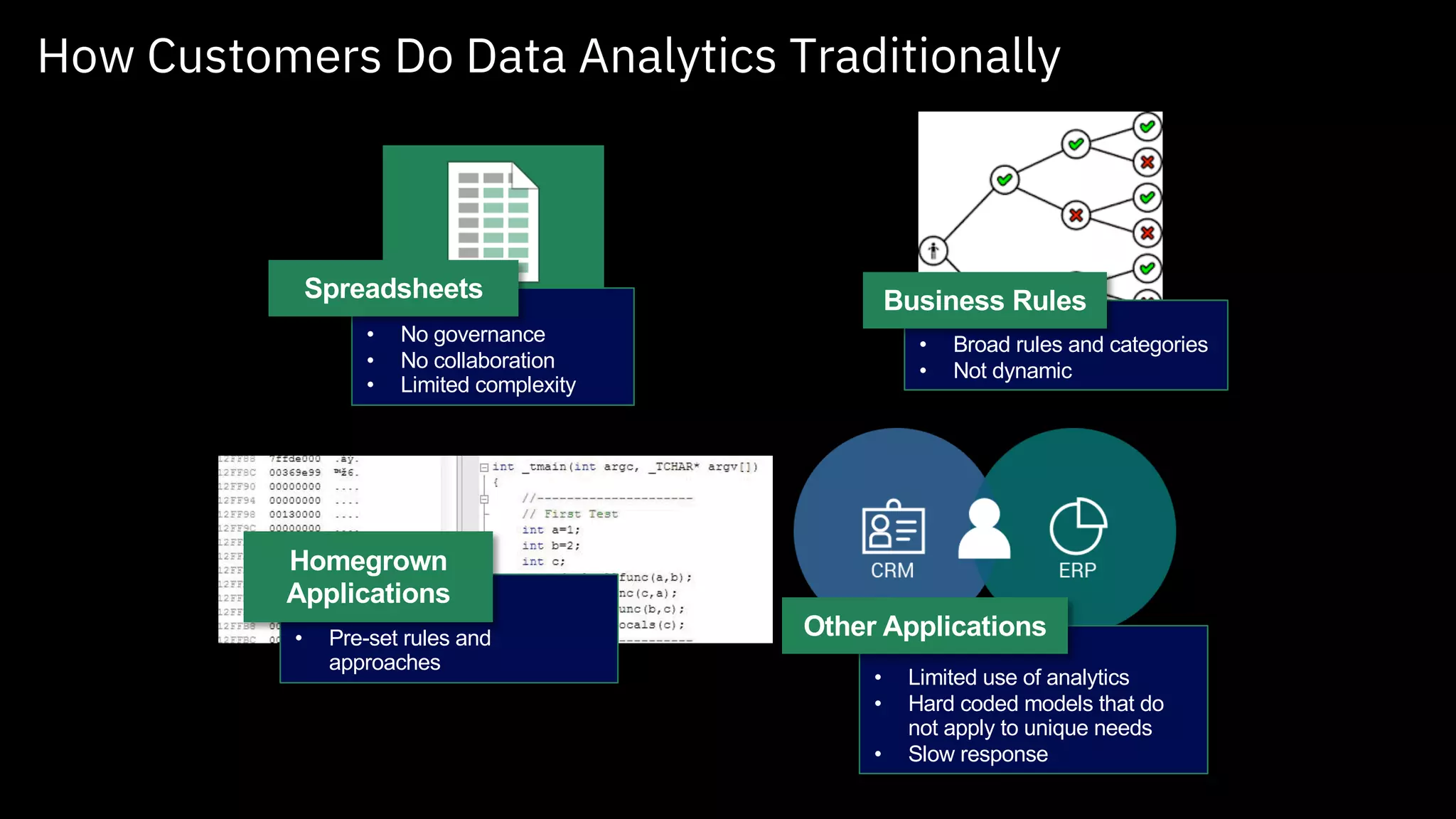
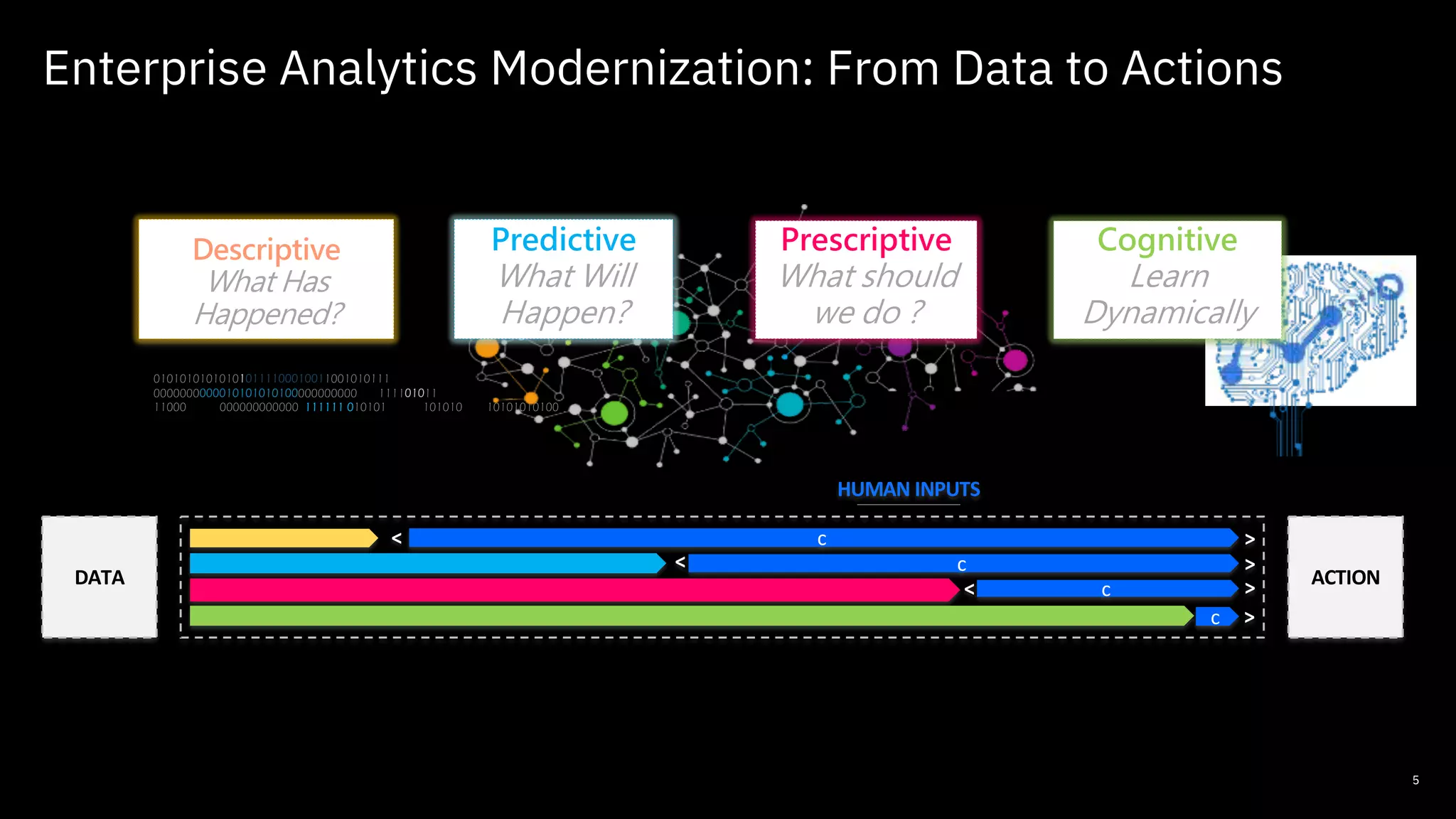
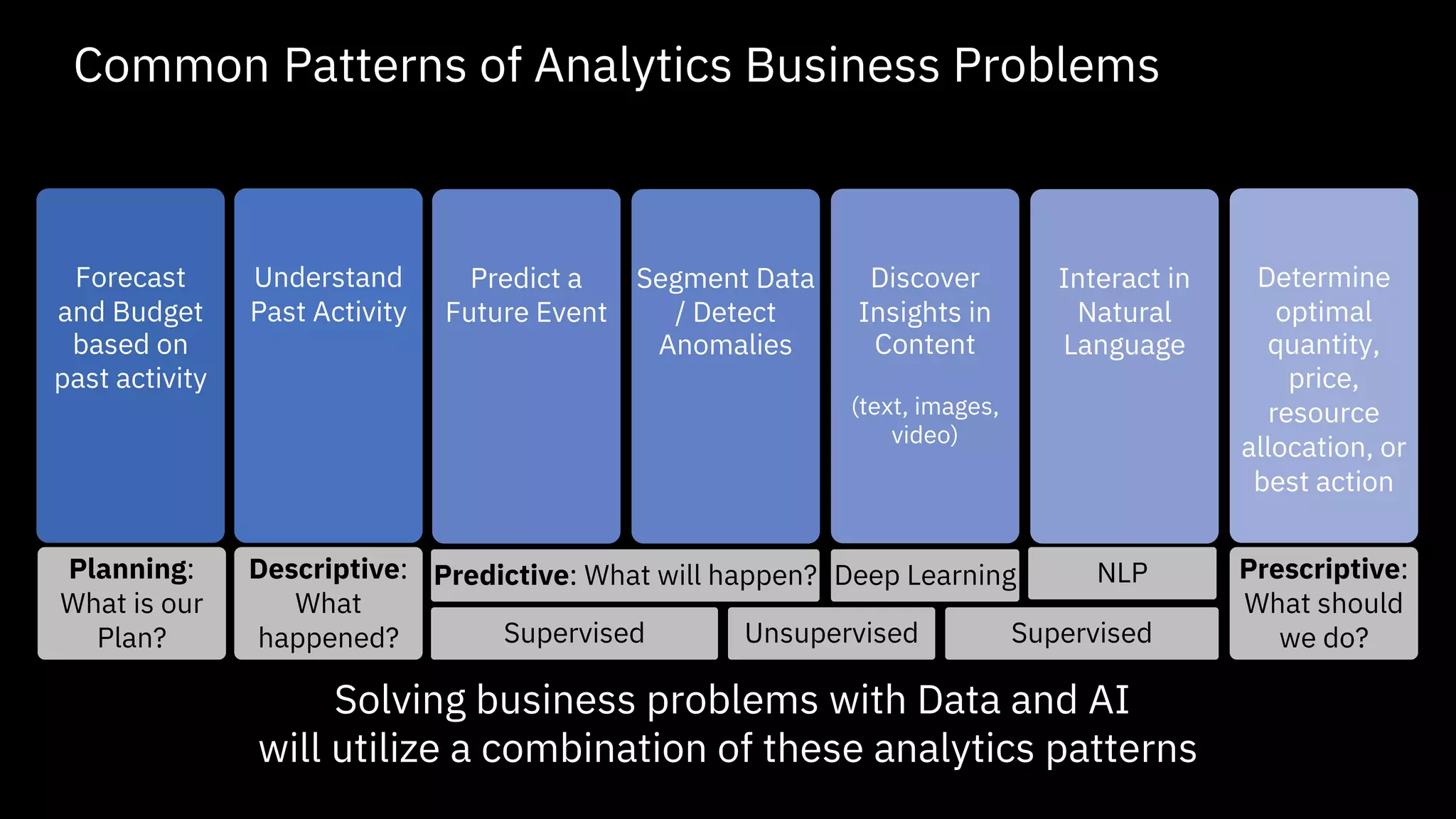
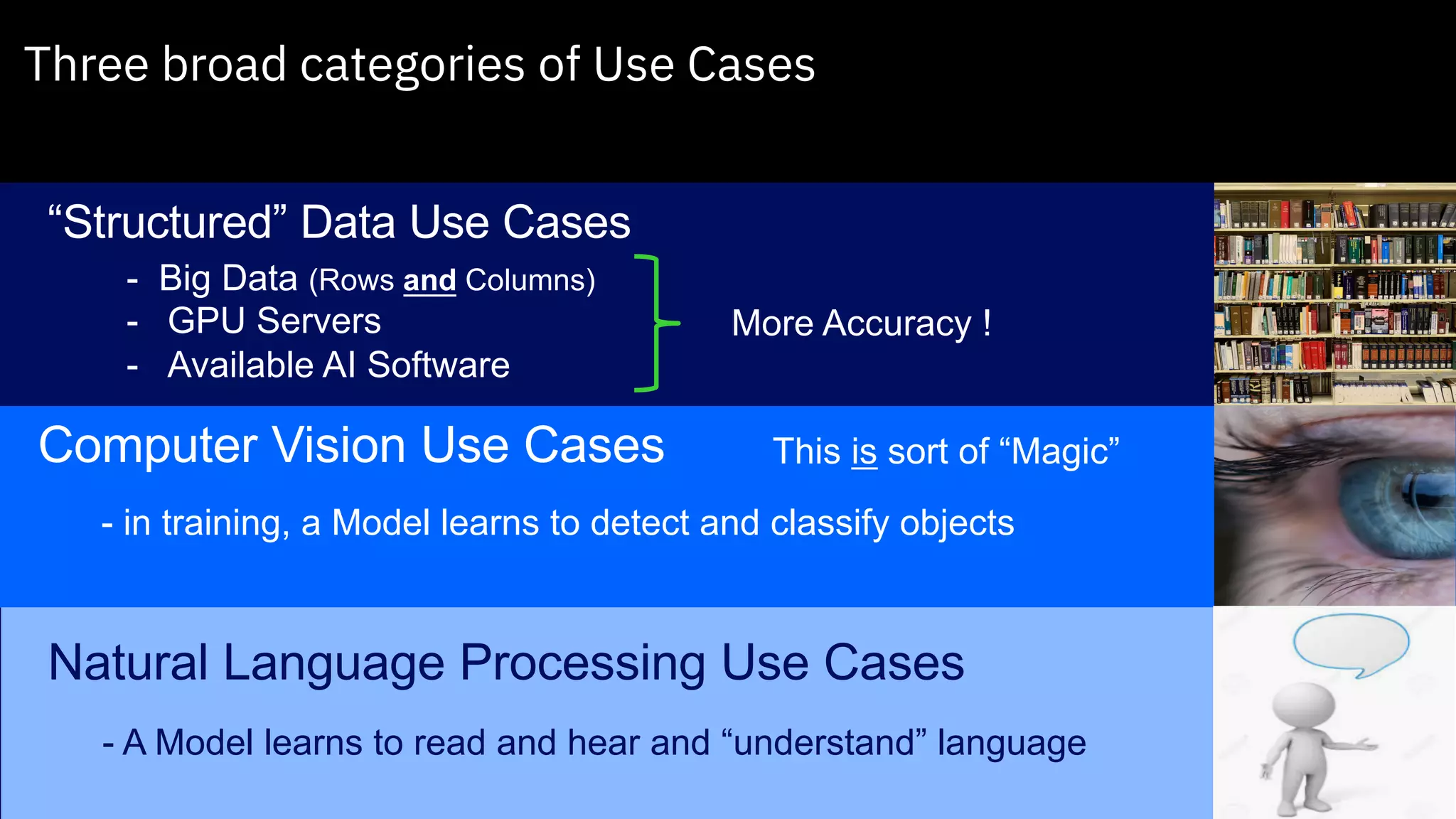
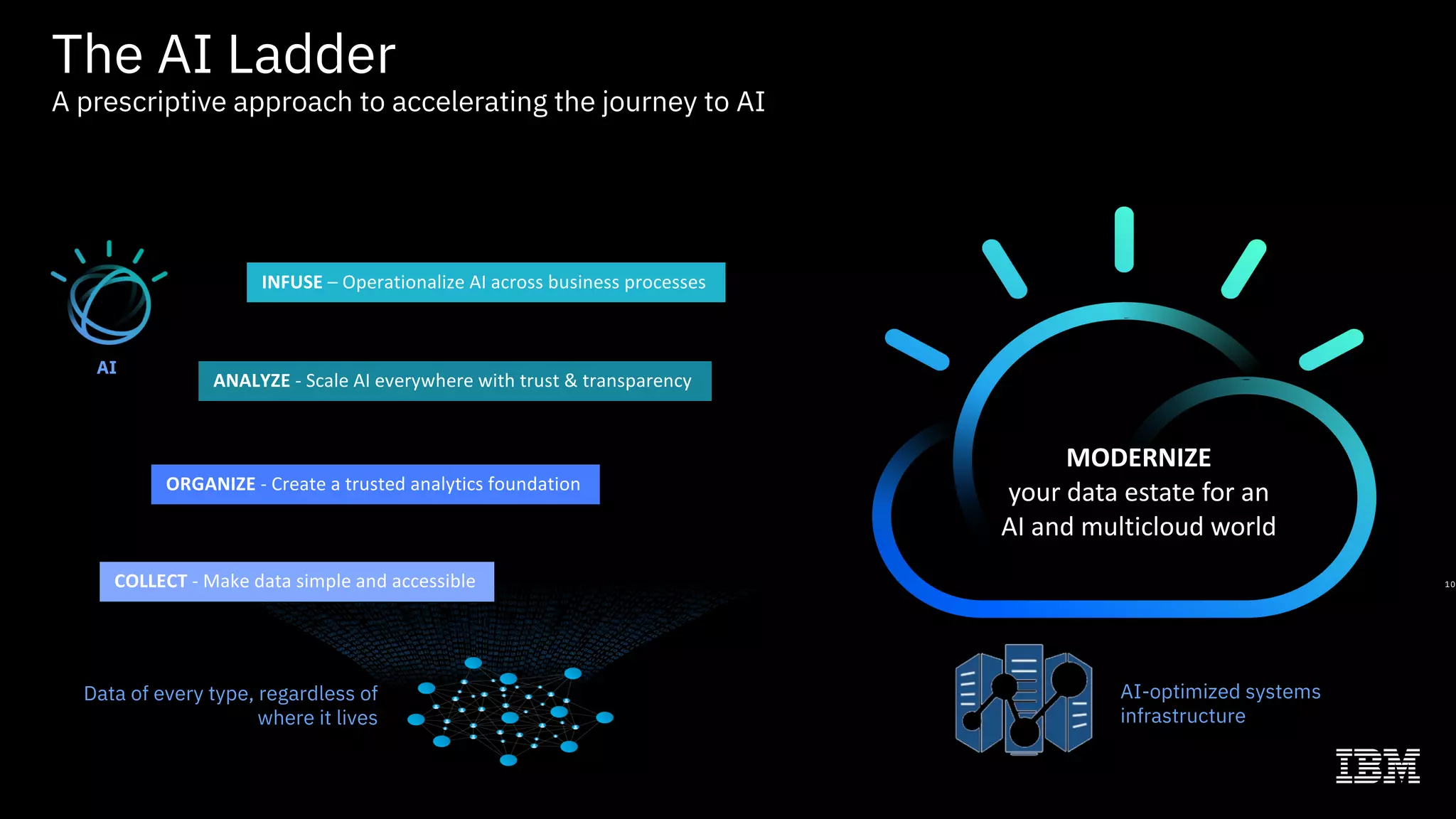
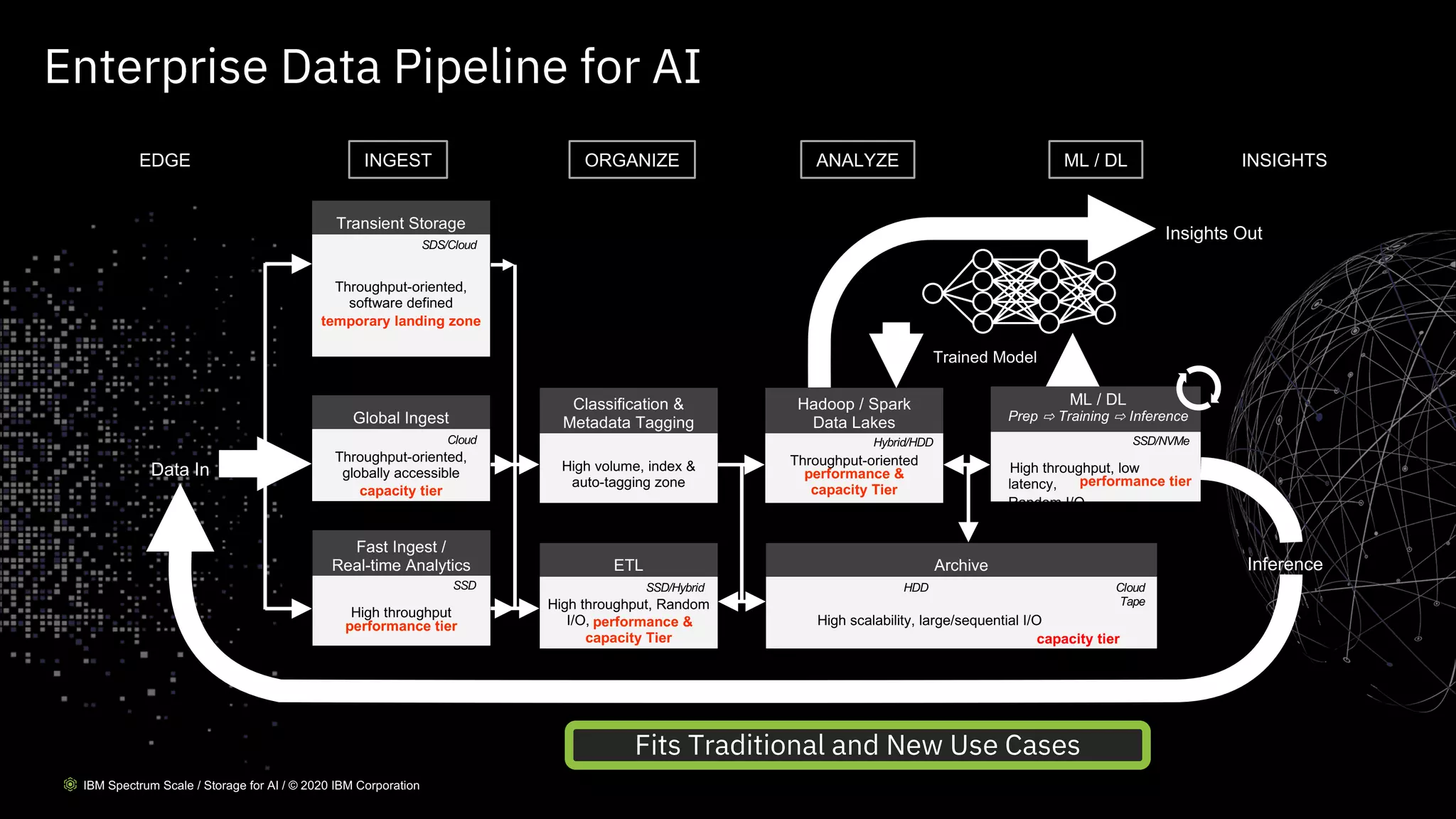
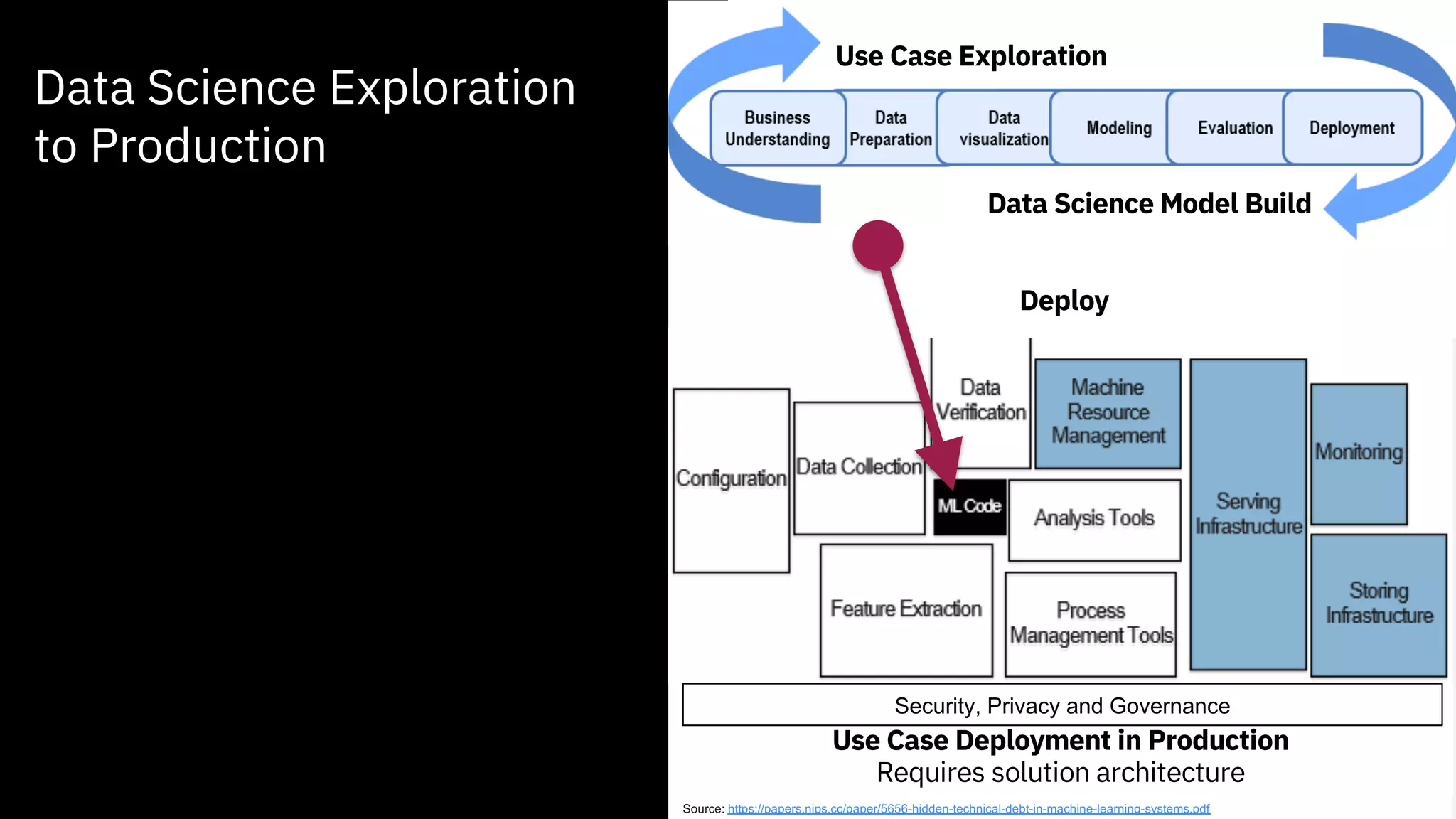
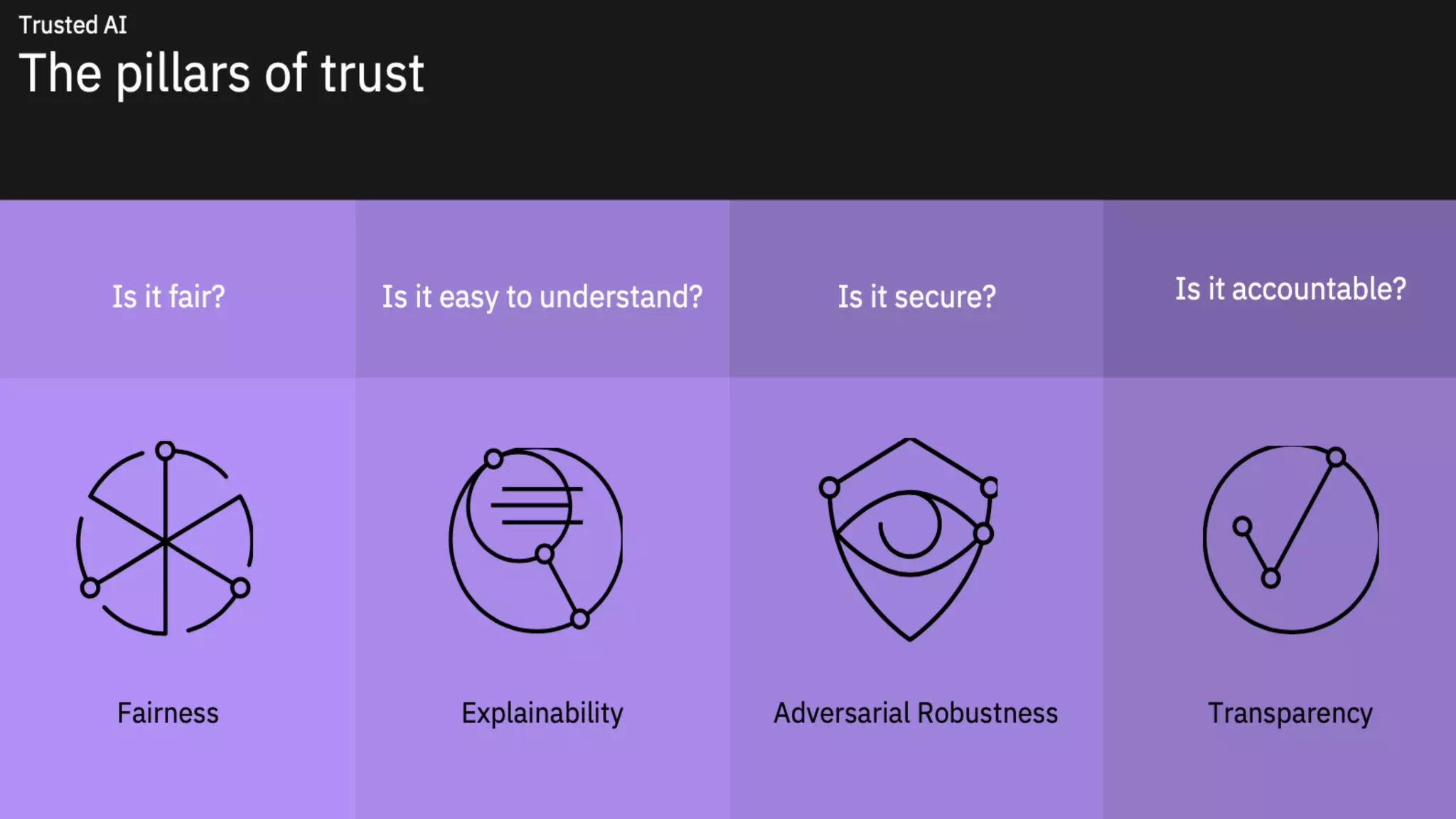
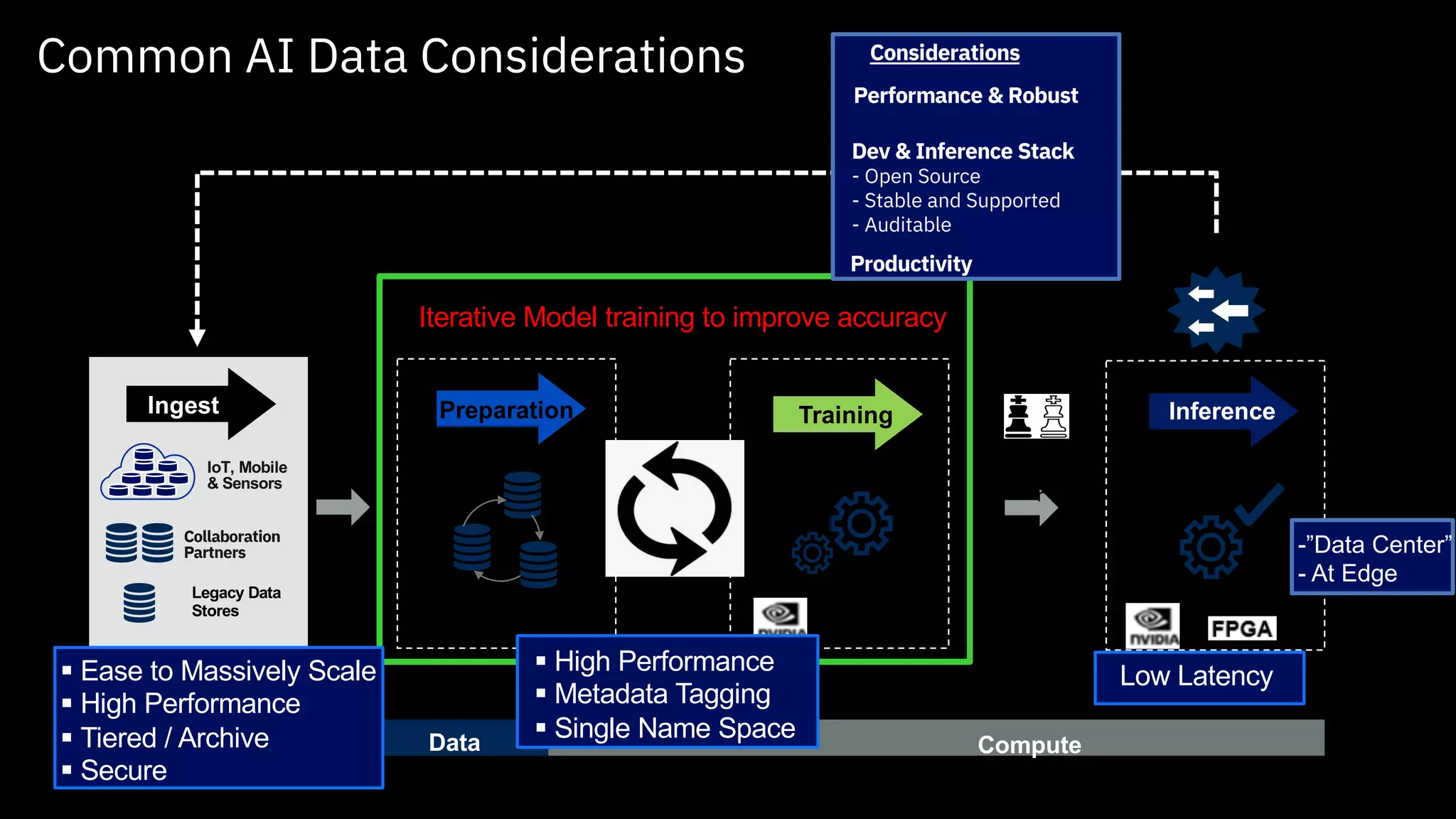
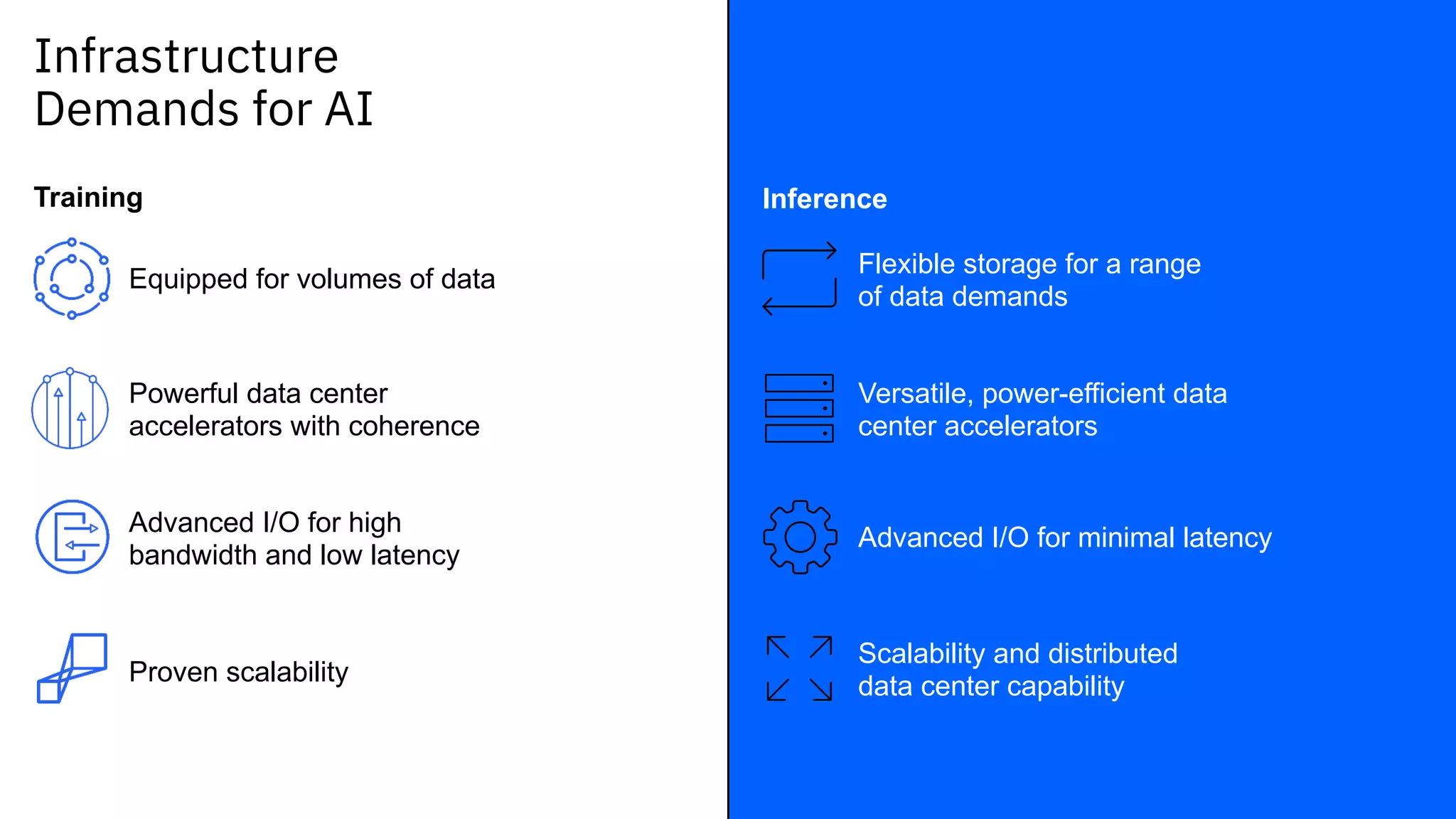
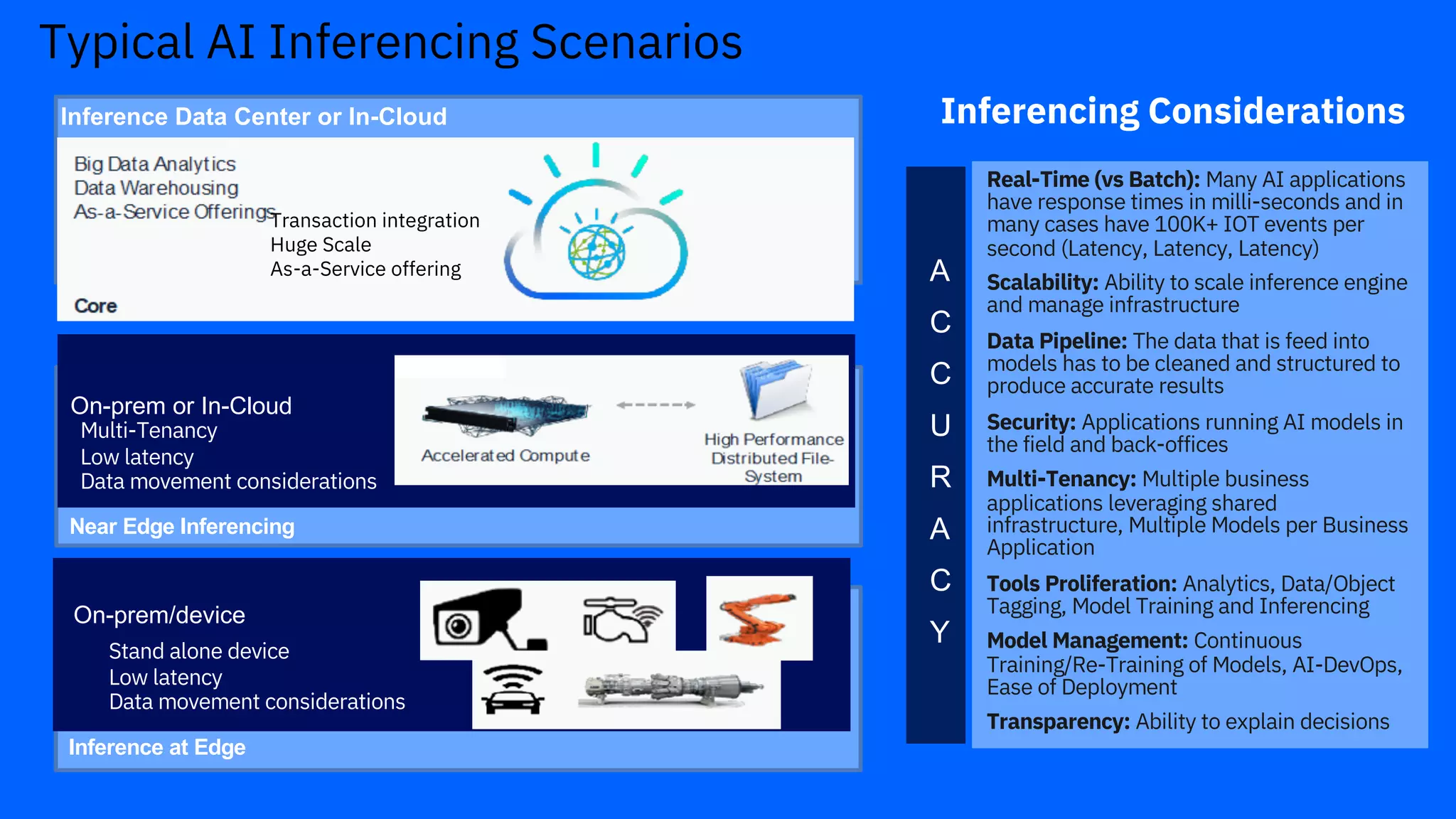
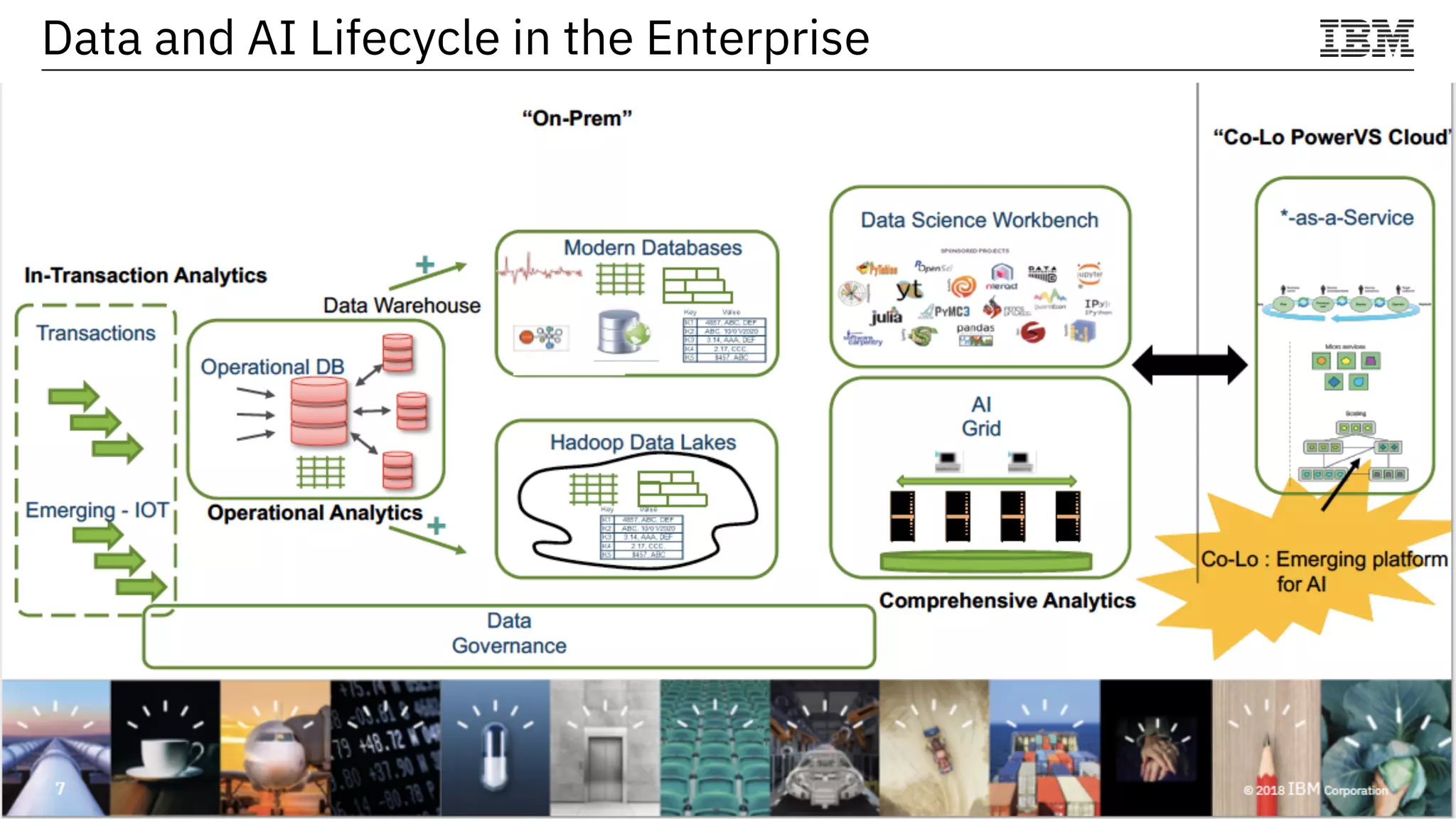
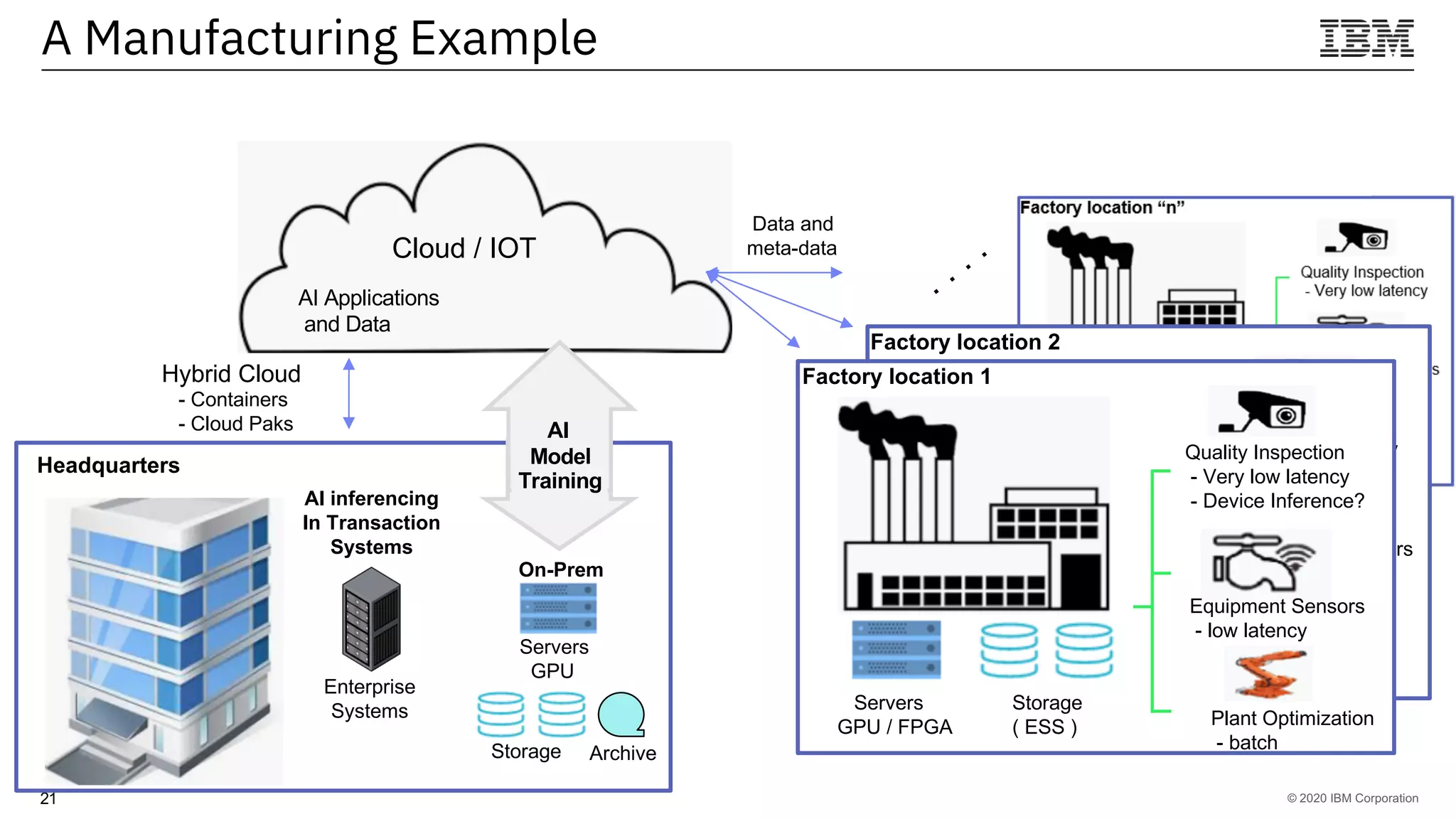
The document outlines the significance of AI in enterprise data analytics, focusing on the AI ladder and lifecycle. It discusses various data use cases, the challenges of traditional analytics methods, and the need for optimized infrastructure to handle AI workloads effectively. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of data-driven decision-making and the operationalization of AI across business processes.