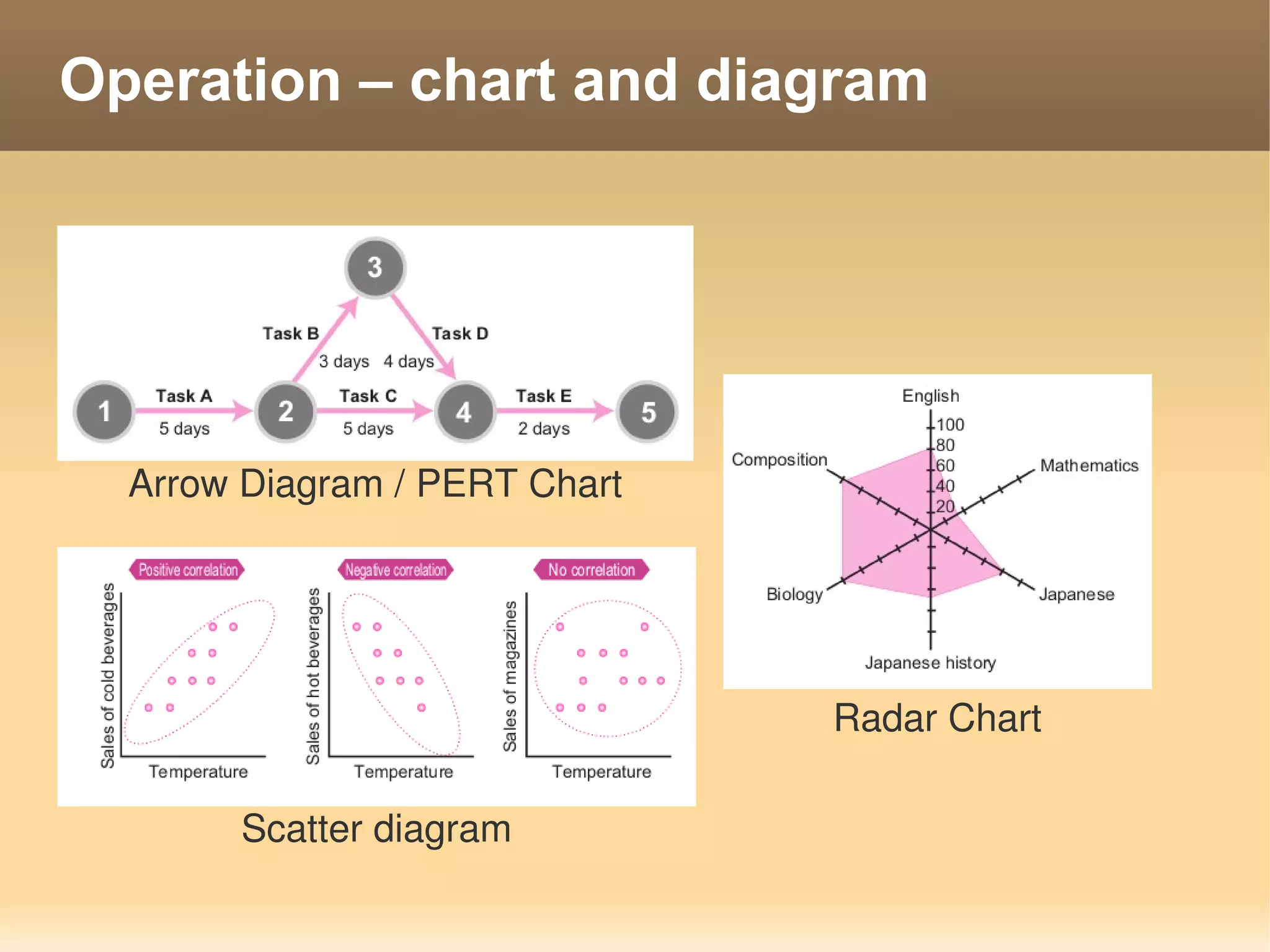
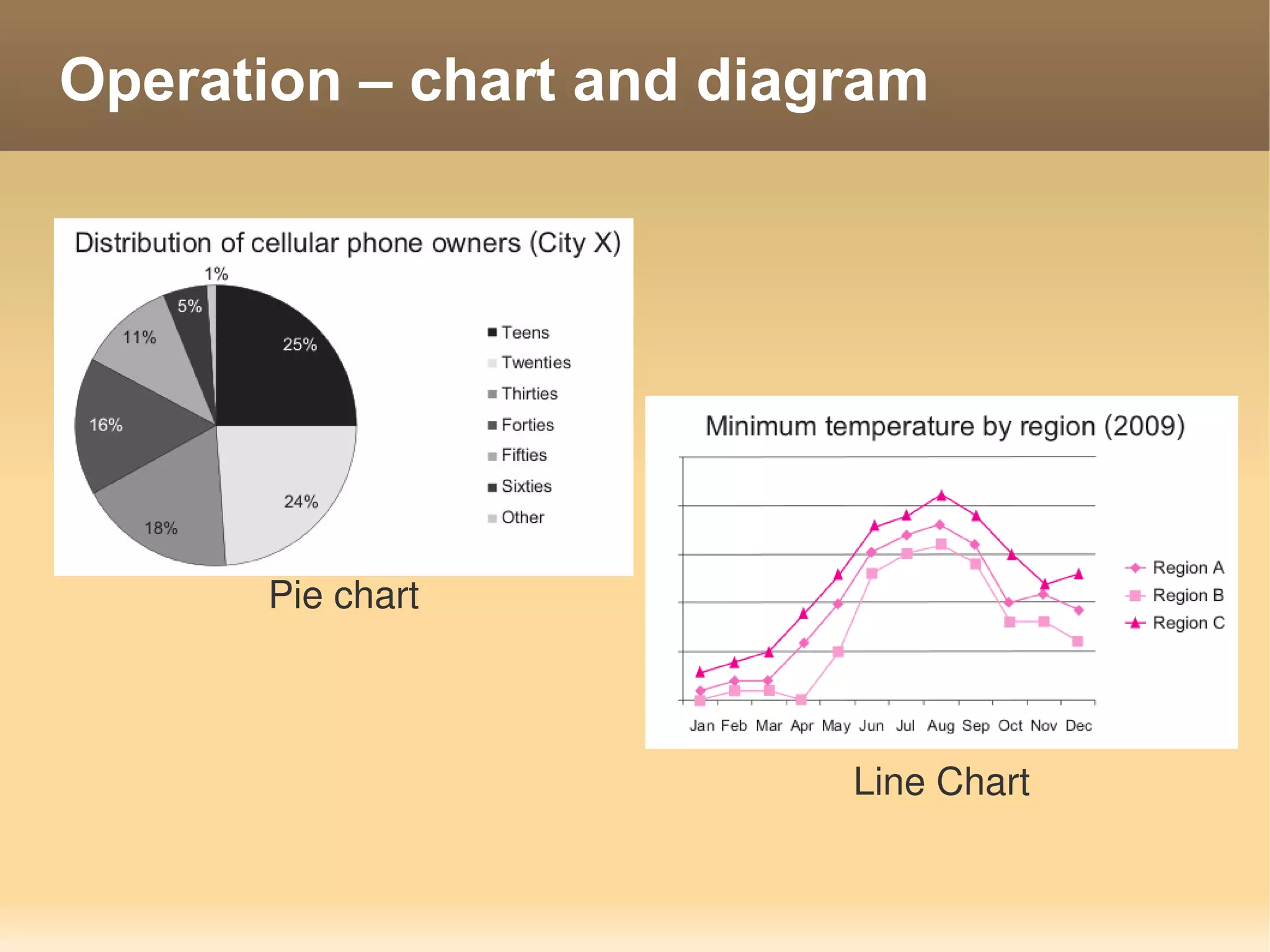
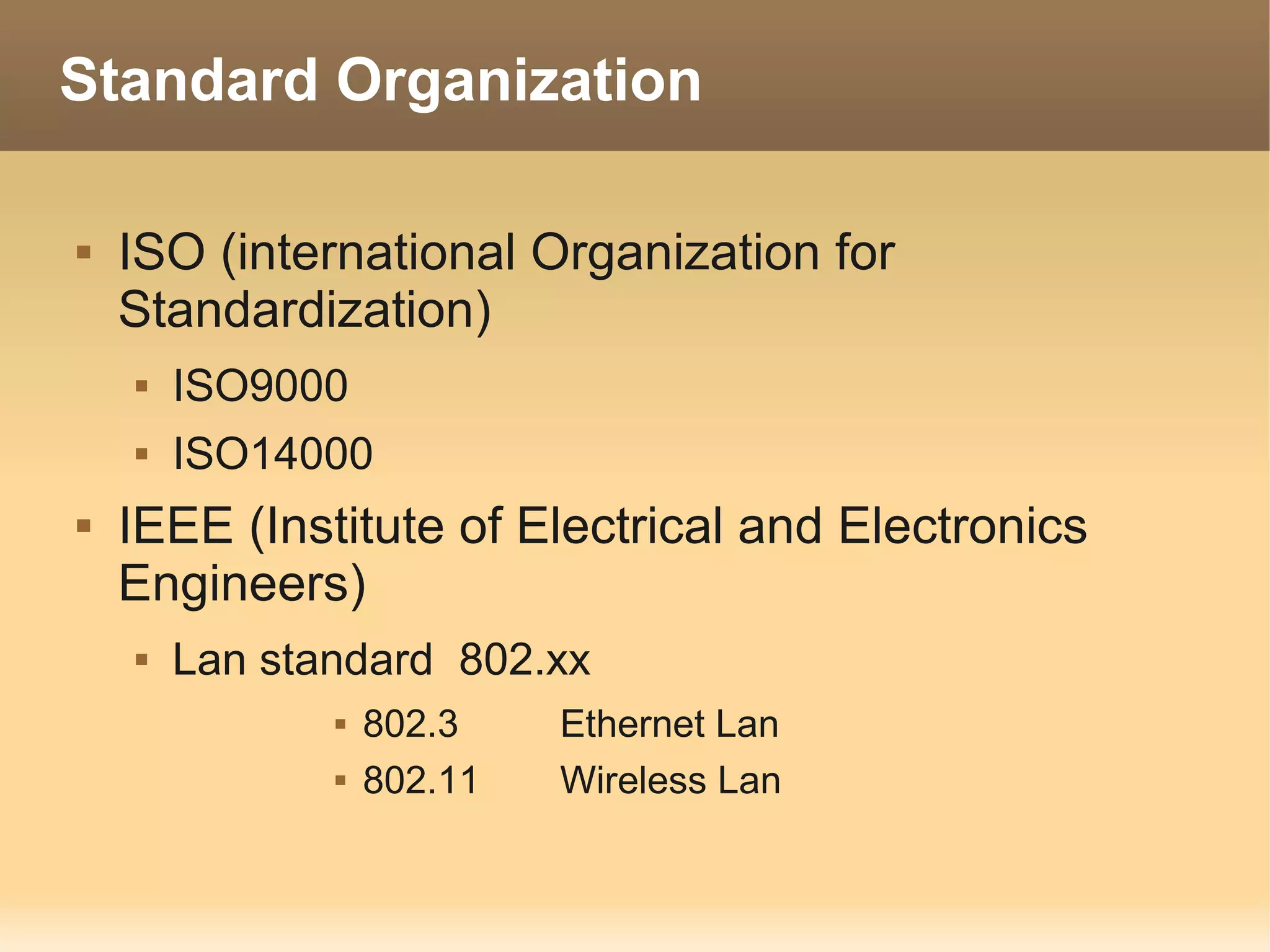
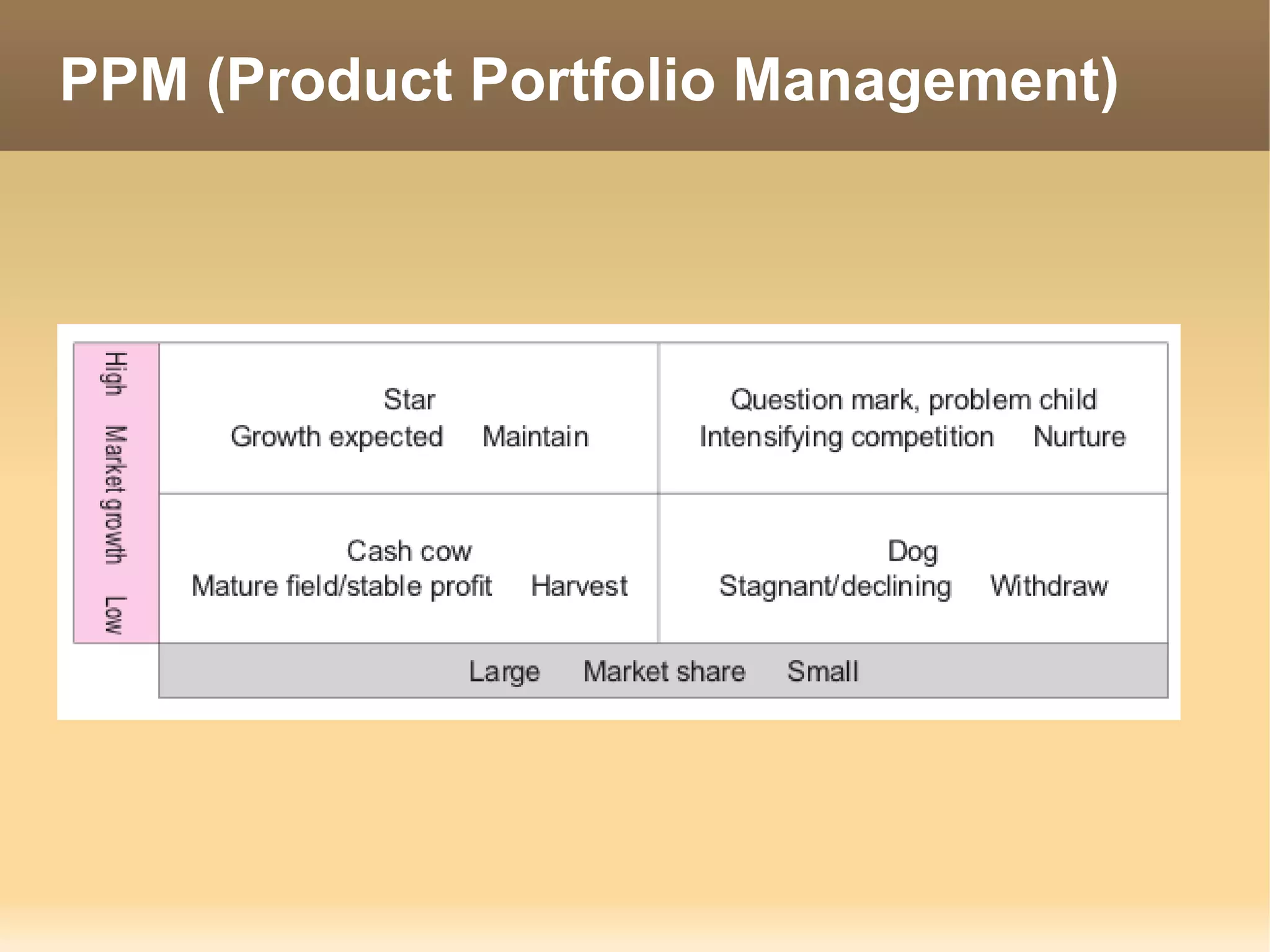
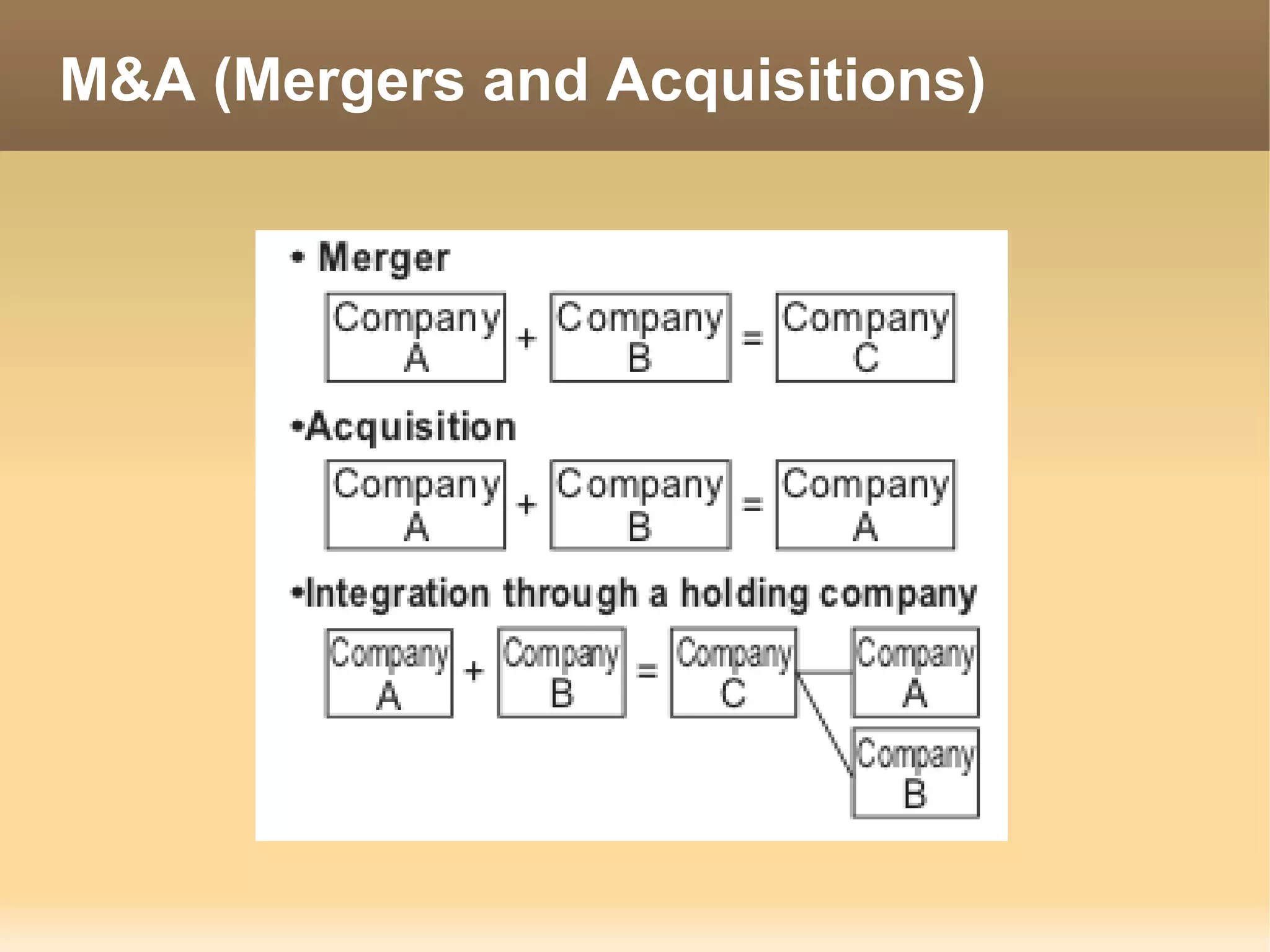
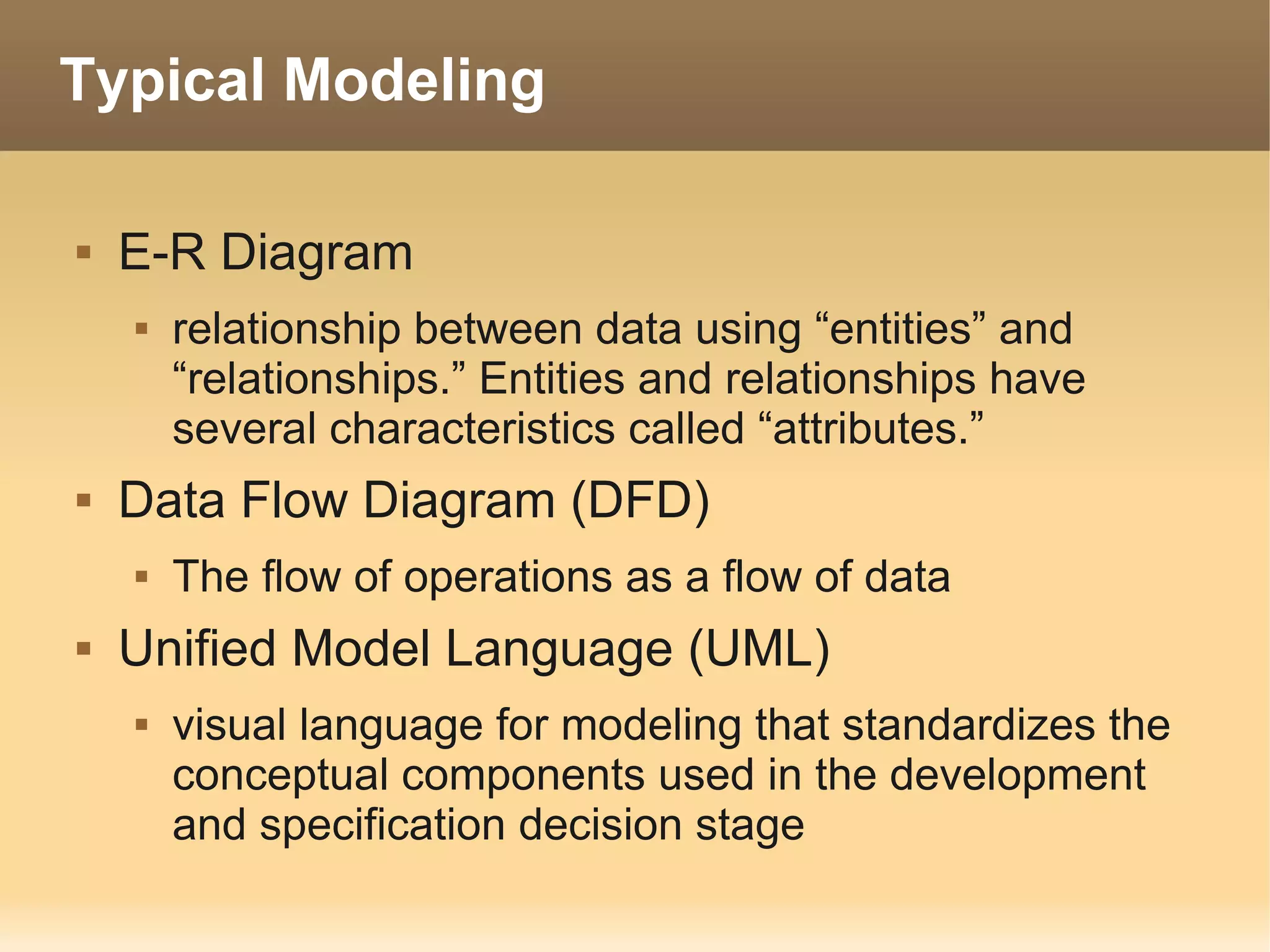
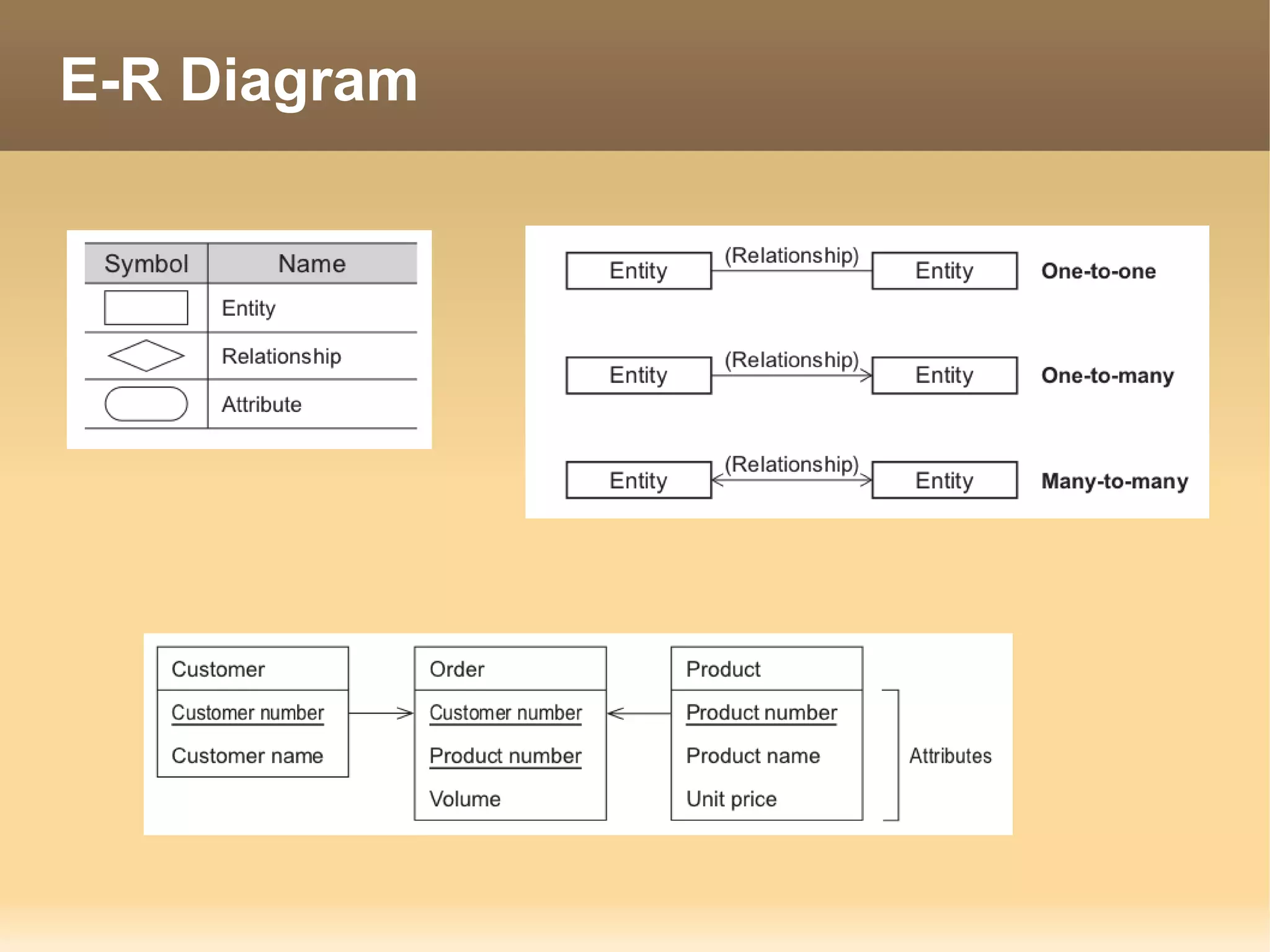
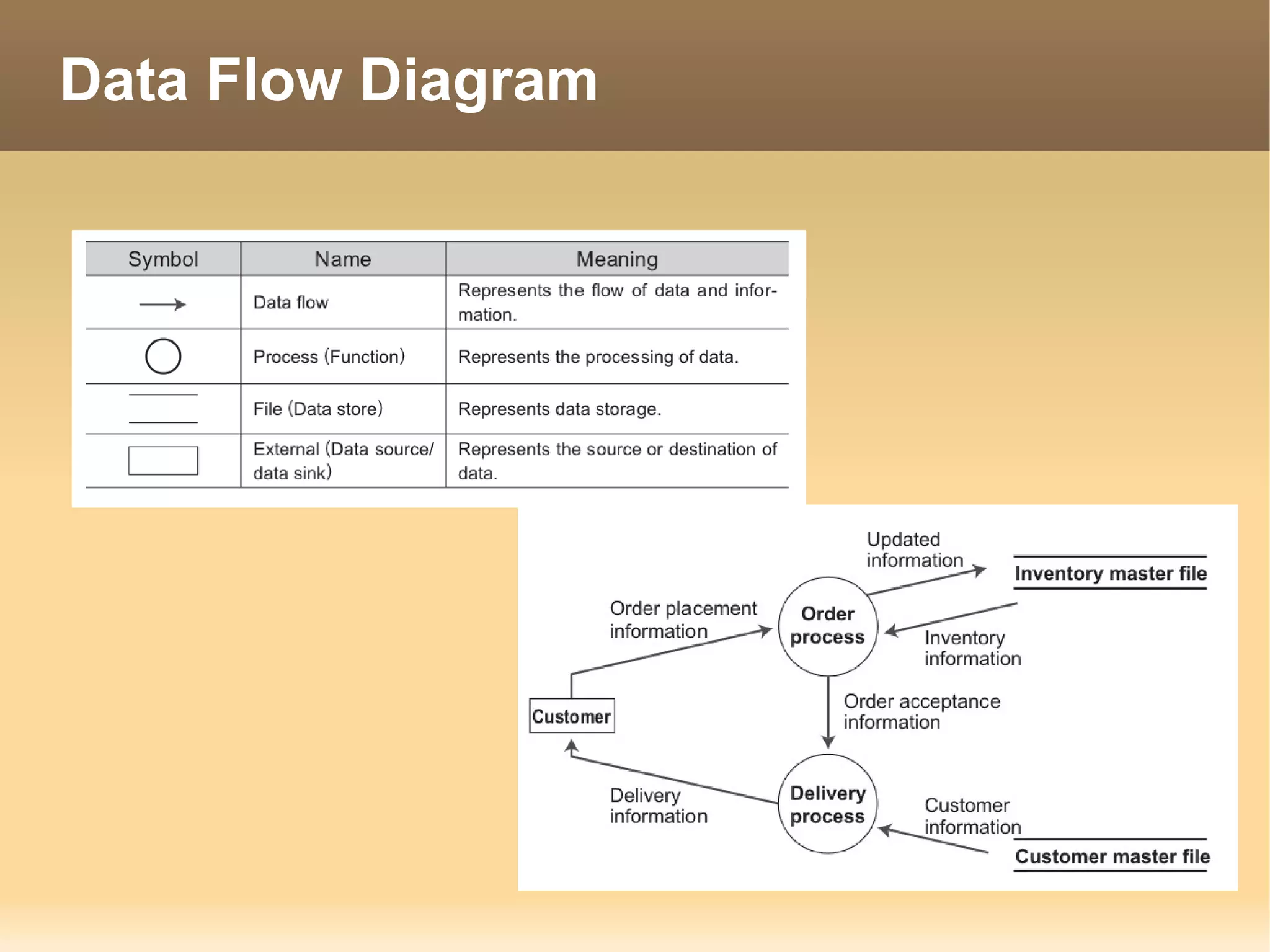
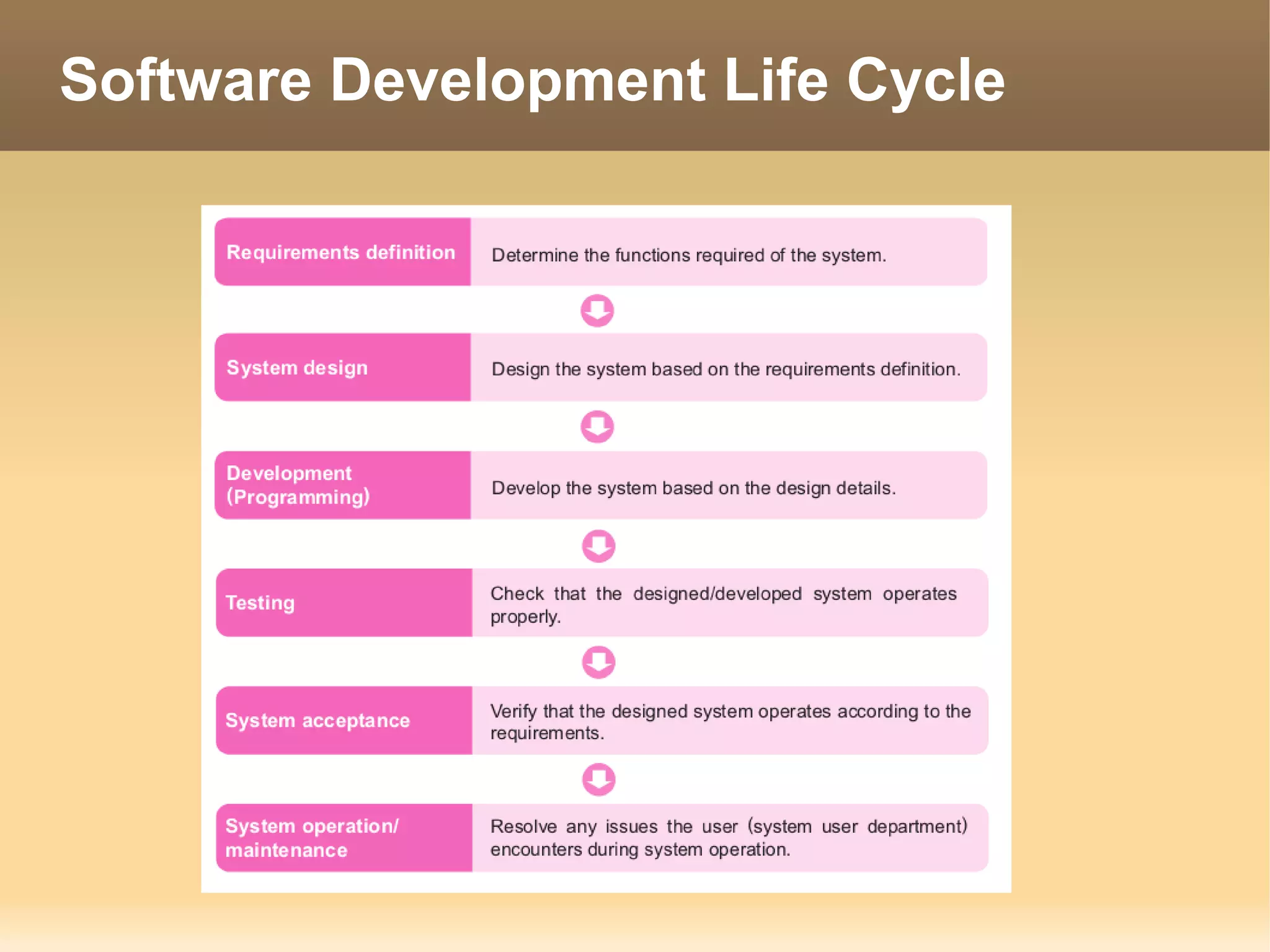
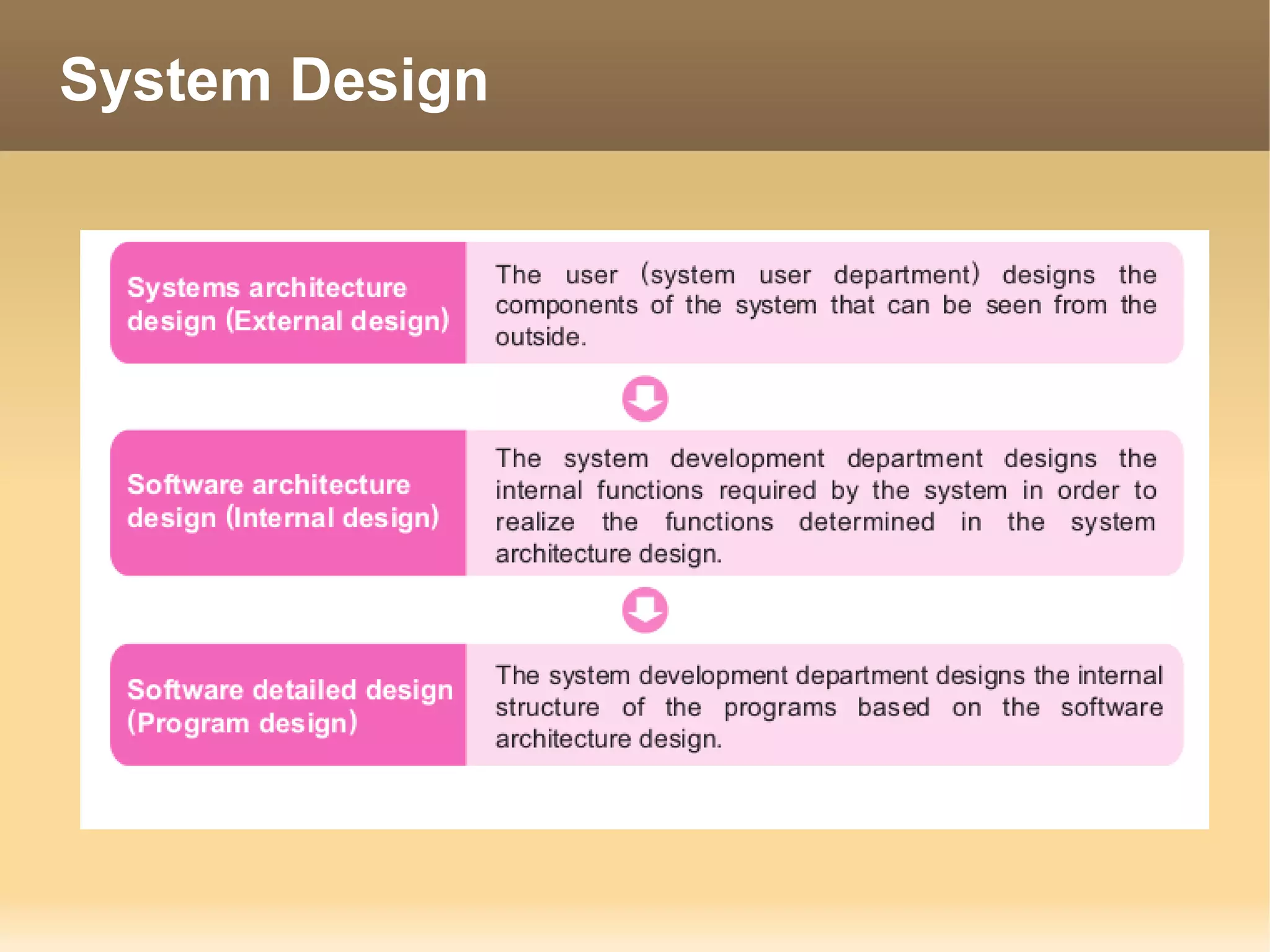
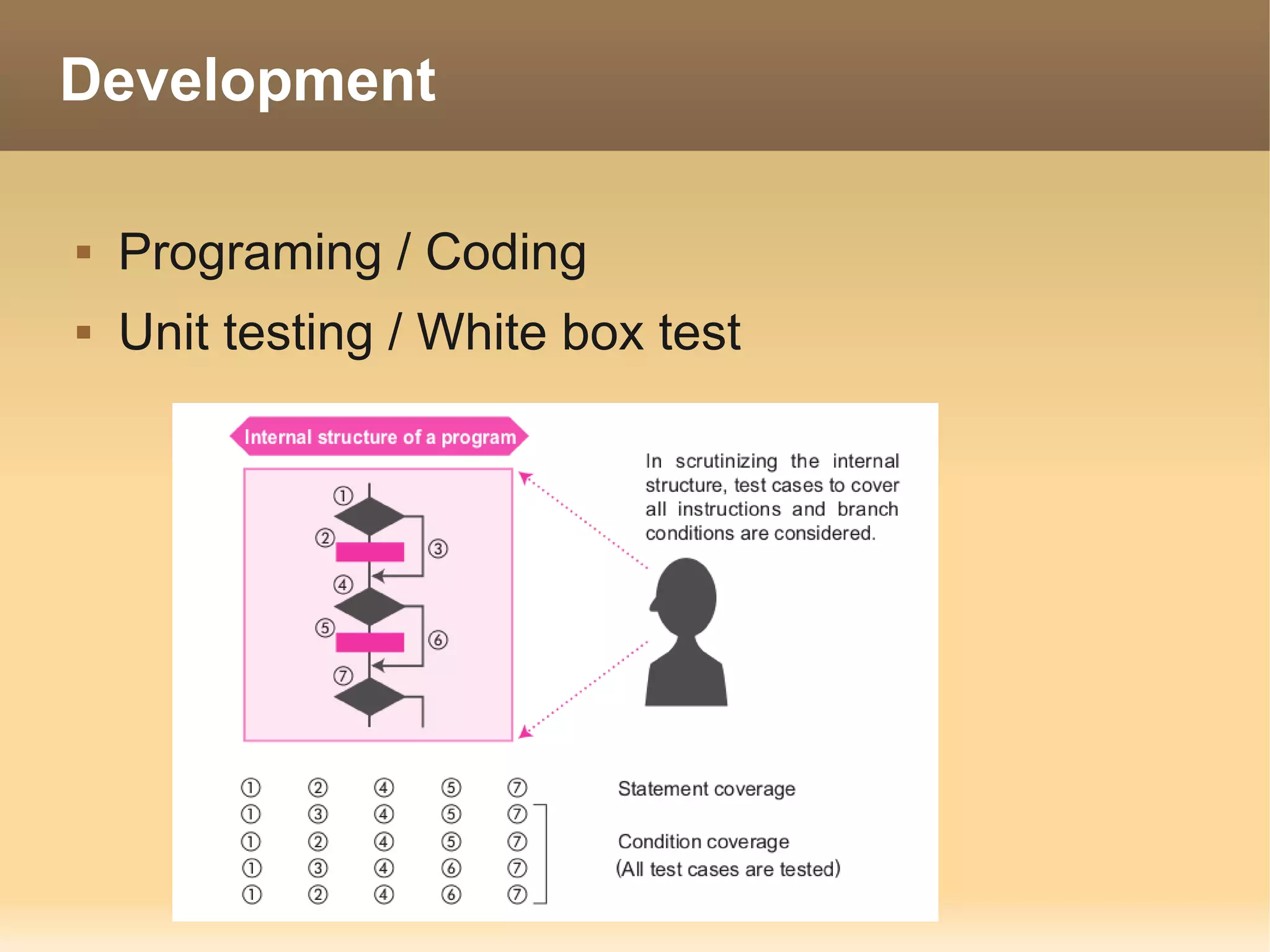
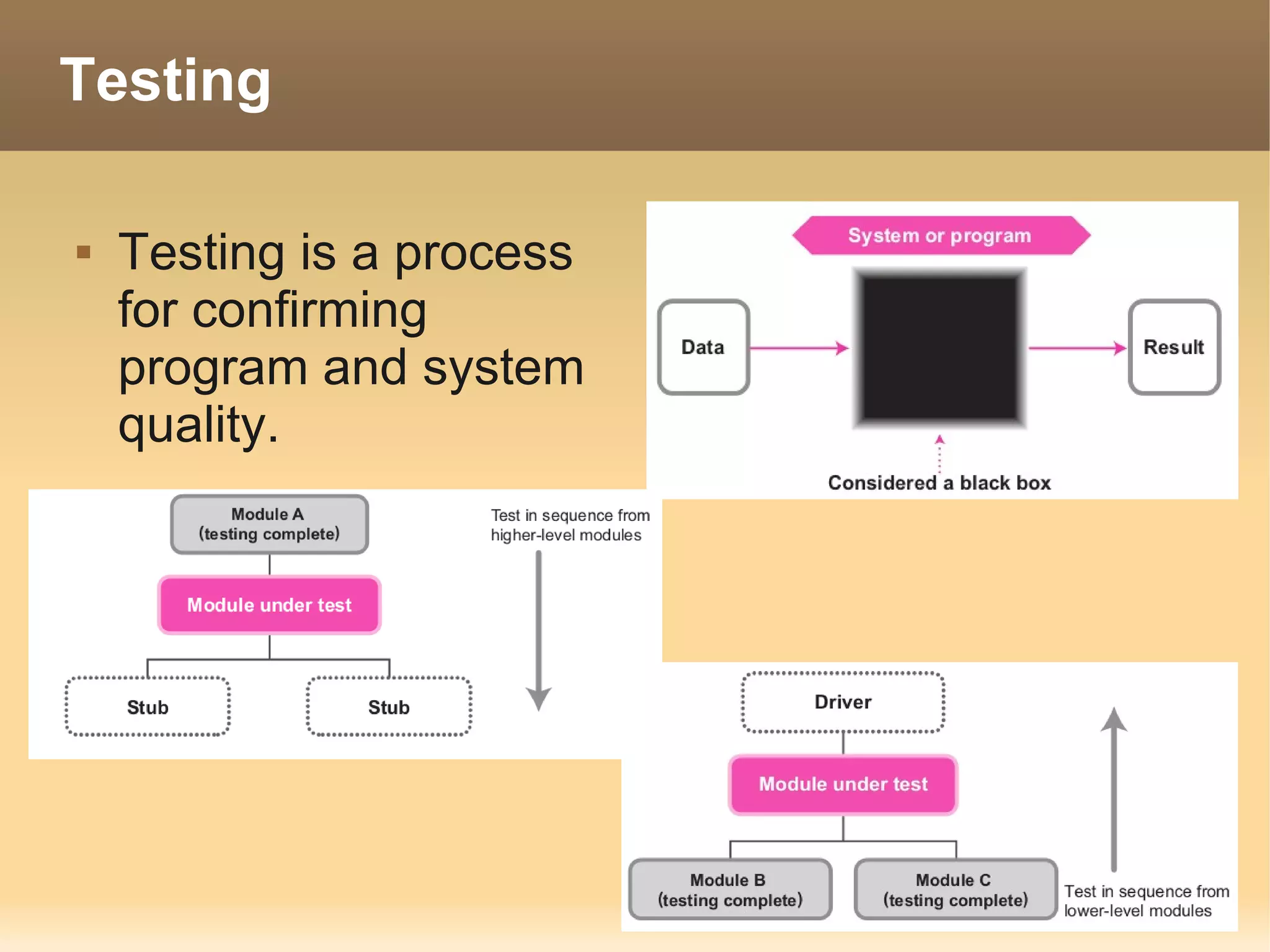
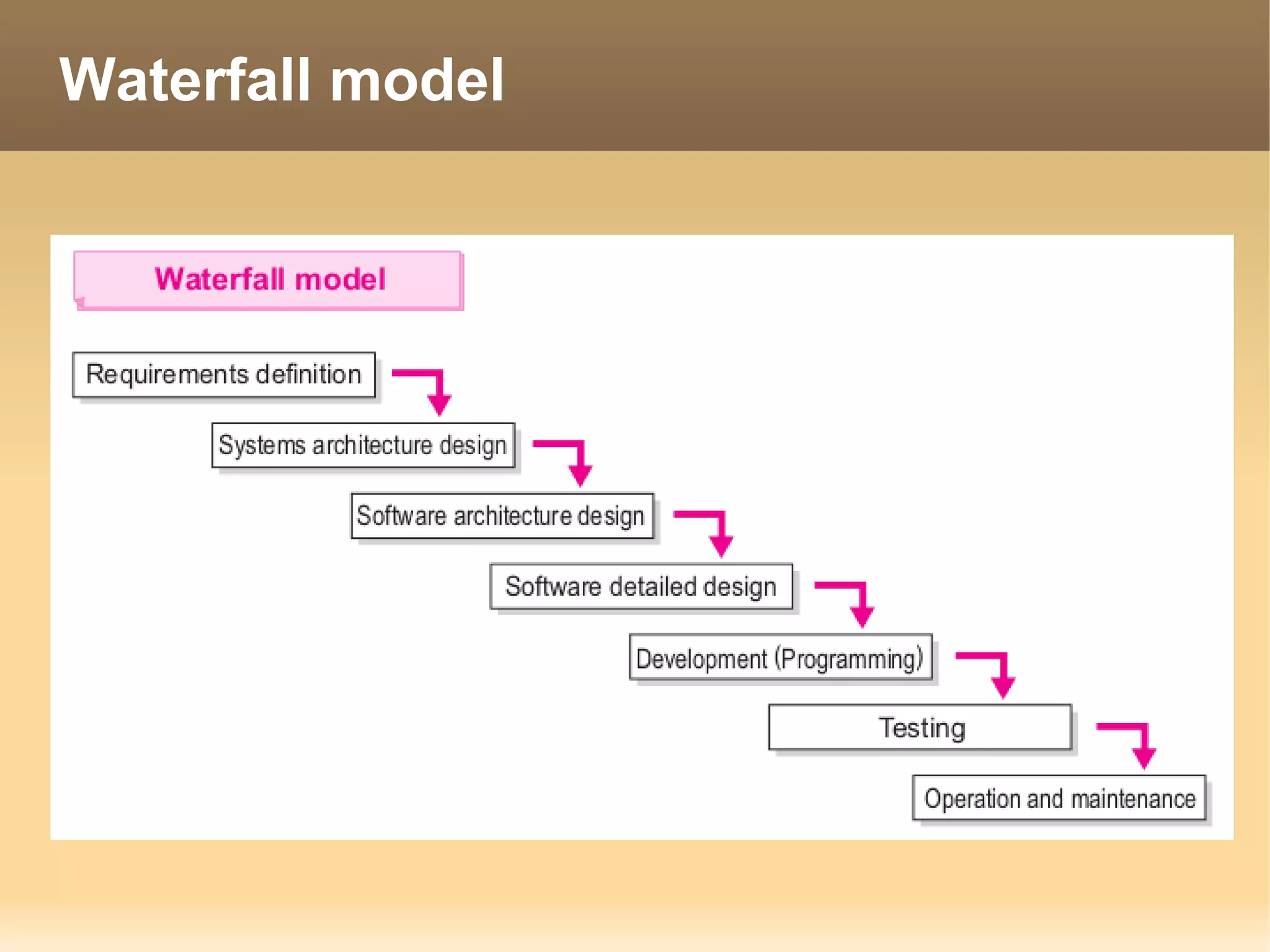
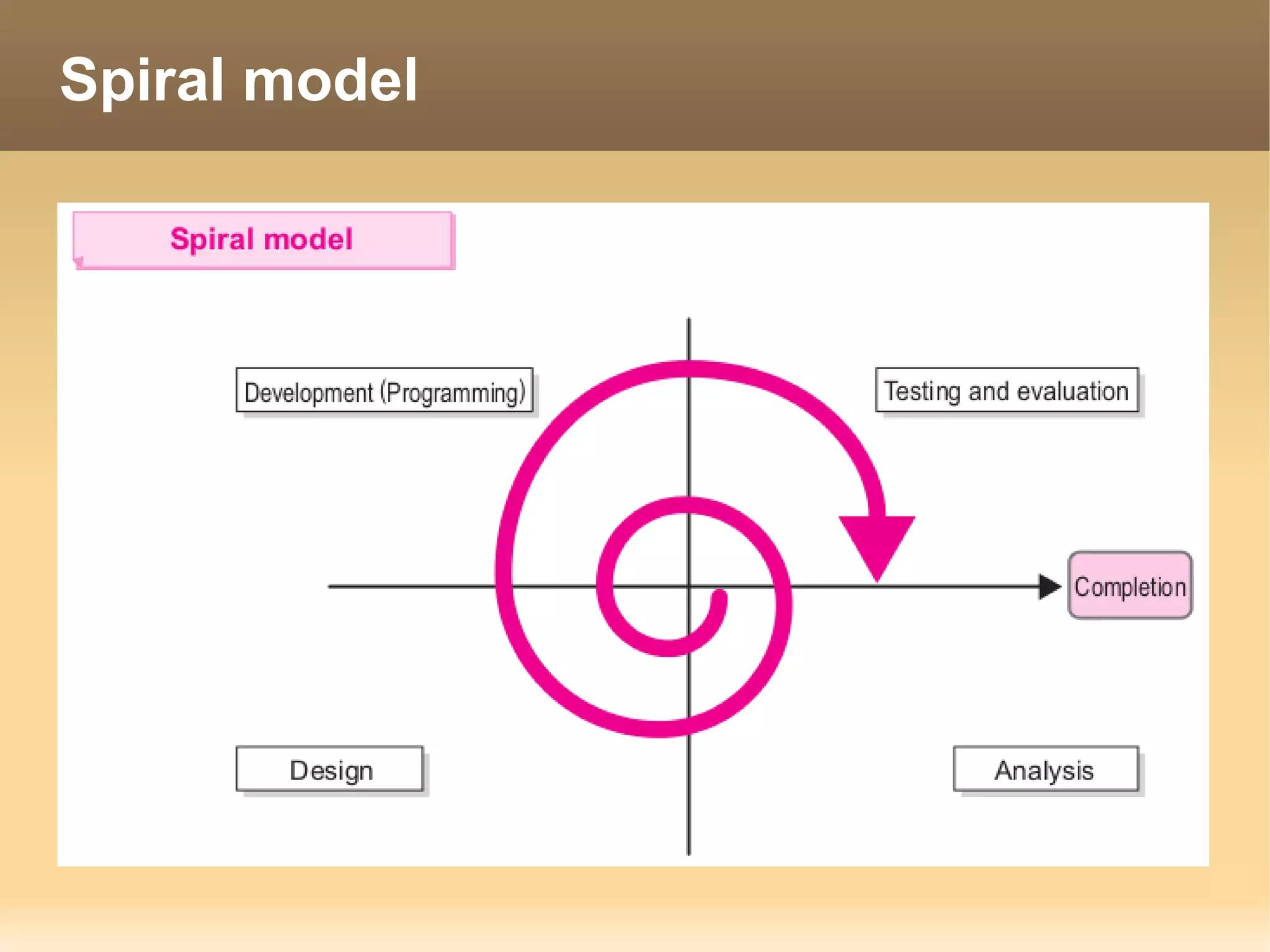
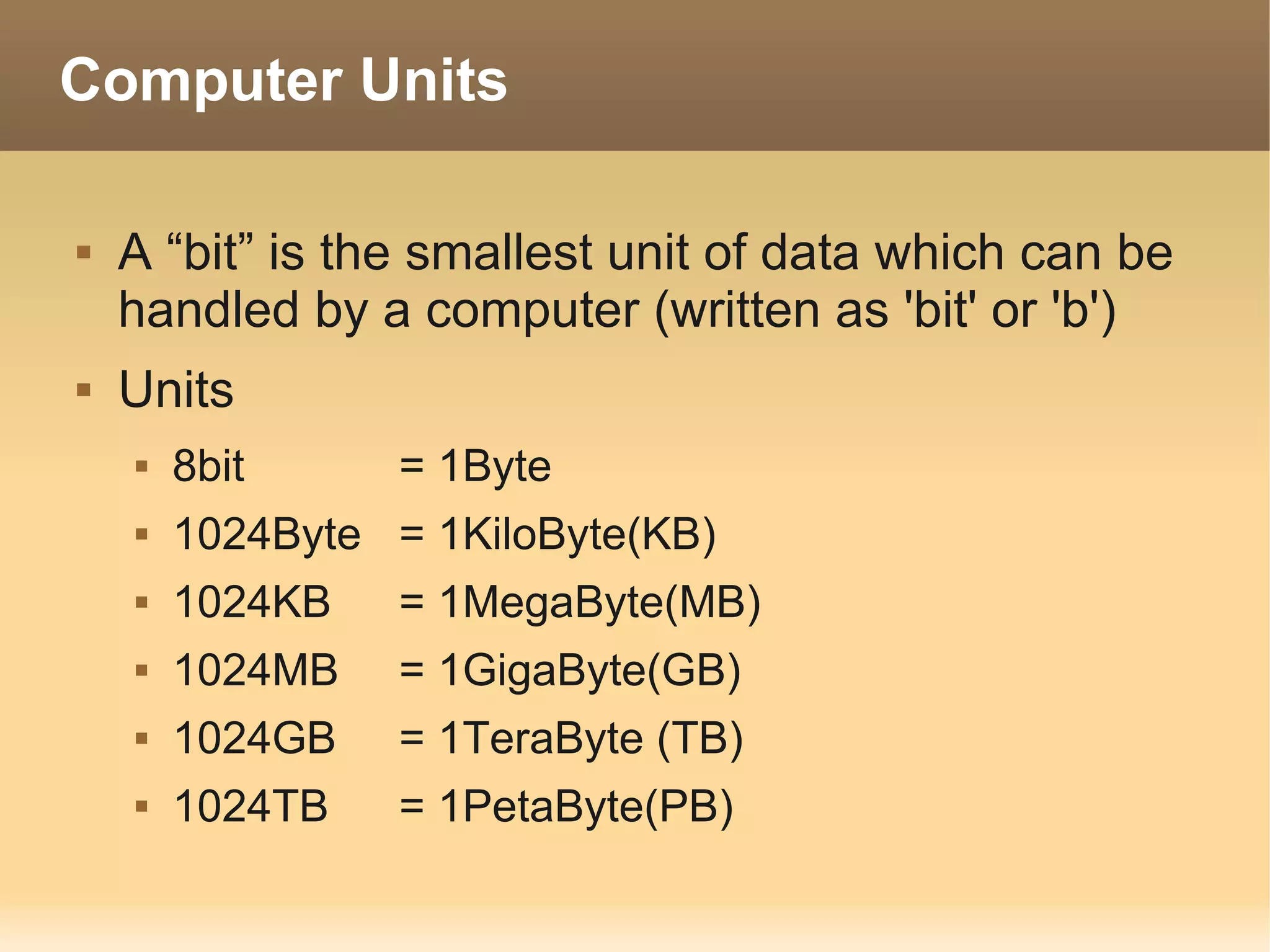
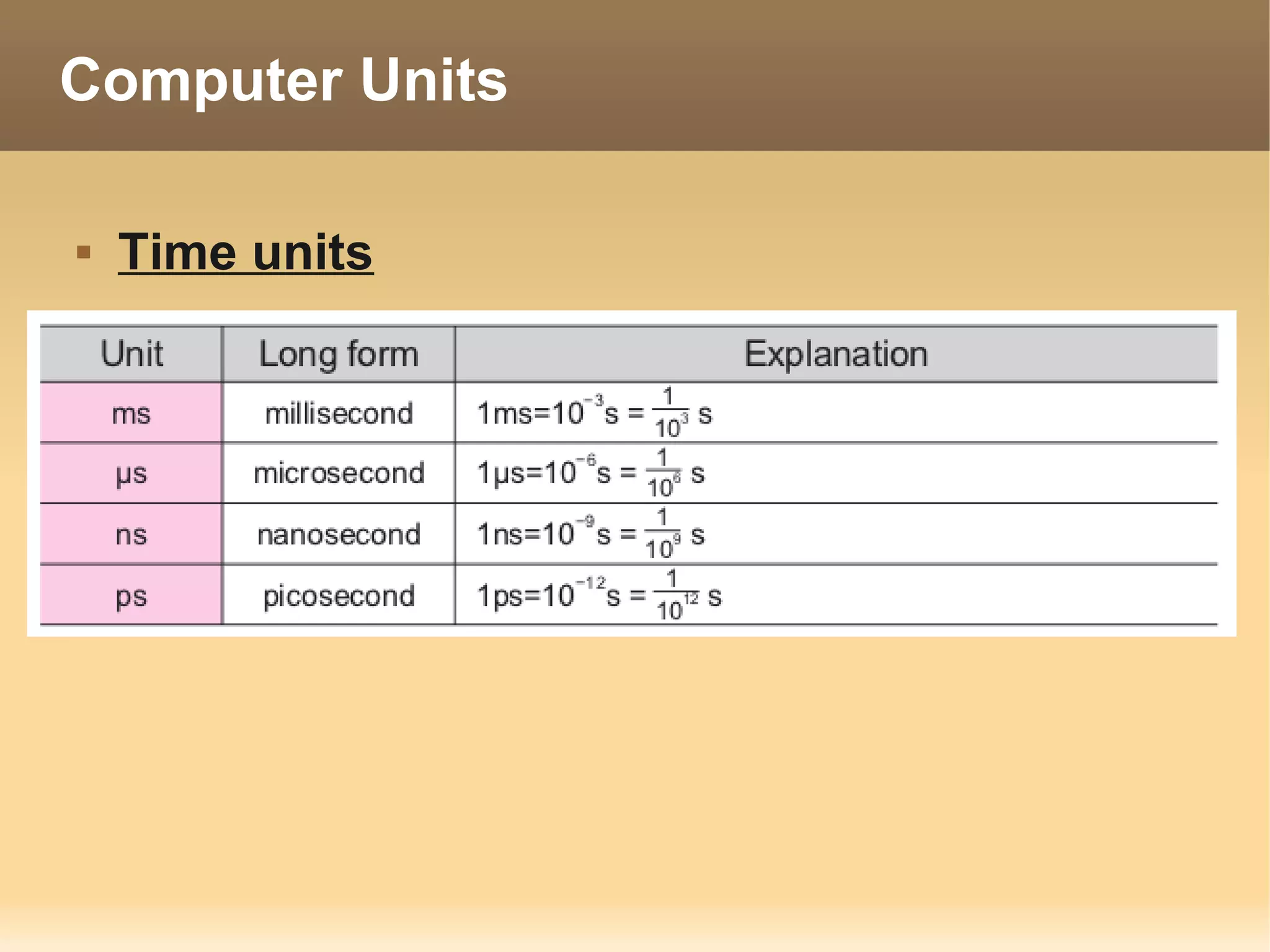
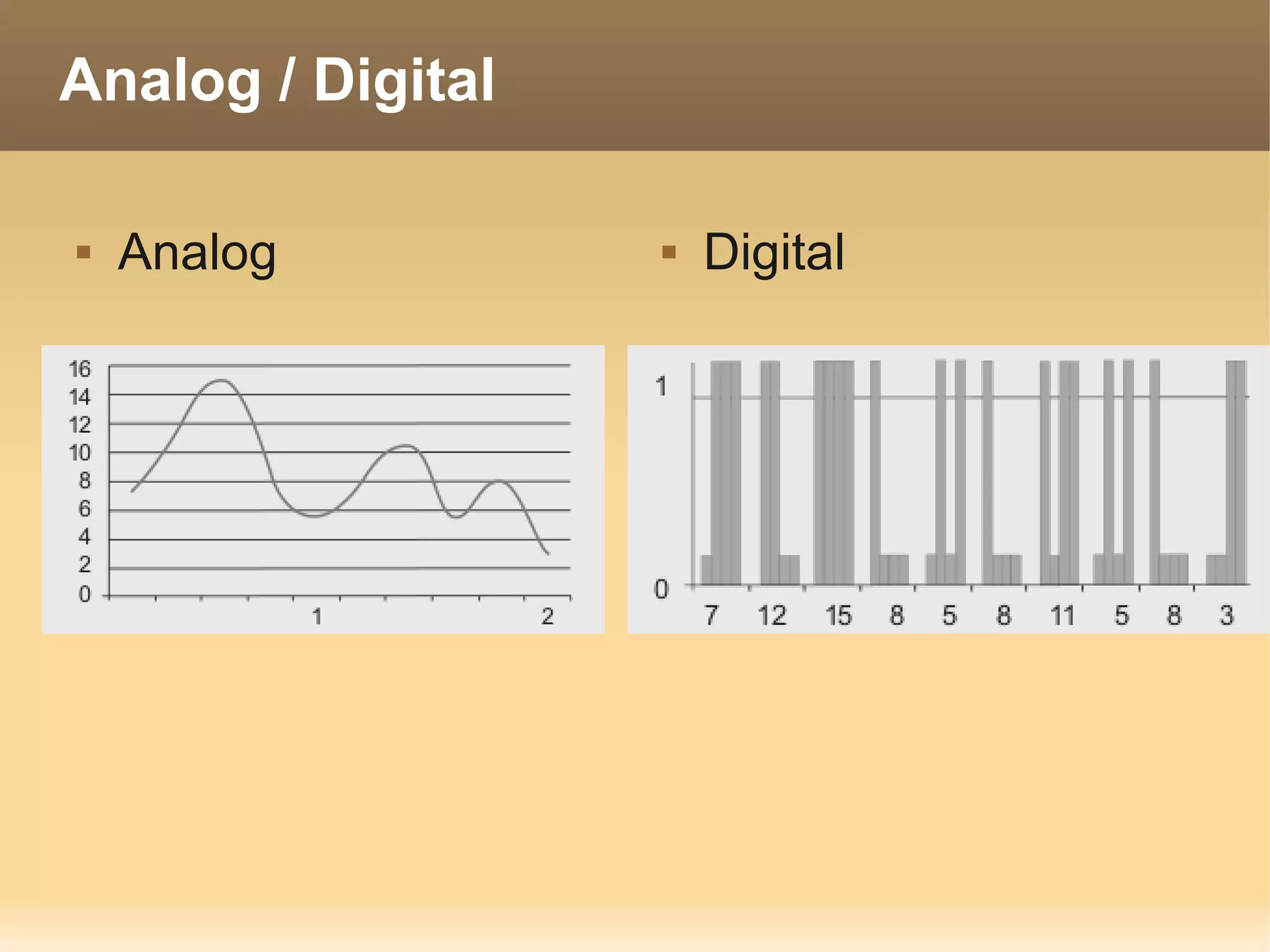
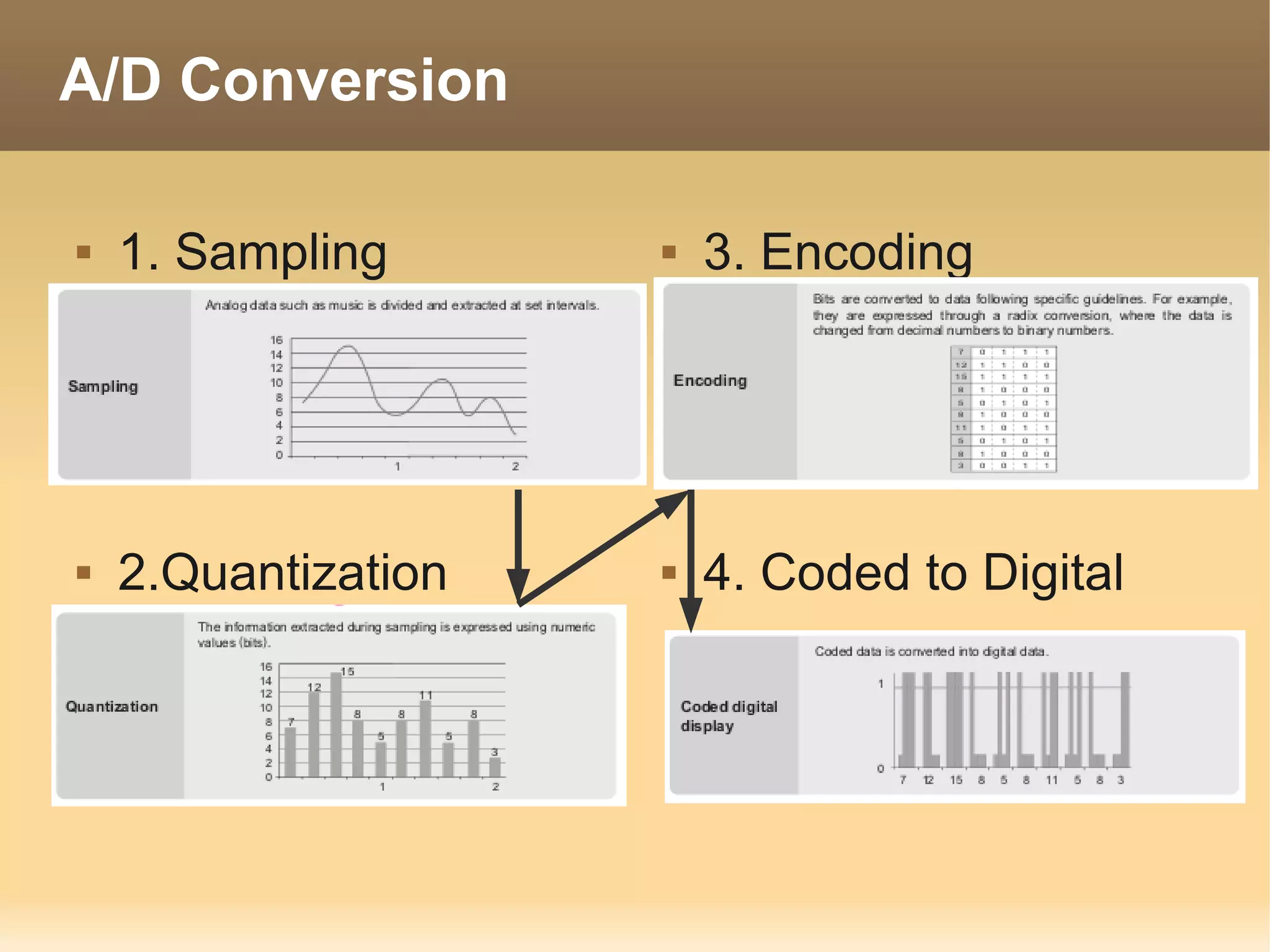
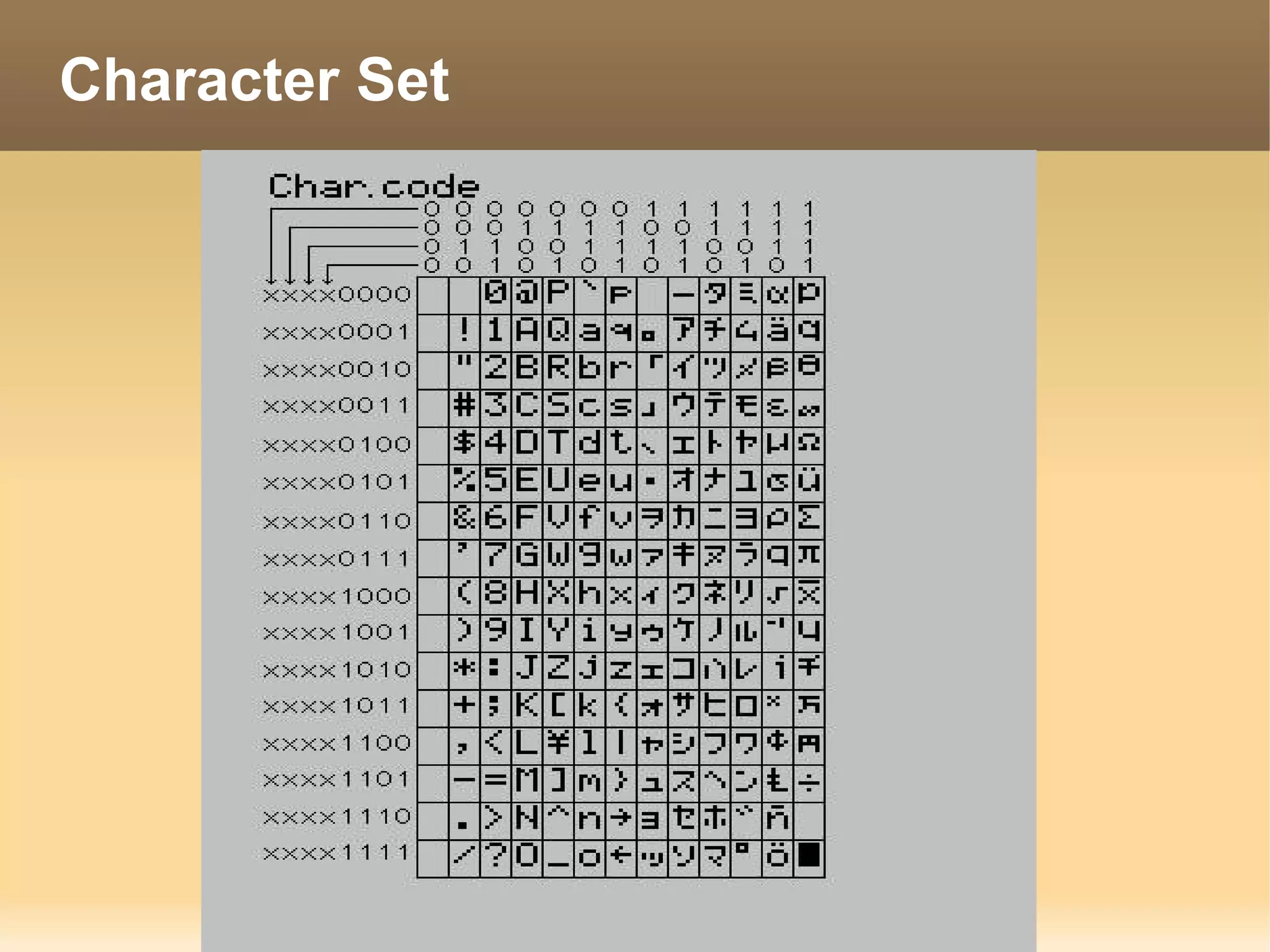
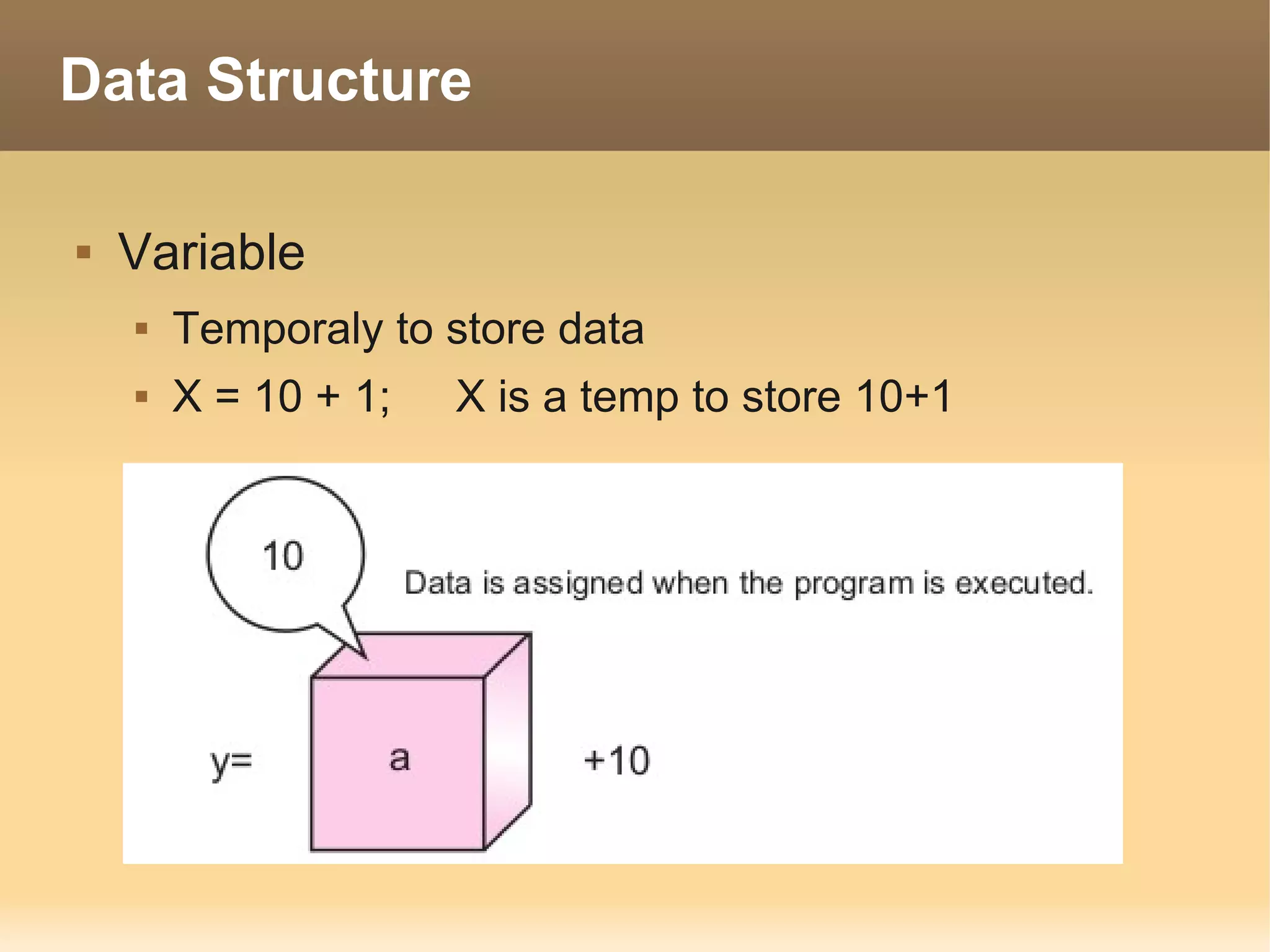
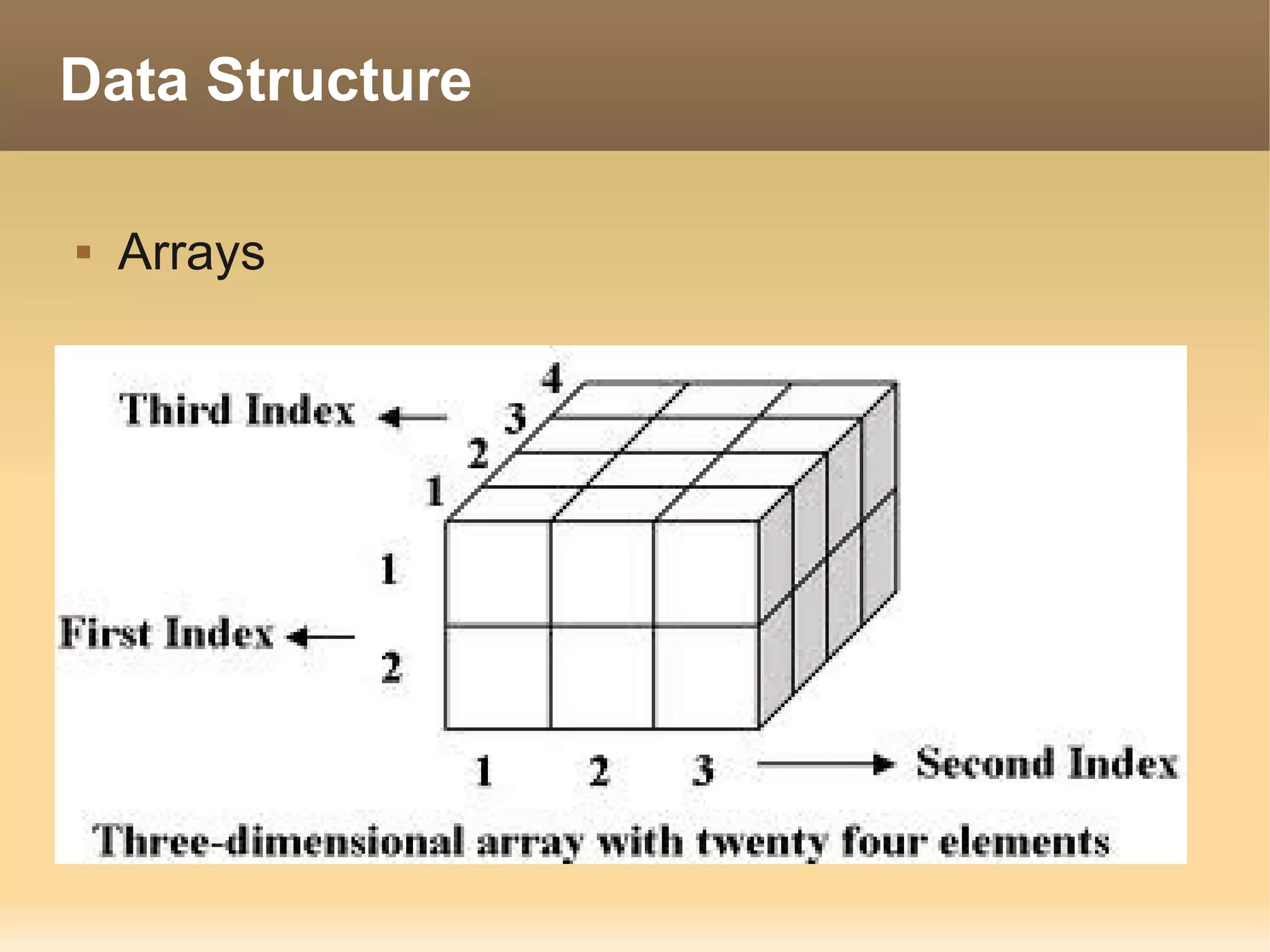
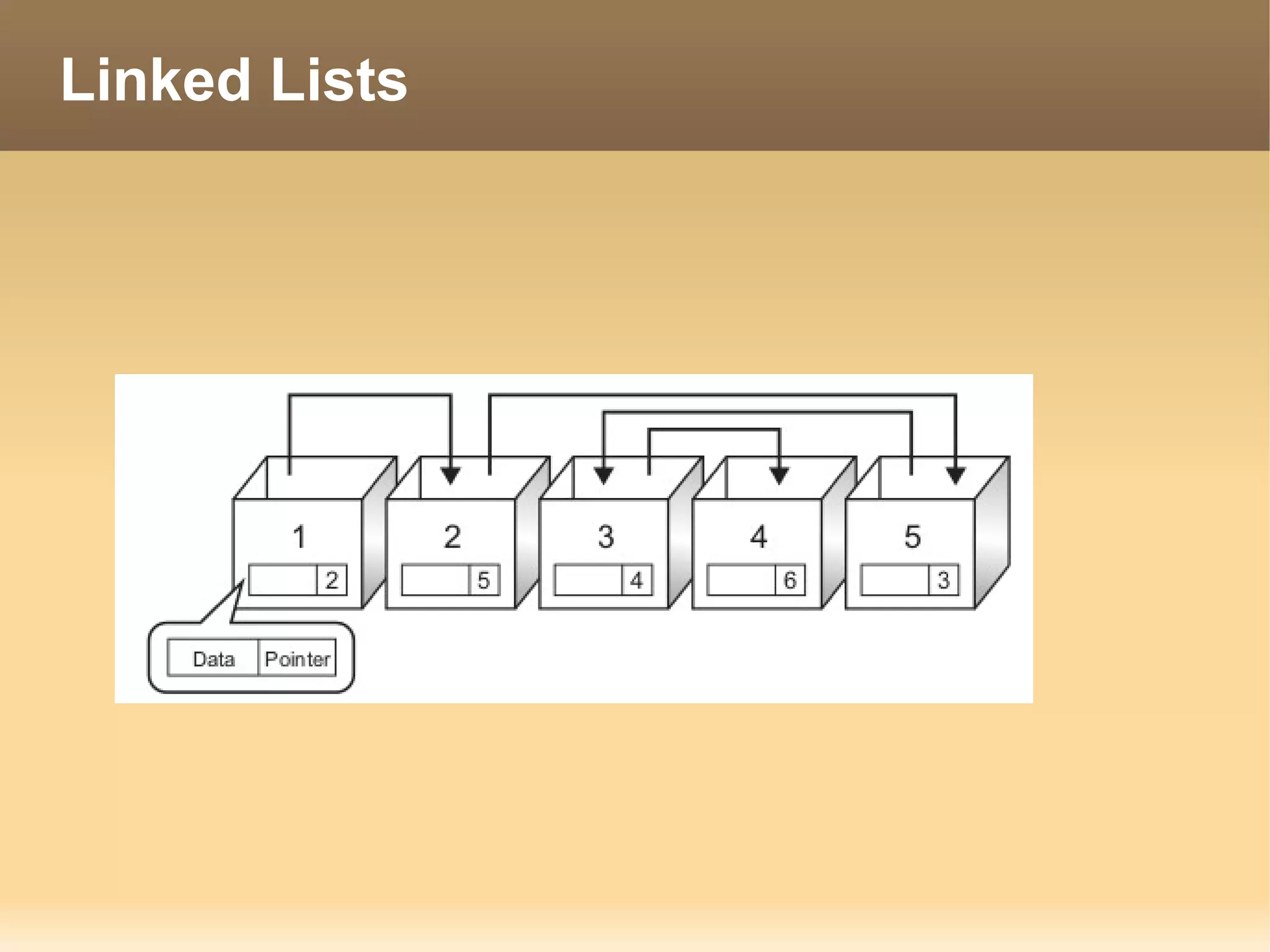
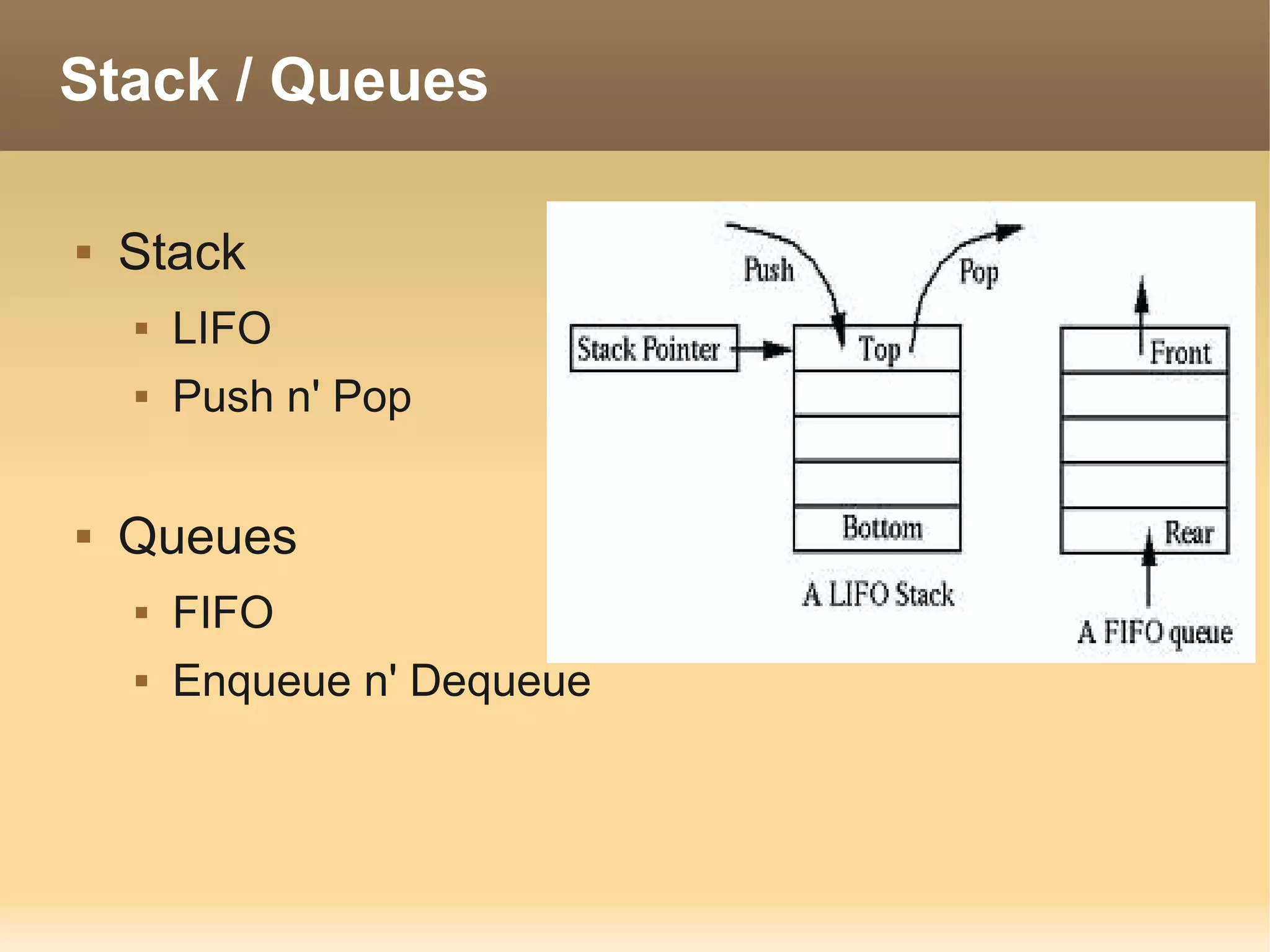
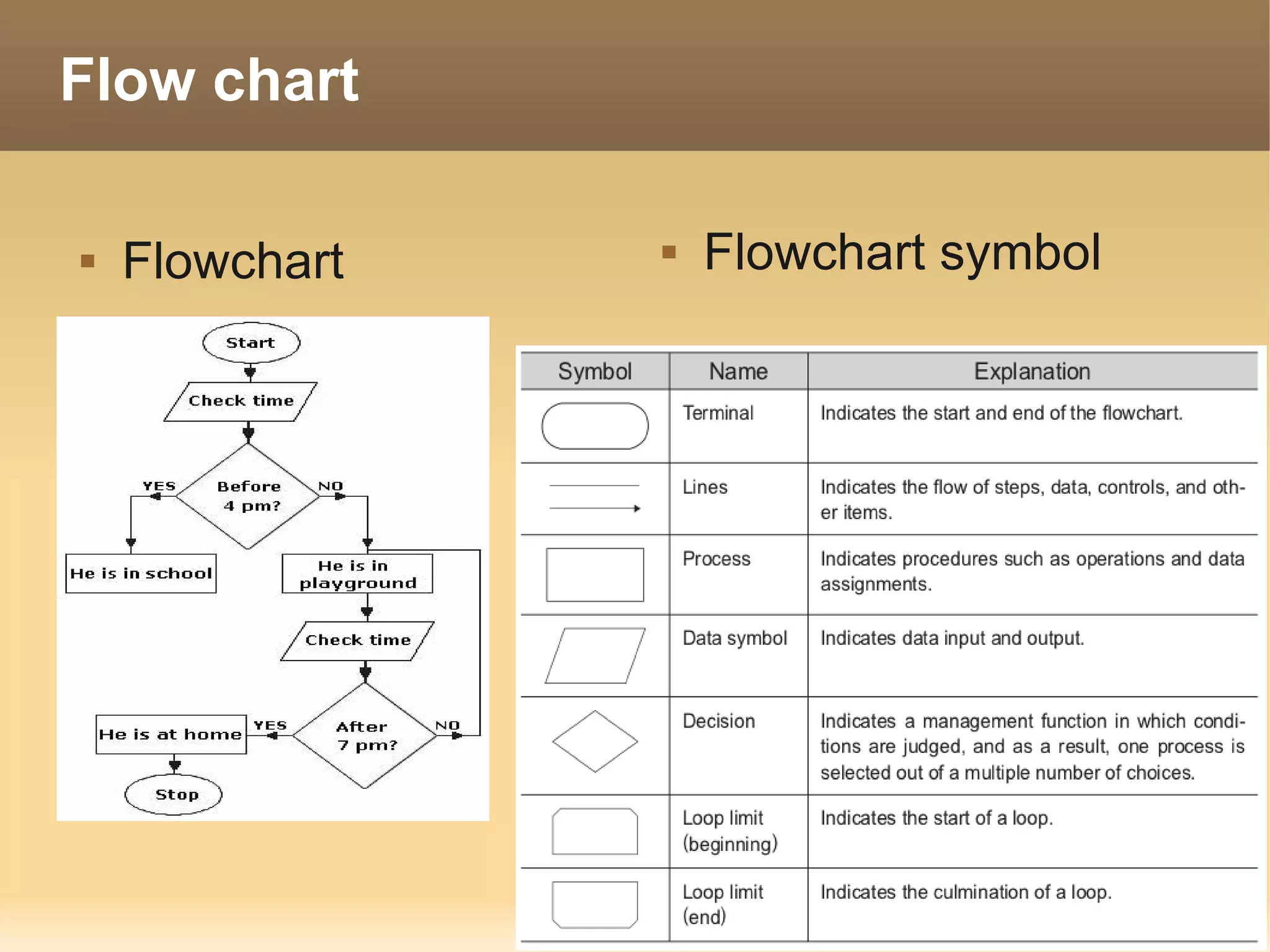
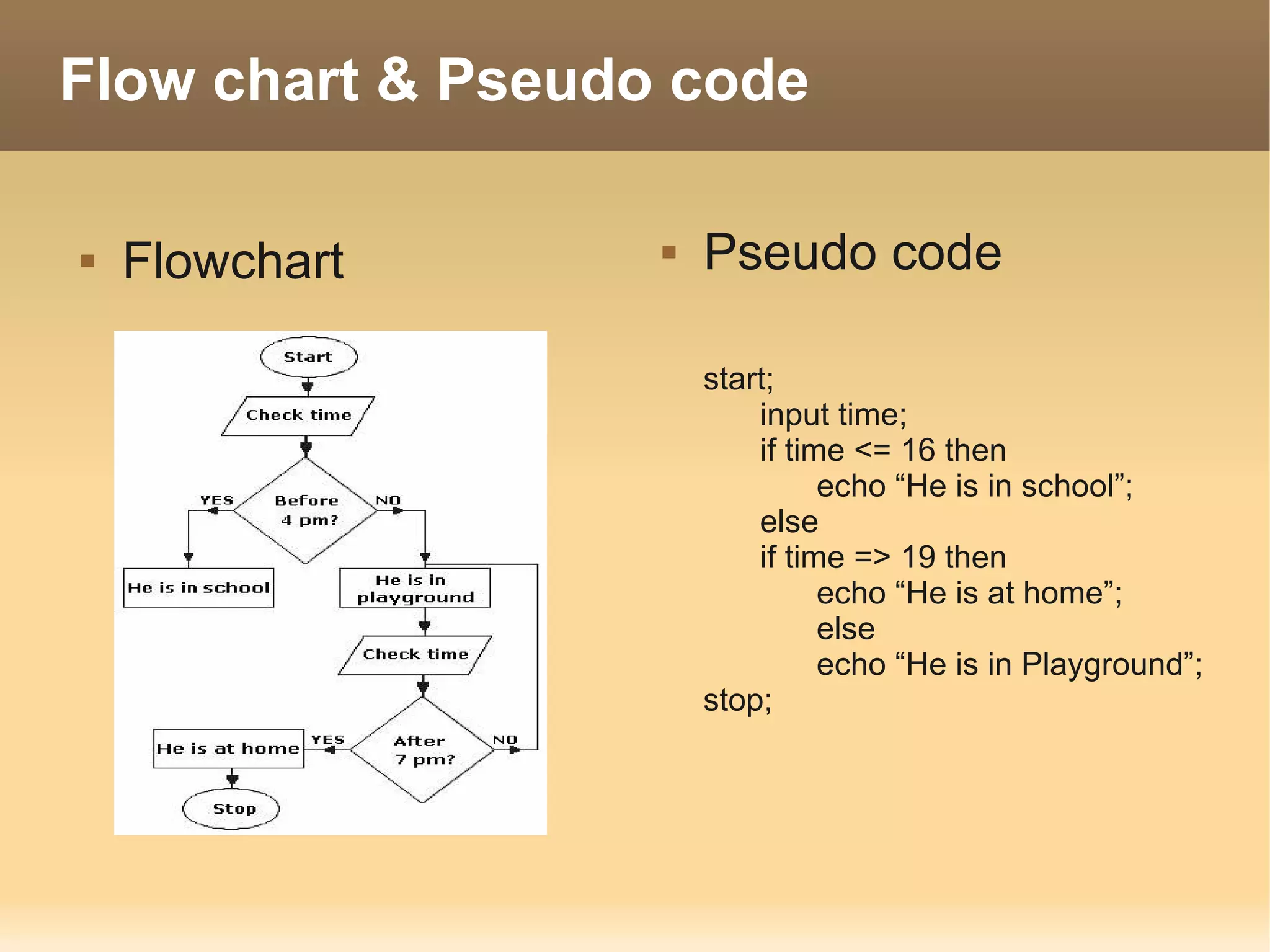
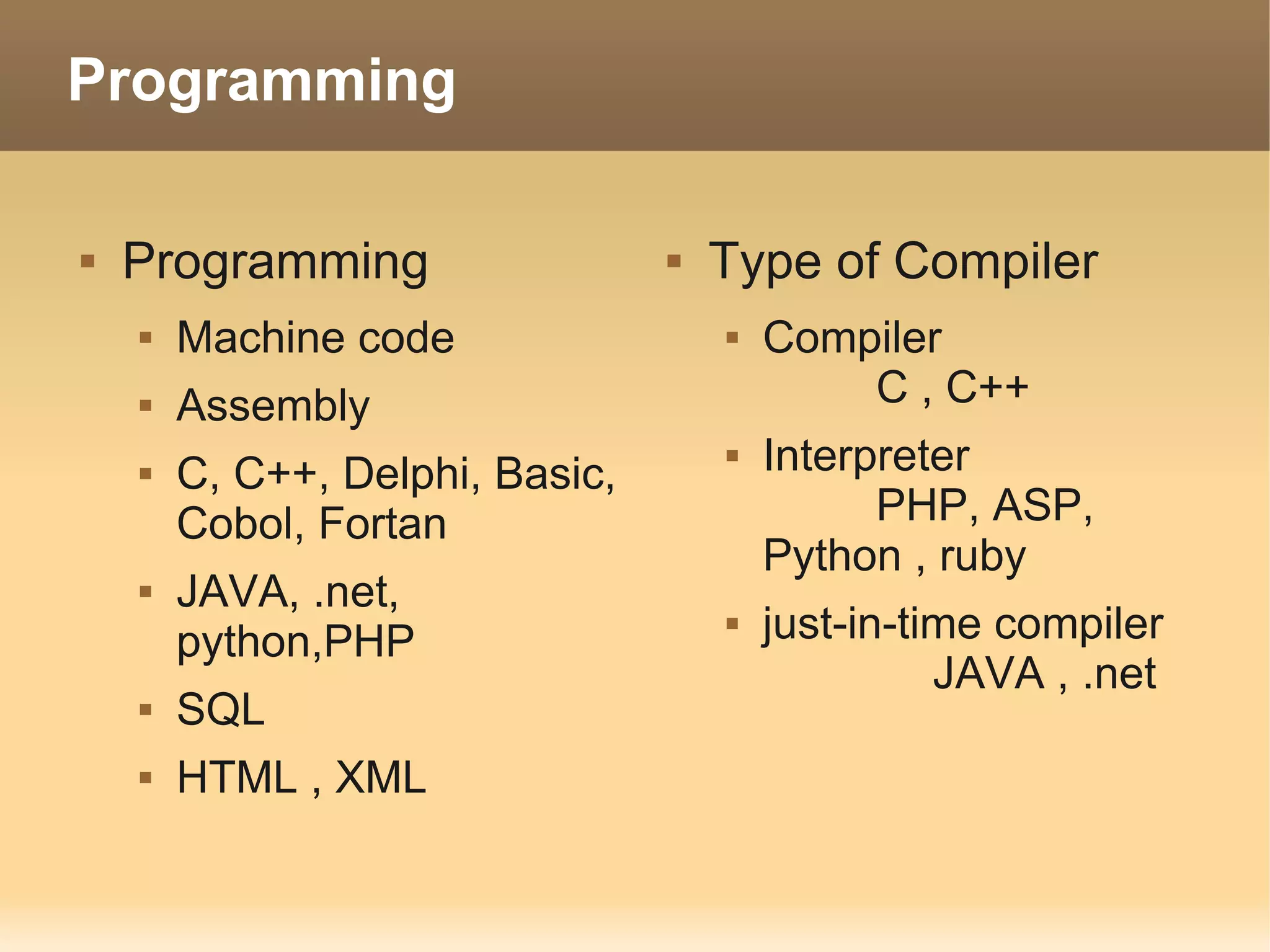
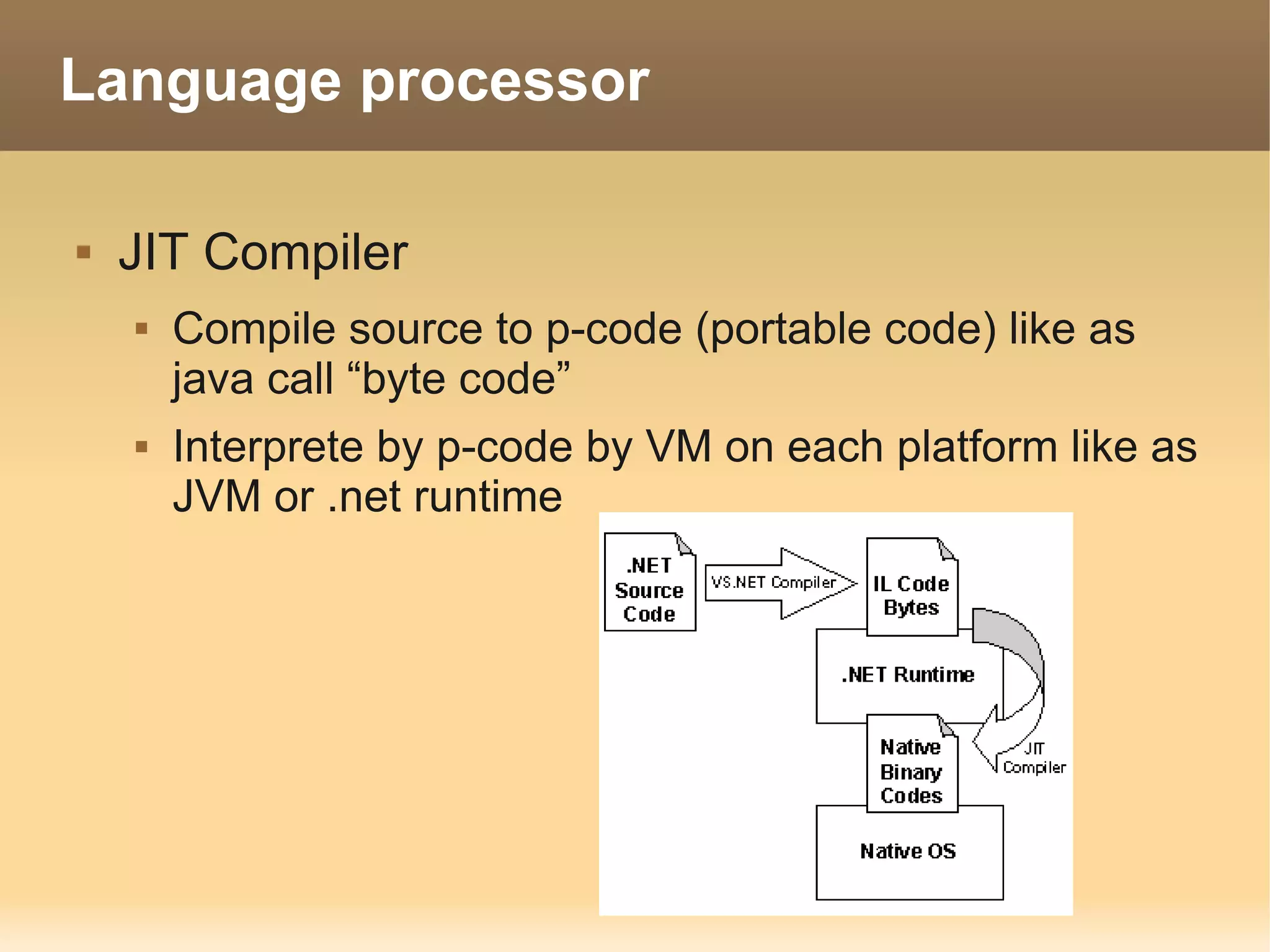
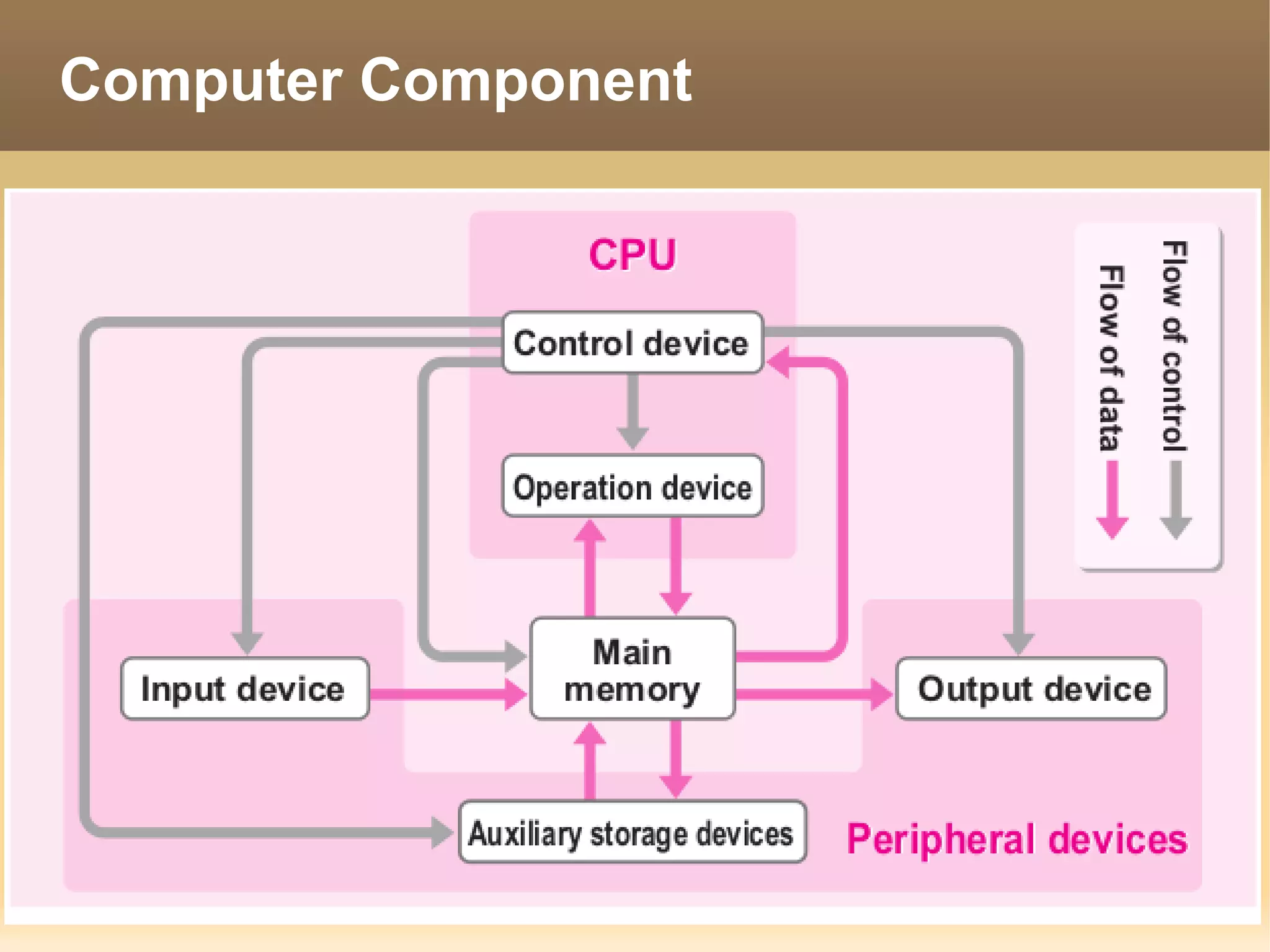
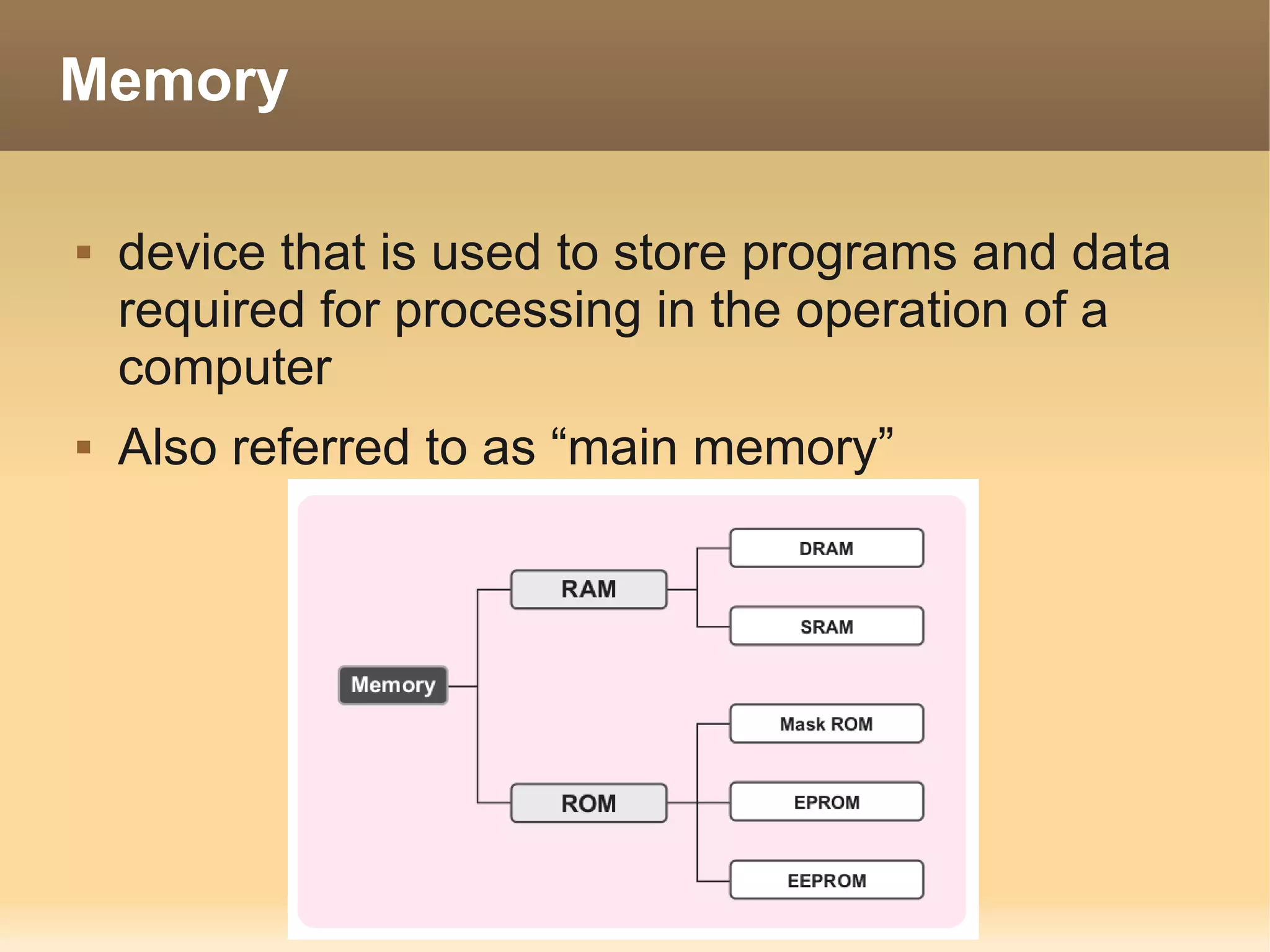
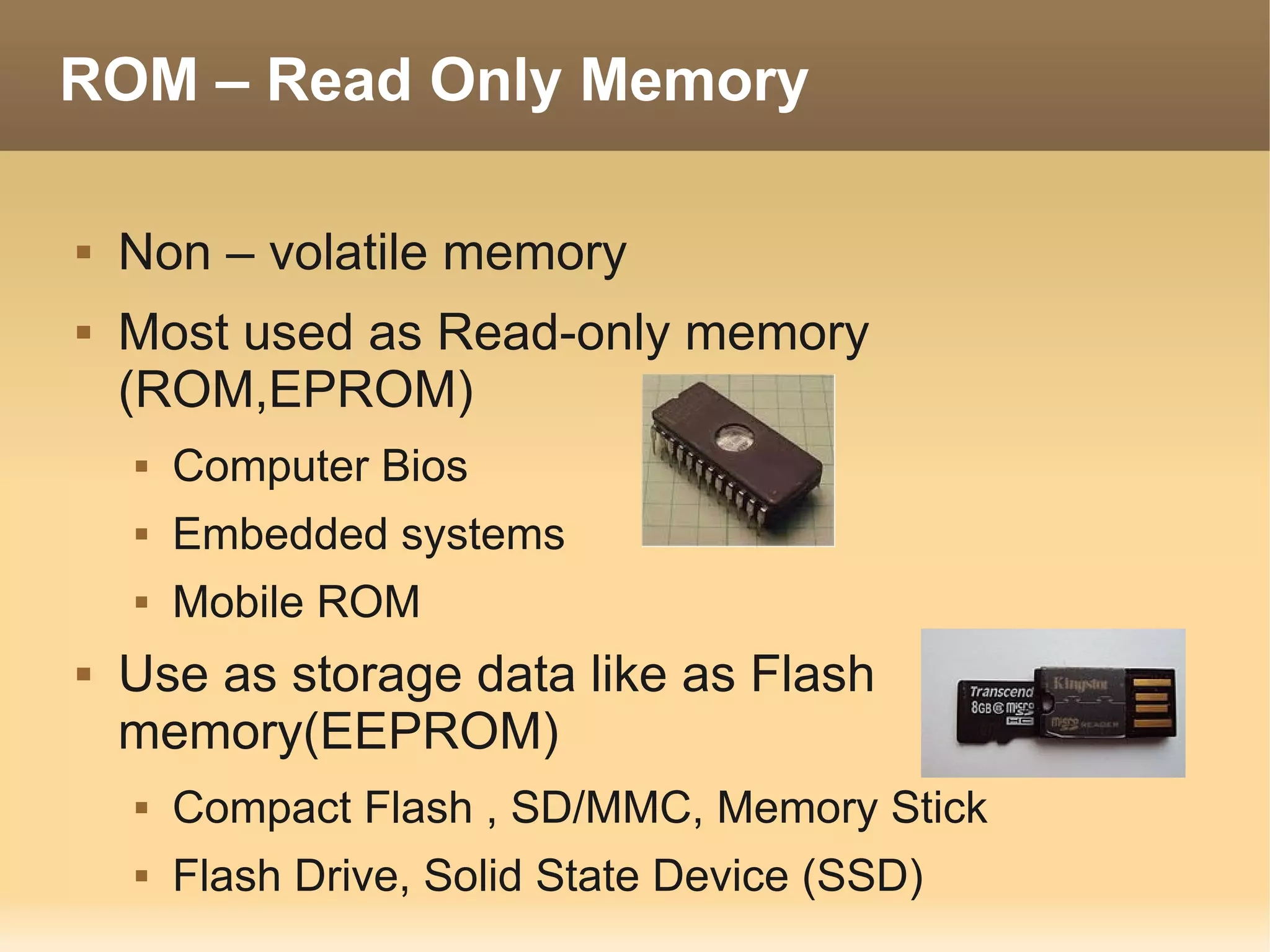
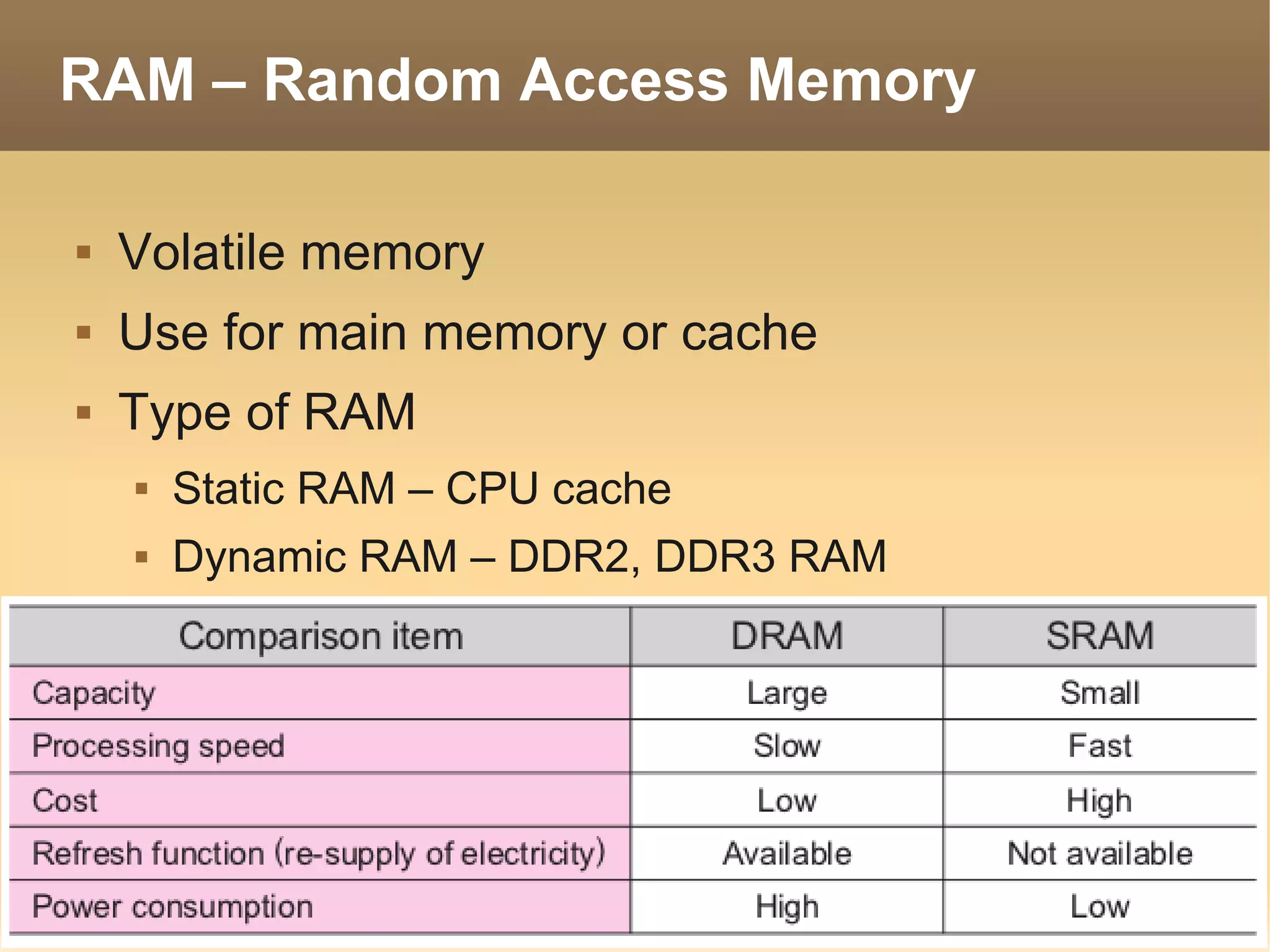
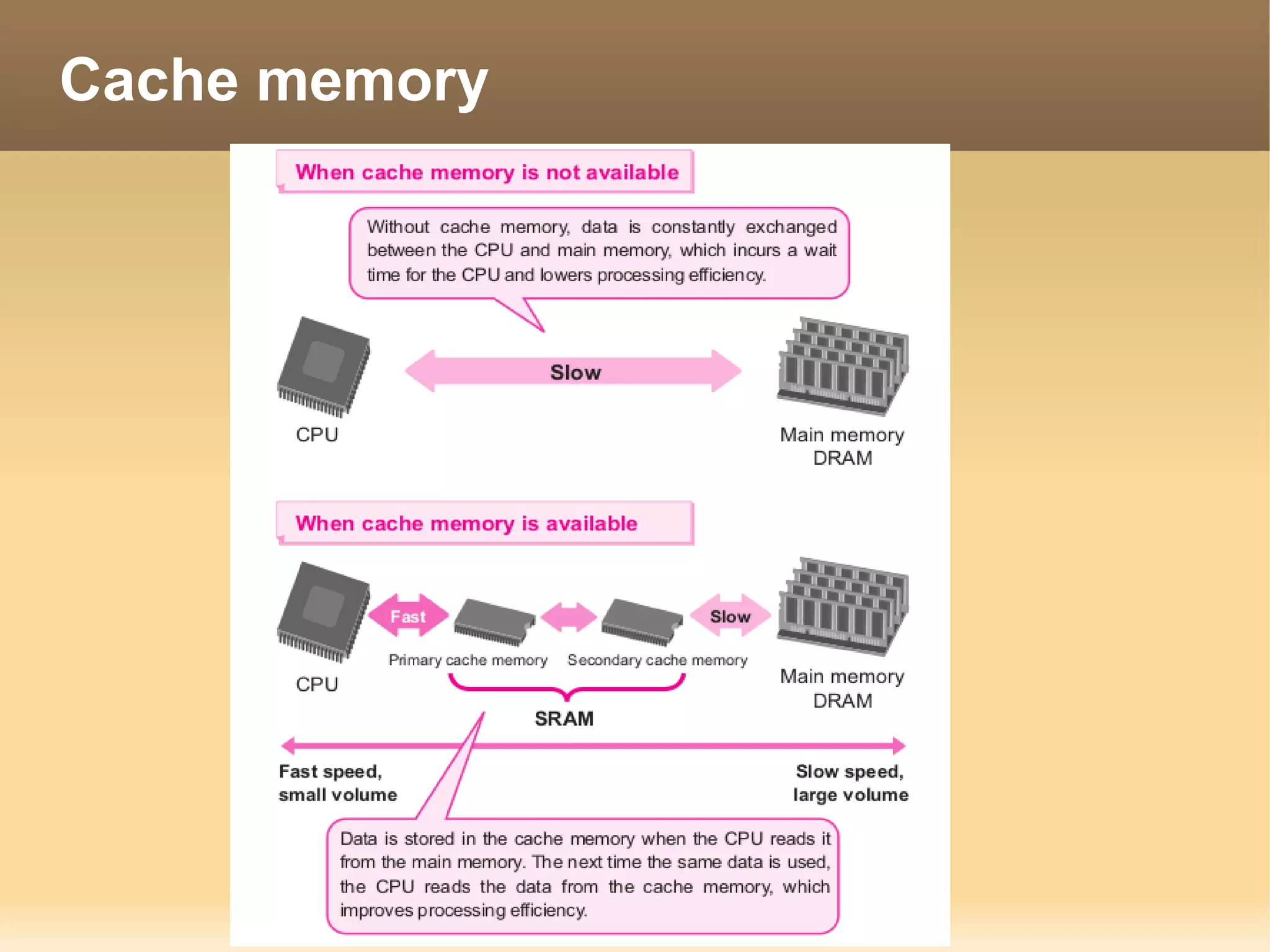
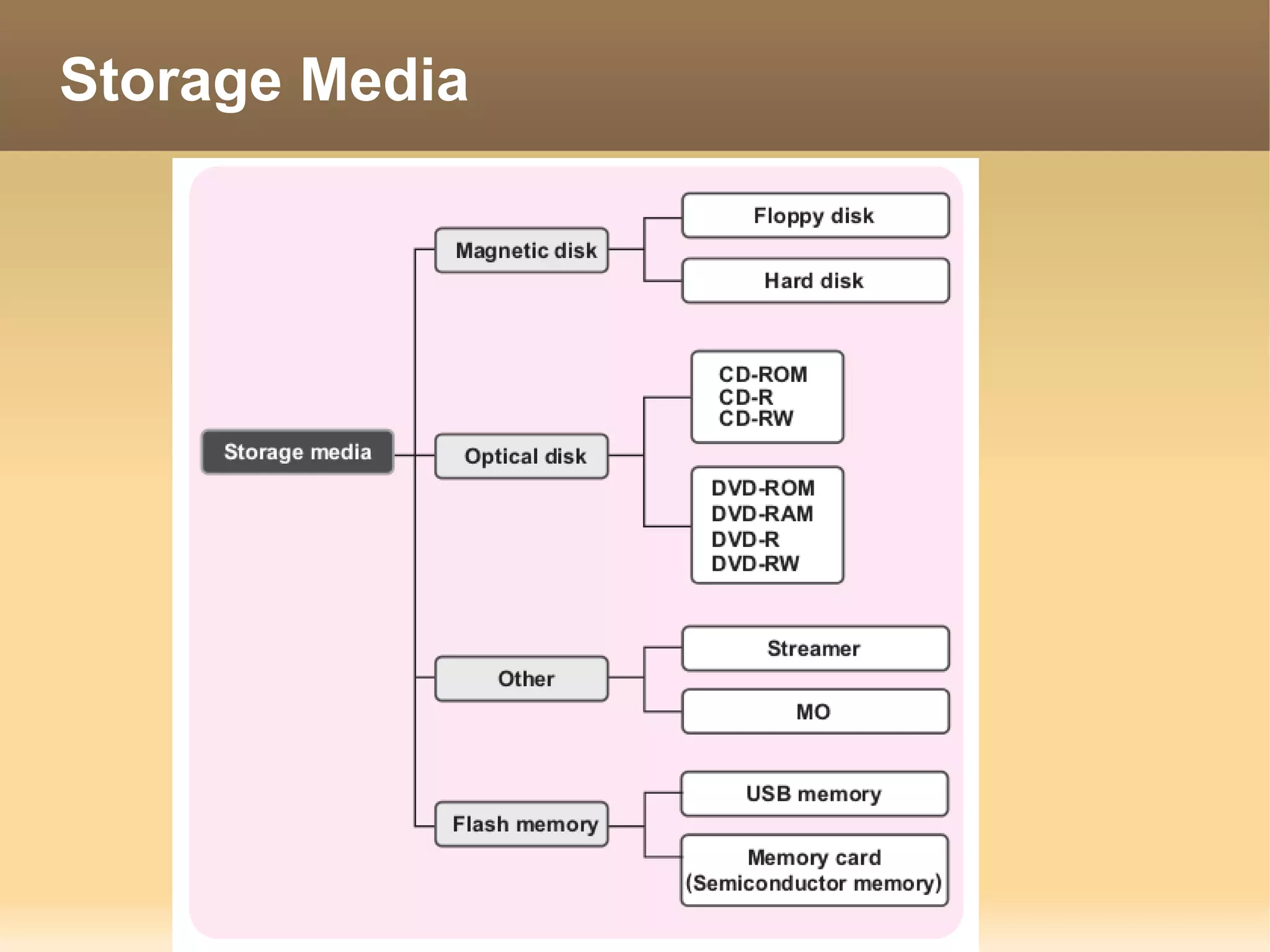
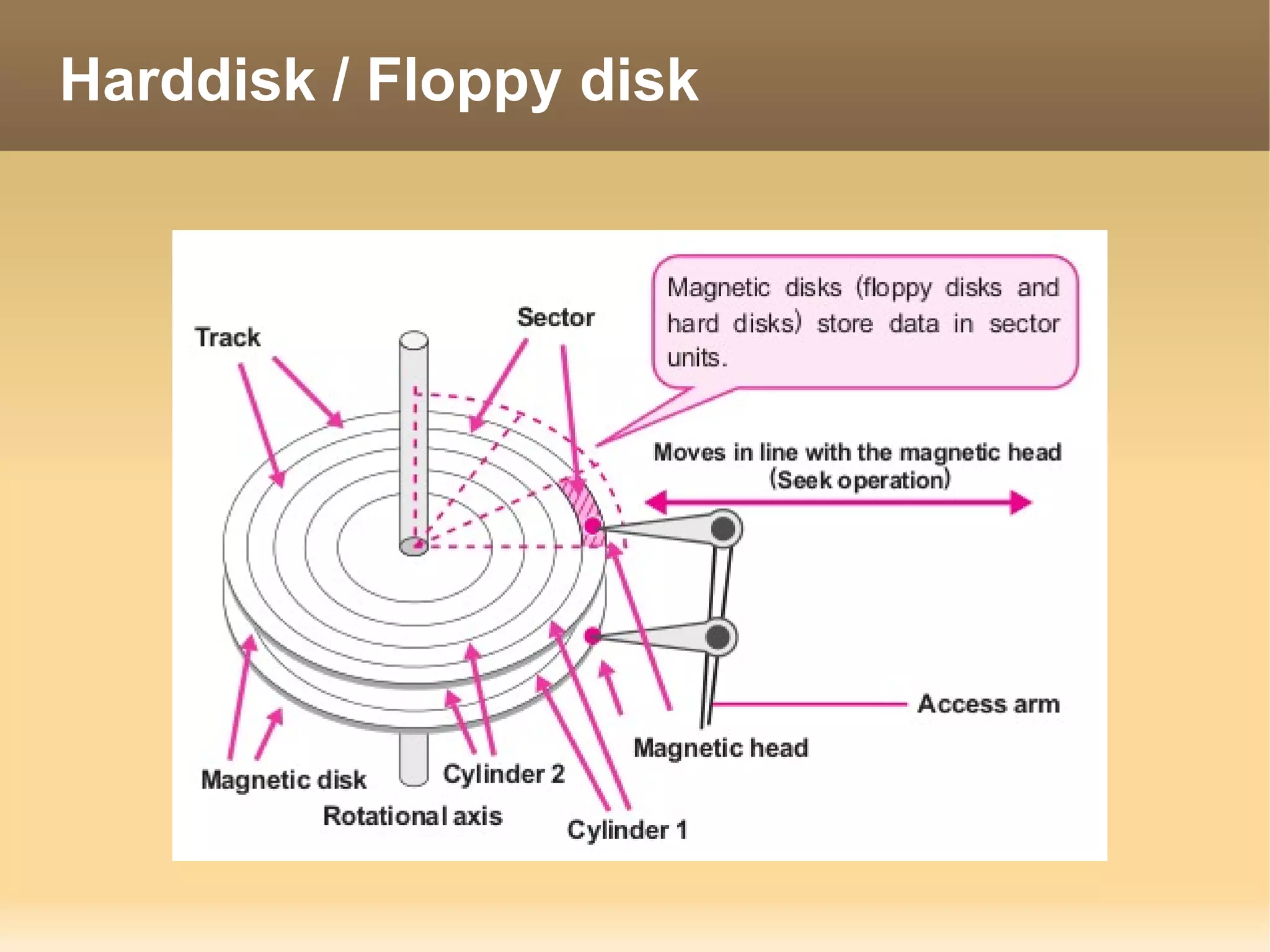
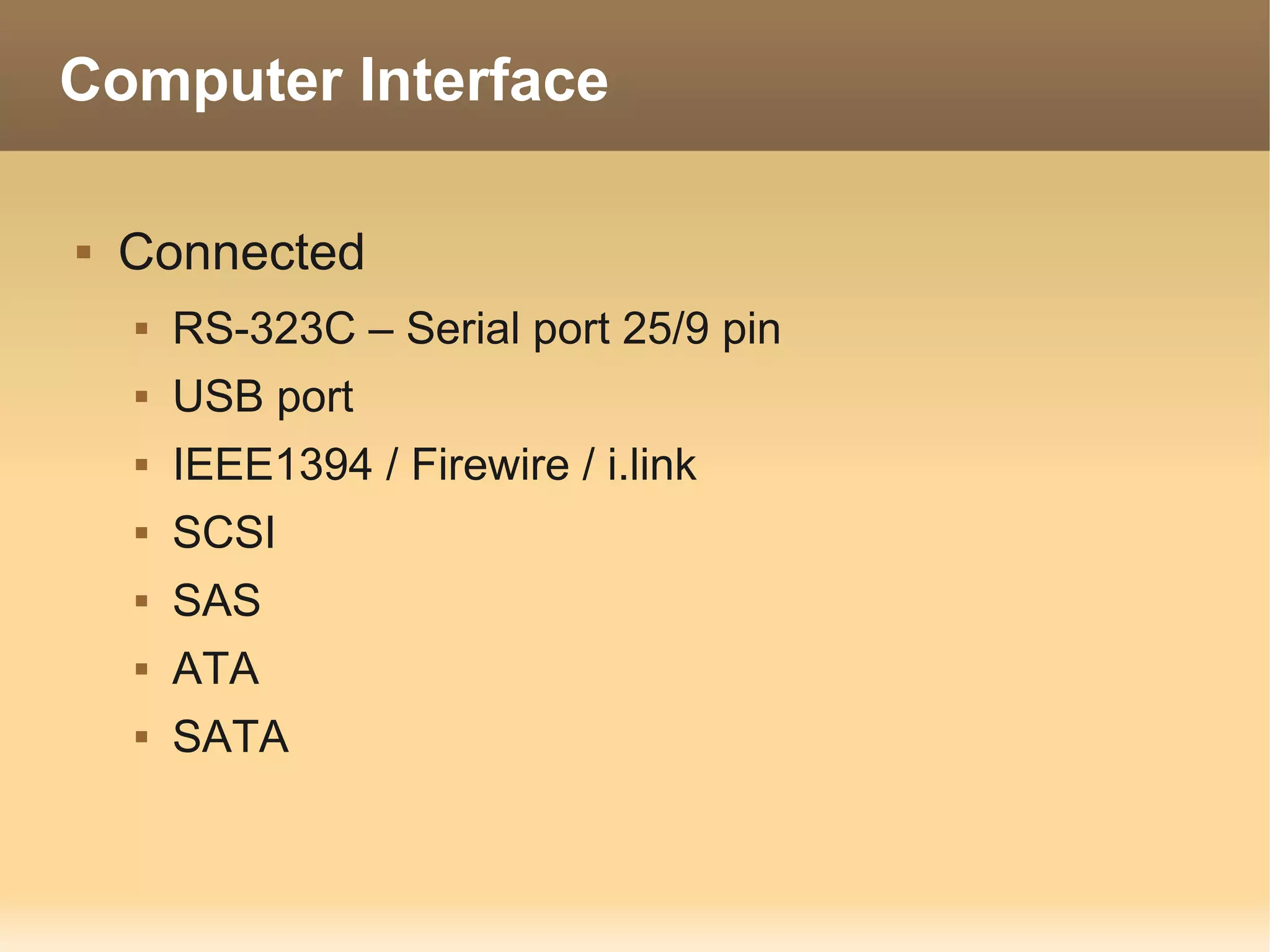
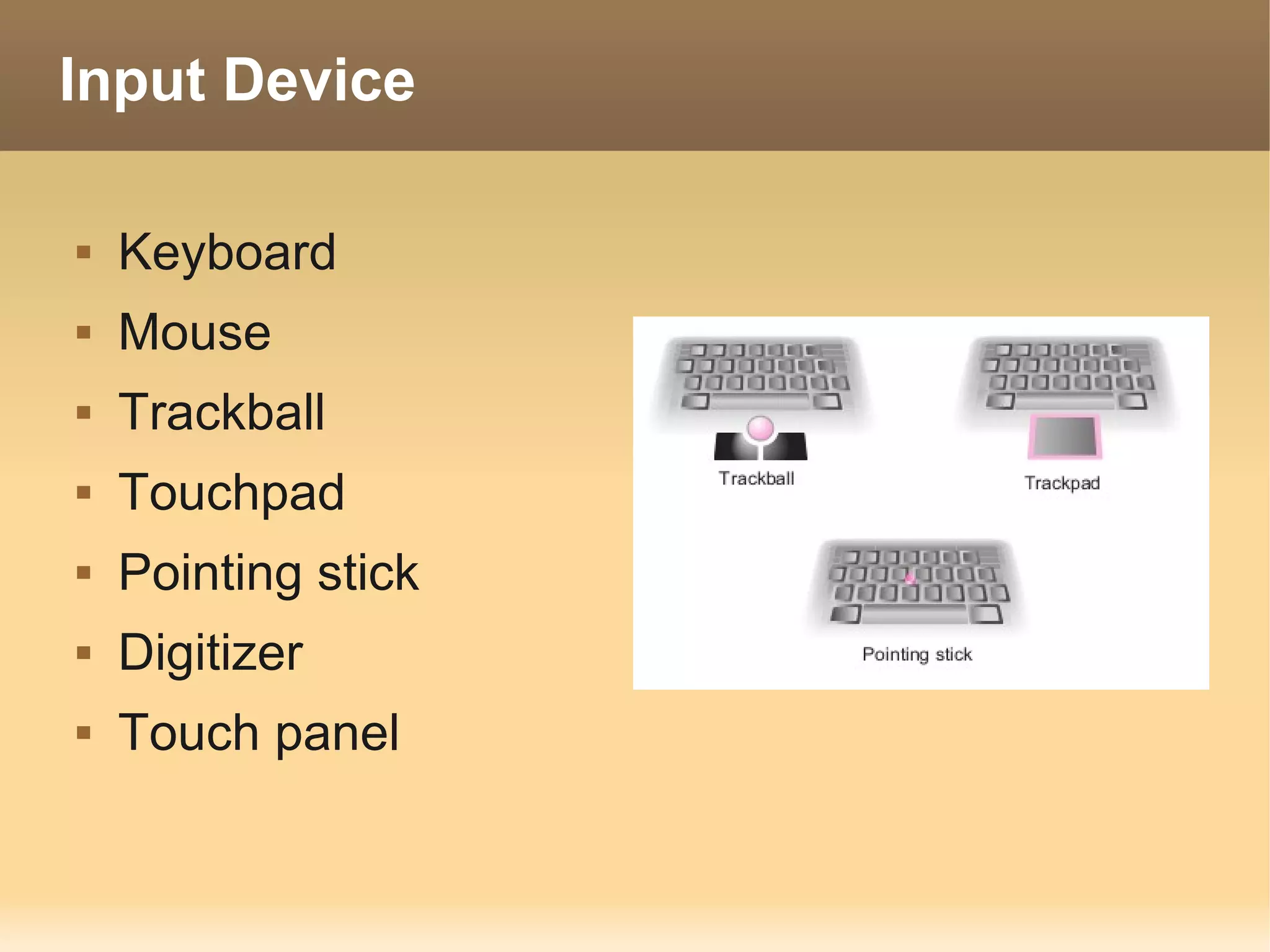
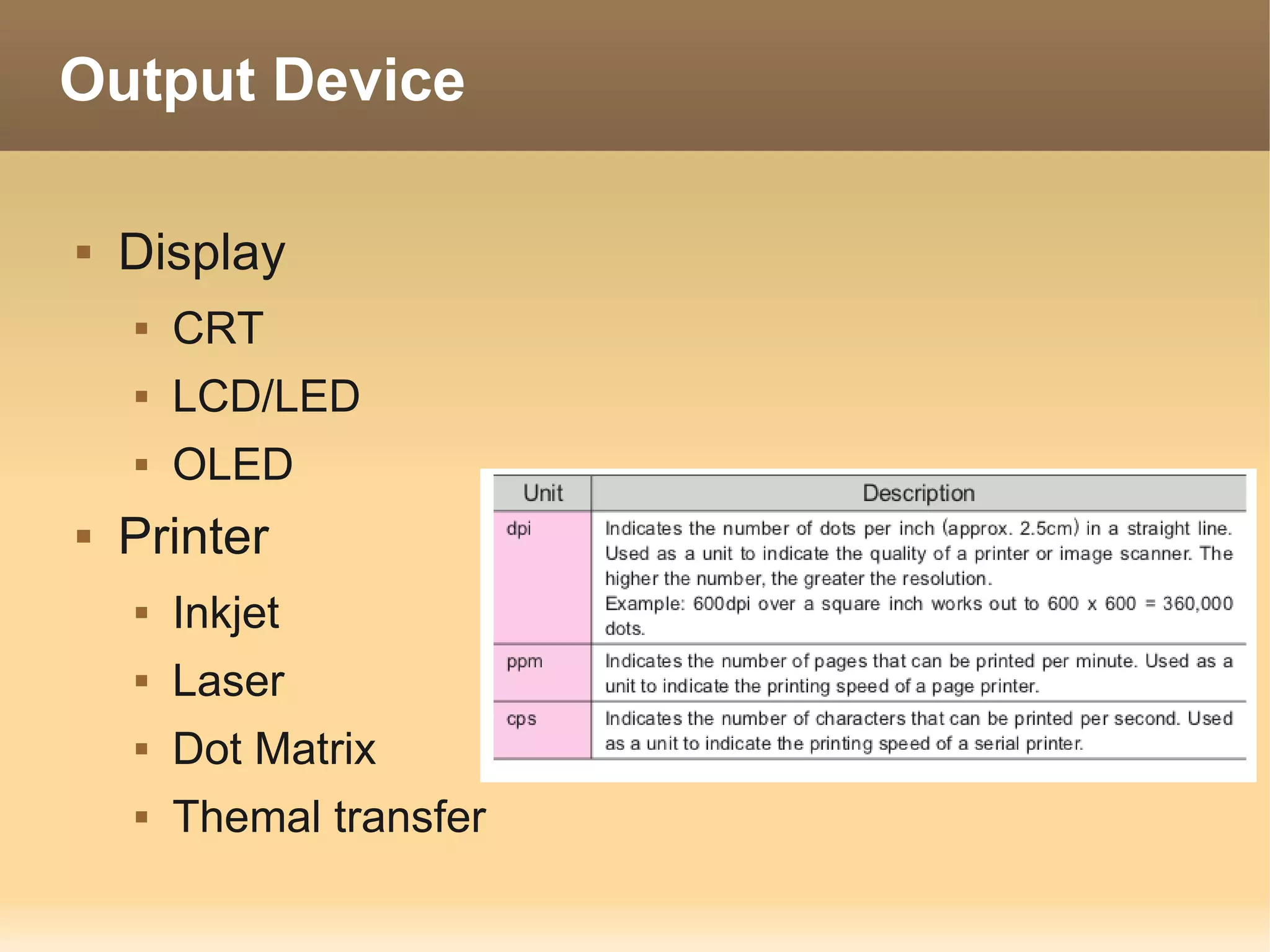
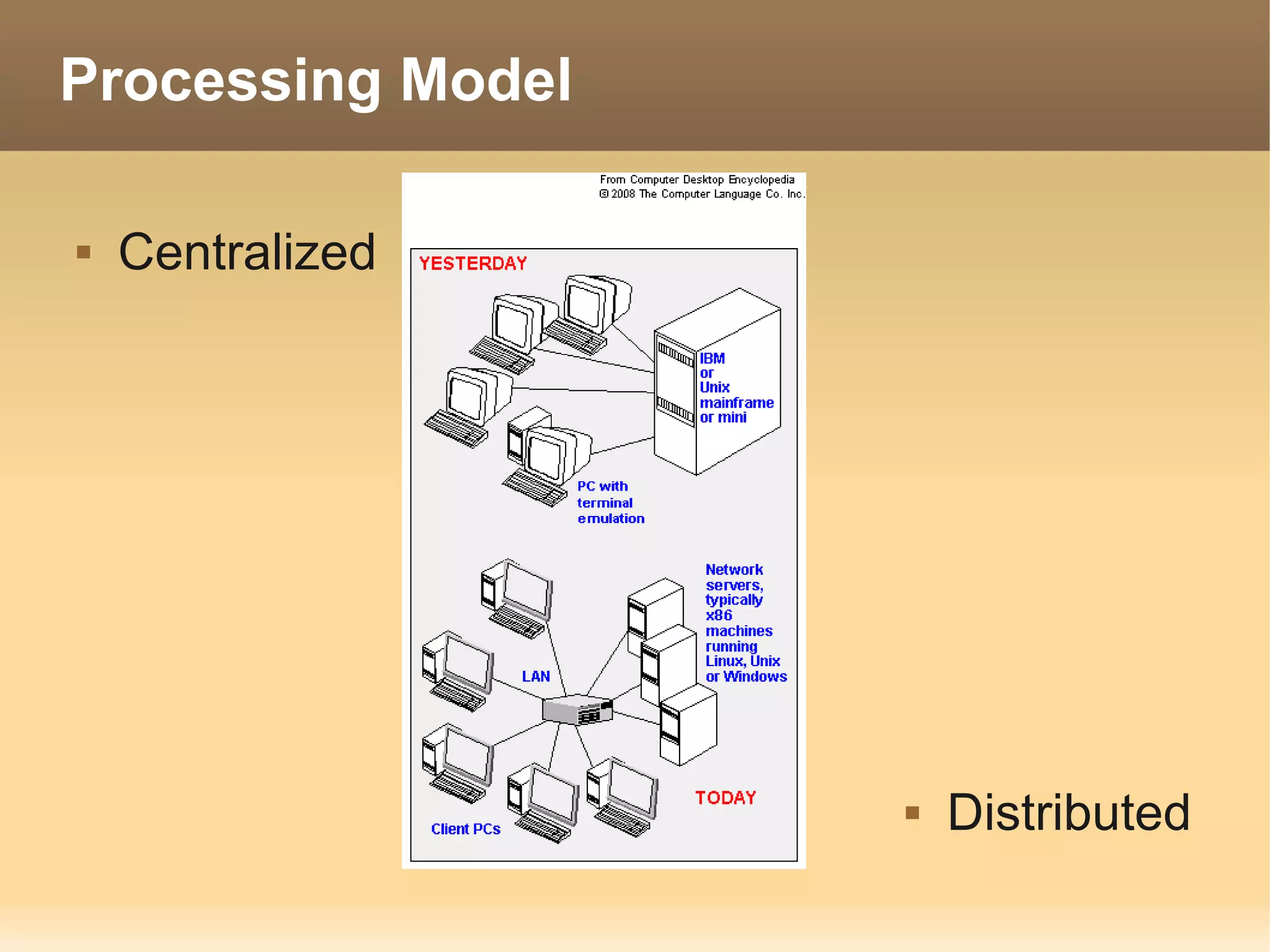
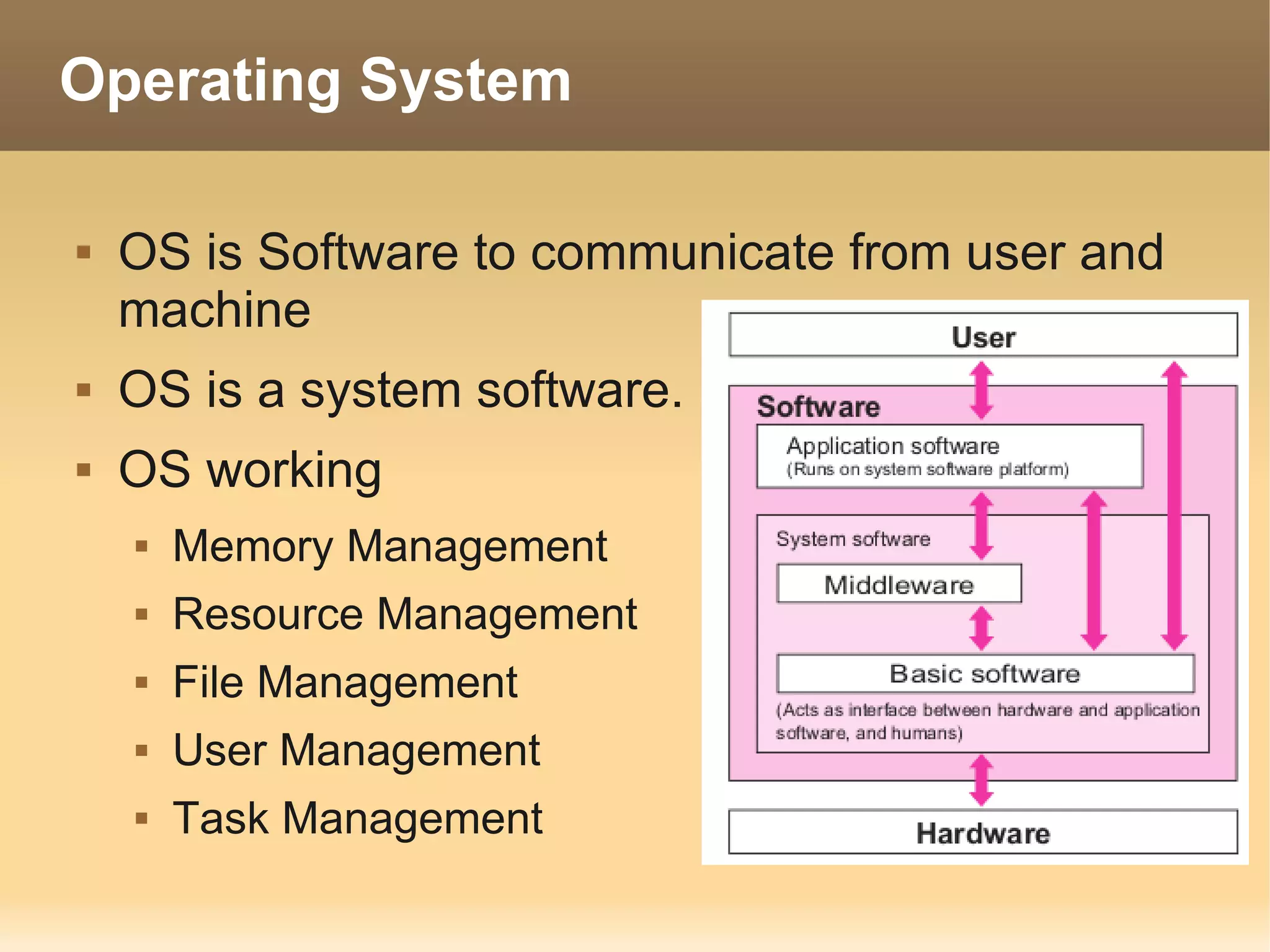
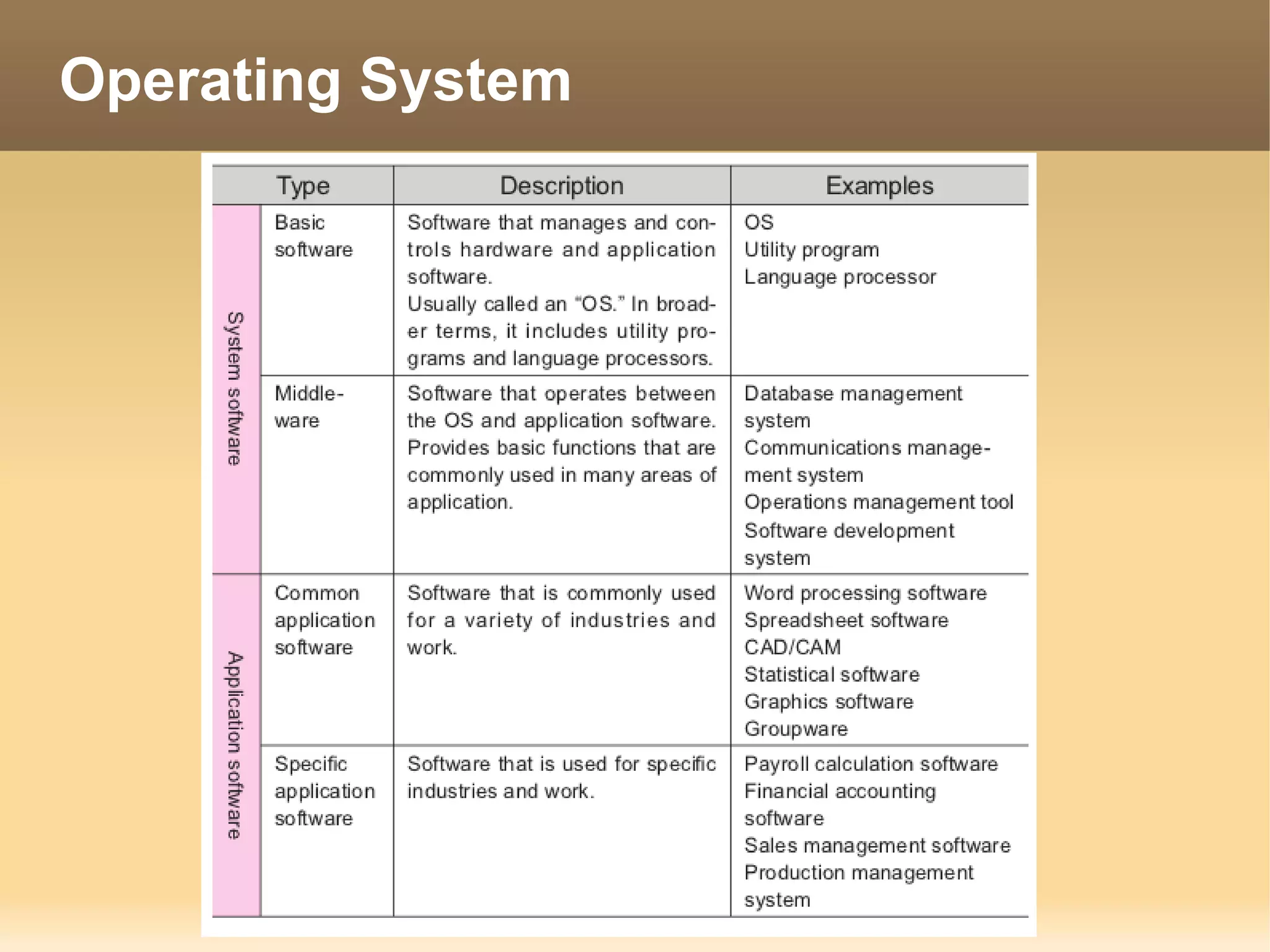
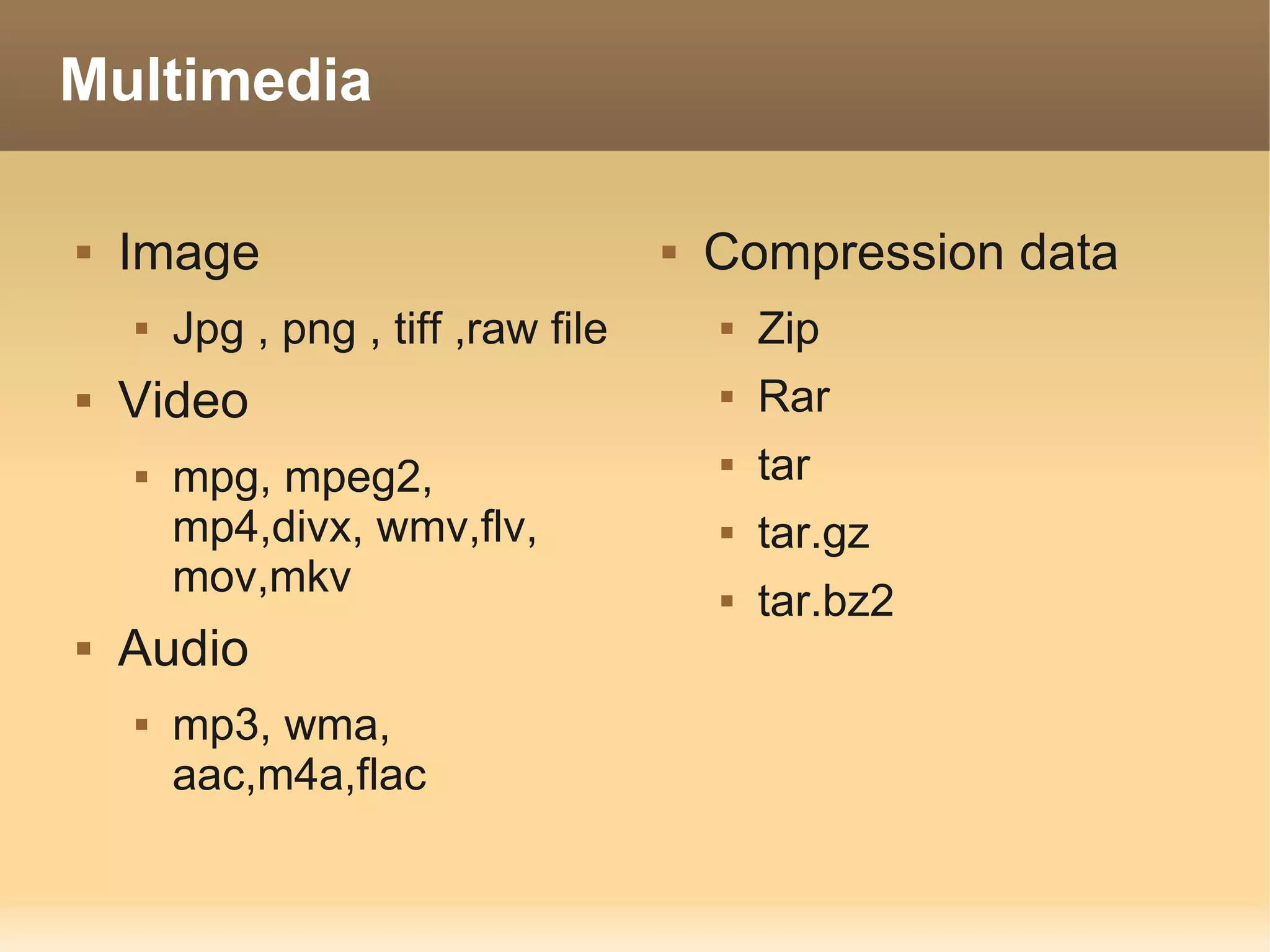
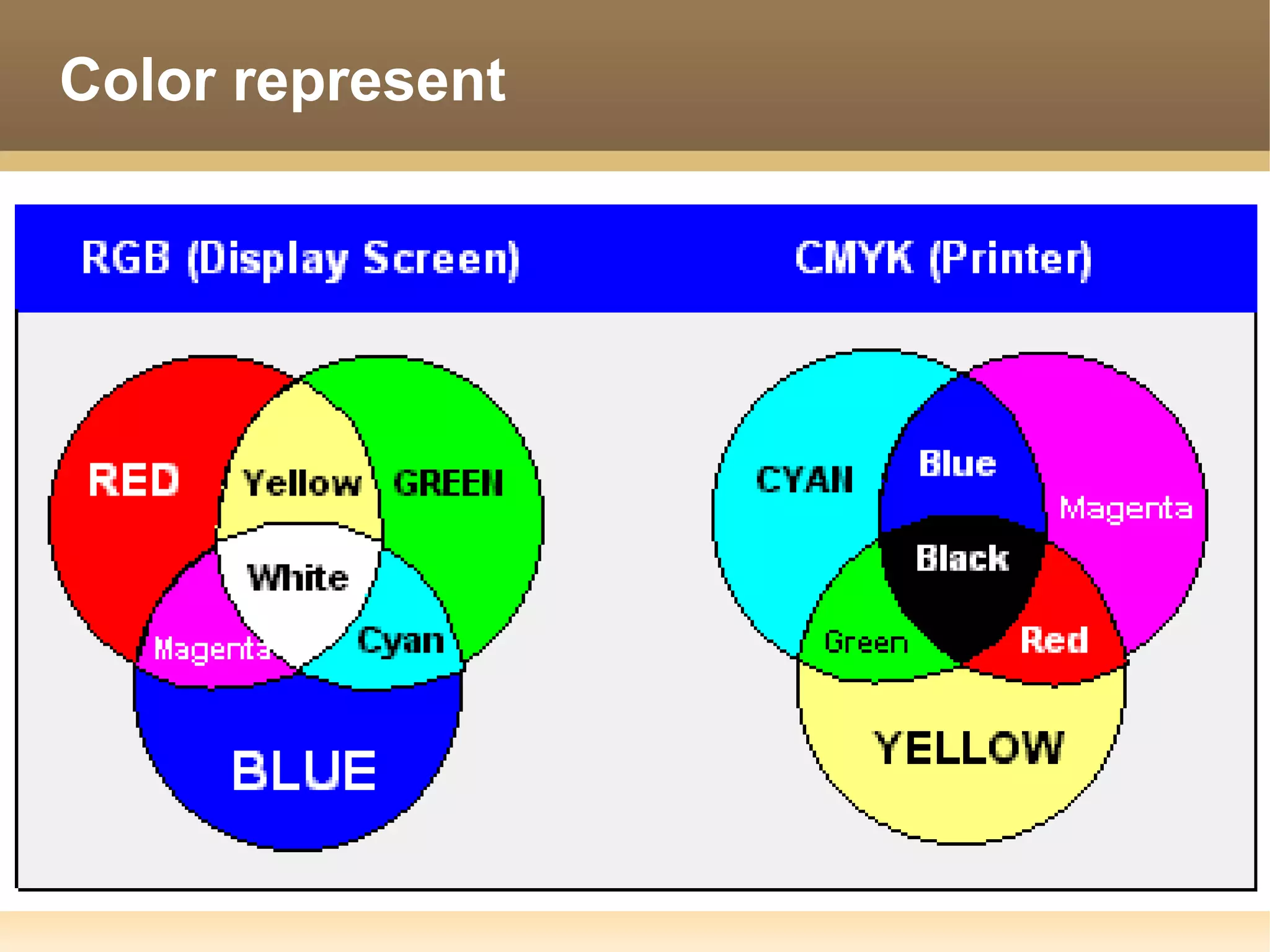
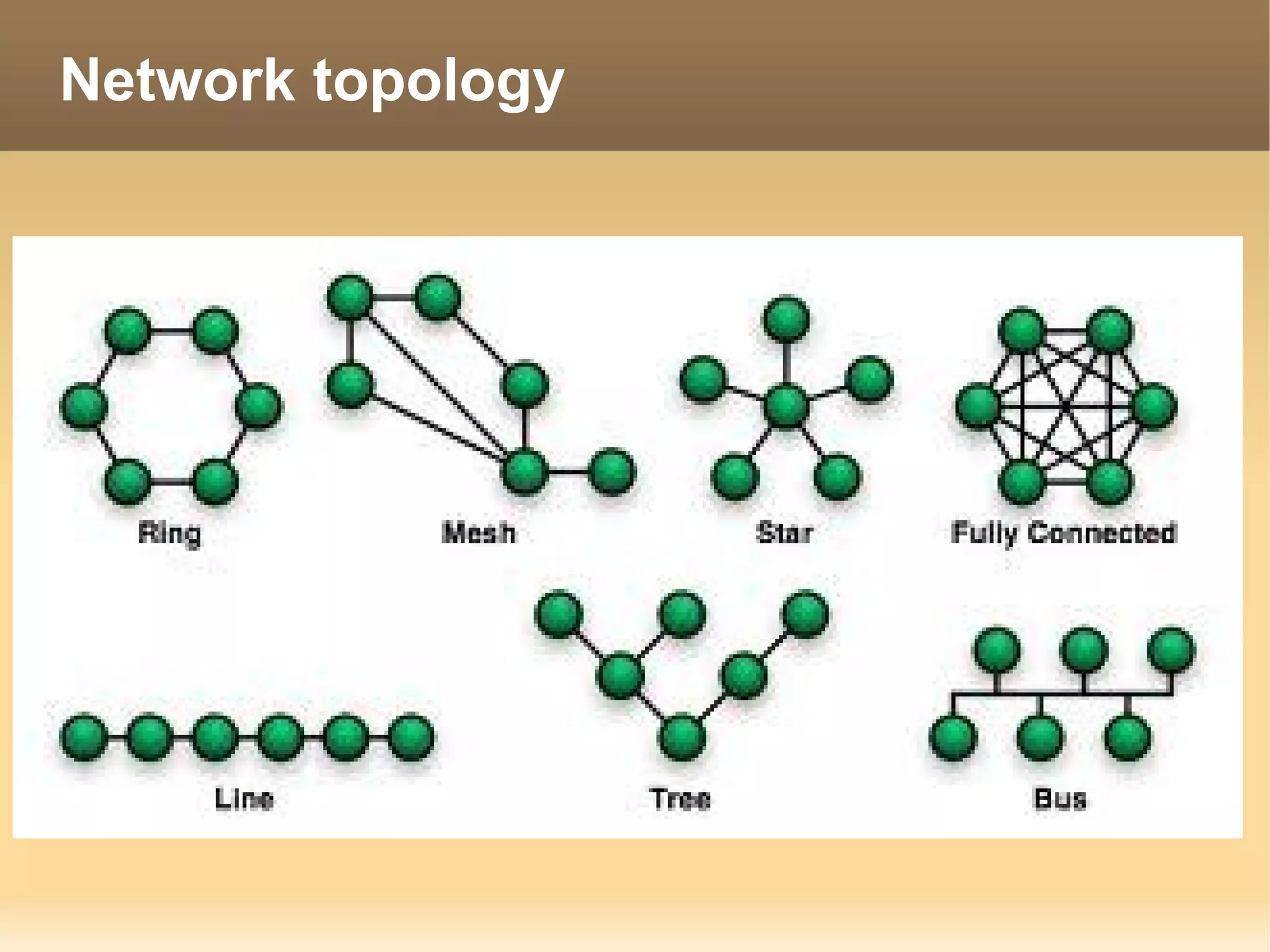
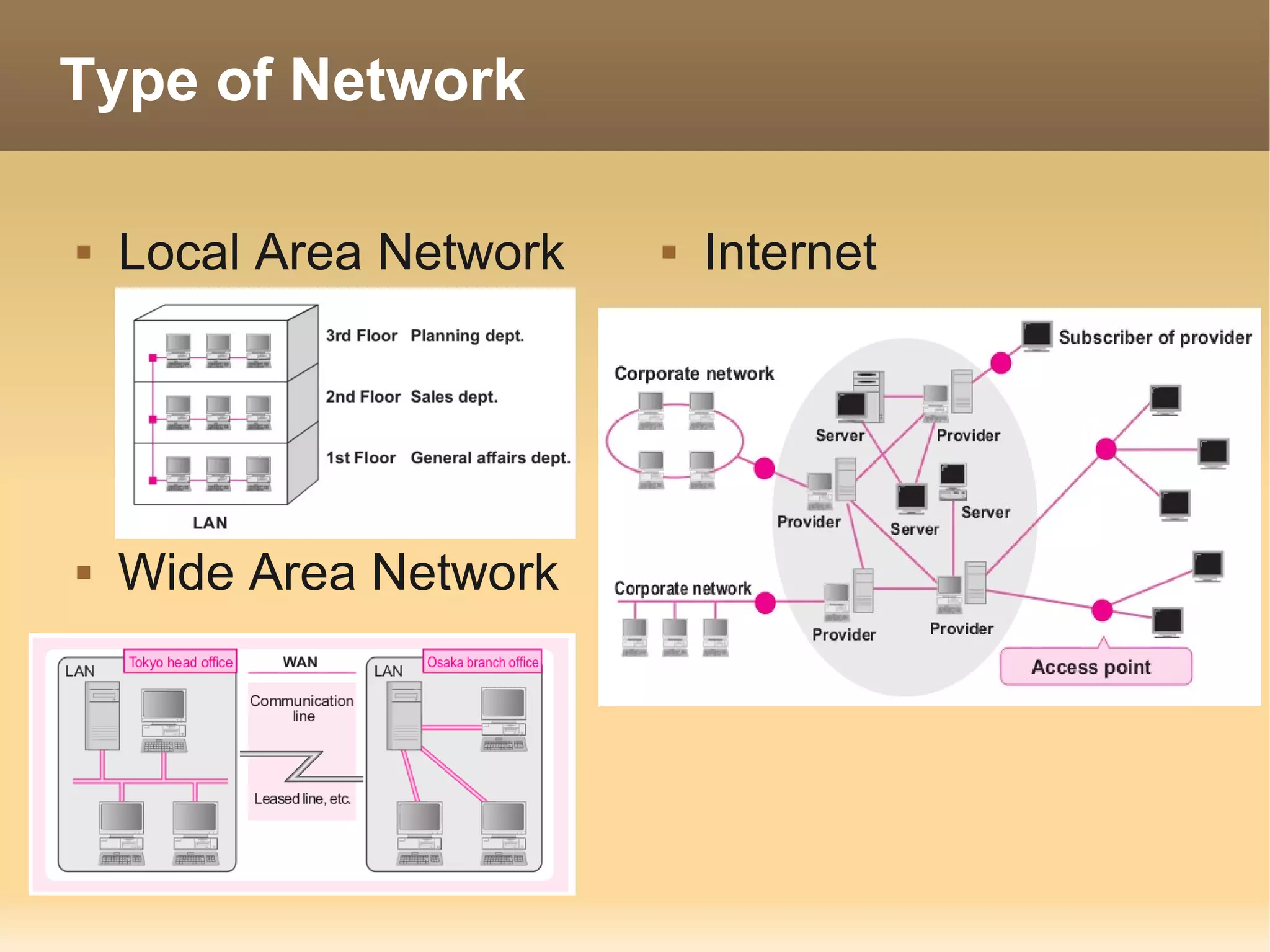
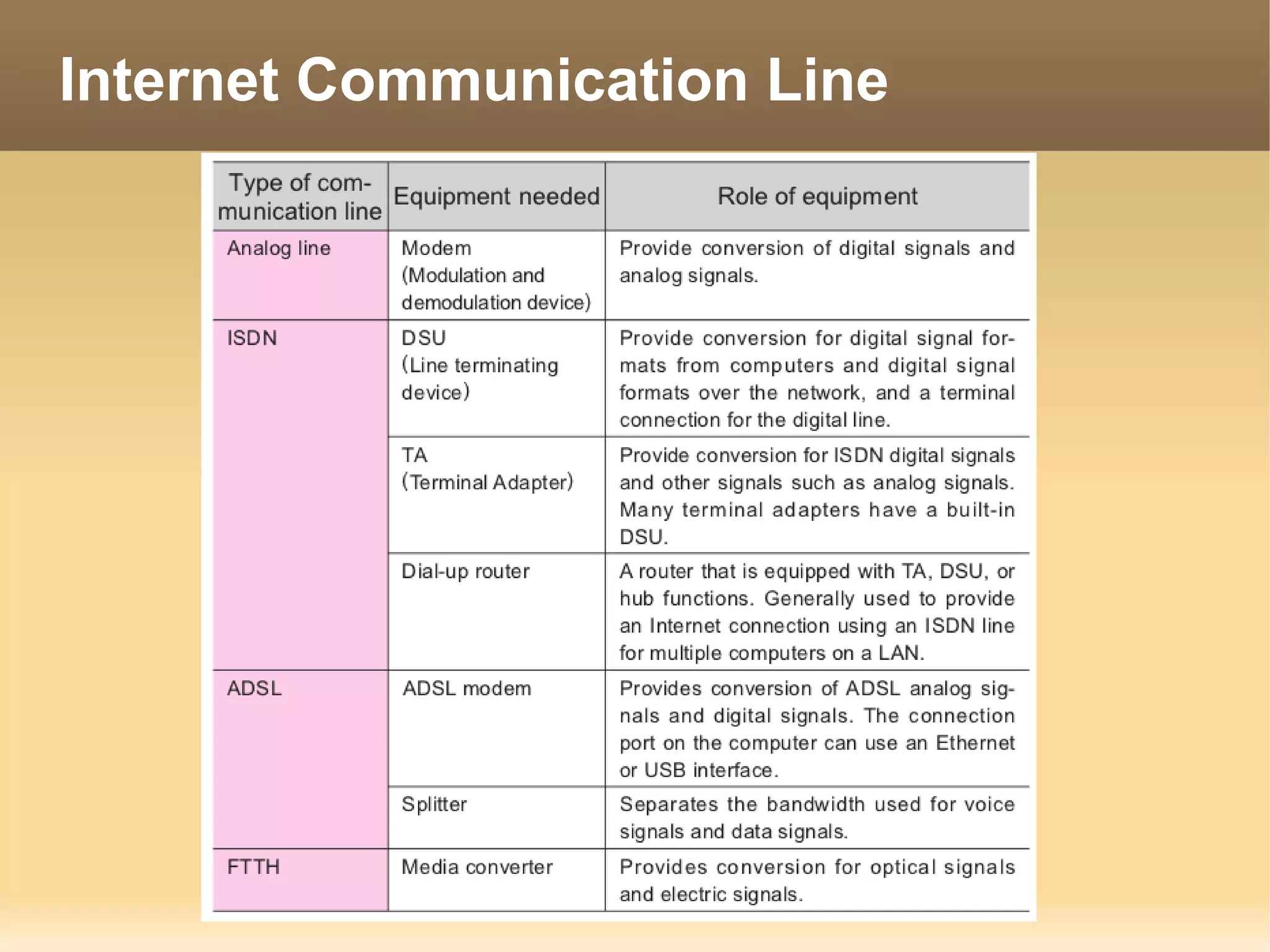
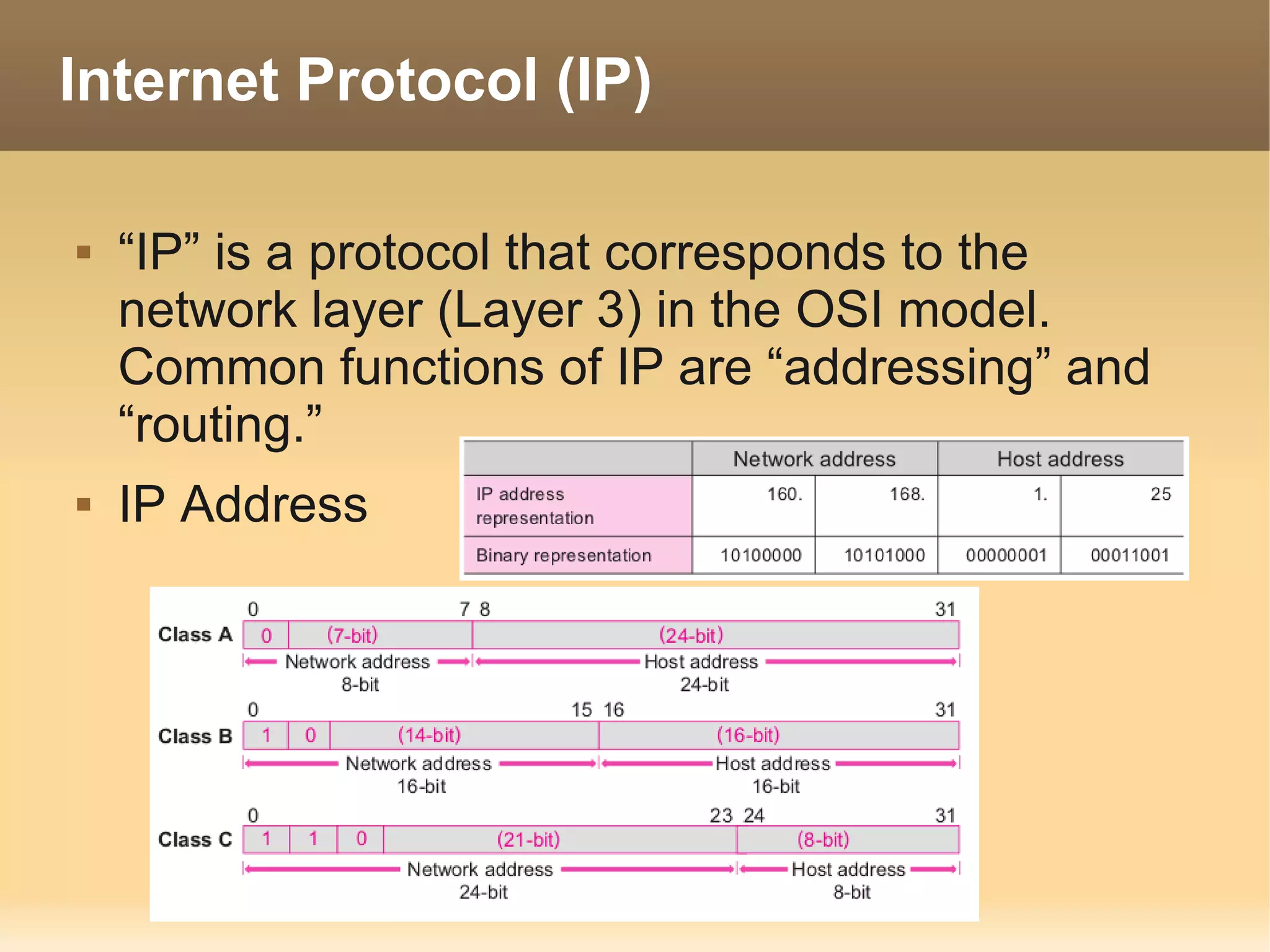
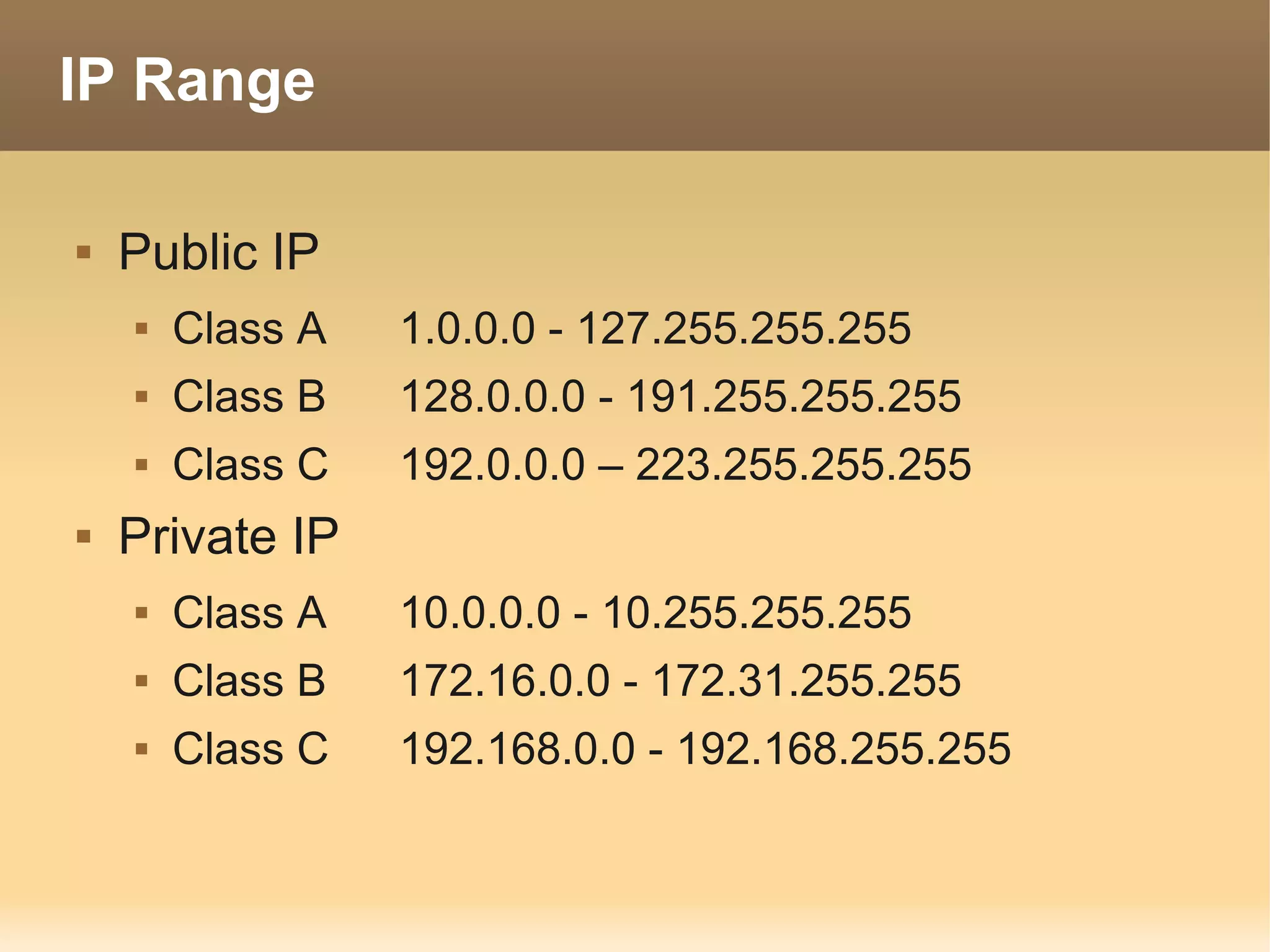
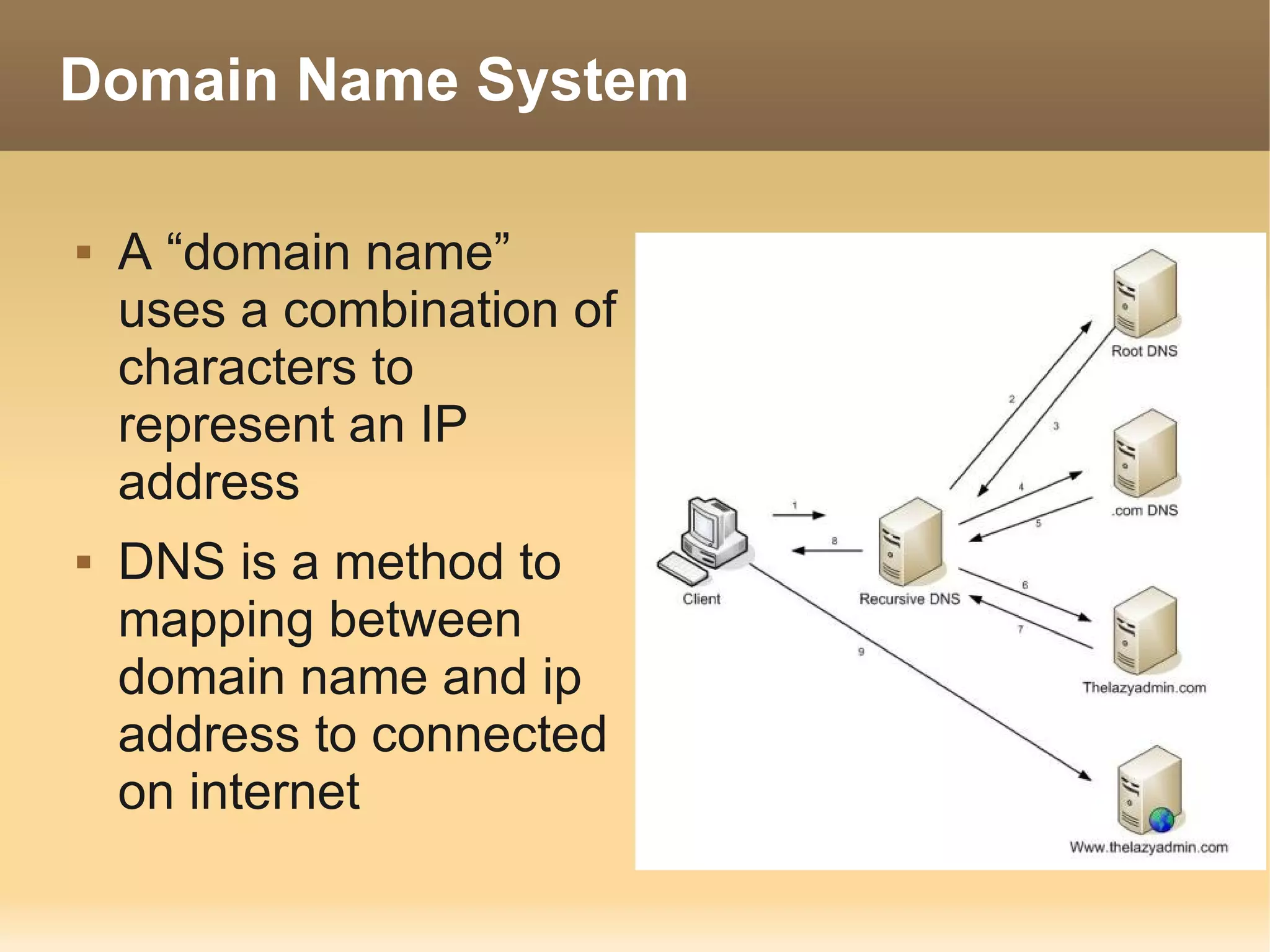
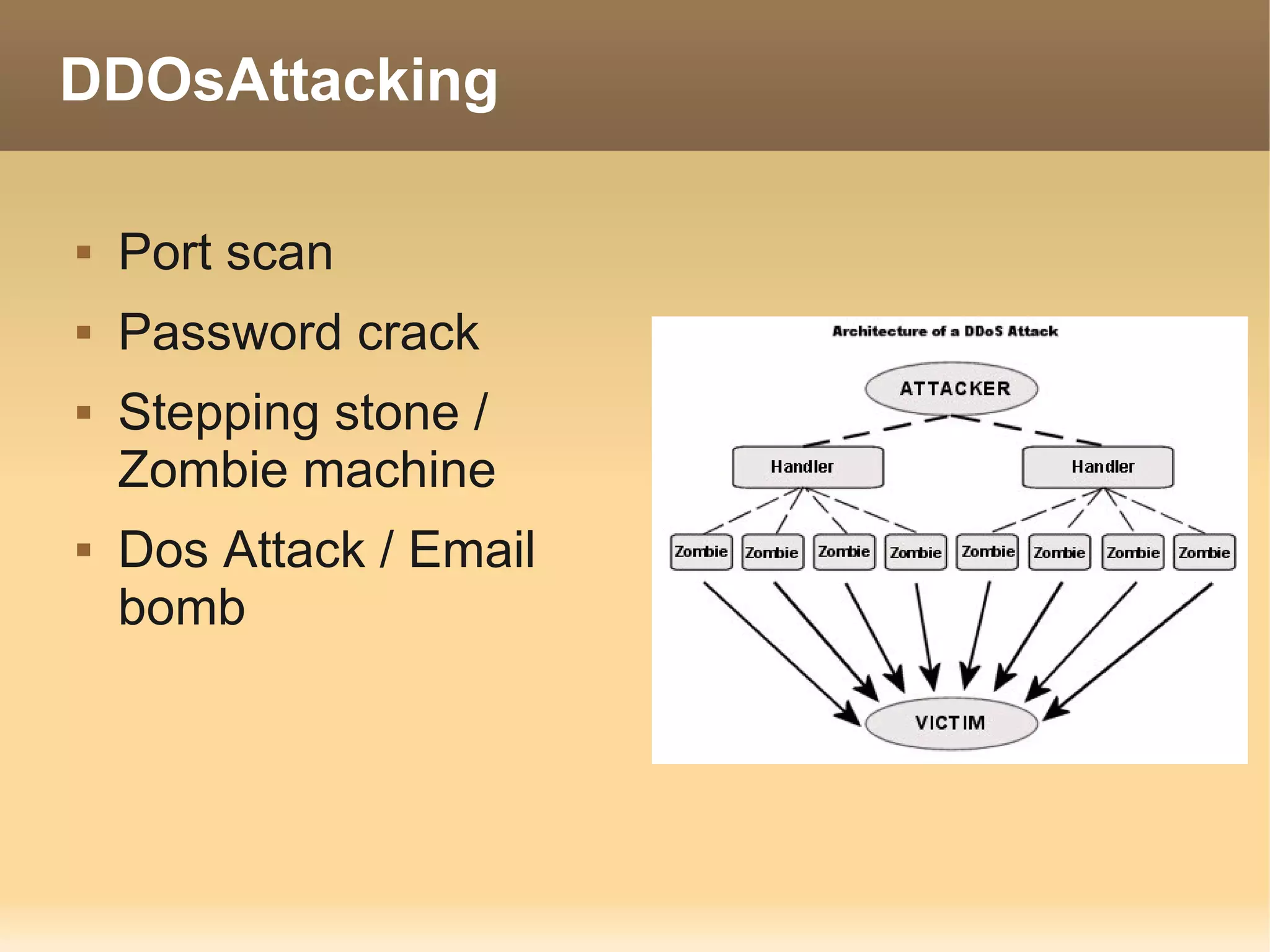
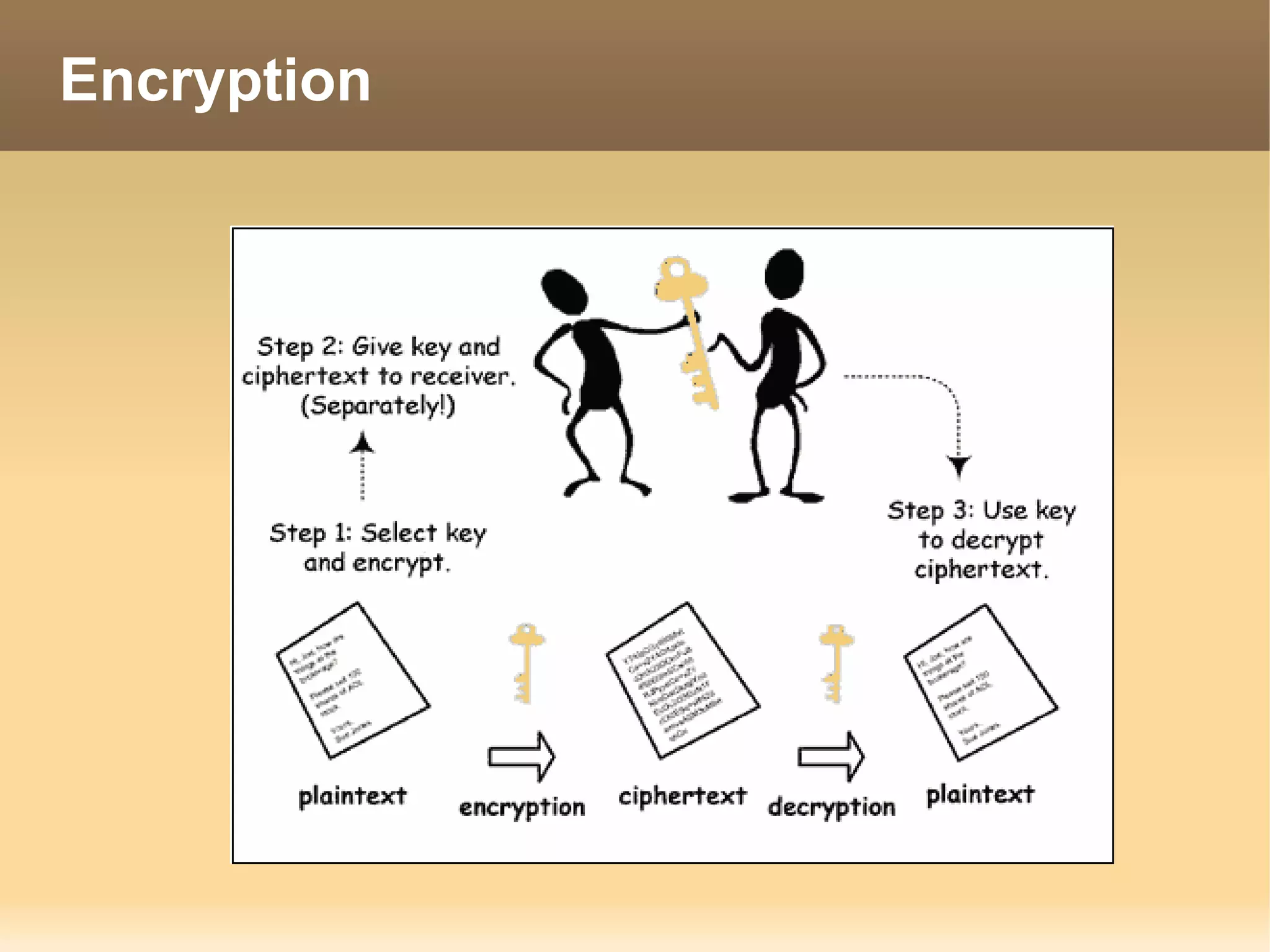
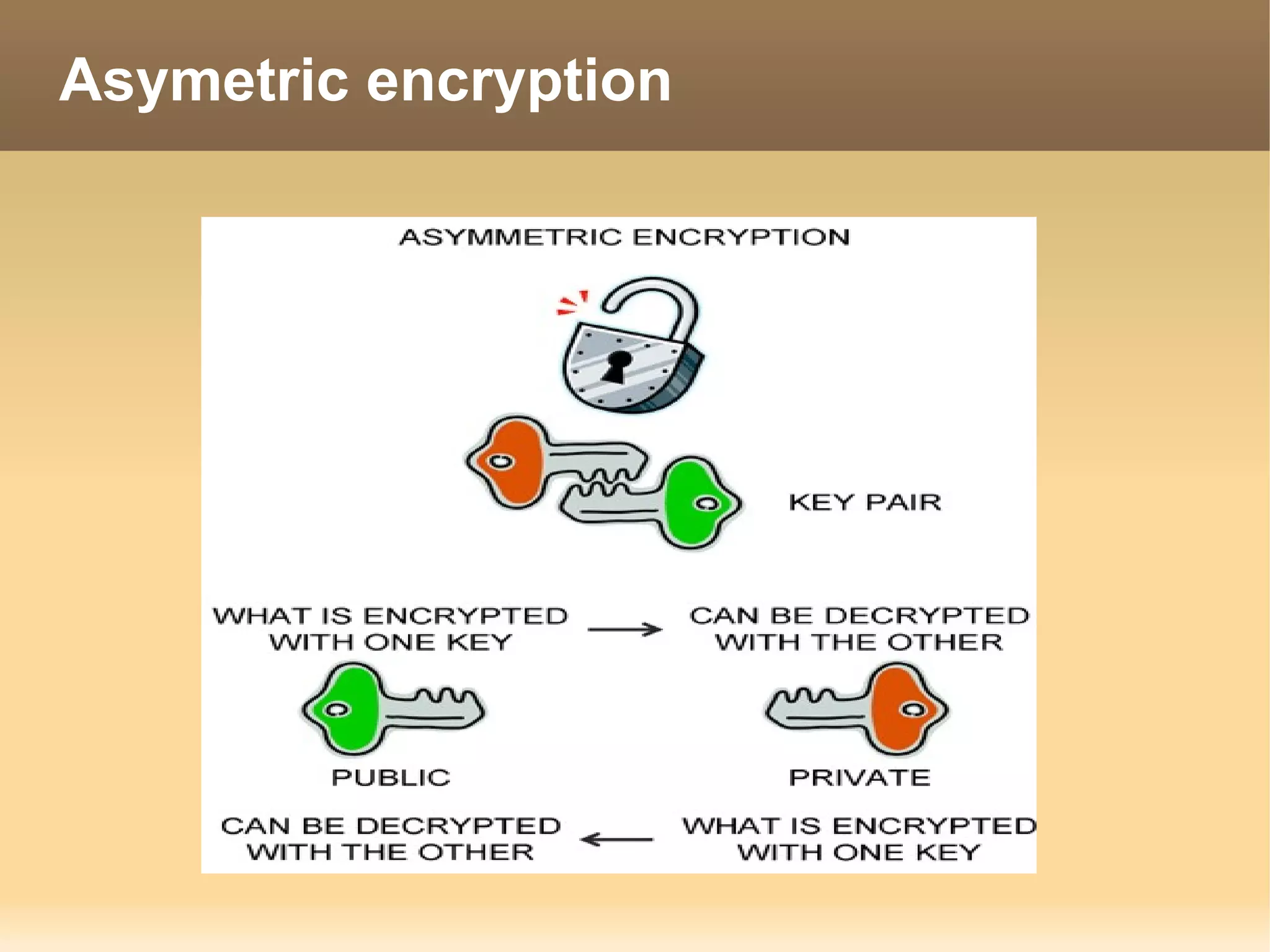
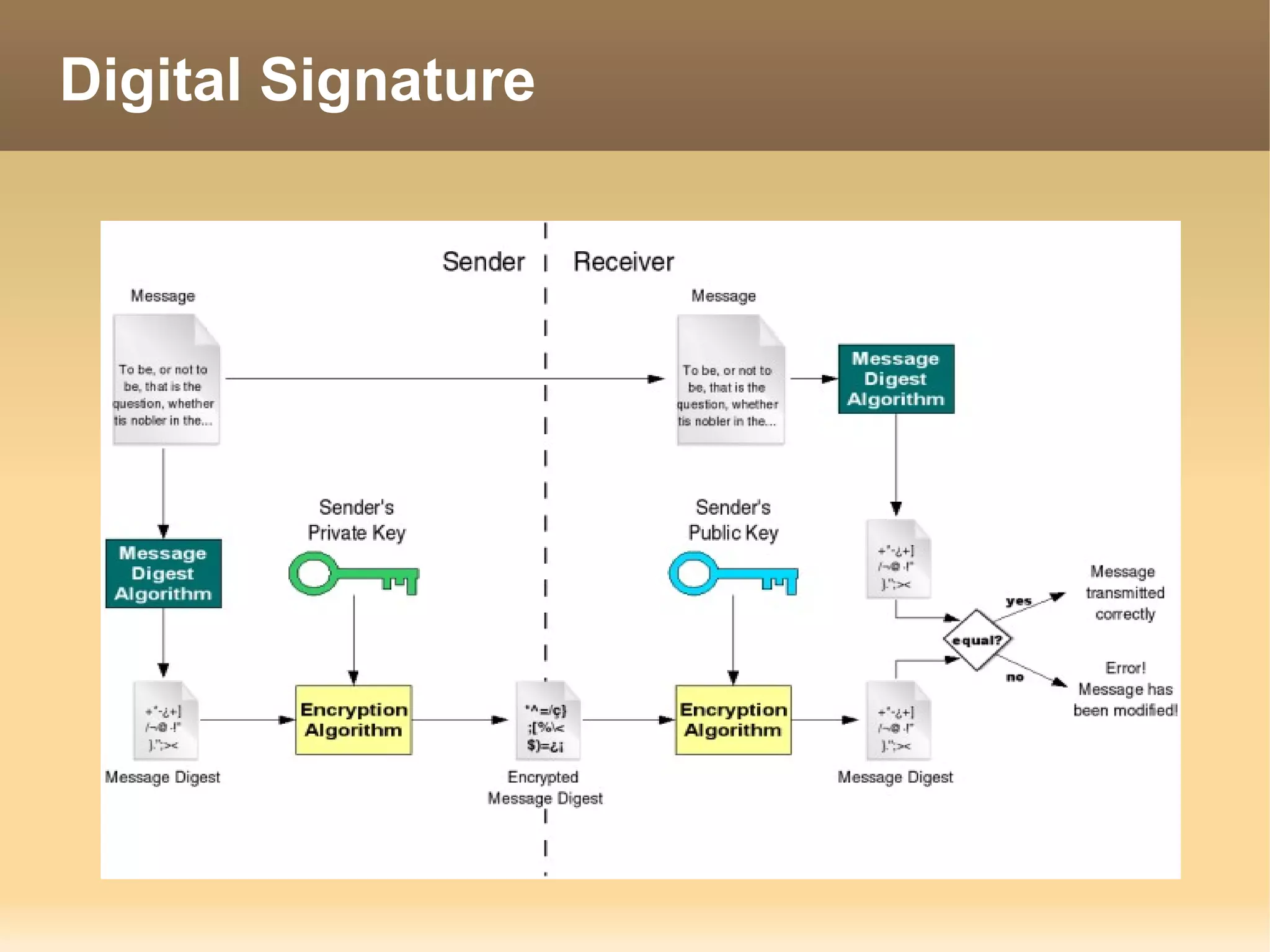
The document provides information about the IT Passport Examination (ITPE) which is a professional certification examination organized through collaboration between organizations in Southeast Asia. The examination is administered by the Information Technology Professionals Examination Council (ITPEC) which was established by member countries to standardize IT professional certifications and ensure they meet international standards. The examination consists of 100 multiple choice questions testing strategies, management, and technology topics over a 165 minute duration. Candidates must achieve an overall score of 60% or higher and 30% or higher in each subject area to pass.